TOGAF 101
The open group vision
- Boundaryless Information Flow
- Boundaries exists but permeable to enable business
The open group mission
- Creation of Boundaryless Information Flow achieved by working with customers and suppliers
The open group architecture forum mission
- Advance the Open Group vision of Boundaryless Information Flow, for and between enterprises
What is an Enterprise
- The TOGAF standard considers an "enterprise" to be any collection of organizations that have common goals
Purpose of Enterprise Architecture
- To optimize across the enterprise the often fragmented legacy of processes into an integrated environment that is responsive to change and supportive of the delivery of the business strategy
Benefits of an Enterprise Architecture
- More effective and efficient business operations
- More effective and efficient Digital Transformation and IT operations
- Better return on existing investment, reduced risk for future investment
- Faster, simpler, and cheaper procurement
What would prompt the development of an Enterprise Architecture?
- Preparation for business transformation needs
- Any radical infrastructure changes initiates
What is an architecture framework?
- An architecture framework is a foundational structure, or set of structures, which can be used for developing different architectures
- It should describe a method for designing a target state of the enterprise in terms of a set of building blocks
- It should contain a set of tools and provide a common vocabulary
- It should also include a list of recommended standards and compliant products that can be used to implement the building blocks
The Value of an architecture framework
- Avoids the initial panic when the scale of the task becomes apparent and provides a practical starting point for an architecture project
- Systematic 'Codified Common Sense'
Why use the TOGAF standard as a framework for Enterprise Architecture?
- The TOGAF standard provides a best practice framework for adding value, and enables the organization to build workable and economic solutions which address their business issues and needs
TOGAF origins
- A customer initiative
- Originally based on TAFIM (US DoD)
- A Framework not Architecture to develop architectures to meet different business needs
What Kind of Architecture does the TOGAF Standard Deal With? (BDAT)
- Business architecture: defines the business strategy, governance, organization, and key business processes
- Data architecture: describes the structure of an organization's logical and physical data assets and data management resources
- Application architecture: provides a blueprint for the applications to be deployed, their interactions, and their relationships to the core business processes
- Technical architecture: describes the logical software and hardware capabilities that are required to support the deployment of business, data, and application services
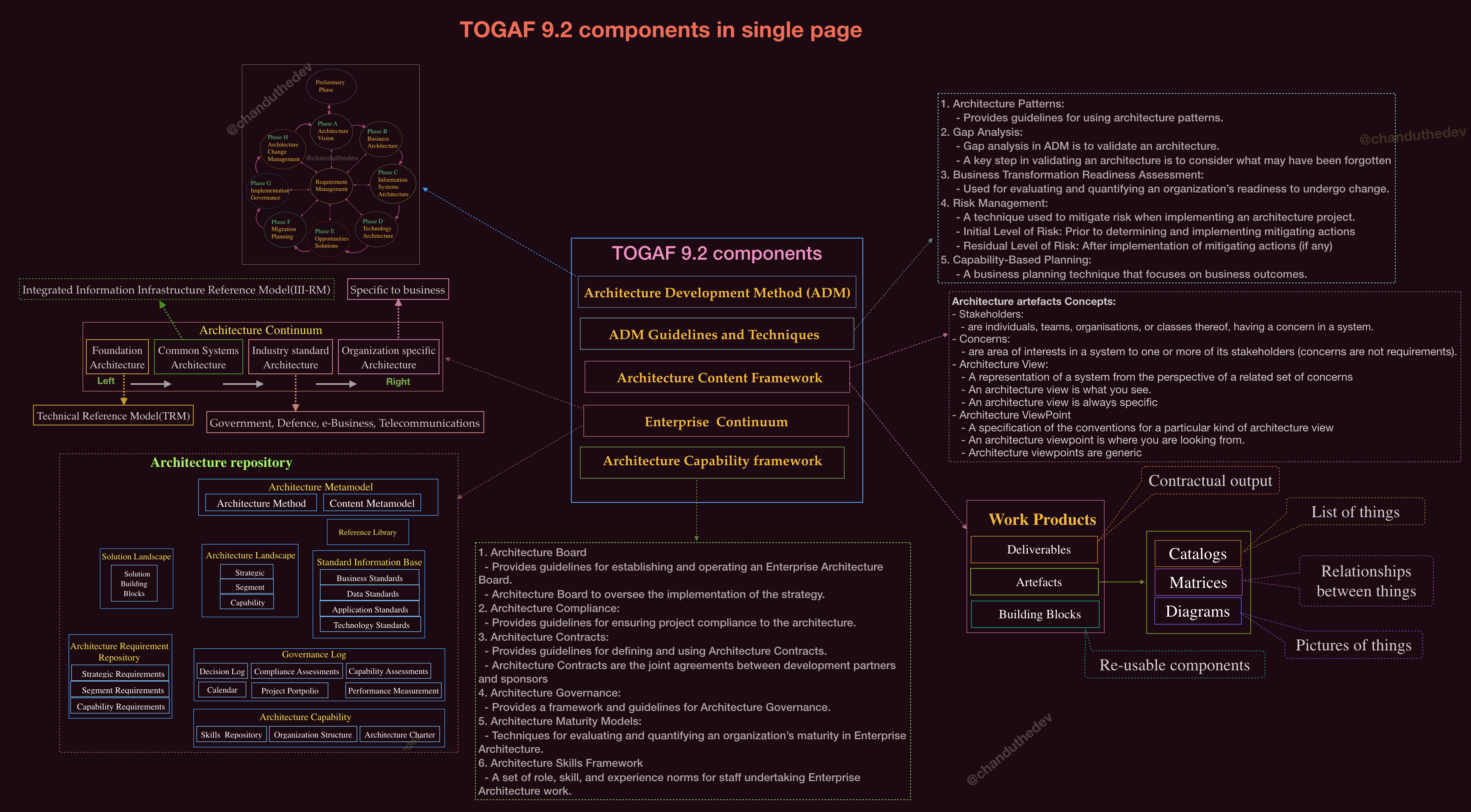
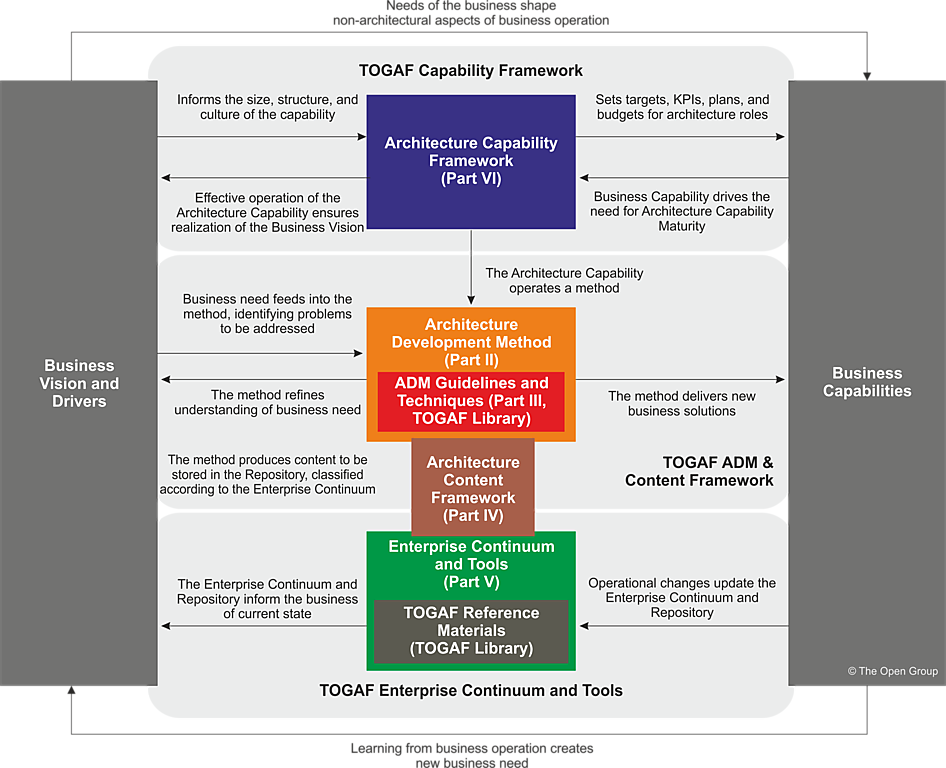
TOGAF Components
