This is PyTorch implementation of the paper:
Lagging Inference Networks and Posterior Collapse in Variational Autoencoders
Junxian He, Daniel Spokoyny, Graham Neubig, Taylor Berg-Kirkpatrick
ICLR 2019
The code seperates optimization of encoder and decoder in VAE, and performs more steps of encoder update in each iteration. This new training procedure mitigates the issue of posterior collapse in VAE and leads to a better VAE model, without changing model components and training objective.
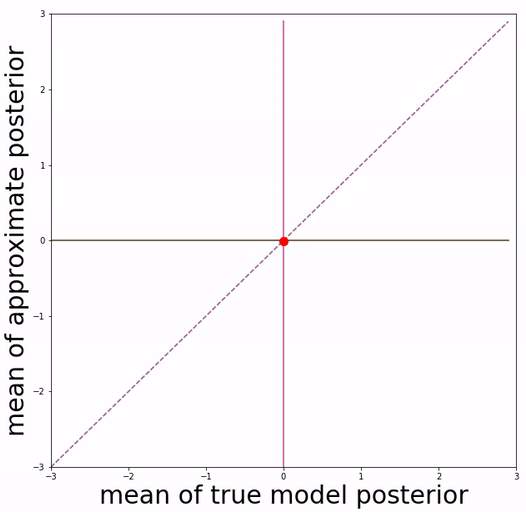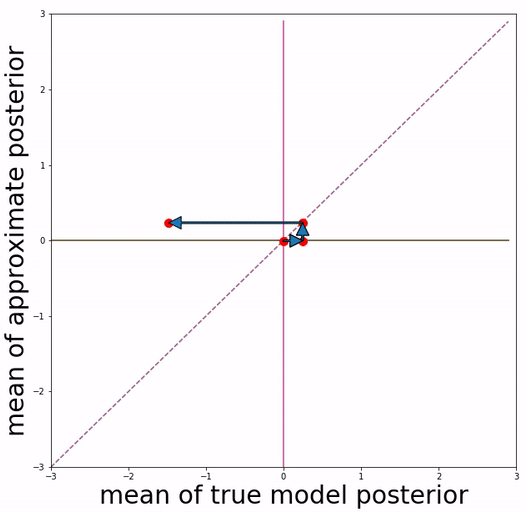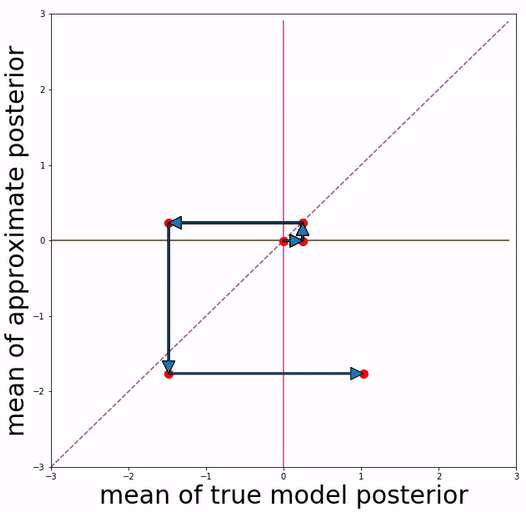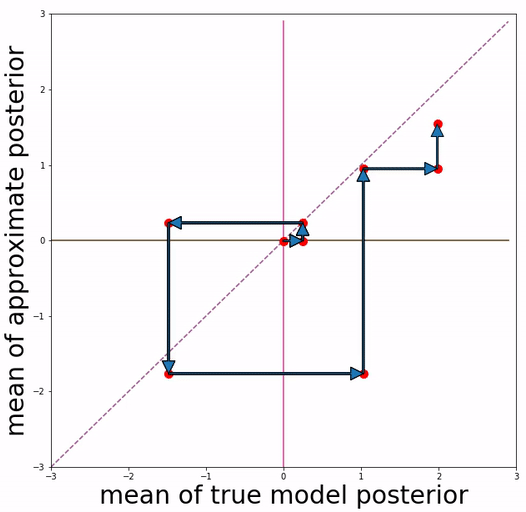
This repo is able to reproduce quantitative experimental results and qualitative visualizations of posterior mean space presented in the paper.
Please contact junxianh@cs.cmu.edu if you have any questions.
