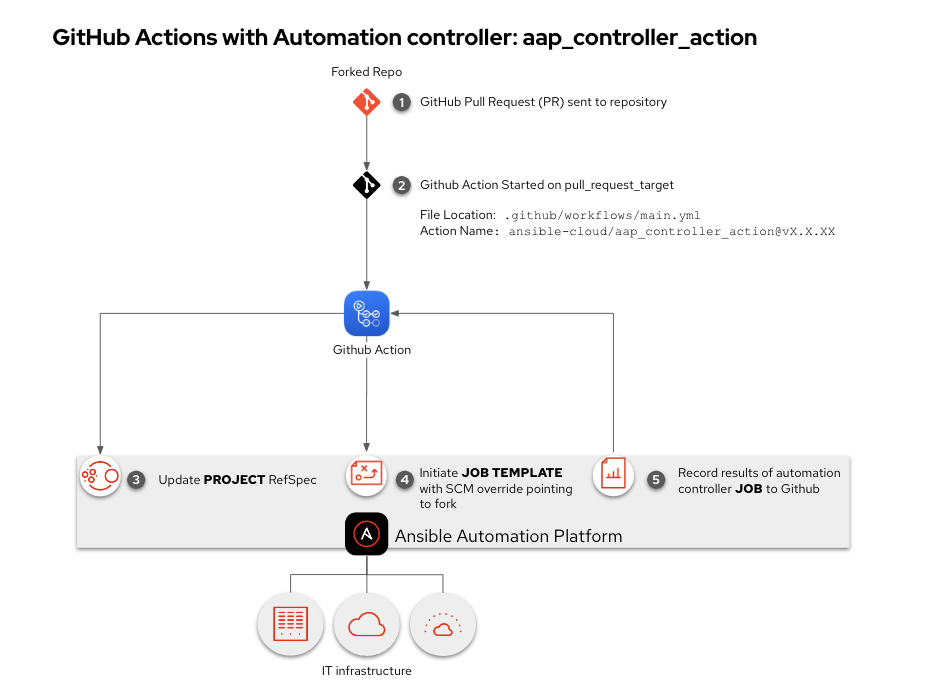
Github Action for Ansible Automation Platform - Automation controller
This would be equivalent of using an Automation controller webhook, but with the added benefit of the output from the job added to Github without additional playbooks needing to be written.
Example of .github/workflows/main.yml
on: push
jobs:
automation_controller_job:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
name: Kick off Automation controller job
steps:
- name: Load the ansible-cloud action
id: controller_job
uses: ansible-cloud/aap_controller_action@v1.2.8
with:
controller_host: ${{ secrets.CONTROLLER_HOST }}
controller_username: ${{ secrets.CONTROLLER_USERNAME }}
controller_password: ${{ secrets.CONTROLLER_PASSWORD }}
job_template: "AWS - ec2 enforce owner tag"
extra_vars: "your_region=us-west-1"
validate_certs: false
In this example we will only initiate the Github Action if there is a Pull Request on our Github repository. We need to have a job_template and controller_project specified. This will make sure that any in-bound pull requests (PRs) are tested rather than your existing project. This will allow people contributing to your Github repo to test their changes before you merge into your downstream repoistory.
Example of .github/workflows/main.yml
on:
pull_request_target:
jobs:
automation_controller_job:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
name: Kick off Automation controller job
steps:
- name: Load the ansible-cloud action
id: controller_job
uses: ansible-cloud/aap_controller_action@vX.X.XX
with:
controller_host: ${{ secrets.CONTROLLER_HOST }}
controller_username: ${{ secrets.CONTROLLER_USERNAME }}
controller_password: ${{ secrets.CONTROLLER_PASSWORD }}
job_template: "test job"
controller_project: "test project"
extra_vars: "your_region=us-west-1"
validate_certs: false
env:
pull_request_event: ${{ github.event.pull_request.number }}
For the Github Pull Request method to work, you need to make sure your specified JOB TEMPLATE has Prompt on launch set for both
- Source Control Branch (which requires the PROJECT to have Allow Branch Override checked)
- Variables
This is also known as Roger Lopez mode. In this example we will only initiate the Github Action if there is a Pull Request on our Github repository. We need to have a workflow_template and controller_project specified. This will make sure that any in-bound pull requests (PRs) are tested on a workflow rather than your existing project. This will allow people contributing to your Github repo to test their changes before you merge into your downstream repoistory.
