Demo integrating Redis Enterprise with Amazon Athena and Amazon QuickSight
Initially started with a CloudFormation template from Amazon Athena Workship. This template has been modified to use Redis Enterprise instead of AWS ElasticCache. Redis Enterprise offers lower TCO with horizontal and vertical scaling as well as improved developer experience with Redis modules. There is an option to deploy the full workshop deployment or just deploy the components necessary for the athena/redis enterprise integration.
- Athena Redis connector
- Athena/QuickSight federated query blog
- Athena/QuickSight federated query lab session
- Redis Enterprise Route53 DNS Management
- Create S3 bucket using provided Cloudformation yaml file and script. Optionally, can use existing S3 bucket
- Bring up Athena Federated Query environment using provided scripts and cloud formation yaml files.
- Run through federated query exercises
- A parameter is provided to choose to bring up the full AWS federated query lab environment or only the resources needed for the redis athena query
- The required DNS entries for Redis Enterprise are included in the cloudformation script
- The RedisEnterprise EC2 resource uses the marketplace AMI with the Redis Enterprise Software pre-installed
- This RE EC2 resource has UserData entries to create the Redis Cluster, create a redis database, and load a very small amount of sample redis data using the github after also installing git
- Two additional nodes are added to the cluster to make it a three node cluster
- The redis connector is also in a nested cloudformation script called RedisConnector.yaml. This connector allows athena to access Redis.
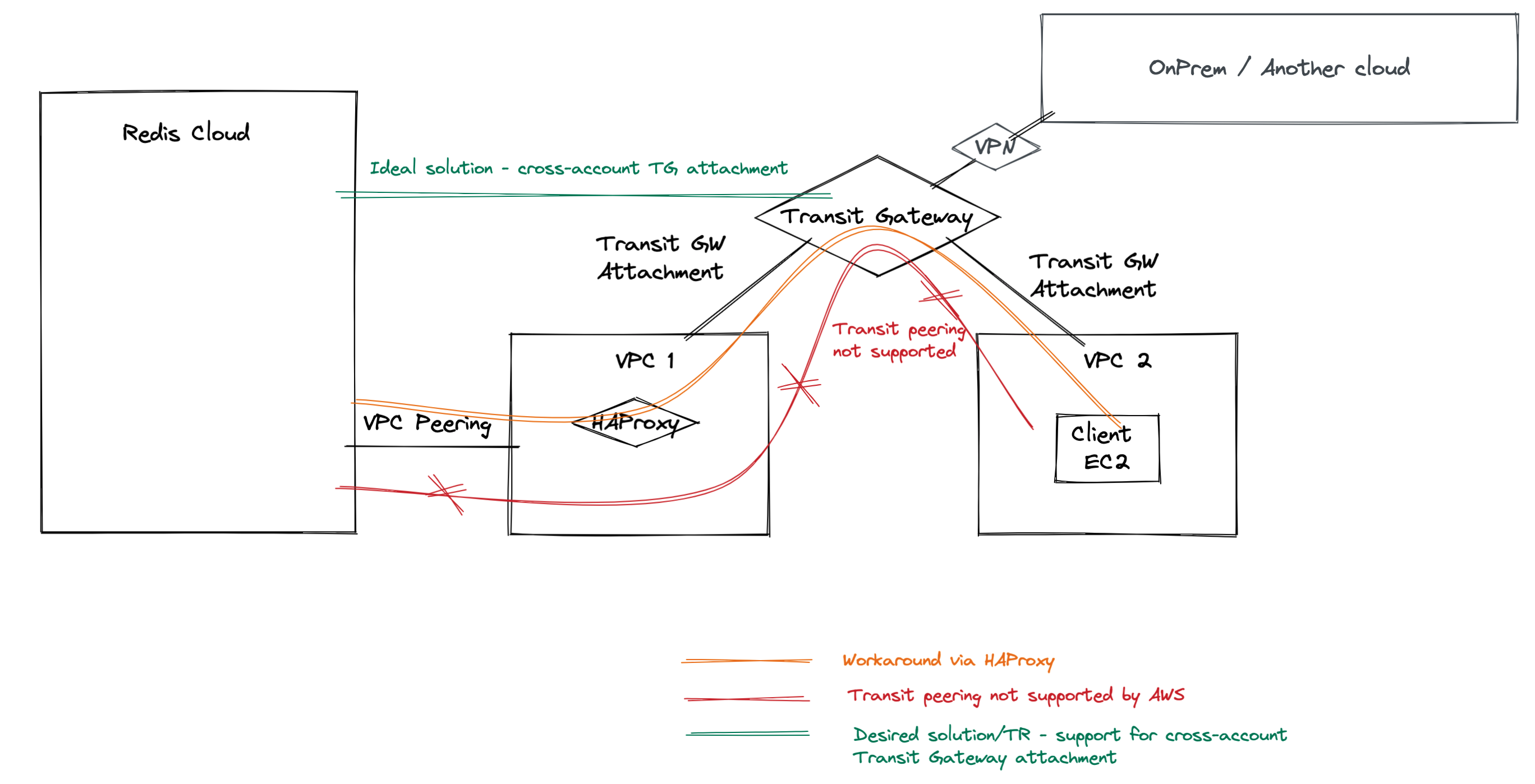
- Optional additional HAProxyVPC.yaml. This allows an HA proxy in a separate VPC to reach to the redis installation in the main VPC. Drawing and much of this work done by co-worker, Anton.