- PART I: Architecture Development Method (ADM) is the core of the TOGAF framework. A step-by-step approach to developing an Enterprise Architecture
- PART II: ADM Guidelines & Techniques contains a collection of guidelines and techniques available for use in applying the TOGAF approach and the TOGAF ADM
- PART II: Architecture Content Framework describes the TOGAF content framework, including a structured metamodel for architectural artifacts, the use of re-usable Architecture Building Blocks (ABBs)
- PART IV: Enterprise Continuum & Tools discusses appropriate taxonomies and tools to categorize and store the outputs of architecture activity within an enterprise
- PART V: Architecture Capability Framework discusses the organization, processes, skills, roles, and responsibilities required to establish and operate an architecture function within an enterprise
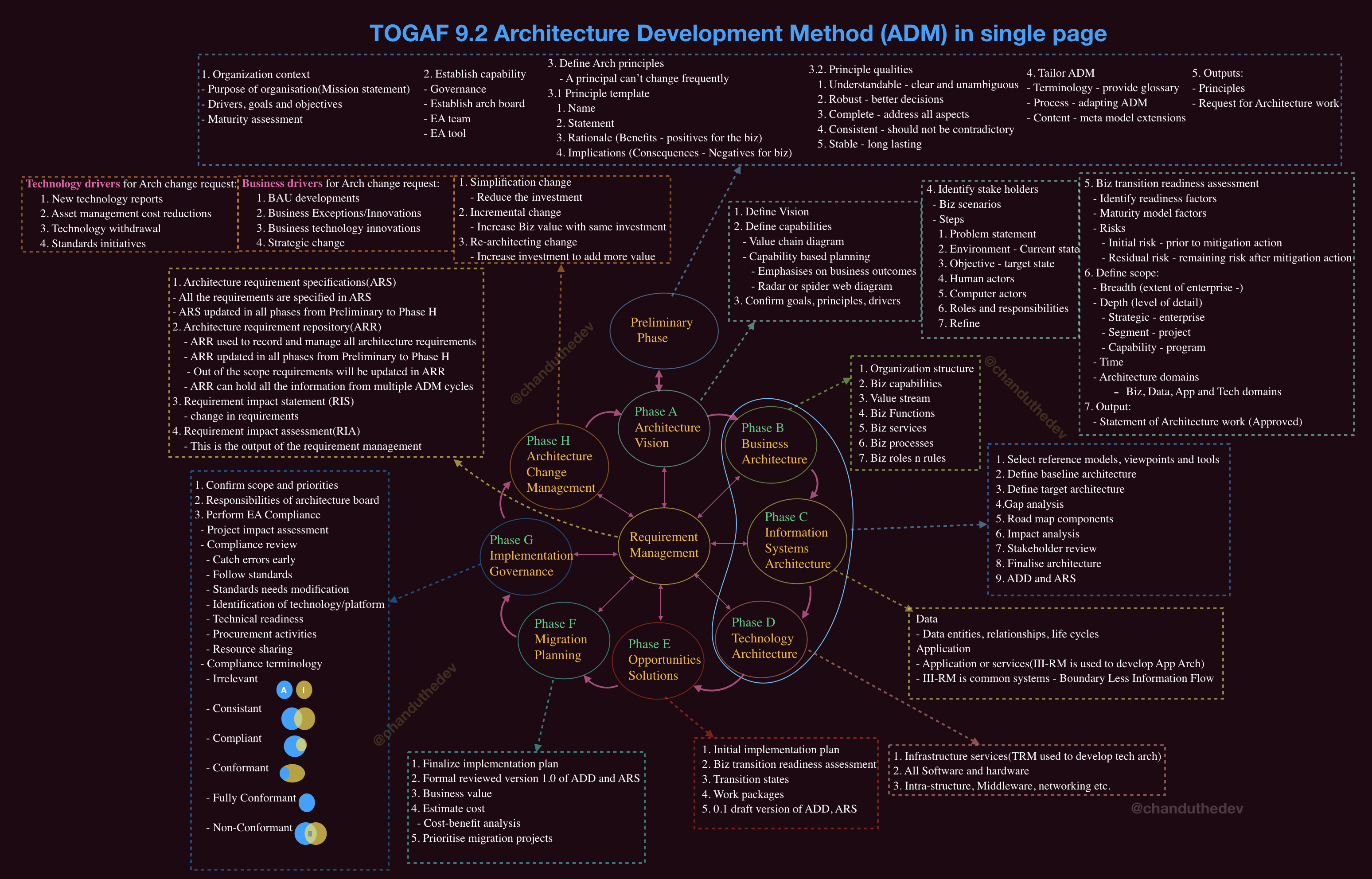
TOGAF Architecture Development Method (ADM)
- TOGAF is an iterative method including multiple phases to develop various architectures
- The TOGAF ADM provides a tested and repeatable process, which aligns Business & IT
- TOGAF ADM is a compresensive method of enterprise architecture (EA) development, based on the best practices
- The ADM is also useful to populate the Foundation Architecture of an enterprise
- Business requirements of an enterprise may be used to identify the necessary definitions and selections in the Foundation Architecture
Architecture Phases A-B-C-D
| Phase | Deliverable | Content | Version |
