Introduction to NETCONF/YANG
Enable NETCONF/YANG
Tooling: NCC the NETCONF-console
NACM Read-Only and the Role Based Access Control (RBAC)
YANGSuite
Conclusion
In this section we will look at YANG data models, why we need them, and how to find them. We will use a tool called YangSuite to find the data models we need, and we will write Python scripts using the models.
Before we start using YANG explorer to look at the data models on our switches, we need to run through a few steps to enable NETCONF, which is not on by default.
Open a SSH session to your C9300 switch and Verify AAA and NETCONF are already configured on the device.
C9300#sh run | sec aaa
aaa new-model
aaa authentication login default local
aaa authorization exec default local
aaa session-id common
C9300#sh run | sec vty
line vty 0 4
exec-timeout 0 0
length 0
transport input all
line vty 5 15
exec-timeout 0 0
length 0
transport input all
C9300#sh run | i netconf
netconf-yang
C9300#show run | i username
username admin privilege 15 secret 9 ....
NCC is essential tooling when working with NETCONF and can be found at https://github.com/CiscoDevNet/ncc. The NCClient tooling is also useful from https://github.com/CiscoDevNet/ncclient as is NETCONF-console from https://pypi.org/project/netconf-console/
The required NETCONF tooling has been preinstalled into the lab envrionment's python3 virtual envrionment 'v' with the ncc folder.
###Access the virtual envrionment:
cd ; cd ncc
virtualenv v
source v/bin/activate
The steps to instal the tooling is below, which has been taken from the Github pages above.
auto@programmability:~$ git clone https://github.com/CiscoDevNet/ncc
Cloning into 'ncc'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 7, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (7/7), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (7/7), done.
remote: Total 1014 (delta 0), reused 1 (delta 0), pack-reused 1007
Receiving objects: 100% (1014/1014), 416.66 KiB | 4.63 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (563/563), done.
auto@programmability:~$ cd ncc
auto@programmability:~/ncc$ virtualenv v
created virtual environment CPython3.8.5.final.0-64 in 370ms
creator CPython3Posix(dest=/home/auto/ncc/v, clear=False, global=False)
seeder FromAppData(download=False, pyparsing=latest, contextlib2=latest, ipaddr=latest, requests=latest, colorama=latest, chardet=latest, six=latest, retrying=latest, pkg_resources=latest, CacheControl=latest, webencodings=latest, progress=latest, pep517=latest, msgpack=latest, appdirs=latest, packaging=latest, certifi=latest, pip=latest, wheel=latest, idna=latest, distro=latest, html5lib=latest, lockfile=latest, setuptools=latest, pytoml=latest, urllib3=latest, distlib=latest, via=copy, app_data_dir=/home/auto/.local/share/virtualenv/seed-app-data/v1.0.1.debian)
activators BashActivator,CShellActivator,FishActivator,PowerShellActivator,PythonActivator,XonshActivator
auto@programmability:~/ncc$ source v/bin/activate
(v) auto@programmability:~/ncc$ pip install --upgrade pip
(v) auto@programmability:~/ncc$ pip install -r requirements.txt
(v) auto@programmability:~/ncc$ pip install --upgrade git+https://github.com/CiscoDevNet/ncclient.git
(v) auto@programmability:~/ncc$ pip install netconf-console
Now that the tooling is accessible explore the use case examples
The NETCONF-console tooling is a simple way to work with the NETCONF API and it is a fully featured tooling, meaning it supports most NETCONF operations and features.
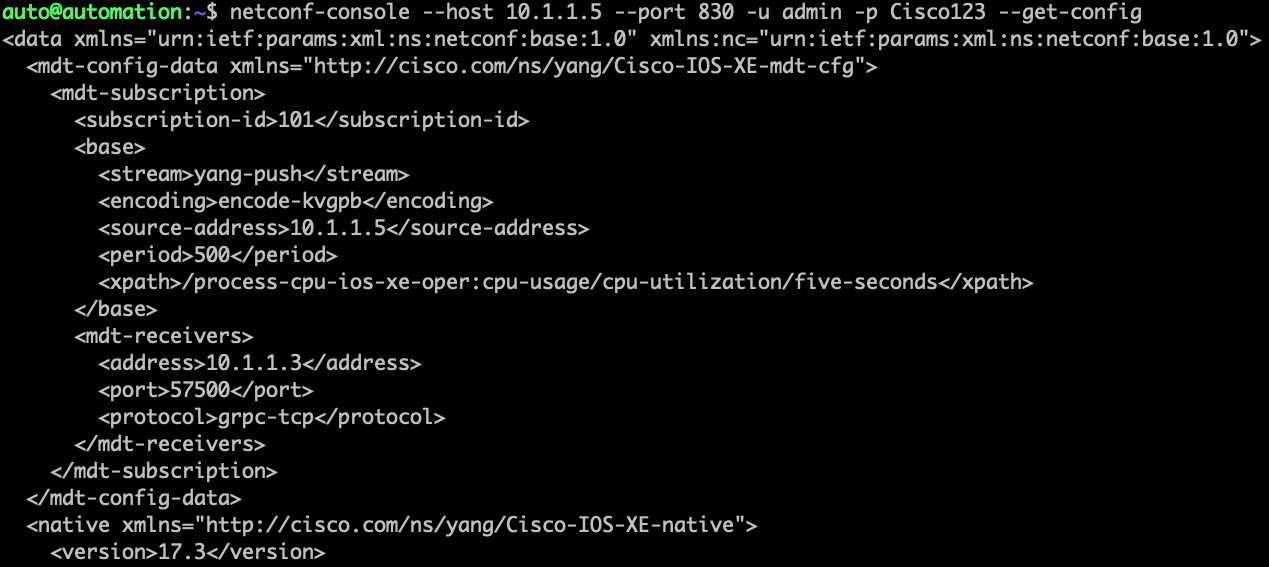
Use the NETCONF-console tooling to connect to the device and get the running configuration. Specify the host, port, username, password, and the operation of get-config
netconf-console --host 10.1.1.5 --port 830 -u admin -p Cisco123 --get-config
The output should look similar to the below:
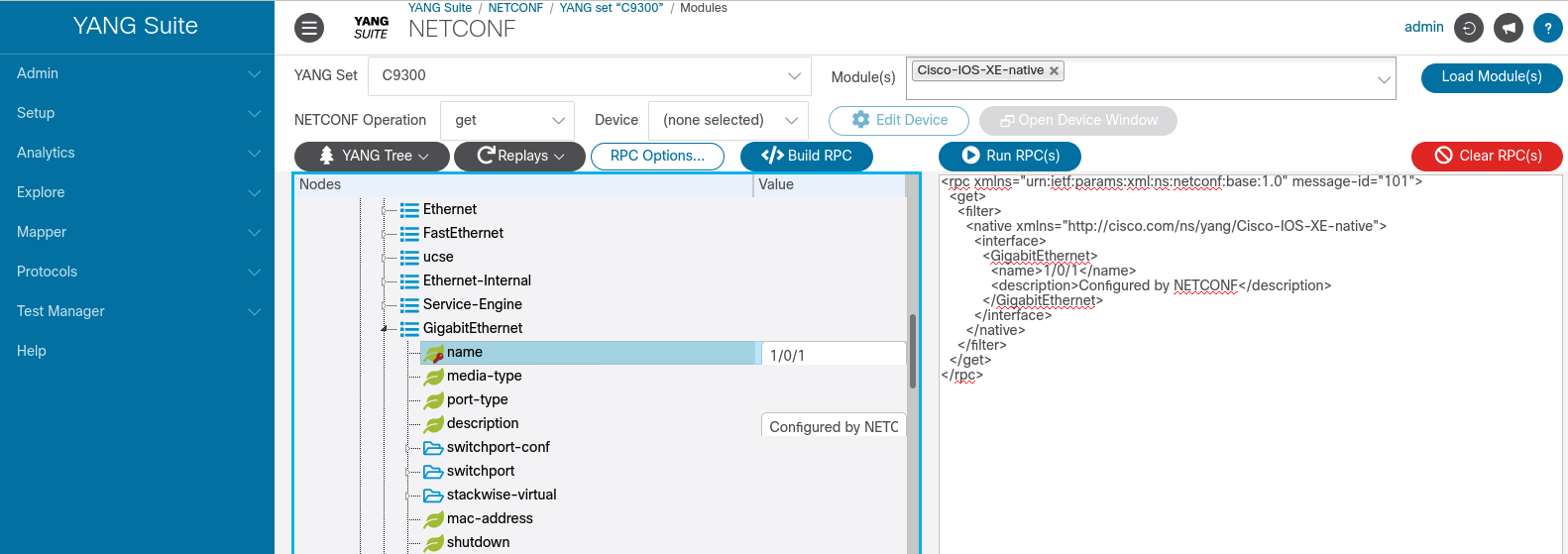
NETCONF-console can also be used to send XML payloads that we generated with YDK, YANGSuite, pYang, or other similar tooling. In this example the XML payload is used to update some interface descriptions.
