Denoising mel-spectrograms with a residual dense network
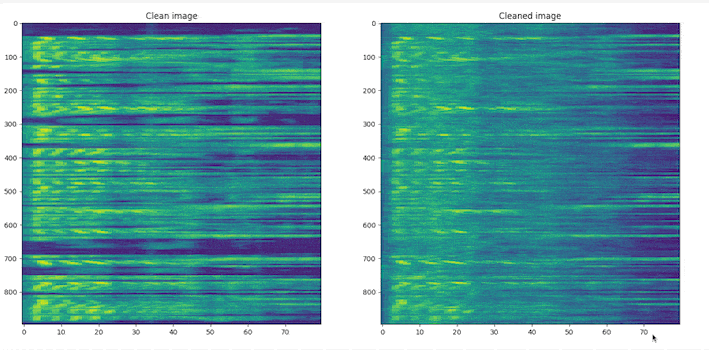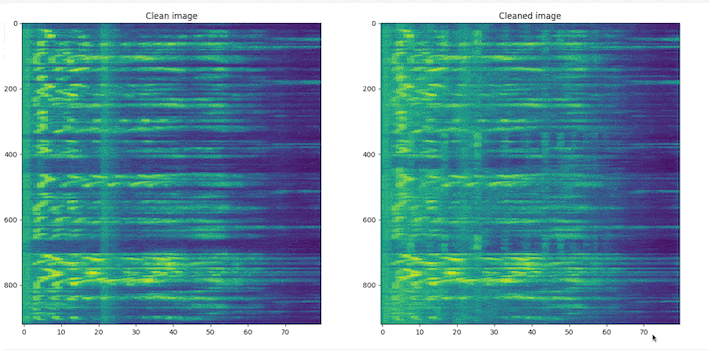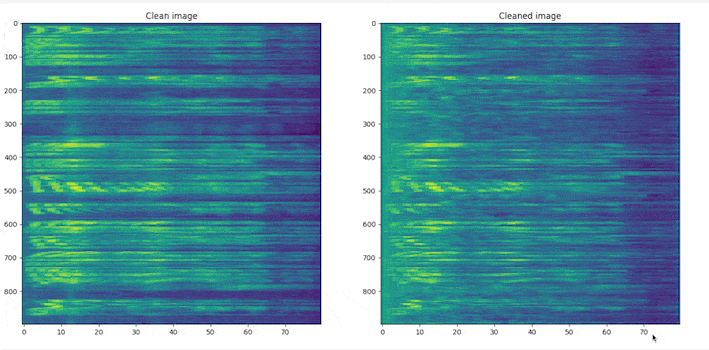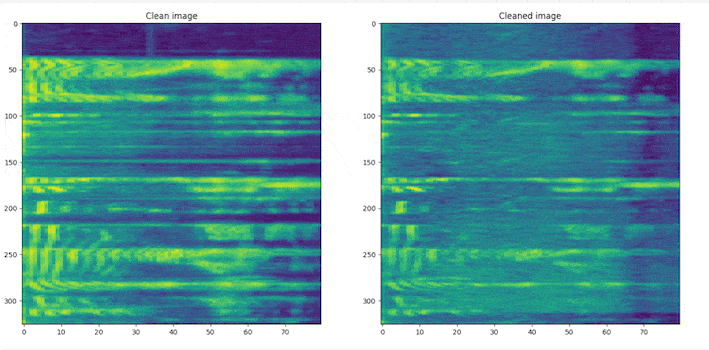
# clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/sdll/audio-denoising
cd audio-denoising
docker build --tag audio-denoising:1.0 .
