- A network consists of two or more computers that are linked in order to share resources or allow electronic communication
Two very common types of networks include:
- Local Area Network
- Wide Area Netowrk
- Network confined to a relatively small area, generally limited to a geographic area such as a school or a building
- Examples of LAN include the Ethernet
- a WAN connects LANs to each other, usually across multiple locations
- The internet is an example of a worldwide public WAN
- Stands for internet Protocol
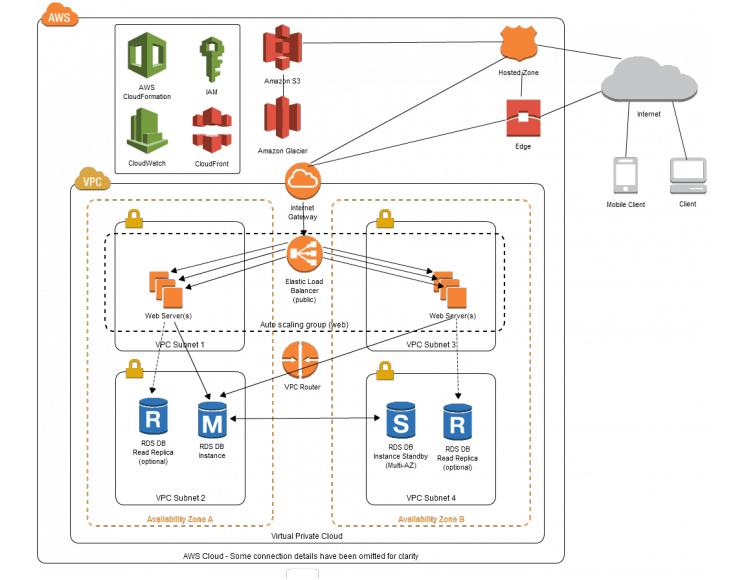
- A VPC is a secure, isolated private cloud which is hosted within a public cloud
Navigate HERE on setting up a VPC using AWS
- Web Tier
- Database Tier
- We create subnets within our VPC, they give different access rules and place resources in different containers
- E.g You would not want your database with contains secret information to be put in a public subnet where there is network traffic. Instead we would want to place it in a private subnet
- Creating subnets allows you to create a logical network division between the different resources you have
- A virtual local area network is a group of computing devices that are all connected to each other without the use of the internet
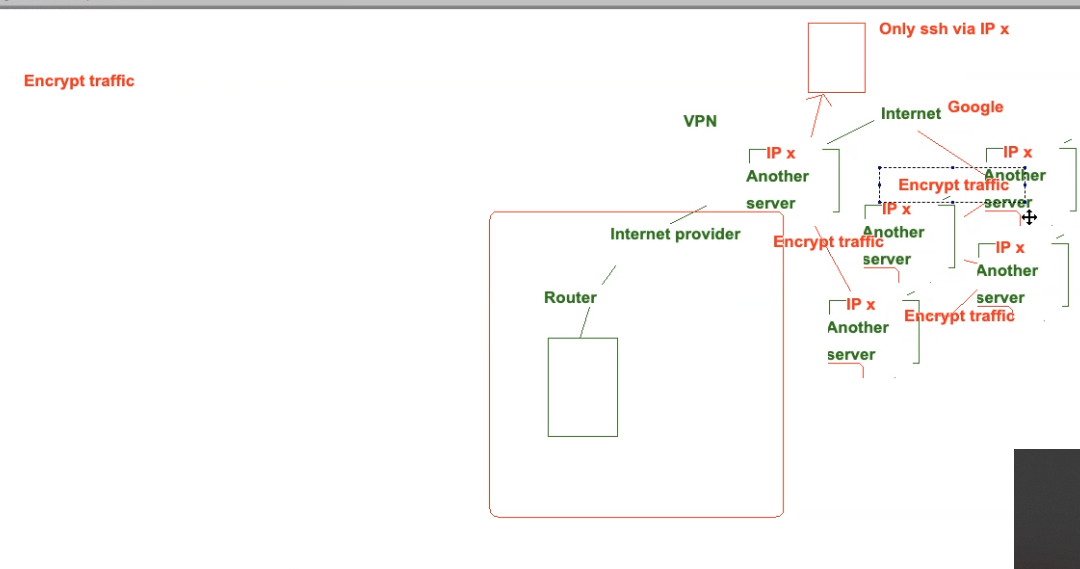
- A virtual private network uses encryption to create a private network over the top of your current public network, this causes the traffic to be scrambled and thus is not easily visible to anyone.
-
As we can see above, the request sent from our internet provider has been sent to multiple other servers before it reaches the desired internet location and thus it is hard to figure out the original location of the request
-
These multiple layers of encyption could also be referred to as a Tor Network
-
An availability zone is one or more discrete data centres with redundant power, networking and connectivity in an AWS region
-
AZ's are logically connected but physically segregated
-
They give customers the ability to operate applications and database that woid
-
An optional virtual router that you can add to your VPC to enable direct connectivity to the internet, allowing communication between your VPC and the outside world.
-
For an EC2 instance to talk to the outside world, the instance must be located on a public subnet that has a route table rule that specifies the IGW as the target
-
Internet can then travel through the IGW into the VPC and then into the route table, from here it can travel to the public subnet where the EC2 is located
-
Virtual Network-level firewalls that are associated to each and every subnet
-
Help control both ingress and egress (incoming, outbound) traffic moving in and out of your VPC and between your subnets.
-
Firewall at the instance level
-
Controls the traffic entering and leaving our instance
- Security Groups are a firewall of an Instance
- Network ACLs are a firewall of a subnet
- Together they act as multiple layers of security
- Note that if we do not allow traffic at the subnet level but allow it at the instance level, it would not pass the the first layer of security and thus would not reach our instance
-
A route table contains a set of rules, called routes, that are used to determine where network traffic from your subnet or gateway is directed.