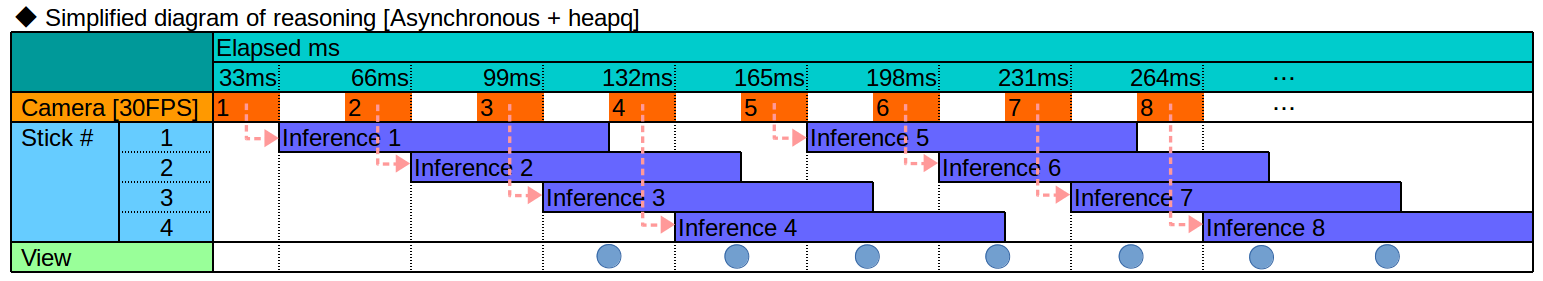
YoloV3 / tiny-YoloV3 + RaspberryPi3 / Ubuntu LaptopPC + NCS/NCS2 + USB Camera + Python
Inspired from https://github.com/mystic123/tensorflow-yolo-v3.git
Performance comparison as a mobile application (Based on sensory comparison)
◯=HIGH, △=MEDIUM, ×=LOW
| No. | Model | Speed | Accuracy | Adaptive distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SSD | × | ◯ | ALL |
| 2 | MobileNet-SSD | △ | △ | Short distance |
| 3 | YoloV3 | × | ◯ | ALL |
| 4 | tiny-YoloV3 | ◯ | × | Long distance |
- [24 FPS] Boost RaspberryPi3 with four Neural Compute Stick 2 (NCS2) MobileNet-SSD / YoloV3 [48 FPS for Core i7]
- [13 FPS] NCS2 x 4 + Full size YoloV3 performance has been tripled
<CPP + YoloV3 - Intel Core i7-8750H, CPU Only, 4 FPS - 5 FPS>

<CPP + tiny-YoloV3 - Intel Core i7-8750H, CPU Only, 60 FPS>

<Python + tiny-YoloV3 + USBCamera, Core i7-8750H, CPU Only, 30 FPS>
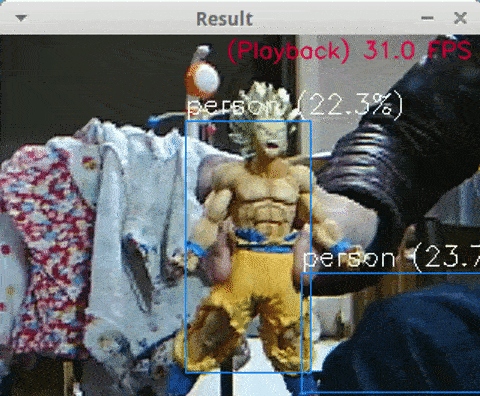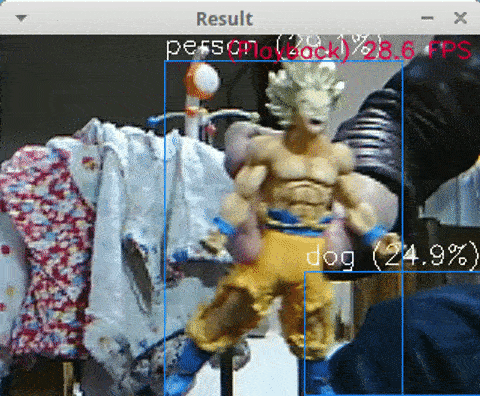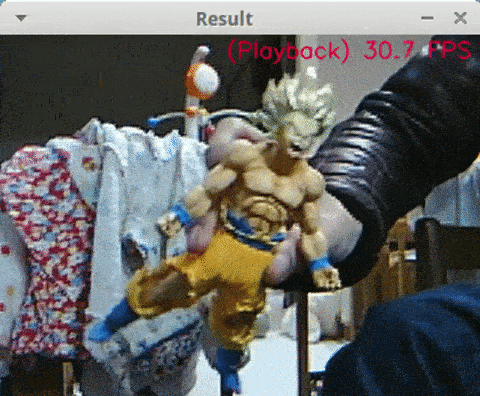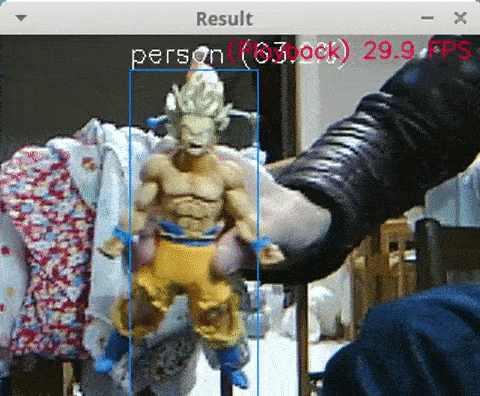
<Python + YoloV3 + MP4, Core i7-8750H, NCS2 x4, 13 FPS>
【Note】 Due to the performance difference of ARM <-> Core series, performance is degraded in RaspberryPi3.
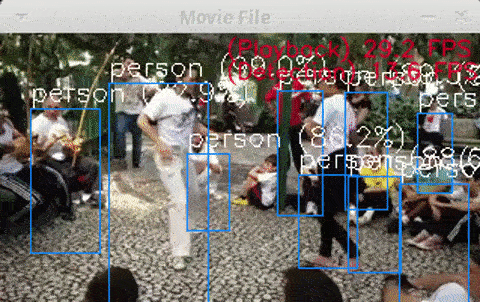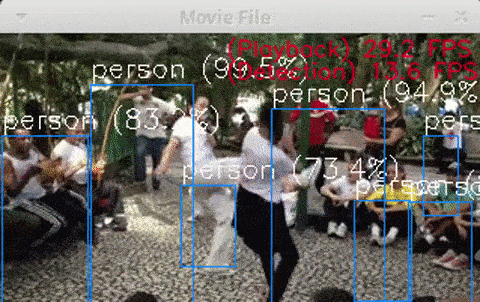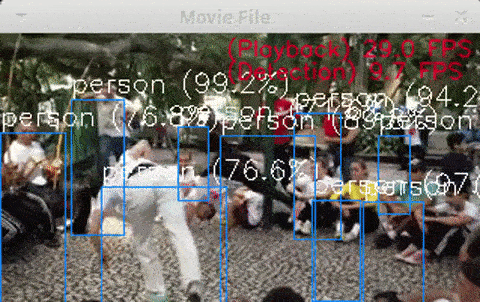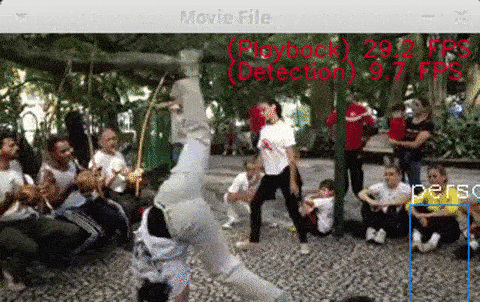
$ python3 openvino_yolov3_test.py$ python3 openvino_tiny-yolov3_MultiStick_test.py -numncs 1$ python3 openvino_yolov3_MultiStick_test.py -numncs 4cpp version is here "cpp/object_detection_demo_yolov3_async"
- LattePanda Alpha (Intel 7th Core m3-7y30) or LaptopPC (Intel 8th Core i7-8750H)
- Ubuntu 16.04 x86_64
- RaspberryPi3
- Raspbian Stretch armv7l
- OpenVINO toolkit 2018 R5 (2018.5.445)
- Python 3.5
- OpenCV 4.0.1-openvino
- Tensorflow v1.11.0 or Tensorflow-GPU v1.11.0 (pip install)
- YoloV3 (MS-COCO)
- tiny-YoloV3 (MS-COCO)
- USB Camera (PlaystationEye) / Movie file (mp4)
- Intel Neural Compute Stick v1 / v2
- Supported Framework Layers
- Supported Caffe Layers
- Supported TensorFlow Layers
- Supported MXNet Layers
- Supported ONNX Layers
Supported Devices (https://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/OpenVINO-InferEngine#inpage-nav-10-2)