docker run -v path_to_dataset:/dataset -v path_to_results:/results --name audio-denoising:1.0
- Options for the model, matching with the weights
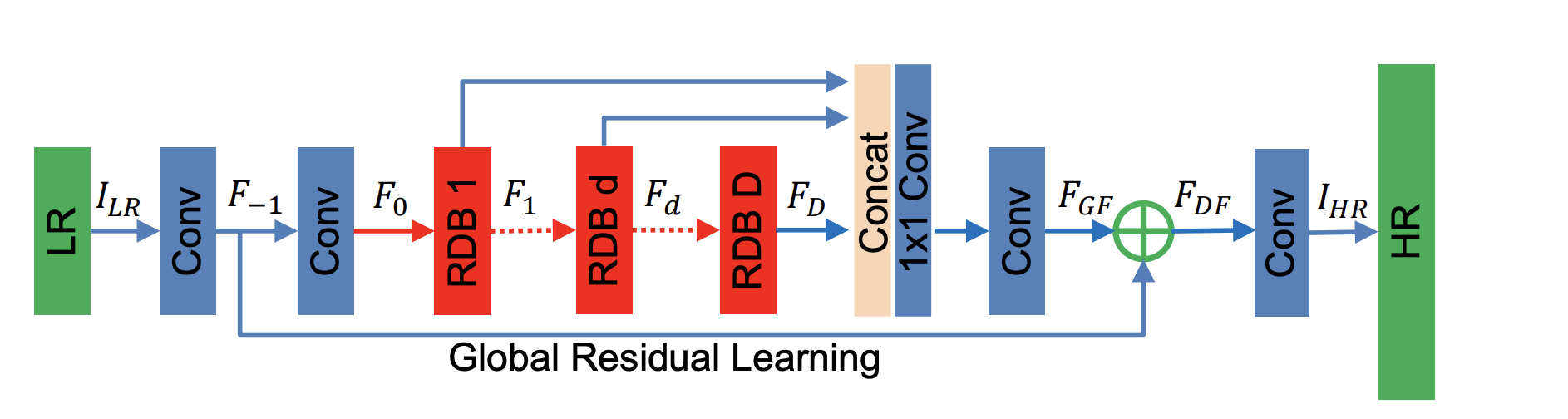
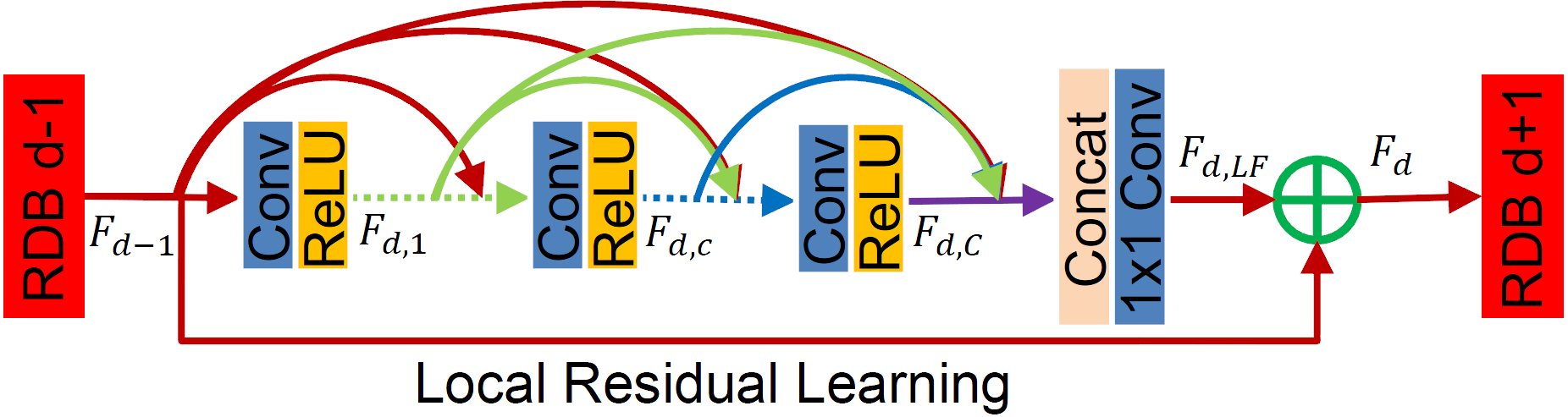
--num-blocks (D): the number of residual dense blocks (RDB)--num-features (G0): the number of feature maps for the conv layers outside RDBs and the number of filters in the RBD output--growth-rate (G): the number of feature maps of each convolutional layer inside RDBs--num-layers (C): the number of convolutional layers stacked inside a RDB--kernel-size: the kernel size for non-1x1 convolutions--num-channels: the number of channels in the input
-
--source-dir: the alternative path replacing /dataset in the example above
-
--target-dir: the alternative path replacing /results in the example above
-
--denoised-subdir (default: denoised): where to write the denoised spectograms
-
--extension (default: npy): the extension for files storing mel-spectograms
-
--weights (default: ./weights/audio_denoising_psnr_65.1736_epoch_15_D_20_C_6_G_16_G0_16.pth): path to the weights
-
--threshold (default: 0.77): the SSIM threshold for determining whether the original image is noisy or not (see ./demo.ipynb for the justification)