In this case the XML is generated from the Cisco-IOS-XE-native.YANG model within the interfaces/GigabitEthernet container. The XML was generated using YANGSuite
We can expand on the XML and modify it for mutiple interfaces as desired:
<native xmlns="http://cisco.com/ns/yang/Cisco-IOS-XE-native">
<interface>
<GigabitEthernet><name>1/0/1</name><description>Configured 1 NETCONF</description></GigabitEthernet>
<GigabitEthernet><name>1/0/2</name><description>Configured 2 NETCONF</description></GigabitEthernet>
<GigabitEthernet><name>1/0/3</name><description>Configured 3 NETCONF</description></GigabitEthernet>
</interface>
</native>
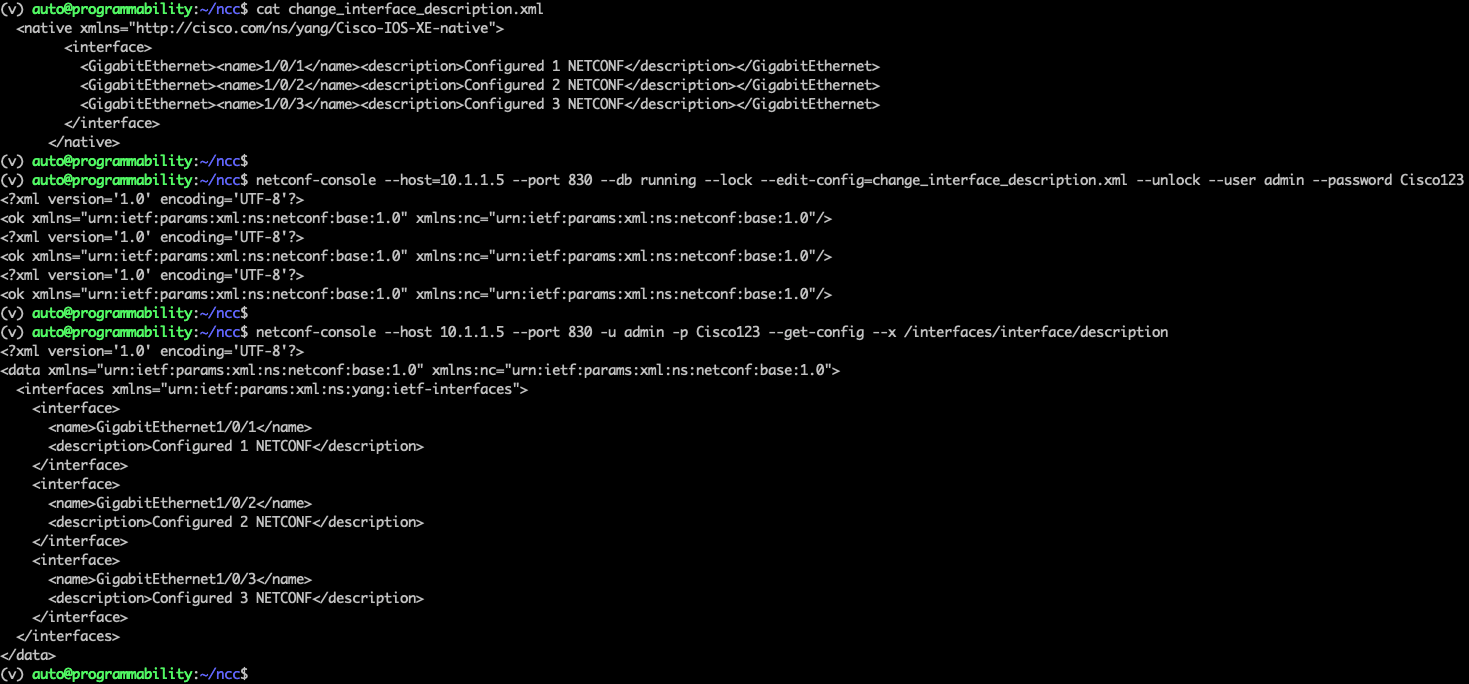
To send the XML payload, use the following NETCONF-console command. The XML from above is specified in the change_interface_description.xml file that NETCONF-console reads and sends to the device.
netconf-console --host=10.1.1.5 --port 830 --db running --lock --edit-config=change_interface_description.xml --unlock --user admin --password Cisco123
To validate that the XML was succesfully sent the configuration of the the interfaces/descriptions can be retreived over NETCONF. This would be similar to "show interface status" CLI
netconf-console --host 10.1.1.5 --port 830 -u admin -p Cisco123 --get-config --x /interfaces/interface/description
In the above example there are 3 commands that are executed:
- Read the XML payload file that will be sent
- Send the XML payload to the NETCONF interface
- Get the interface description configuration from NETCONF
The commands used are:
cat change_interface_description.xml
netconf-console --host=10.1.1.5 --port 830 --db running --lock --edit-config=change_interface_description.xml --unlock --user admin --password Cisco123
netconf-console --host 10.1.1.5 --port 830 -u admin -p Cisco123 --get-config --x /interfaces/interface/description
Add content here :)
YANG Suite is a tool developed by Cisco to help you visualize YANG data models downloaded from a device, to test sending and receiving data to/from devices using YANG models, as well as a NETCONF RPC Builder Application to experiment with YANG Data Models. It is meant to replace YANG Explorer but while YANG Explorer is an Open Source tool, YANG Suite is currently available for Cisco Internal use only.
