Deadline: 2021-08-13
- 設計一個多項式函數類別
Polynomial和變數類別Variable,支援以下功能:- 計算多項式函數
- 對多項式函數進行微分
- 實作
plot_polynomial(file, function, p_x, x, formula),輸出一張 png 檔:- 畫出多項式函數圖形
- 給定一個點,畫出經過該點的多項式函數的切線
- 參數:
file: 輸出的檔案名稱function: 多項式函數的 instancep_x: 點坐標x: 圖表的 x 軸formula: 數學式描述
- NumPy
- Matplotlib
- pytest
In libs/functional.py:
from typing import List, Union
import numpy as np
class Variable:
def __init__(self, value=None):
self.value = value
self.grad = None
class Polynomial:
def __init__(self, a: List = None):
self.a = np.array(a)
def __call__(self, x: Union[float, np.ndarray]) -> Variable:
passIn libs/visualization.py:
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
from libs.functional import Polynomial
from libs.visualization import plot_polynomial
class TestPlotPolynomial:
def test_plot_polynomial_1(self):
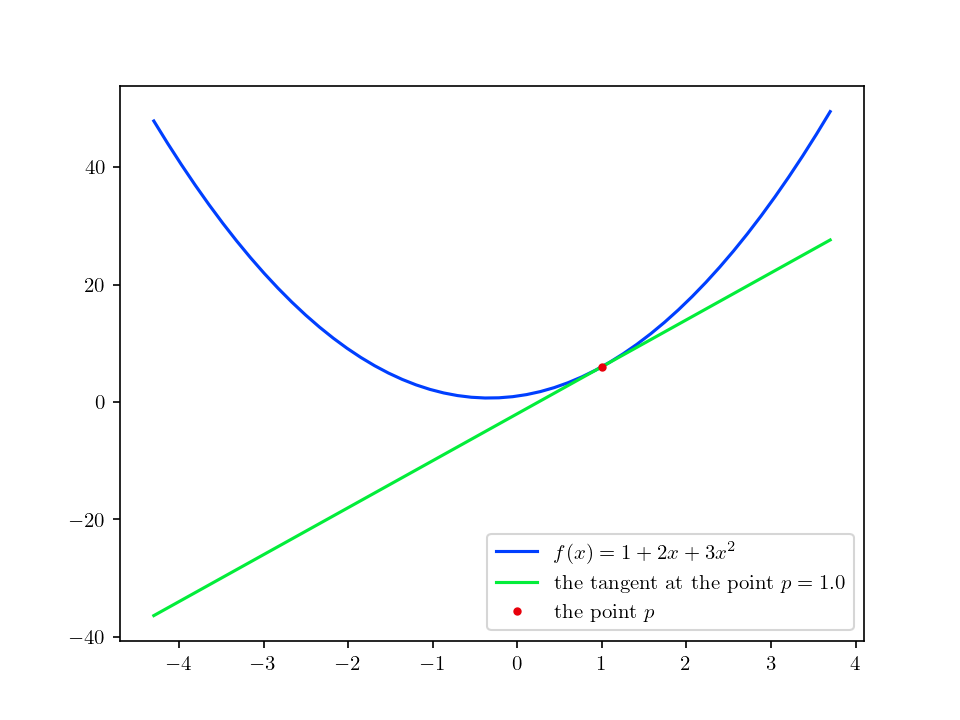
f = Polynomial(a=[1., 2., 3.]) # 1 + 2x + 3x^2
file = Path('test_plot_polynomial_1.png')
x = np.linspace(-4.3, 3.7)
plot_polynomial(file=file, function=f, p_x=1., x=x, formula='1 + 2x + 3x^2')
assert file.exists()
def test_plot_polynomial_2(self):
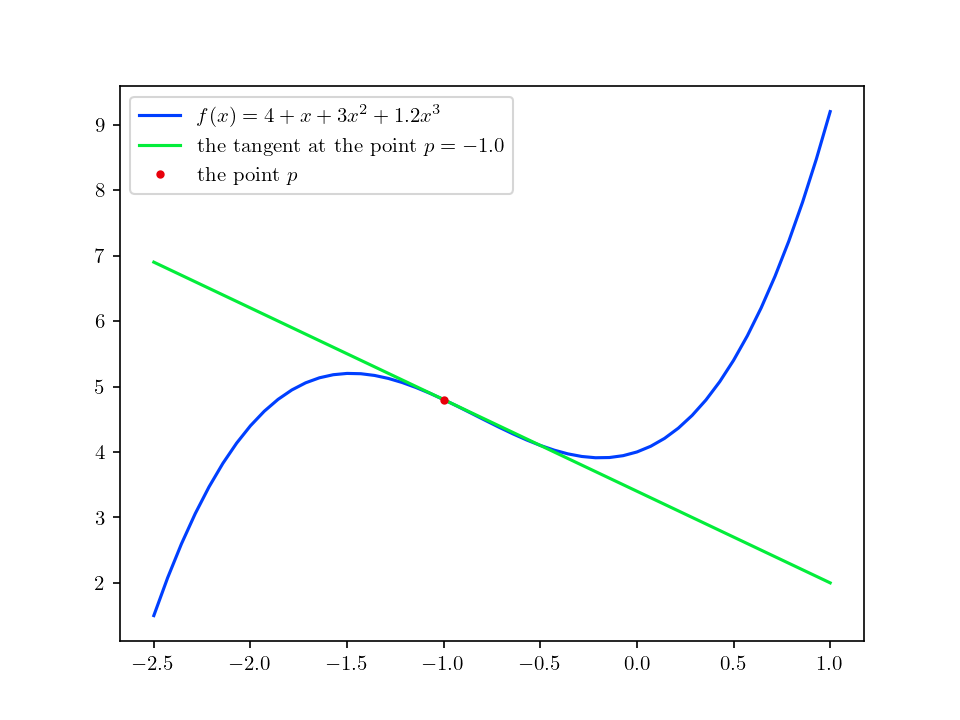
f = Polynomial(a=[4., 1., 3., 1.2]) # 4 + x + 3x^2 + 1.2x^3
file = Path('test_plot_polynomial_2.png')
x = np.linspace(-2.5, 1.0)
plot_polynomial(file=file, function=f, p_x=-1., x=x, formula='4 + x + 3x^2 + 1.2x^3')
assert file.exists()In tests/test_functional.py:
import numpy as np
from libs.functional import Polynomial
class TestPolynomial:
def test_io(self):
f = Polynomial(a=[1., 2., 3.]) # 1 + 2x + 3x^2
assert f(4.).value == 57.