|---|---|---|---|
| A: Architecture Vision | Architecture Vision | Business Architecture, Data Architecture, Application Architecture, Technology Architecture | 0.1 |
| B: Business Architecture | Architecture Definition Document | Business Architecture | 1.0 |
| C: Information System Architecture | Architecture Definition Document | Data Architecture, Application Architecture | 1.0 |
| D: Technology System Architecture | Architecture Definition Document | Technology Architecture | 1.0 |
Activities Phase A (Architecture Vision)
- Establish the Project
- Identify Business Goals and Business Drivers
- Review Architecture Principles, including Business Principles
- Define Scope
- Define Constraints
- Identify Stakeholders and Concerns, Business Requirements
- Create Architecture Vision (Baseline/Target Business, Data, Applications, Technology Architecture, Version 0.1
- Develop Statement of Architecture Work and Secure Approval
Activities in Phase B-C-D (Business/Data/Application/Technology Architectures)
- Select reference models, viewpoints, and tools
- Develop Baseline Architecture Description
- Develop Target Architecture Description
- Perform gap analysis
- Define candidate roadmap components
- Resolve impacts across the Architecture Landscape
- Conduct formal stakeholder review
- Finalize the Architecture
- Create the Architecture Definition Document
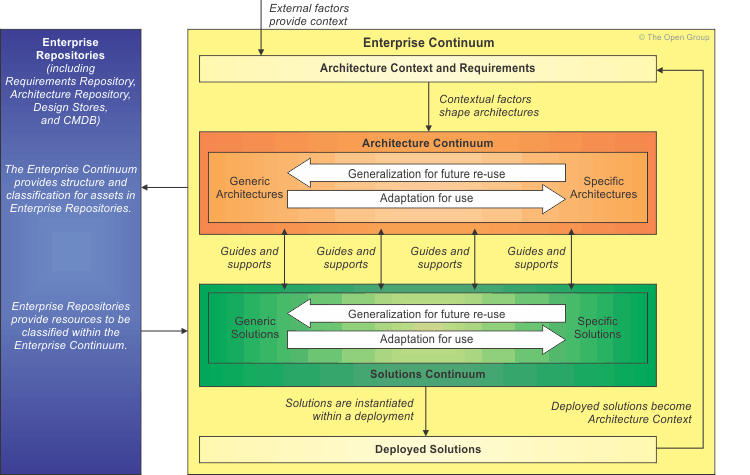
Enterprise Continuum
- The Enterprise Continuum is as a view of the repository of all the architecture assets.