Open YANG Suite and read configuration data:
Step 1. Open a web browser and access YangSuite at http://10.1.1.3:8480
Step 2. Login using the provided credentials
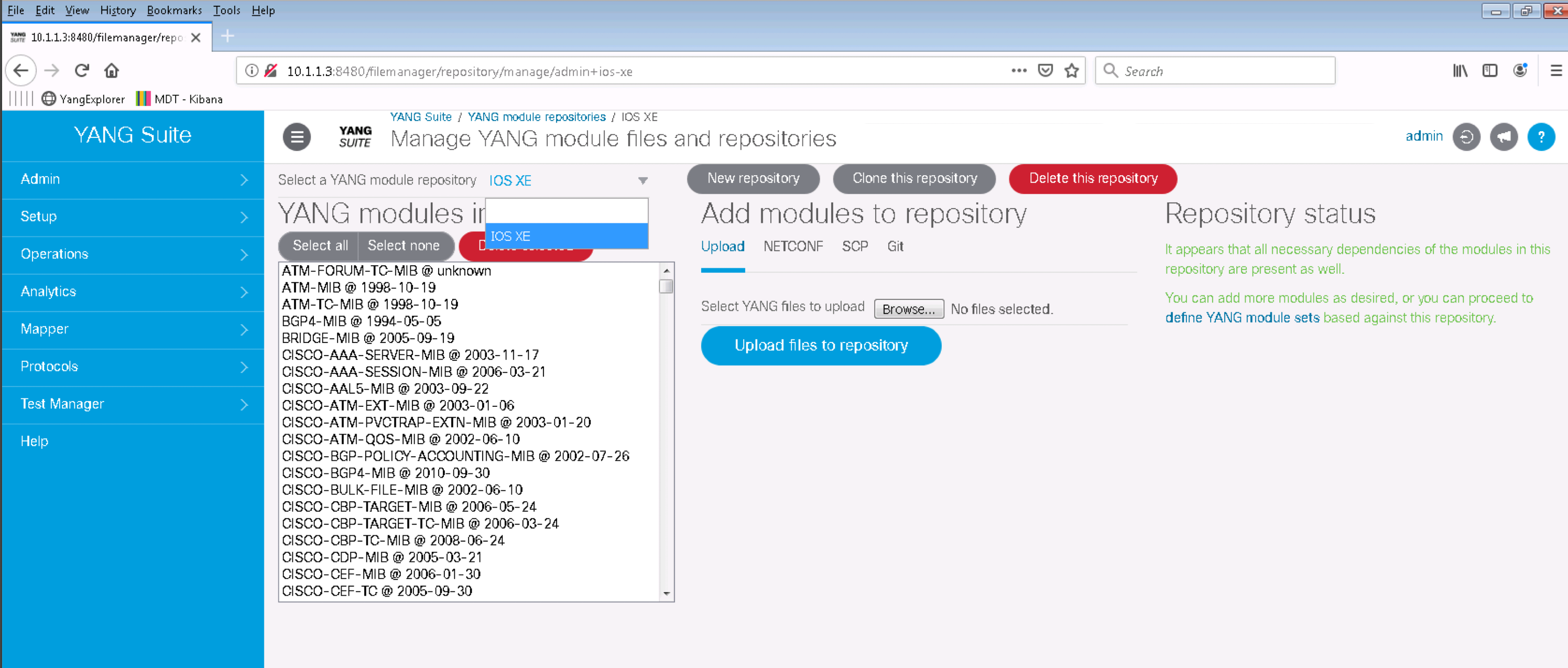
Step 3. YANG Suite allows you to work with different YANG Modules repositories. This is very useful especially if working with different device releases at the same time. Click the Setup menu and then YANG files and repositories. Select IOS XE from the Select a YANG module repository drop down menu. A list of YANG Modules will appear:
These are all the YANG Modules supported on IOS XE. They have been directly downloaded from the Catalyst 9300 using the NETCONF protocol.
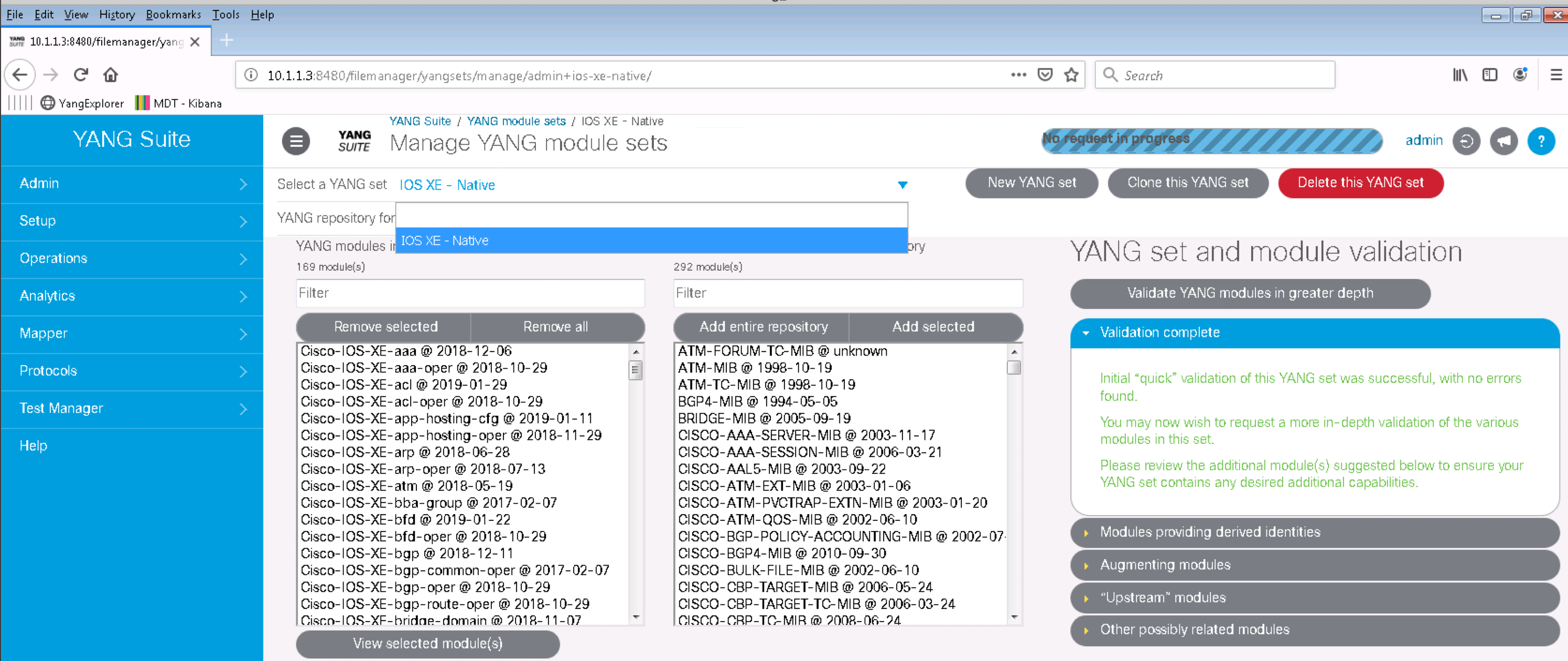
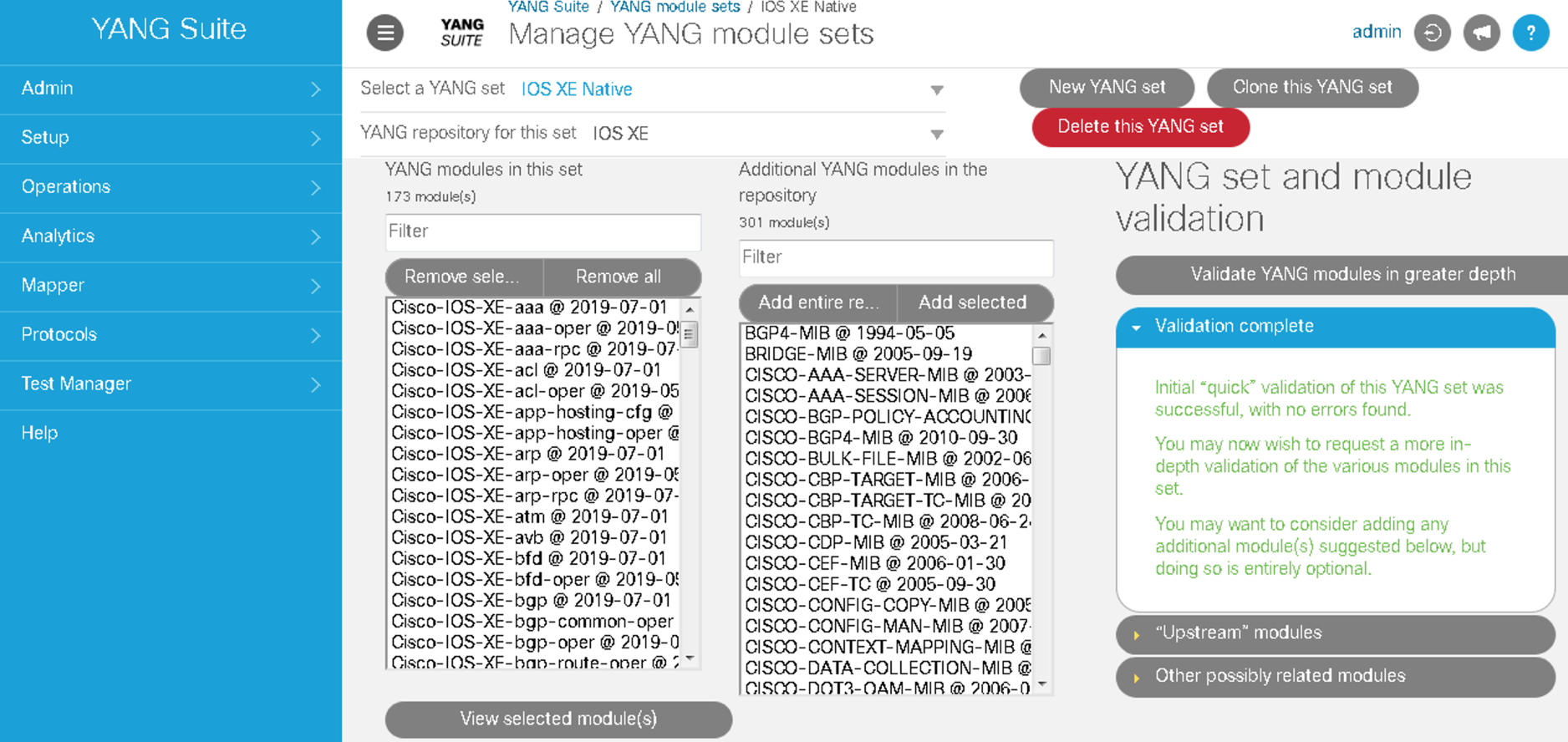
Setp 4. The YANG modules repository you can create subsets of modules called sets. Click in the YANG module sets under the Setup menu on the left pane.