| Layers | GPU | CPU | MYRIAD | GNA | FPGA | ShapeInfer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activation-Clamp | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Activation-ELU | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Activation-Leaky ReLU | Supported | Not Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Activation-PReLU | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Activation-ReLU | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Activation-ReLU6 | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Activation-Sigmoid/Logistic | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Activation-TanH | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| ArgMax | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| BatchNormalization | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Concat | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Const | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported |
| Convolution-Dilated | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Convolution-Grouped | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Convolution-Ordinary | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Crop | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| CTCGreedyDecoder | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Deconvolution | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Supported | Supported |
| DetectionOutput | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Eltwise-Max | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Eltwise-Mul | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Eltwise-Sum | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Flatten | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| FullyConnected (Inner Product) | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| GRN | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Interp | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| LRN (Norm) | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Memory | Not Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| MVN | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Normalize | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Permute | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Pooling(AVG,MAX) | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Power | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Supported | Supported |
| PriorBox | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| PriorBoxClustered | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Proposal | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| PSROIPooling | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| RegionYolo | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| ReorgYolo | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Resample | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Reshape | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| ROIPooling | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Scale | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported |
| ScaleShift | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| SimplerNMS | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Slice | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| SoftMax | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| SpatialTransformer | Not Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Split | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Tile | Supported | Supported | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Unpooling | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported |
| Upsampling | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported |
https://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/OpenVINO-InferEngine#inpage-nav-9
1.OpenVINO R5 Full-Install. Execute the following command.
$ cd ~
$ curl -sc /tmp/cookie "https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&id=1tlDW_kDOchWbkZbfy5WfbsW-b_GpXgr7" > /dev/null
$ CODE="$(awk '/_warning_/ {print $NF}' /tmp/cookie)"
$ curl -Lb /tmp/cookie "https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&confirm=${CODE}&id=1tlDW_kDOchWbkZbfy5WfbsW-b_GpXgr7" -o l_openvino_toolkit_p_2018.5.445.tgz
$ tar -zxf l_openvino_toolkit_p_2018.5.445.tgz
$ rm l_openvino_toolkit_p_2018.5.445.tgz
$ cd l_openvino_toolkit_p_2018.5.445
$ sudo -E ./install_cv_sdk_dependencies.sh
## GUI version installer
$ sudo ./install_GUI.sh
or
## CUI version installer
$ sudo ./install.sh2.Configure the Model Optimizer. Execute the following command.
