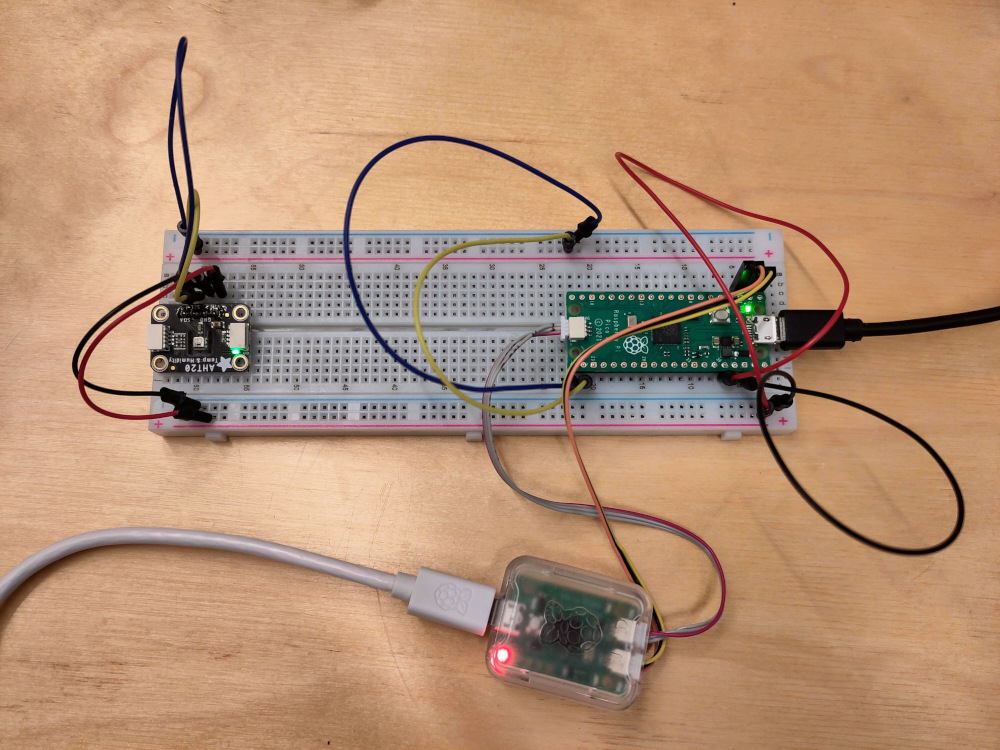
Rust embedded-HAL driver for the AHT20 temperature and humidity sensor.
You can read my blog post AHT20 thermometer driver which details the creation of this driver.
There is an example app for the Raspberry Pi Pico in the
examples/rp-pico/ directory. You can run that with cargo run --release. It will read the temperature and humidity and print it the
console.
Using the AHT20 driver in your own project should be possible with any platform that supports the embedded-HAL. See awesome-embedded-rust for a list of supported platforms. I've used this driver with the Raspberry Pi Pico.
Some HALs don't yet support version 1.0 of the embedded HAL, if you need to use one of those, you can still use a version in the 1.x series of this driver (for example v1.2.2). This applies to for example the stm32f103, which supports board like the fairly common Blue Pill board.
In order to use the aht20-driver you'll need to configure an I2C device that
implements the embedded HAL blocking
I2C traits.
You will also need something which implements the
DelayNS
trait, like for example
Timer
in the case of the Raspberry Pi Pico. For other microcontrollers, this may be
called things like "delay".
The example in this repository shows an example for the Raspberry Pi Pico
board. Once you have those configured - pass those to the AHT20::new method
to create the device driver. You will need to call the init method on it,
which will calibrate the sensor and return a new struct with methods for
measuring and resetting the sensor.
Once calibrated you can call the measure method which will return a
measurement containing temperature and humidity values in relative humidity %,
and degrees Celsius.
// Configure the AHT20 temperature and humidity sensor.
let mut aht20_uninit = aht20_driver::AHT20::new(i2c, aht20_driver::SENSOR_ADDRESS);
let mut aht20 = aht20_uninit.init(&mut timer).unwrap();
// Take the temperature and humidity measurement.
let aht20_measurement = aht20.measure(&mut timer).unwrap();
rprintln!("temperature (aht20): {:.2}C", aht20_measurement.temperature);
rprintln!("humidity (aht20): {:.2}%", aht20_measurement.humidity);There is an alternative measuring function called measure_no_fp which also
performs a measurement, but which does not require floating point calculations.
This can be good for microcontrollers with limited amounts of RAM, or no
floating point support. This can both make the binary smaller, and the
calculations faster for those microcontrollers. The trade-off is that the
accuracy is limited - only round numbers are returned from this function.
Defmt, the embedded logging framework, is
used by default by this library. If you don't want to use defmt logging in
your project, then you can turn it off. See the Feature flags section below.
To use this library with defmt active in your project - you'll need to follow
the defmt setup guide. The steps are
simple, and boil down to adding a linker argument to your .cargo/config.toml,
selecting a logging implementation (like defmt-rtt), and importing it into your
code (use defmt_rtt as _; for the aforementioned implementation).
By default the warning level is set to "warn". To see logs that are of lower
severity, (like info) you can change the log level by setting the DEFMT_LOG
env var. Example:
DEFMT_LOG=info cargo run
There is currently only one feature flag use-defmt, and it's on by default.
This feature is on my default. Disabling the default features with
default-features = false in your Cargo.toml will let you turn off defmt
logging. Example:
aht20-driver = { version = "1.2.2", default-features = false }
If there's more features in the future, and you'd like to disable default features but keep using defmt logging then you can turn the feature on with:
aht20-driver = { version = "1.2.2", default-features = false , features = ["use-defmt"] }
Please open an issue, start a conversation under discussions, or submit a pull request - all are welcome.
I'd love to know if you're using the driver, and I'd like to link to your projects so that others can learn from them.
aht20-driver is distributed under the terms of both the MIT License and the
Apache License 2.0.
See the LICENSE-APACHE and LICENSE-MIT files for license details.