Step 5. Now select IOS XE - Native from the Select a YANG set drop down menu. All the IOS XE Native models are displayed in the box on the left
YANG Suite automatically runs a validation check to make sure all the modules dependencies are met and provides an automatic remediation in case some dependencies are missing. In this case, all models and their dependencies have been preloaded into the tooling.
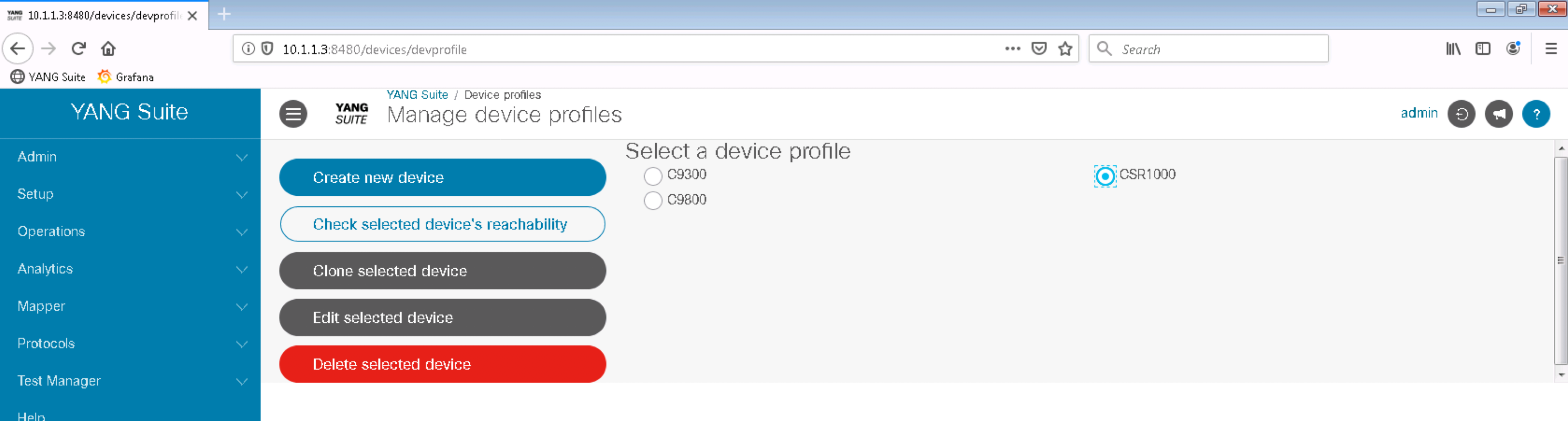
Step 6. Click on the Setup menu and then click on Device profiles on the left pane. It should display 3 device profiles on the right side:
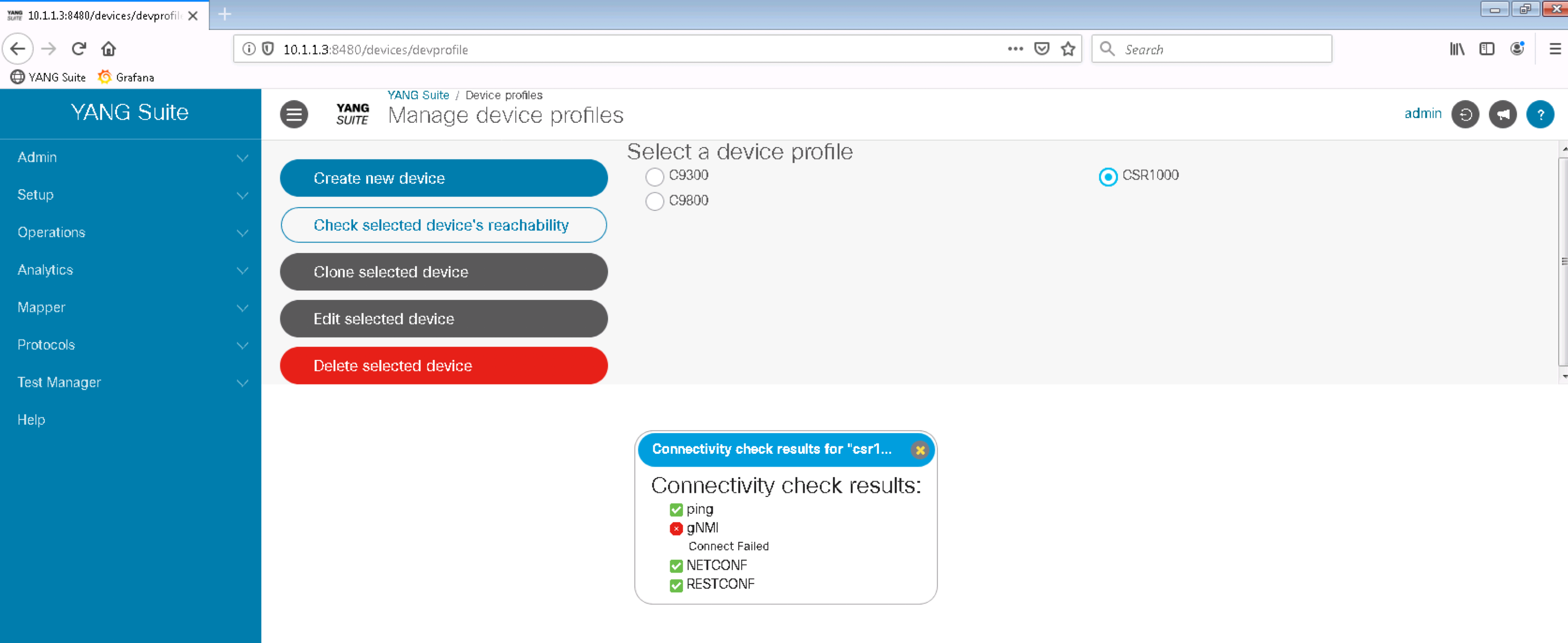
Select CSR1000 profile and click on Check selected device's reachability. All checks should be OK except gNMI which may not yet been configured or enabled on the devices.