$ cd /opt/intel/computer_vision_sdk/install_dependencies
$ sudo -E ./install_cv_sdk_dependencies.sh
$ nano ~/.bashrc
source /opt/intel/computer_vision_sdk/bin/setupvars.sh
$ source ~/.bashrc
$ cd /opt/intel/computer_vision_sdk/deployment_tools/model_optimizer/install_prerequisites
$ sudo ./install_prerequisites.sh3.【Optional execution】 Additional installation steps for the Intel® Movidius™ Neural Compute Stick v1 and Intel® Neural Compute Stick v2
$ sudo usermod -a -G users "$(whoami)"
$ cat <<EOF > 97-usbboot.rules
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idProduct}=="2150", ATTRS{idVendor}=="03e7", GROUP="users", MODE="0666", ENV{ID_MM_DEVICE_IGNORE}="1"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idProduct}=="2485", ATTRS{idVendor}=="03e7", GROUP="users", MODE="0666", ENV{ID_MM_DEVICE_IGNORE}="1"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idProduct}=="f63b", ATTRS{idVendor}=="03e7", GROUP="users", MODE="0666", ENV{ID_MM_DEVICE_IGNORE}="1"
EOF
$ sudo cp 97-usbboot.rules /etc/udev/rules.d/
$ sudo udevadm control --reload-rules
$ sudo udevadm trigger
$ sudo ldconfig
$ rm 97-usbboot.rules4.【Optional execution】 Additional installation steps for processor graphics (GPU)
$ cd /opt/intel/computer_vision_sdk/install_dependencies/
$ sudo -E su
$ uname -r
4.15.0-42-generic #<--- display kernel version sample
### Execute only when the kernel version is older than 4.14
$ ./install_4_14_kernel.sh
$ ./install_NEO_OCL_driver.sh
$ sudo reboot[Note] Only the execution environment is introduced.
1.Execute the following command.
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt upgrade
$ curl -sc /tmp/cookie "https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&id=1rBl_3kU4gsx-x2NG2I5uIhvA3fPqm8uE" > /dev/null
$ CODE="$(awk '/_warning_/ {print $NF}' /tmp/cookie)"
$ curl -Lb /tmp/cookie "https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&confirm=${CODE}&id=1rBl_3kU4gsx-x2NG2I5uIhvA3fPqm8uE" -o l_openvino_toolkit_ie_p_2018.5.445.tgz
$ tar -zxvf l_openvino_toolkit_ie_p_2018.5.445.tgz
$ rm l_openvino_toolkit_ie_p_2018.5.445.tgz
$ sed -i "s|<INSTALLDIR>|$(pwd)/inference_engine_vpu_arm|" inference_engine_vpu_arm/bin/setupvars.sh2.Execute the following command.
$ nano ~/.bashrc
### Add 1 row below
source /home/pi/inference_engine_vpu_arm/bin/setupvars.sh
$ source ~/.bashrc
### Successful if displayed as below
[setupvars.sh] OpenVINO environment initialized
$ sudo usermod -a -G users "$(whoami)"
$ sudo reboot3.Update USB rule.
$ sh inference_engine_vpu_arm/install_dependencies/install_NCS_udev_rules.sh
### It is displayed as follows
Update udev rules so that the toolkit can communicate with your neural compute stick
[install_NCS_udev_rules.sh] udev rules installed[Note] OpenCV 4.0.1 will be installed without permission when the work is finished.
If you do not want to affect other environments, please edit environment variables after installation is completed.
$ cd ~
$ curl -sc /tmp/cookie "https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&id=1dvR3pdM6vtkTWqeR-DpgVUoDV0EYWil5" > /dev/null
$ CODE="$(awk '/_warning_/ {print $NF}' /tmp/cookie)"
$ curl -Lb /tmp/cookie "https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&confirm=${CODE}&id=1dvR3pdM6vtkTWqeR-DpgVUoDV0EYWil5" -o bazel
$ sudo cp ./bazel /usr/local/bin
$ rm ./bazelhttps://github.com/PINTO0309/Bazel_bin.git
Simple structure analysis.
