The API.AI Android SDK makes it easy to integrate speech recognition with API.AI natural language processing API on Android devices. API.AI allows using voice commands and integration with dialog scenarios defined for a particular agent in API.AI.
Two permissions are required to use the API.AI Android SDK:
- android.permission.INTERNET for internet access
- android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO for microphone access
Add this dependencies to your project to use SDK
compile 'ai.api:sdk:2.0.7@aar'
// api.ai SDK dependencies
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:23.2.1'
Currently, speech recognition is performed using Google's Android SDK, either on the client device or in the cloud. Recognized text is passed to the API.AI through HTTP requests. Also you can try Speaktoit recognition engine (Use AIConfiguration.RecognitionEngine.Speaktoit).
Authentication is accomplished through setting the client access token when initializing an AIConfiguration object. The client access token specifies which agent will be used for natural language processing.
Note: The API.AI Android SDK only makes query requests, and cannot be used to manage entities and intents. Instead, use the API.AI user interface or REST API to create, retrieve, update, and delete entities and intents.
- Running the Sample Code
- Getting Started with Your Own App
- Tutorial
- Brief Integration Instruction (for experienced developers)
- Feature examples
- Troubleshooting
The API.AI Android SDK comes with a simple sample that illustrates how voice commands can be integrated with API.AI. Use the following steps to run the sample code:
- Have an API.AI agent created that has entities and intents. See the API.AI documentation on how to do this.
- Open Android Studio.
- Import the api-ai-android-master directory.
- Open the SDK Manager and be sure that you have installed Android Build Tools 19.1.
- In the Project browser, open apiAISampleApp/src/main/java/ai.api.sample/Config.
- Towards the top of the file, you will see a declaration of a static final string called ACCESS_TOKEN. Set its value to be the client access token of your agent.
- Attach an Android device, or have the emulator set up with an emulated device.
- From the Run menu, choose Debug (or click the Debug symbol). Choose your device.
- You should see an app running with three buttons: Listen, StopListen, and Cancel.
- Click Listen and say a phrase that will be understood by your agent. Wait a few seconds. The Java will appear that is returned by the API.AI service.
This section describes what you need to do to get started with your own app that uses the API.AI Android SDK. The first part provides an overview of how to use the SDK, and the second part is a tutorial with detailed step-by-step instructions for creating your own app.
If you are an experienced developer you might use brief integration instruction.
To implement speech recognition and natural language processing features in your app, you must first add the API.AI SDK library to your project. There are two ways to accomplish this. The first way is recommended:
-
Add a dependency to your build.gradle file. Add the following line to your build.gradle file. (In the sample app, the apiAISampleApp/build.gradle is an example of how to do this.)
compile 'ai.api:sdk:2.0.7@aar' -
(Not recommended) Download the library source code from github, and attach it to your project.
Now you can use API.AI service features in your app using either integrated speech recognition or using your own speech recognition.
Once you've added the SDK library, follow these steps:
-
Add two permissions into the AndroidManifest:
- android.permission.INTERNET
- android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO
-
Create a class that implements the AIListener interface. This class will process responses from API.AI.
public interface AIListener { void onResult(AIResponse result); // here process response void onError(AIError error); // here process error void onAudioLevel(float level); // callback for sound level visualization void onListeningStarted(); // indicate start listening here void onListeningCanceled(); // indicate stop listening here void onListeningFinished(); // indicate stop listening here }
-
Create an instance of AIConfiguration, specifying the access token, locale, and recognition engine.
final AIConfiguration config = new AIConfiguration("CLIENT_ACCESS_TOKEN", AIConfiguration.SupportedLanguages.English, AIConfiguration.RecognitionEngine.System);
-
Use the AIConfiguration object to get a reference to the AIService, which will make the query requests.
AIService aiService = AIService.getService(context, config);
-
Set the AIListener instance for the AIService instance.
aiService.setListener(yourAiListenerInstance);
-
Launch listening from the microphone via the startListening method. The SDK will start listening for the microphone input of the mobile device.
aiService.startListening();
-
To stop listening and start the request to the API.AI service using the current recognition results, call the stopListening method of the AIService class.
aiService.stopListening();
-
To cancel the listening process without sending a request to the API.AI service, call the cancel method of the AIService class.
aiService.cancel();
-
If there are no errors, you can get the result using the AIResponse.getResult method. From there, you can obtain the action and parameters.
public void onResult(final AIResponse response) { Log.i(TAG, "Action: " + result.getAction()); // process response object }
This section assumes that you have performed your own speech recognition and that you have text that you want to process as natural language. Once you've added the SDK library, follow these steps:
-
Add this permission into the AndroidManifest:
- android.permission.INTERNET
-
Create an instance of AIConfiguration, specifying the access token, locale, and recognition engine. You can specify any recognition engine, since that value will not be used.