Example of .github/workflows/main.yml
on:
pull_request_target:
jobs:
automation_controller_job:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
name: Kick off Automation controller job
steps:
- name: Load the ansible-cloud action
id: controller_job
uses: ansible-cloud/aap_controller_action@vX.X.XX
with:
controller_host: ${{ secrets.CONTROLLER_HOST }}
controller_username: ${{ secrets.CONTROLLER_USERNAME }}
controller_password: ${{ secrets.CONTROLLER_PASSWORD }}
workflow_template: "test workflow"
controller_project: "test project"
extra_vars: "your_region=us-west-1"
validate_certs: false
env:
pull_request_event: ${{ github.event.pull_request.number }}
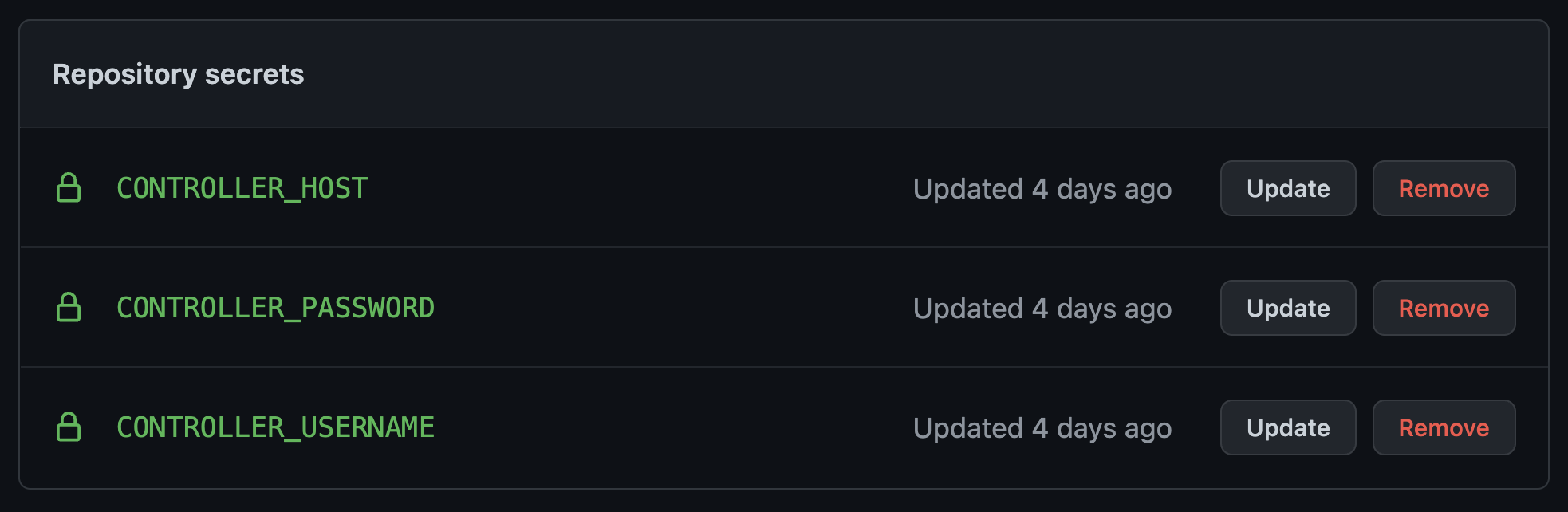
You need to setup 3 (three) secrets:
- CONTROLLER_HOST - this is the DNS name or IP address of your Automation controller.
- CONTROLLER_USERNAME - the username to access Automation controller
- CONTROLLER_PASSWORD - the password to access Automation controller
Example screenshot of Github Secrets