Repeat the same process for the other 2 devices to confirm they are reachable and their programmatic interfaces are up
Step 7. YANG Suite provides an intuitive way to navigate the YANG modules.
Note: Cisco supports OpenConfig and IETF YANG models as well as Cisco Native models. The native models, like the Cisco-IOS-XE- models, are required when standards do not support all aspects of Cisco features or functionality.
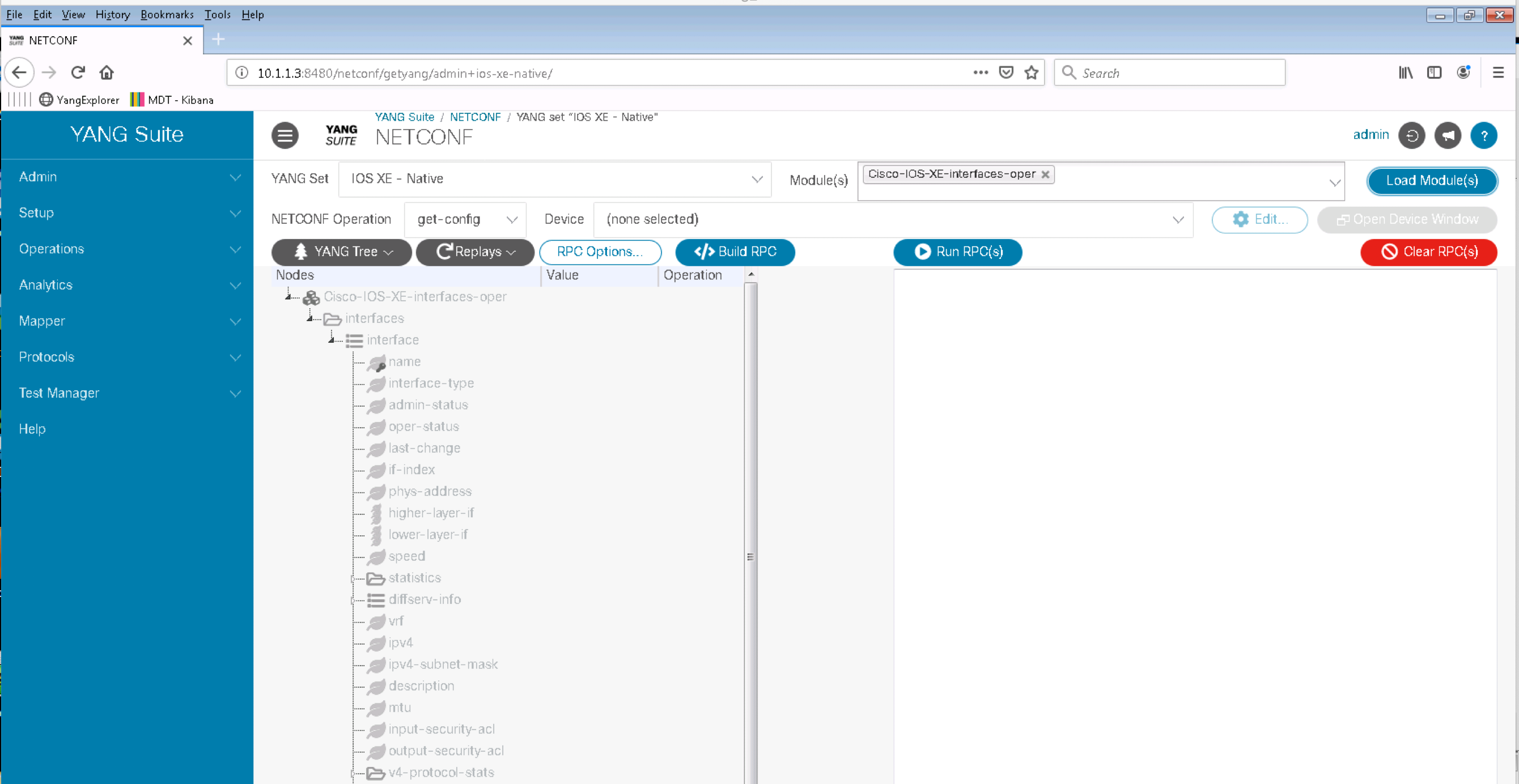
Click on the Operations menu and then Explore YANG on the left pane. Select IOS XE - Native from the Select a YANG set drop down menu.
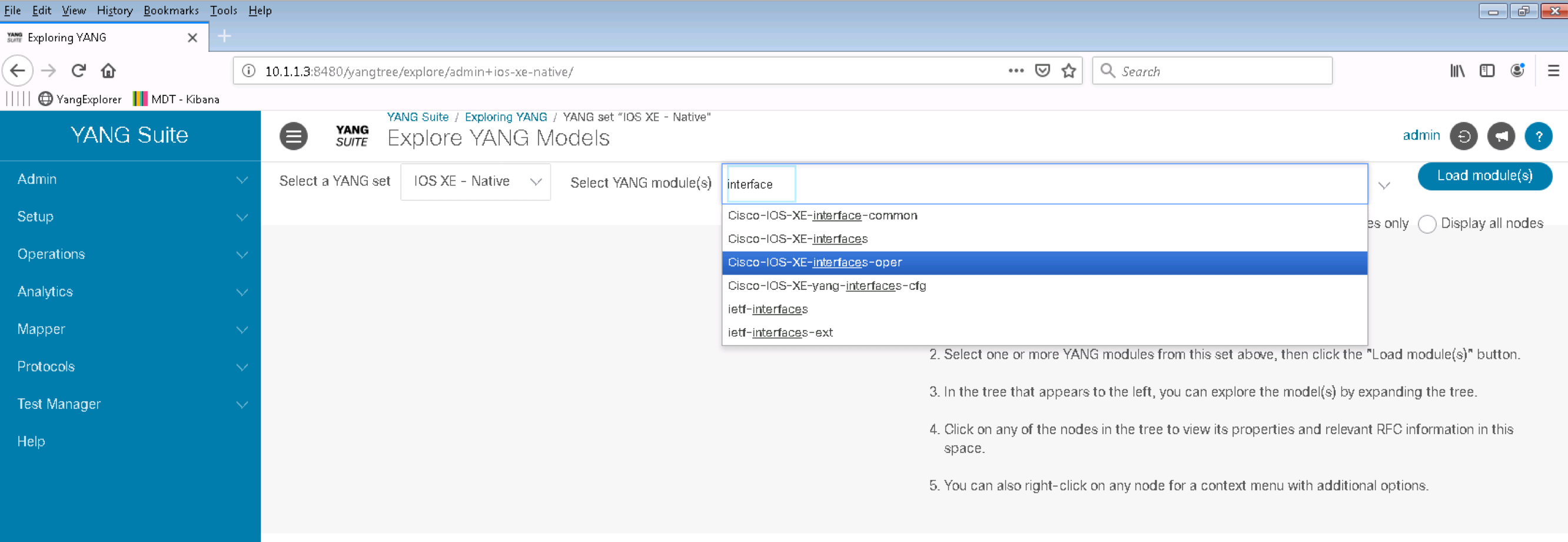
Type interface in the Select YANG module(S) box and select the Cisco-IOS-XE-interfaces-oper module:
Click on the Load module(s) button and expand the Cisco-IOS-XE-interfaces-oper module clicking on the triangle on the left:
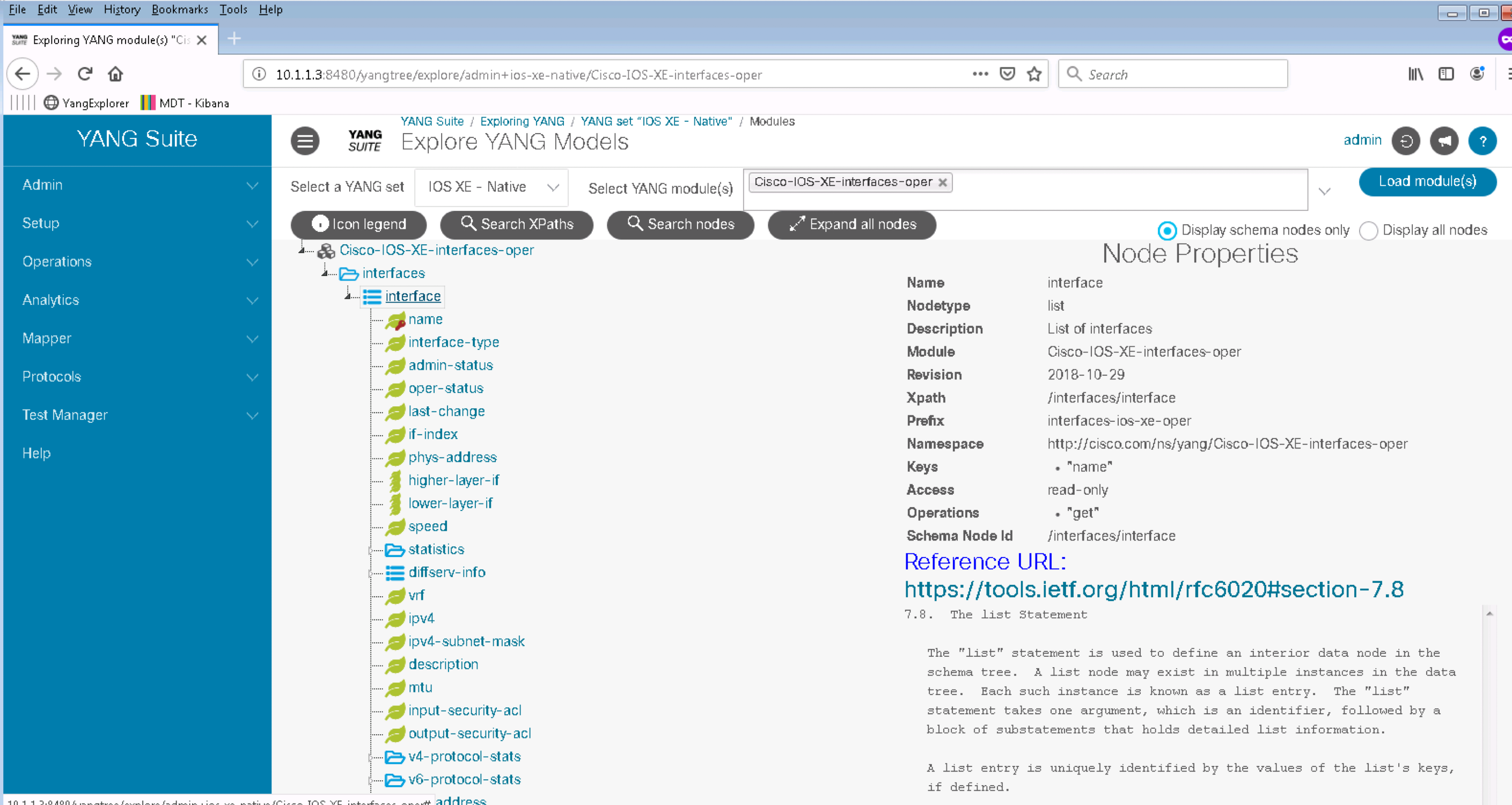
Examine the structure of the model and its content.