-
Create an AIDataService instance using the configuration object.
-
Create the empty AIRequest instance. Set the request text using the method setQuery.
-
Send the request to the API.AI service using the method aiDataService.request(aiRequest).
-
Process the response.
The following example code sends a query with the text "Hello".
First, it initialize aiDataService and aiRequest instances
final AIConfiguration config = new AIConfiguration(ACCESS_TOKEN,
AIConfiguration.SupportedLanguages.English,
AIConfiguration.RecognitionEngine.System);
final AIDataService aiDataService = new AIDataService(config);
final AIRequest aiRequest = new AIRequest();
aiRequest.setQuery("Hello");Then it calls the aiDataService.request method. Please note, that you must call aiDataService.request method from background thread, using AsyncTask class, for example.
new AsyncTask<AIRequest, Void, AIResponse>() {
@Override
protected AIResponse doInBackground(AIRequest... requests) {
final AIRequest request = requests[0];
try {
final AIResponse response = aiDataService.request(aiRequest);
return response;
} catch (AIServiceException e) {
}
return null;
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(AIResponse aiResponse) {
if (aiResponse != null) {
// process aiResponse here
}
}
}.execute(aiRequest);After implementing AIListener interface, you can get the response from api.ai inside your listener like this:
public void onResult(final AIResponse response) {
// Use the response object to get all the results
}Here is how to get different part of the result object:
-
Get the status
final Status status = response.getStatus(); Log.i(TAG, "Status code: " + status.getCode()); Log.i(TAG, "Status type: " + status.getErrorType());
-
Get resolved query
final Result result = response.getResult(); Log.i(TAG, "Resolved query: " + result.getResolvedQuery());
-
Get action
final Result result = response.getResult(); Log.i(TAG, "Action: " + result.getAction());
-
Get speech
final Result result = response.getResult(); final String speech = result.getFulfillment().getSpeech(); Log.i(TAG, "Speech: " + speech);
-
Get metadata
final Result result = response.getResult(); final Metadata metadata = result.getMetadata(); if (metadata != null) { Log.i(TAG, "Intent id: " + metadata.getIntentId()); Log.i(TAG, "Intent name: " + metadata.getIntentName()); }
-
Get parameters
final Result result = response.getResult(); final HashMap<String, JsonElement> params = result.getParameters(); if (params != null && !params.isEmpty()) { Log.i(TAG, "Parameters: "); for (final Map.Entry<String, JsonElement> entry : params.entrySet()) { Log.i(TAG, String.format("%s: %s", entry.getKey(), entry.getValue().toString())); } }
This section contains a detailed tutorial about creating new app and connect it to API.AI.
Follow these steps to set up your environment and create new android app with API.AI integration:
- Create an API.AI agent with entities and intents, or use one that you've already created. See the API.AI documentation for instructions on how to do this.
- Open Android Studio. (Download it if you don't have it.)
- From the start screen (or File menu) , choose New Project....
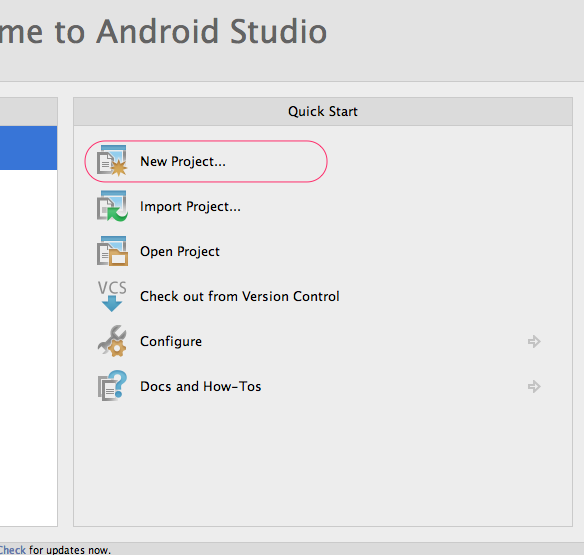
- In the New Project dialog, fill Application name and Company Domain, then click Next.