$ cd ~
$ git clone -b v1.11.0 https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow.git
$ cd tensorflow
$ git checkout -b v1.11.0
$ bazel build tensorflow/tools/graph_transforms:summarize_graph
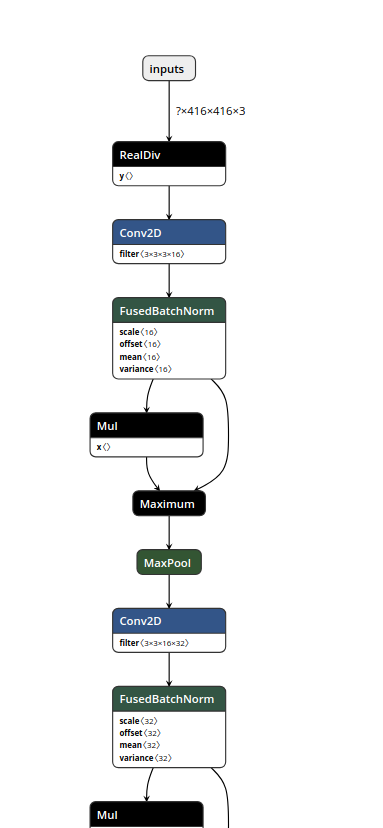
$ bazel-bin/tensorflow/tools/graph_transforms/summarize_graph --in_graph=xxxx.pbYoloV3
Found 1 possible inputs: (name=inputs, type=float(1), shape=[?,416,416,3])
No variables spotted.
Found 1 possible outputs: (name=output_boxes, op=ConcatV2)
Found 62002034 (62.00M) const parameters, 0 (0) variable parameters, and 0 control_edges
Op types used: 536 Const, 372 Identity, 87 Mul, 75 Conv2D, 72 FusedBatchNorm, 72 Maximum, 28 Add, \
24 Reshape, 14 ConcatV2, 9 Sigmoid, 6 Tile, 6 Range, 5 Pad, 4 SplitV, 3 Pack, 3 RealDiv, 3 Fill, \
3 Exp, 3 BiasAdd, 2 ResizeNearestNeighbor, 2 Sub, 1 Placeholder
To use with tensorflow/tools/benchmark:benchmark_model try these arguments:
bazel run tensorflow/tools/benchmark:benchmark_model -- \
--graph=/home/b920405/git/OpenVINO-YoloV3/pbmodels/frozen_yolo_v3.pb \
--show_flops \
--input_layer=inputs \
--input_layer_type=float \
--input_layer_shape=-1,416,416,3 \
--output_layer=output_boxestiny-YoloV3
Found 1 possible inputs: (name=inputs, type=float(1), shape=[?,416,416,3])
No variables spotted.
Found 1 possible outputs: (name=output_boxes, op=ConcatV2)
Found 8858858 (8.86M) const parameters, 0 (0) variable parameters, and 0 control_edges
Op types used: 134 Const, 63 Identity, 21 Mul, 16 Reshape, 13 Conv2D, 11 FusedBatchNorm, 11 Maximum, \
10 ConcatV2, 6 Sigmoid, 6 MaxPool, 4 Tile, 4 Add, 4 Range, 3 RealDiv, 3 SplitV, 2 Pack, 2 Fill, \
2 Exp, 2 Sub, 2 BiasAdd, 1 Placeholder, 1 ResizeNearestNeighbor
To use with tensorflow/tools/benchmark:benchmark_model try these arguments:
bazel run tensorflow/tools/benchmark:benchmark_model -- \
--graph=/home/b920405/git/OpenVINO-YoloV3/pbmodels/frozen_tiny_yolo_v3.pb \
--show_flops \
--input_layer=inputs \
--input_layer_type=float \
--input_layer_shape=-1,416,416,3 \
--output_layer=output_boxesConvert to text format.
$ python3 tfconverter.py
### ".pbtxt" in ProtocolBuffer format is output.
### The size of the generated text file is huge.Use Tensorboard.
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.platform import gfile
with tf.Session() as sess:
model_filename ="xxxx.pb"
with gfile.FastGFile(model_filename, "rb") as f:
graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read())
g_in = tf.import_graph_def(graph_def)
LOGDIR="path/to/logs"
train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(LOGDIR)
train_writer.add_graph(sess.graph)$ tensorboard --logdir=path/to/logsAccess http://localhost:6006 from the browser.
Use netron.
$ sudo -H pip3 install netron$ netron -b [MODEL_FILE]Access http://localhost:8080 from the browser.
https://ncsforum.movidius.com/discussion/1302/intel-neural-compute-stick-2-information
OpenVINO failing on YoloV3's YoloRegion, only one working on FP16, all working on FP32