Two important pieces of YANG model metadata are the XPath and the Prefix. These fields are used with Model Driven Telemetry to retrieve information with. If a telemetry subscription were to be created based on the IOS XE Interfaces YANG data model, the Xpath of "/interfaces/interface" and "interfaces-ios-xe-oper" would be used to retrieve and publish information from those models.
Click on the interface list icon. On the right side you should see all the info related to interface list, including a reference to the public documentation on YANG lists:
Step 8. YANGSuite allows you to interact with the devices using most of the programmatic interfaces: NETCONF, RESTCONF, gNMI, and gRPC. This step uses the NETCONF programmatic interface:
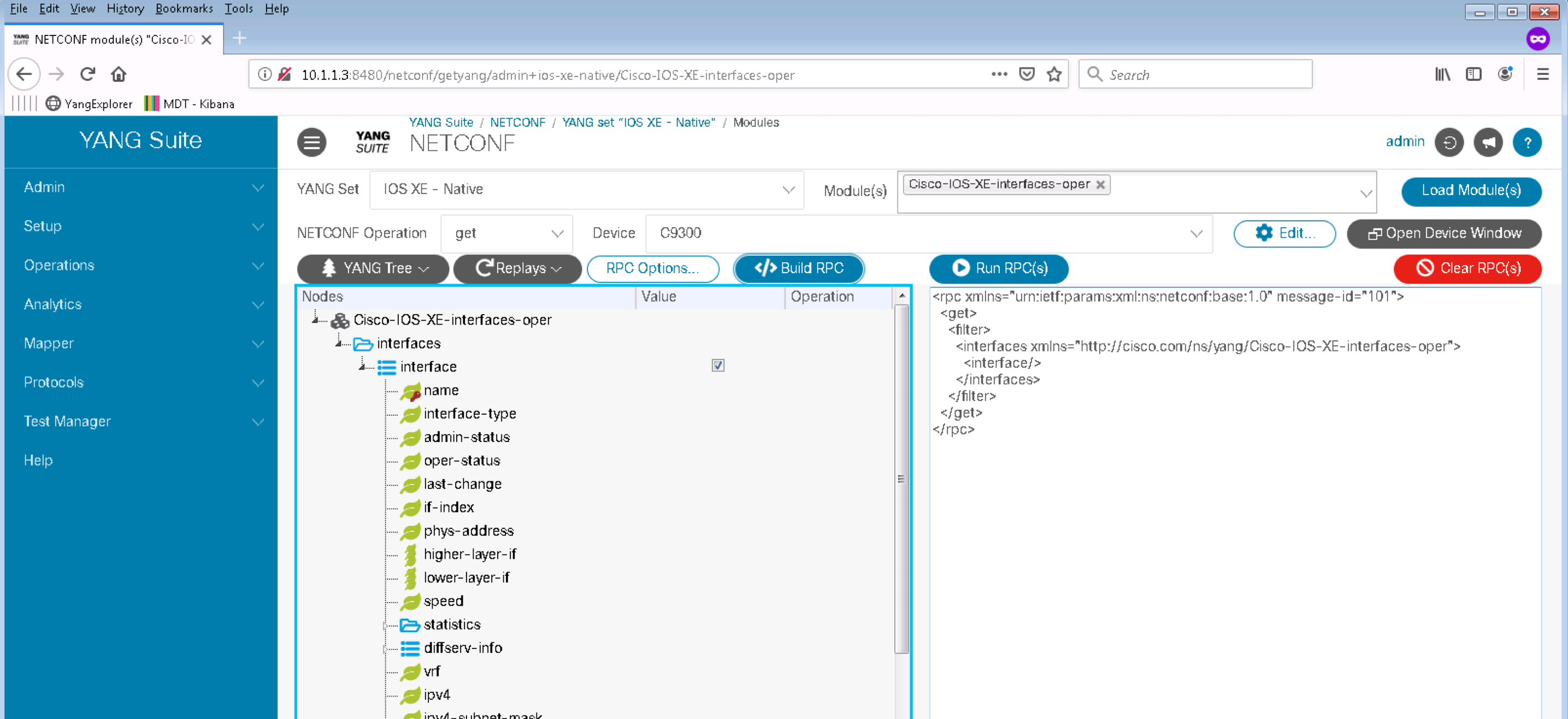
Click on the Protocols menu and then NETCONF. Select IOS XE - Native from the YANG set drop down menu. Type interface in Module(s) box, select the Cisco-IOS-XE-interfaces-oper module, click the Load Modules(s) button and expand the module tree to see the full tree listing.