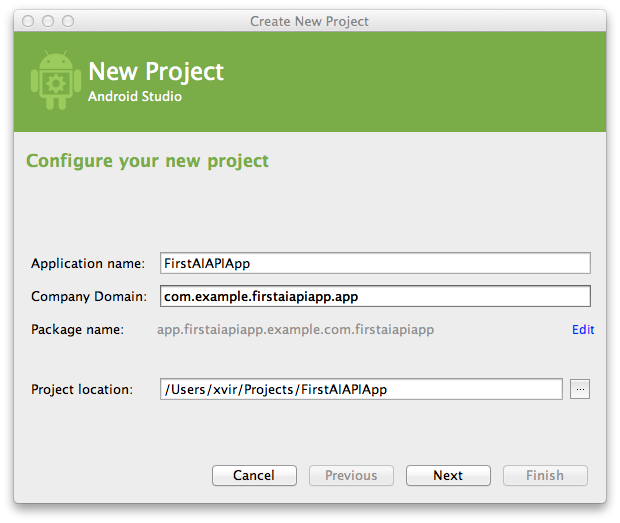
- Choose minimum SDK for project, minimum supported by API.AI SDK is 9 Gingerbread. Click Next.
- Select Blank Activity and click Next.
- Enter the main activity name and click Finish.
Next you will integrate with the SDK to be able to make calls. Follow these steps:
-
Open AndroidManifest.xml under app/src/main.
-
Just above the
<application>tag, add these line in order to give the app permission to access the internet and the microphone:<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO" />
-
Save AndroidManifest.xml.
-
Next, you need to add a new dependency for the AI.API library. Right click on your module name (it should be app) in the Project Navigator and select Open Module Settings. Click on the Dependencies tab. Click on the + sign on the bottom left side and select Library dependency.
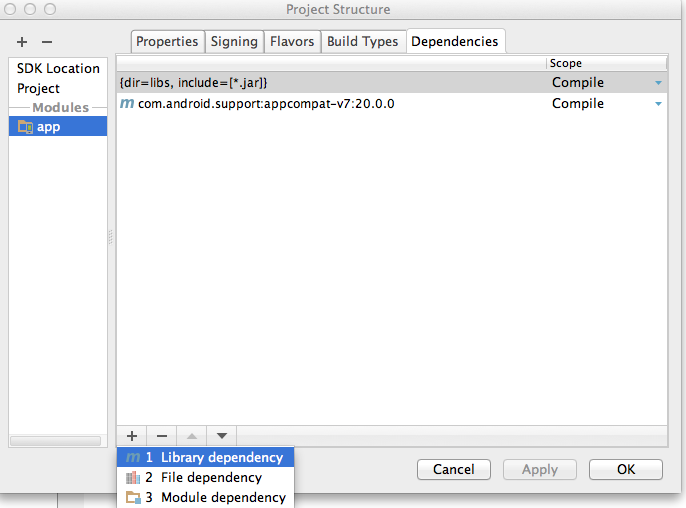
-
In the opened dialog search ai.api, choose ai.api:sdk:2.0.5 item and append
@aarto the end of library name (see image) then click OK.
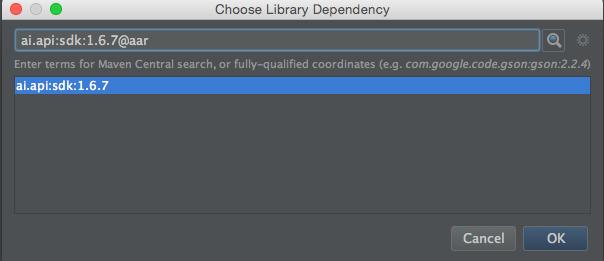
- Also you need to add dependencies of the SDK library : com.android.support:appcompat-v7, com.google.code.gson:gson, commons-io:commons-io. Add them in the same way.
-
Open MainActivity.java under app/src/main/java/com.example.yourAppName.app, or whatever your package name is.