*IMPORTANT NOTE: Creating this demo application in your AWS account will create and consume AWS resources, which will cost money. Costing information is available at AWS DMS Pricing The template will cost money for the other resources as well.
- Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/jphaugla/redisAthenaQuickSight.git- Set up the environment file for use case. Edit setEnvironment.sh file for your environment. Some notes on the setEnvironment script...
- Pay special attention to the DNS entries. The cloudformation sets up DNS using a hosted zone name. Use the following link for a full explanation of AWS Route53 DNS management with Redis Enterprise Port 53 is enabled in the Security Group for DNS
- The LocalIp is used to limit ssh access to AWS resources. The AWS checkip URL is used. If you want this wide open, comment out this line and replace with "0.0.0.0/0"
- The *CREATE_ALL parameter is defaulted to FALSE. If set to true, it will create all the resources needed for the full AWS lab including EMR, Aurora, DynamoDB, etc.
- read through the comments in the setEnvironment.sh script for more details
- Some tips on creating an AWS account with AWS Account instructions
- After reviewing "Introduction" and "Getting Started", proceed to run the Athena Basic Stack from the workshop Template. This is not needed if only proving out the redis part.
- However, stop before running the "Labs Federated Queries, User Defined Functions, Custom Connector & Machine Learning". Instead, use these steps:
# sets up the environment
source setEnvironment.sh
# deploy an s3 bucket
# this can be skipped if already have an S3 bucket to use
./cfns3deploy.sh
# package the nested stack up to the S3 bucket
./cfnpackage.sh
# deploy the stack
./cfndeploy.shThis is no longer necessary as this has been put into the userdata section of the Redis EC2 instance. Since the connection to EMR is hardcoded in an S3 bucket, the redis load fails when running in EMR. The rest of the Federated sources load successfully. Run the following steps to load the nation and active_orders tables into Redis Enterprise
- Use aws s3 cli to get the two needed data files (these actually are also available in the github under data)
./downloadFiles.sh- transfer files to the redis instance
scp -i <path to your private key> loadscripts.sh ec2-user@<redisPublicIP>:/home/ec2-user
scp -i <path to your private key> data ec2-user@<redisPublicIP>:/home/ec2-user- load 2 data files using the load script
sudo bash
./loadscripts.shselect * from "lambda:redis".redis.nation limit 10;
- The Labs - Athena Basics section does not use the Redis connector but does have the section on "Visualize with QuickSight".
- The important part for the Redis Connector is Labs - Federated Queries.
- to create the HAProxy, set environment variable CREATE_HA_PROXY to true
- the installation of haproxy2 and the haproxy2.cfg file is taken care of in cloudformation scripts
- haproxy is not started however and will not work until the VPCs have been peered
- Get the VPCID for the HAProxy VPC from the stack output for HAVPCStack.VpcId
- Get the VPCID for the main VPC from the stack output for VPCStack.VpcId
- Create the peering connection with the VPCStack.VpcId as the requester and the HAVPCStack.VpcId as teh accepter
- Enable DNS routing for this peering. This link is helpful.
- Add routing table entries-easiest way to do this is the use the AWS Reachability Analyzer
- select the haproxy instance as the source
- select redis vm1 instance as the target
- follow the recomndations to add the new routes to enable this connectivity
- Enable haproxy restart and start haproxy
sudo systemctl start haproxy
sudo systemctl enable haproxy - should now be able to from the haproxy node do a successful redis-cli connection with no parameters
Also important is the cleanup section as the cloudformation scripts can't delete some of the resources created.