YANG Suite automatically verifies which NETCONF operation are allowed for the given YANG Modules. All the IOS XE Native modules with names that end with "-oper" are Operational Data Modules. These modules support NETCONF GET operation. The module in the figure above is grayed out because the NETCONF Operation selected is edit-config instead.
Click on get in the NETCONF Operation pane and they shouldn't be grayed out anymore because get is allowed on the given module.
Select a device C9300 from the Device list, click on the Value column for the "interface" row, and a check-box will appear. Click on Build RPC button. A NETCONF RPC should appear in the left pane:
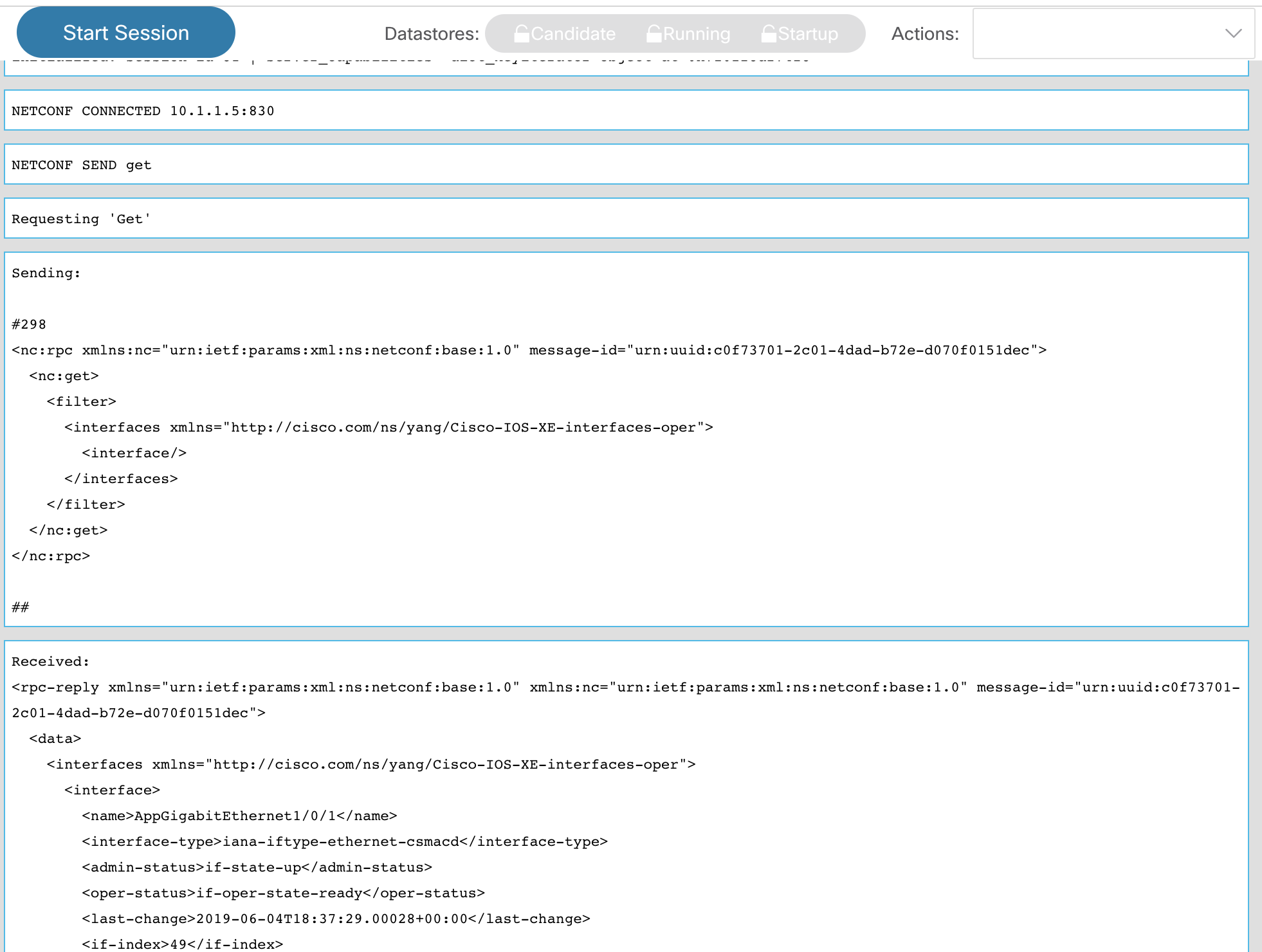
Click on the Run RPC(s) button on the upper right of the RPC window. A new tab with the NETCONF RPC execution should open:
Examine the output. It includes the session details (10.1.1.5:830), the operation type (get) the RPC sent, the operation result code (OK) and finally the output received from the device with all the operational state of all device interfaces.
Step 9. YANG modules allow filtering in order to get only what's really needed. Let's get a specific interface configuration using an IETF module.
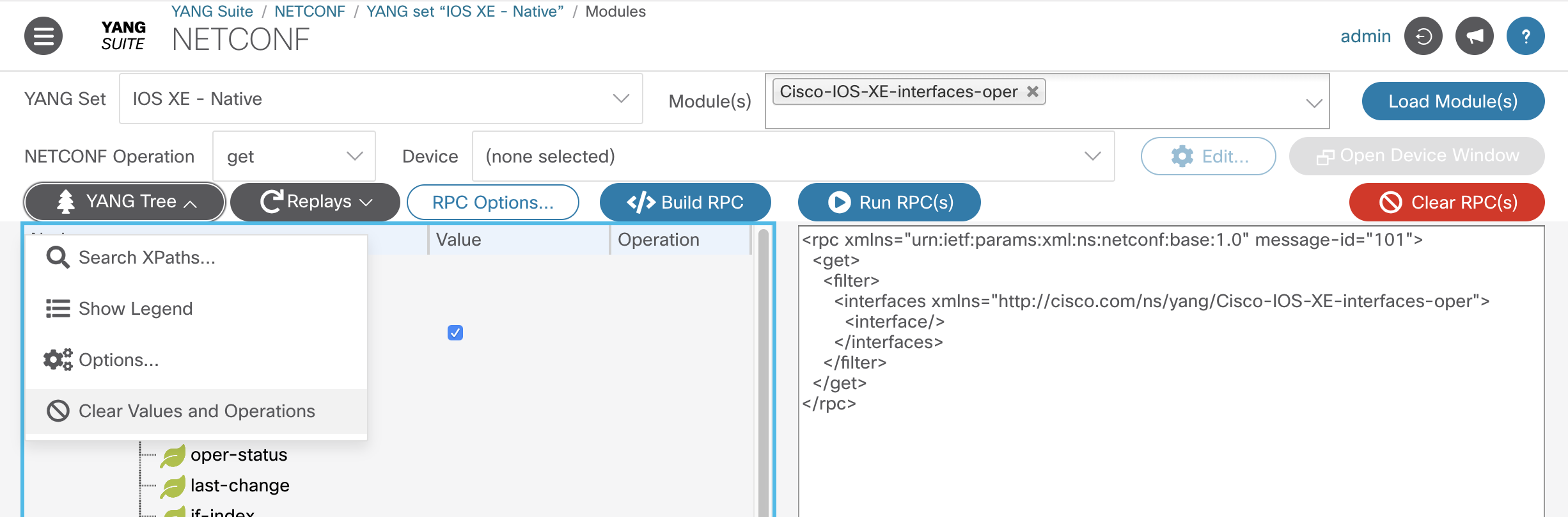
Close the tab with the RPC output and then click on the Clear Values and Operations under YANG Tree and Clear RPC(s) buttons to reset all the values.