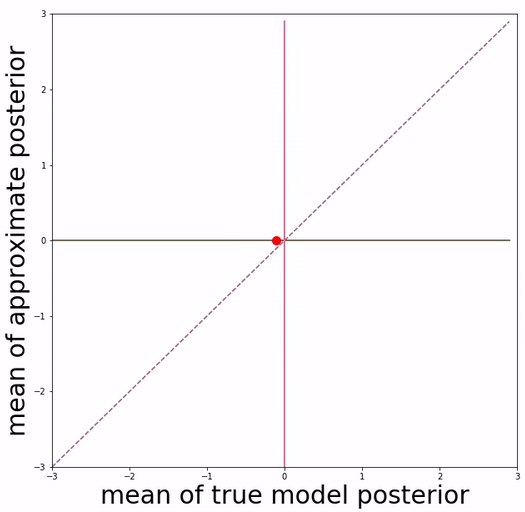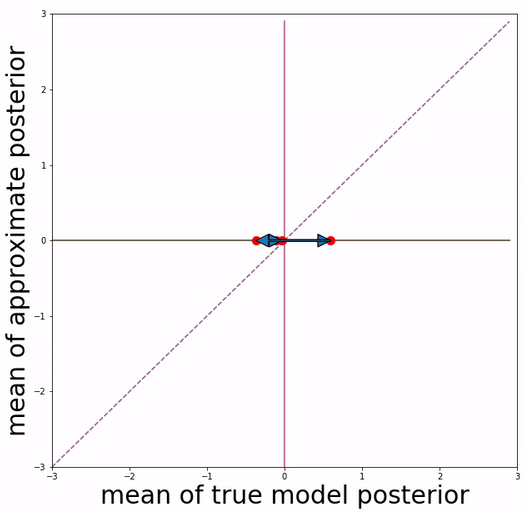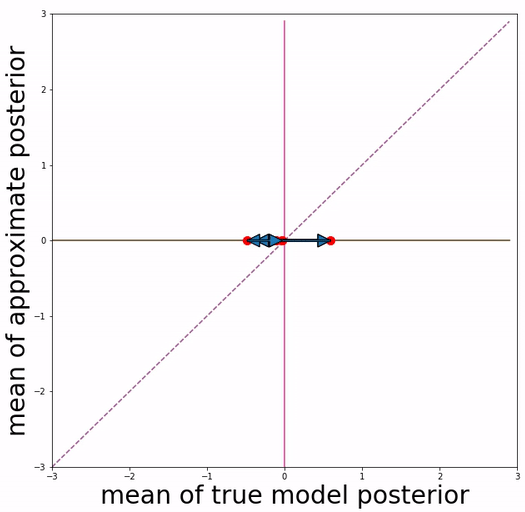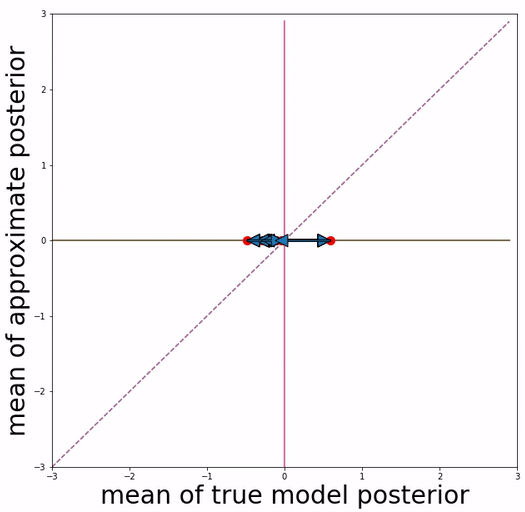
(a) basic VAE training (b) Aggressive VAE training
Hi, Allison Parrish here. Huge thanks to the researchers for making this code available! This fork has a few additional pieces I added in, to make the code a bit easier to work with out-of-the-box for my own creative uses, and hopefully for others' uses as well.
- I modified the code so it's possible to train with the SentencePiece models
and pre-trained embeddings included with
BPEmb. Using this functionality, I trained a
model on one million lines of poetry sampled from the Gutenberg Poetry
Corpus. Here's a ZIP
file containing the tokenized dataset, a pre-trained model, and
hyperparameters for training the
model
(116MB). (To use, download this file and decompress in this directory.) This
model uses BPEmb's English model with 200-dimensional vectors and a
vocabulary size of 25000. The included notebook
prep-poetry-sample-data.ipynbshows how to prepare your own dataset from this corpus with a different number of lines of poetry or different vocabulary sizes/dimensions. - The
vaesampler.pyfile defines a classBPEmbVaeSamplerwhich makes it easy to programmatically sample and reconstruct sentences from the included pre-trained model, including code to stitch text back together from theBPEmbtokens. The code invae-sampler.ipynbtakes theBPEmbVaeSamplerclass through its paces. You can run this notebook on Binder! - The model is Runway-ready; the included
runway_model.pyandrunway.ymlmake it possible to build a Runway image and run the model in the Runway app. (Thank you Runway for supporting my work on this fork!) - I added a
temperatureparameter toLSTMDecoder's.sample_decode()method to set the temperature for softmax sampling when decoding. - The training code in
text.pynow saves the model weights on every epoch. (I found that it was helpful to be able to pick-and-choose between epochs, based on the reconstruction and KL loss figures.) - The
MonoTextDataclass will now read from gzipped datasets. - The included
requirements.txtshould be all you need to get the code and model up and running.
