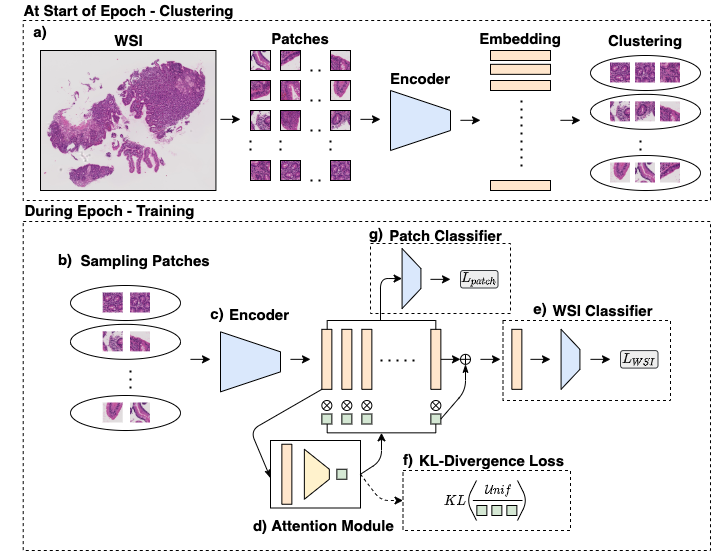
Implementation of Cluster-to-Conquer: A Framework for End-to-End Multi-Instance Learning for Whole Slide Image Classification approach. In this work, we propose an end-to-end framework with following features:
- Cluster-based sampling for diverse patch selection from a WSI
- Attention-based aggregation for slide-level prediction
- Inclusion of KL-divergence in the loss for regularizing the intra-cluster variance
In recent years, the availability of digitized Whole Slide Images (WSIs) has enabled the use of deep learning-based computer vision techniques for automated disease diagnosis. However, WSIs present unique computational and algorithmic challenges. WSIs are gigapixel-sized (~100K pixels), making them infeasible to be used directly for training deep neural networks. Also, often only slide-level labels are available for training as detailed annotations are tedious and can be time-consuming for experts. Approaches using multiple-instance learning (MIL) frameworks have been shown to overcome these challenges. Current state-of-the-art approaches divide the learning framework into two decoupled parts: a convolutional neural network (CNN) for encoding the patches followed by an independent aggregation approach for slide-level prediction. In this approach, the aggregation step has no bearing on the representations learned by the CNN encoder. We have proposed an end-to-end framework that clusters the patches from a WSI into k-groups, samples k' patches from each group for training, and uses an adaptive attention mechanism for slide level prediction; Cluster-to-Conquer (C2C). We have demonstrated that dividing a WSI into clusters can improve the model training by exposing it to diverse discriminative features extracted from the patches. We regularized the clustering mechanism by introducing a KL-divergence loss between the attention weights of patches in a cluster and the uniform distribution. The framework is optimized end-to-end on slide-level cross-entropy, patch-level cross-entropy, and KL-divergence loss.
Use the main notebook for experimenting and orchestrating the training. It can be easily modified to python script for scalable training. The train funciton in the notebook requires an input file containing following columns:
- path - location of patches
- wsi - unique identifier corresponding to each patch
- label - binary label (0 or 1)
- is_valid - if wsi is part of validation split
C2C/
├── models
├─── resnet.py
├── dataloader.py
├── train.py
├── cluster.py
├── loss.py
├── eval_model.py
├── utils.pyIf you find our work useful Please consider citing our paper:
@article{sharma2021cluster,
title={Cluster-to-Conquer: A Framework for End-to-End Multi-Instance Learning for Whole Slide Image Classification},
author={Sharma, Yash and Shrivastava, Aman and Ehsan, Lubaina and Moskaluk, Christopher A and Syed, Sana and Brown, Donald},
year={2021}
}Under review at MIDL: https://openreview.net/forum?id=7i1-2oKIELU