-
Expand the import section and add the following lines to import the necessary API.AI classes:
import ai.api.AIListener; import ai.api.android.AIConfiguration; import ai.api.android.AIService; import ai.api.model.AIError; import ai.api.model.AIResponse; import ai.api.model.Result; import com.google.gson.JsonElement; import java.util.Map;
-
Open activity_main.xml under app/src/main/res/layout. This will open the layout in the designer.
-
Select and delete the "Hello World" TextView.
-
Drag a Button (under Widgets) to the top of the screen. Change the id property to "listenButton" and the text property to "Listen".
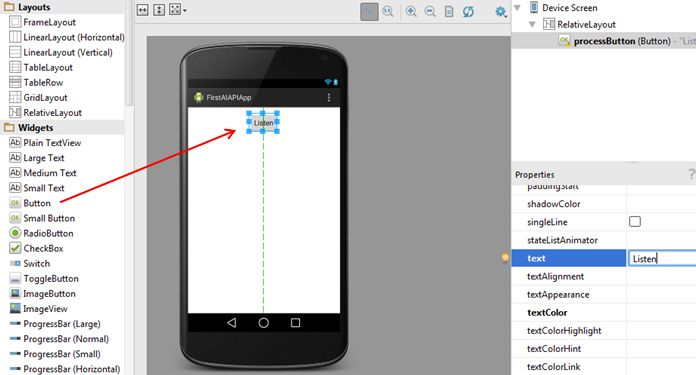
-
Drag a Plain TextView (under Widgets) under the button. Expand it so that it covers the rest of the bottom of the screen. Change the id property to "resultTextView" and the text property to an empty string.
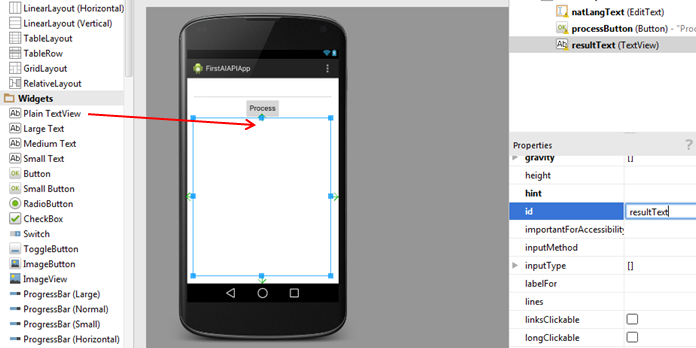
-
Now return to the MainActivity.java file. Add three import statements to access our widgets:
import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.TextView;
-
Create two private members in MainActivity for the widgets:
private Button listenButton; private TextView resultTextView;
-
At the end of the OnCreate method, add these lines to initialize the widgets:
listenButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.listenButton); resultTextView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.resultTextView);
-
Use the MainActivity as the class that will be called when events occur by having it implement the AIListener class. Replace the class declaration with this:
public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity implements AIListener { -
In the MainActivity class, create a private member for the AIService class named
aiService.private AIService aiService;
-
In the OnCreate method, add the following line to set up the configuration to use system speech recognition. Replace CLIENT_ACCESS_TOKEN with your client access token.
final AIConfiguration config = new AIConfiguration("CLIENT_ACCESS_TOKEN", AIConfiguration.SupportedLanguages.English, AIConfiguration.RecognitionEngine.System);
-
Below this line, initialize the AI service and add this instance as the listener to handle events.
aiService = AIService.getService(this, config); aiService.setListener(this);
-
Add method to start listening on the button click:
public void listenButtonOnClick(final View view) { aiService.startListening(); }
-
Return to activity_main.xml and click on the Listen button. In the properties pane, set the onClick property to listenButtonOnClick.