I should note that the reason I wanted to play around with a model like this to begin with is Robin Sloan's brilliant Voyages in Sentence Space.
And now back to the original README!
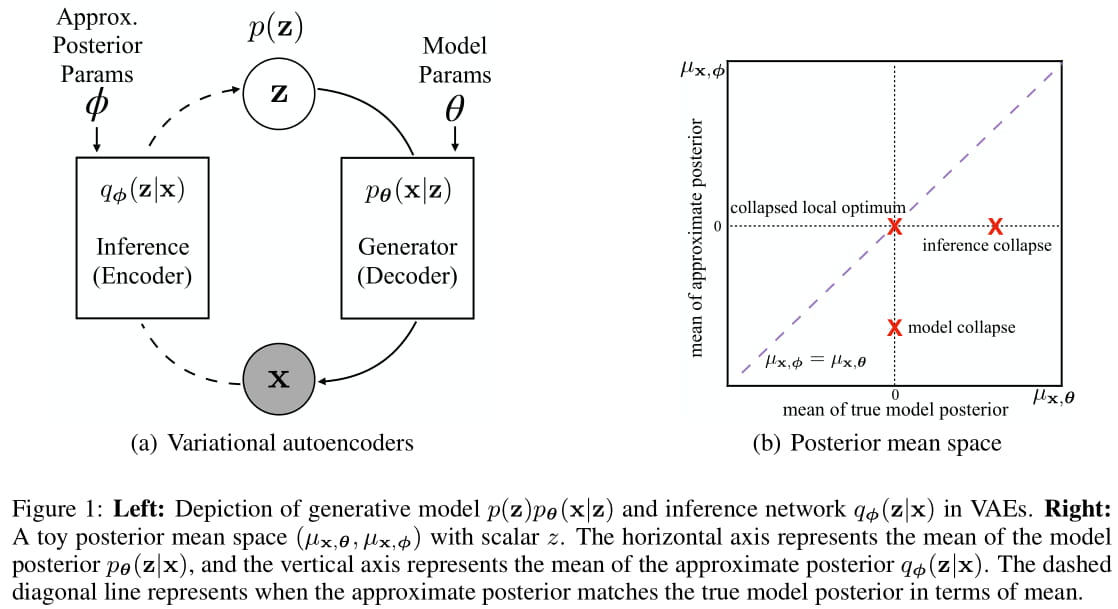
Our approach is inspired by the definition of "posterior mean space", which helps observe the posterior status over course of training and analyze VAE training behavior from the perspective of training dynamics. In the paper we experimented with a toy dataset and a scalar latent variable, so that posterior mean space is on a 2-d plane.
- Python >= 3.6
- PyTorch >= 0.4
Datasets used in this paper can be downloaded with:
python prepare_data.py
By default it downloads all four datasets used in the paper, downloaded data is located in ./datasets/. A --dataset option can be provided to specify the dataset name to be downloaded:
python prepare_data.py --dataset yahoo
The argument should be synthetic, yahoo, yelp, or omniglot.
Example script to train VAE on text data (training uses GPU when available):
python text.py --dataset yahoo --aggressive 1 --warm_up 10 --kl_start 0.1
image data:
python image.py --dataset omniglot --aggressive 1 --warm_up 10 --kl_start 0.1
Logs would be printed on standard output and also saved into folder logs.
Here:
-
--datasetspecifies the dataset name, currently it supportssynthetic,yahoo,yelpfortext.pyandomniglotforimage.py -
--aggressivecontrols whether applies aggressive training or not -
--kl_startrepresents starting KL weight (set to 1.0 to disable KL annealing) -
--warm_uprepresents number of annealing epochs (KL weight increases fromkl_startto 1.0 linearly in the firstwarm_upepochs)
To run the code on your own text/image dataset, you need to create a new configuration file in ./config/ folder to specifiy network hyperparameters and datapath. If the new config file is ./config/config_abc.py, then --dataset needs to be set as abc accordingly.
We project 500 data samples onto posterior mean space and observe the change over course of training.