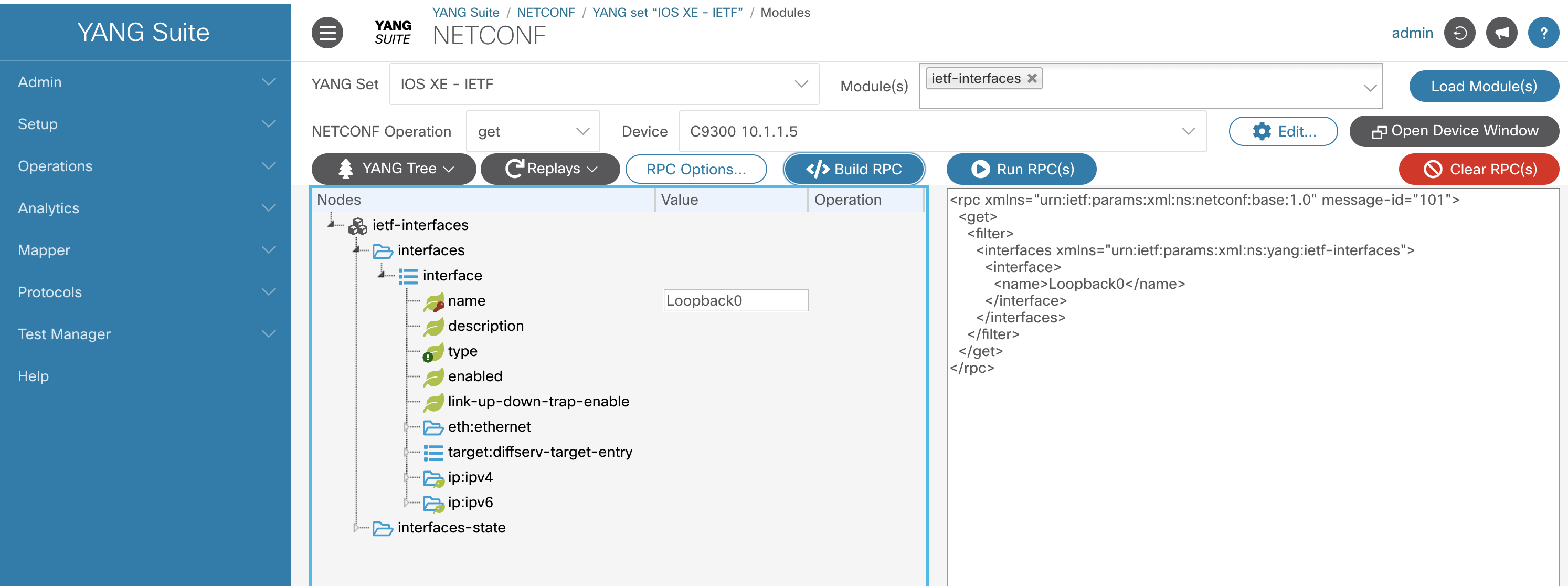
Select IOS XE - IETF module set, type interface in the Module(s) box, select the IETF-interfaces module, click the Load Module(s) button and expand the module by clicking the triangles to the left of ietf-interfaces, interfaces, and then interface.
Click on the Value column in the name row, type Loopback0, click on Build RPC(s).
Note: Be sure not to put a space between "Loopback" and "0"!
Check the RPC and you should see a Loopback0 filter:
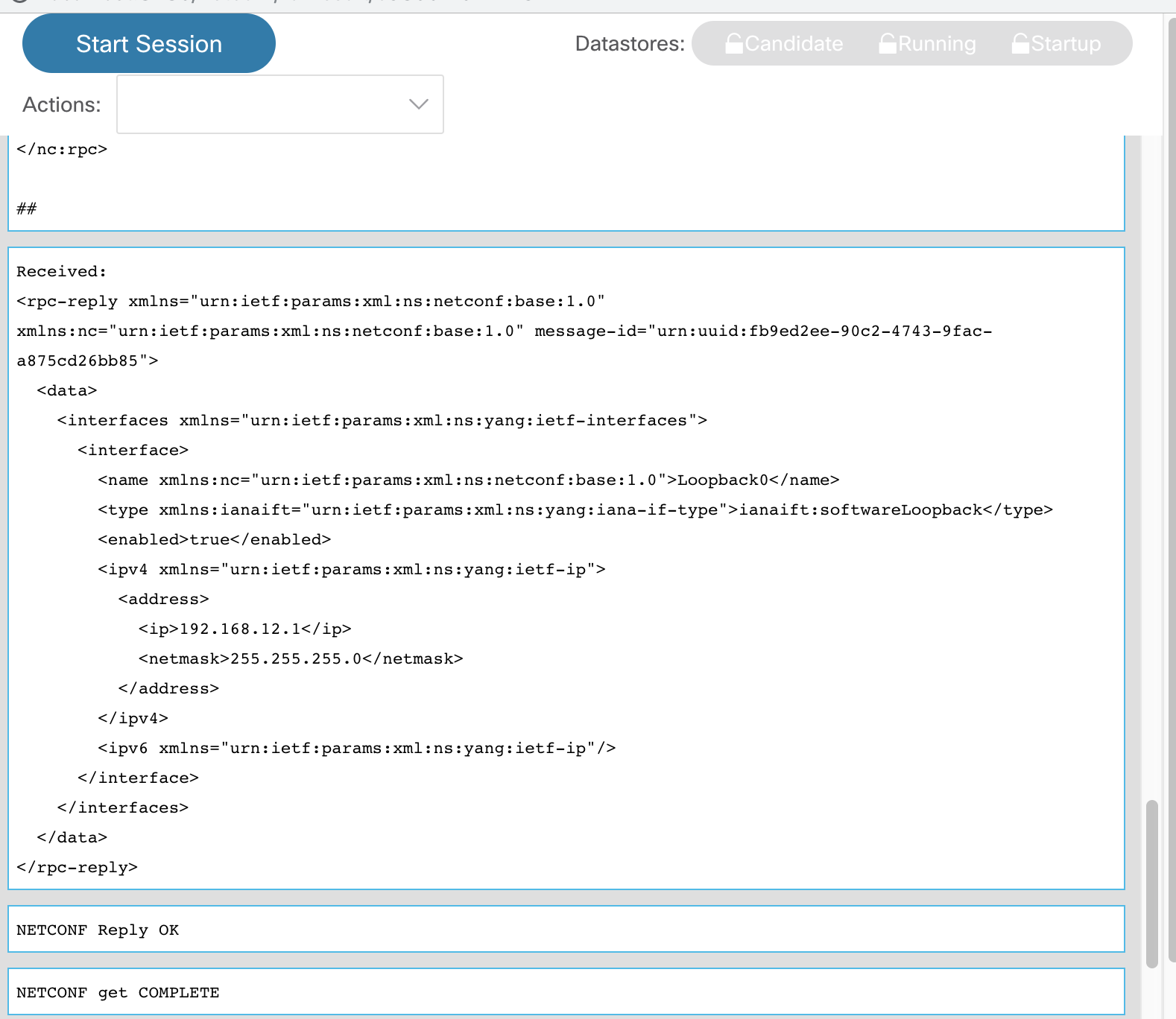
Click on Run RPC(S). This time you should see the Loopback interface configuration only.
Step 10. YANG Suite can be used to modify the device configuration as well.
Click on the Clear Values and Operations and Clear RPCs buttons to reset all the values.
Select edit-config from the NETCONF Operation list. Click on the Value column in the name row and type Loopback0. Click on the Value column in the description row and type configured by YANG Suite. Click on the Build RPC and then Run RPC(s) button.
Verify the Loopback0 description using YANG Suite and the skills just learned.
In this module the YANGSuite tooling was introduced and used to explore the NETCONF programmatic interfaces as well as to understand details of the associated YANG data models.