- It can contain architecture descriptions, models, building blocks, patterns, viewpoints, and other artifacts
- It contains the architectures that exist both within the enterprise and in the IT industry at large
- The Enterprise Continuum enables the organization of re-usable architecture artifacts and solution assets to maximize the enterprise architecture investment opportunities
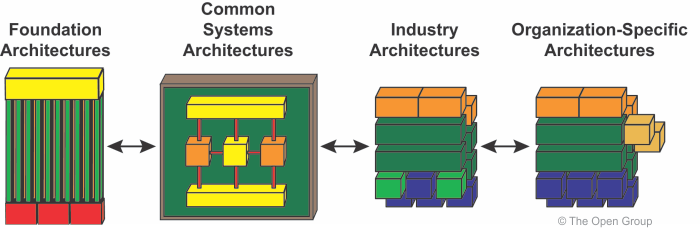
Architecture Continuum
- The Architecture Continuum illustrates how architectures are developed and evolved across a continuum ranging from Foundation Architectures
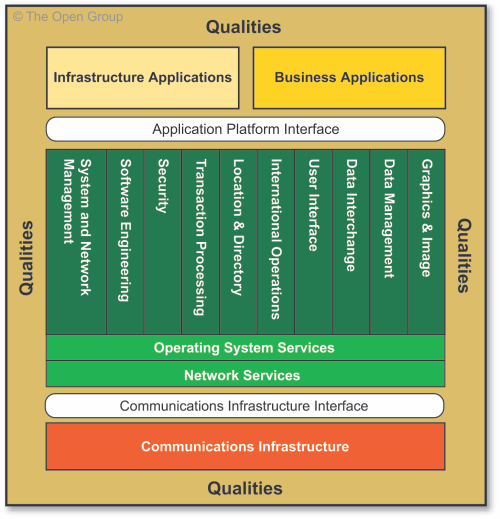
Foundation Architecture: Technical Reference Model
- The TOGAF Foundation Architecture is an architecture of generic services and functions that provides a foundation on which more specific architectures and architectural components can be built
- This Foundation Architecture is embodied within the Technical Reference Model (TRM), which provides a model and taxonomy of generic platform services
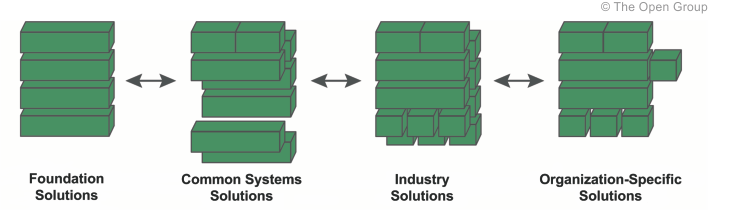
Solutions Continuum
- The Solutions Continuum is a population of the architecture with reference building blocks
- The Solutions Continuum represents the detailed specification and construction of the architectures at the corresponding levels of the Architecture Continuum
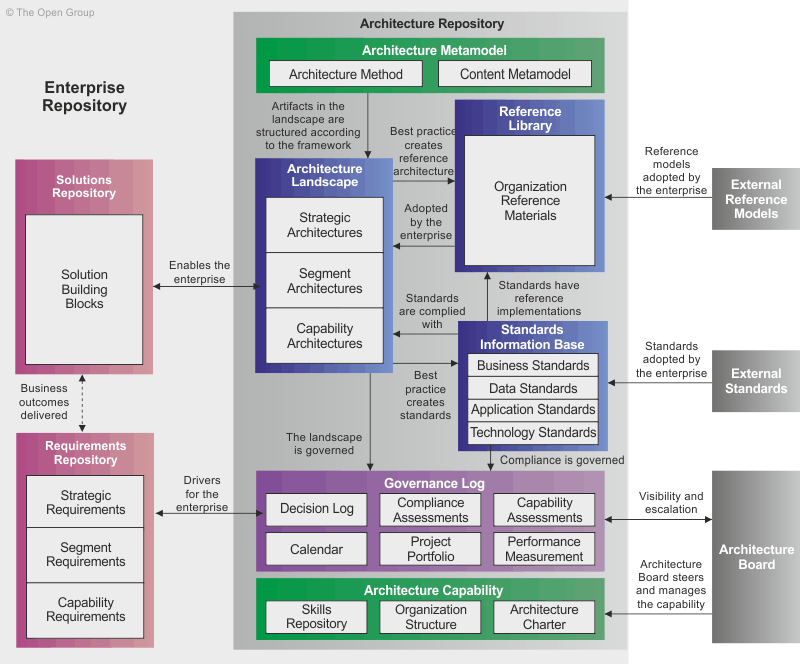
Architecture Repository
- The Architecture Repository provides the capability to link architectural assets to components of the Detailed Design, Deployment, and Service Management Repositories
- At a high level, six classes of architectural information are expected to be held within an Architecture Repository:
- The Architecture Metamodel describes the organizationally tailored application of an architecture framework, including a method for architecture development and a metamodel for architecture content
- The Architecture Capability defines the parameters, structures, and processes that support governance of the Architecture Repository
- The Architecture Landscape presents an architectural representation of assets in use, or planned, by the enterprise at particular points in time
- The Standards Information Base captures the standards with which new architectures must comply, which may include industry standards, selected products and services from suppliers, or shared services already deployed within the organization
- The Reference Library provides guidelines, templates, patterns, and other forms of reference material that can be leveraged in order to accelerate the creation of new architectures for the enterprise
- The Governance Log provides a record of governance activity across the enterprise