-
Add the following method to show the results when the listening is complete:
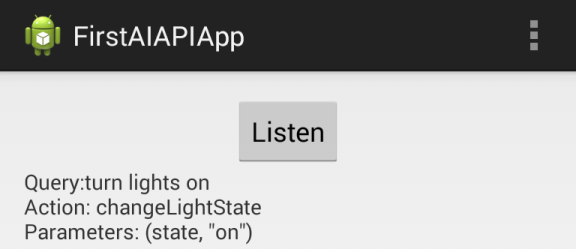
public void onResult(final AIResponse response) { Result result = response.getResult(); // Get parameters String parameterString = ""; if (result.getParameters() != null && !result.getParameters().isEmpty()) { for (final Map.Entry<String, JsonElement> entry : result.getParameters().entrySet()) { parameterString += "(" + entry.getKey() + ", " + entry.getValue() + ") "; } } // Show results in TextView. resultTextView.setText("Query:" + result.getResolvedQuery() + "\nAction: " + result.getAction() + "\nParameters: " + parameterString); }
-
Add the following method to handle errors:
@Override public void onError(final AIError error) { resultTextView.setText(error.toString()); }
-
Add the following empty methods to implement the AIListener interface:
@Override public void onListeningStarted() {} @Override public void onListeningCanceled() {} @Override public void onListeningFinished() {} @Override public void onAudioLevel(final float level) {}
- Attach an Android device to your computer or have a virtual device ready.
- Make sure that your module is selected in the dropdown, and then click the Debug button.
- The app should now be running on your device or virtual device. Click the Listen button and then speak a phrase that will work with your intent. Wait a few seconds. The result should appear in the result TextView.
To specify additional contexts in the query you can use RequestExtras object.
First create list of contexts you need:
List<AIContext> contexts = new ArrayList<>();
contexts.add(new AIContext("firstContext"));
contexts.add(new AIContext("secondContext"));Then create RequestExtras instance and use it for request
RequestExtras requestExtras = new RequestExtras(contexts, null);
aiService.startListening(requestExtras);To specify user entities in the query you can use RequestExtras object.
First create list of entities you need:
final Entity myDwarfs = new Entity("dwarfs");
myDwarfs.addEntry(new EntityEntry("Ori", new String[] {"Ori", "Nori"}));
myDwarfs.addEntry(new EntityEntry("Bifur", new String[] {"Bofur","Bombur"}));
final List<Entity> entities = Collections.singletonList(myDwarfs);Then create RequestExtras instance and use it for request
RequestExtras requestExtras = new RequestExtras(null, entities);
aiService.startListening(requestExtras);Also you can upload user entities with separate method
aiService.uploadUserEntities(entities);Do these steps to make SDK work with Bluetooth devices:
-
Create implementation of the BluetoothController near your Application class
private class BluetoothControllerImpl extends BluetoothController { public BluetoothControllerImpl(Context context) { super(context); } @Override public void onHeadsetDisconnected() { Log.d(TAG, "Bluetooth headset disconnected"); } @Override public void onHeadsetConnected() { Log.d(TAG, "Bluetooth headset connected"); if (isInForeground() && !bluetoothController.isOnHeadsetSco()) { bluetoothController.start(); } } @Override public void onScoAudioDisconnected() { Log.d(TAG, "Bluetooth sco audio finished"); bluetoothController.stop(); if (isInForeground()) { bluetoothController.start(); } } @Override public void onScoAudioConnected() { Log.d(TAG, "Bluetooth sco audio started"); } }
-
Add to your
Applicationclass integer field to count Activities andBluetoothControllerclass implementation for Bluetooth managementprivate int activitiesCount; private BluetoothControllerImpl bluetoothController;
-
Add helper methods to your
Applicationclassprotected void onActivityResume() { if (activitiesCount++ == 0) { // on become foreground bluetoothController.start(); } } protected void onActivityPaused() { if (--activitiesCount == 0) { // on become background bluetoothController.stop(); } } private boolean isInForeground() { return activitiesCount > 0; }
-
You need to call this methods from
onPauseandonResumeof every Activity, it can be solved with base class for all your activitiespublic class BaseActivity extends ActionBarActivity { private AIApplication app; private static final long PAUSE_CALLBACK_DELAY = 500; private final Handler handler = new Handler(); private Runnable pauseCallback = new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { app.onActivityPaused(); } }; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); app = (AIApplication) getApplication(); } @Override protected void onResume() { super.onResume(); app.onActivityResume(); } @Override protected void onPause() { super.onPause(); handler.postDelayed(pauseCallback, PAUSE_CALLBACK_DELAY); } }
A complete example can be found in the Sample Application.
- If you get an error when trying to install app that says "INSTALL_FAILED_OLDER_SDK", then check you have Android SDK 19 and build tools 19.1 installed.
Please read and follow the steps in the CONTRIBUTING.md.
See LICENSE.
Your use of this sample is subject to, and by using or downloading the sample files you agree to comply with, the Google APIs Terms of Service.
This is not an official Google product.