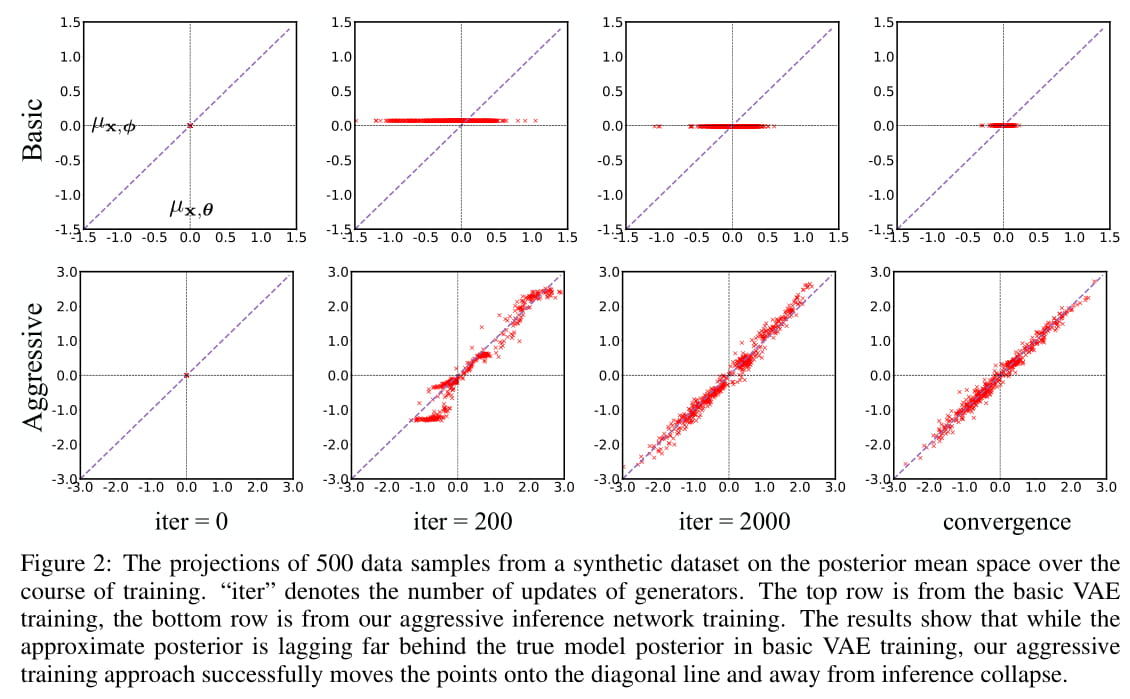
To reproduce this visualization figure, first train the model on the toy dataset to save statistics required for visualization (training uses GPU when available):
python toy.py --aggressive 1 --plot_mode multiple
Here --plot_mode can be specified as single to reproduce the single-point trajectory figure (Figure 3 in the paper). This command trains a VAE model with aggressive training on synthetic data, and the required statistics is saved in folder plot_data (folder would be created automatically if non-existing).
Then run the plotting script:
python plot_scripts/plot_multiple.py --aggressive 1 --iter 2000
Here --aggressive specifies the aggressive training mode (should be the same as training), --iter specifies for which iteration the figure is plotted, we save the plotting data every 200 iterations by default at training time. The generated figures would be saved in folder plot_figure as pdf files (folder would be created automatically if non-existing).
Similarly, run plot_single.py is able to generate the single-point trajectory figure.
Text generation is supported through sampling from either the prior or posterior (i.e. reconstruction).
Generation from prior (by default it generates 100 samples):
python text.py --dataset [dataset] --decode_from [pretrained model path]
Reconstruction:
python text.py --dataset [dataset] --decode_from [pretrained model path] --decode_input [a text file for reconstruction]
--decode_input file has one raw sentence per line, which is the same format as training data.
Optional --decoding_strategy argument can be used to specifiy decoding strategy as {greedy, beam, sample}. By default greedy decoding is performed. Generated sentences are saved in folder samples.
To plot the KL and mutual information curves over course of training (Figure 5 in the paper), first run:
python text.py --dataset yelp --aggressive 1 --warm_up 10 --kl_start 1.0
Then please refer to plot_scripts/plot_log.ipynb as an example to read the log file and generate plots.
@inproceedings{he2018lagging,
title={Lagging Inference Networks and Posterior Collapse in Variational Autoencoders},
author={Junxian He and Daniel Spokoyny and Graham Neubig and Taylor Berg-Kirkpatrick},
booktitle={Proceedings of ICLR},
year={2019}
}