assert f(5.).value == 86.
def test_io_array(self):
f = Polynomial(a=[1., 2., 3.]) # 1 + 2x + 3x^2
x = np.array([4., 5.])
y = np.array([57., 86.])
assert np.all(f(x).value == y)
def test_grad(self):
f = Polynomial(a=[1., 2., 3.]) # 1 + 2x + 3x^2
# gradient: <2 + 6x>
assert f(4.).grad == 26.
assert f(5.).grad == 32.In tests/visualization.py:
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
from libs.functional import Polynomial
from libs.visualization import plot_polynomial
class TestPlotPolynomial:
def test_plot_polynomial_1(self):
f = Polynomial(a=[1., 2., 3.]) # 1 + 2x + 3x^2
file = Path('test_plot_polynomial_1.png')
x = np.linspace(-4.3, 3.7)
plot_polynomial(file=file, function=f, p_x=1., x=x, formula='1 + 2x + 3x^2')
assert file.exists()
def test_plot_polynomial_2(self):
f = Polynomial(a=[4., 1., 3., 1.2]) # 4 + x + 3x^2 + 1.2x^3
file = Path('test_plot_polynomial_2.png')
x = np.linspace(-2.5, 1.0)
plot_polynomial(file=file, function=f, p_x=-1., x=x, formula='4 + x + 3x^2 + 1.2x^3')
assert file.exists()test_plot_polynomial_1.png:
test_plot_polynomial_2.png:
Deadline: 2021-08-20
給定 data
point
,利用 SGD 解出 linear regression.
In libs/functional.py:
from typing import Tuple
import numpy as np
def regression_sgd(x, y, num_samples, num_iterations, batch_size, learning_rate) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
passIn libs/visualization.py:
def plot_regression(file, x, y, prediction, groundtruth):
passIn tests/test_functional.py:
import numpy as np
from libs.functional import regression_sgd
def test_regression_solved_correctly():
m_gt, b_gt = 2.4, 1.0
num_samples = 100
x = np.random.uniform(-10, 10, num_samples)
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, num_samples)
y = m_gt * x + b_gt + noise
num_iterations = 1000
batch_size = 10
learning_rate = 0.001
m, b = regression_sgd(x, y, num_samples, num_iterations, batch_size, learning_rate)
assert m.shape == (num_iterations + 1,) and b.shape == (num_iterations + 1,)
assert np.isclose(m[-1], m_gt, 1e-01)In tests/visualization.py:
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
from libs.functional import regression_sgd
from libs.visualization import plot_regression
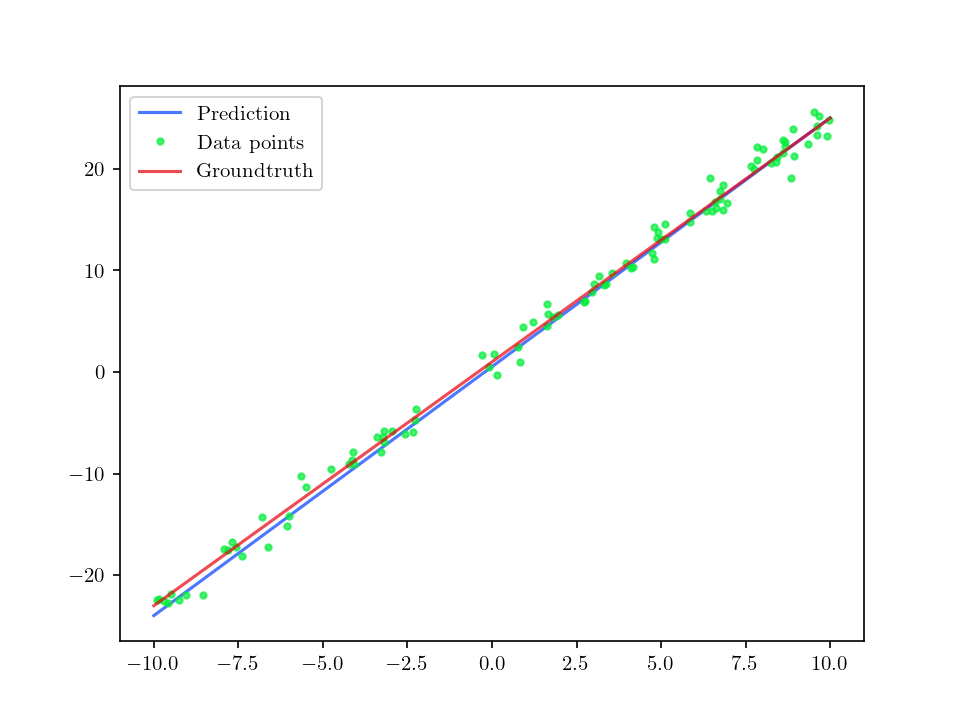
def test_plot_regression():
m_gt, b_gt = 2.4, 1.0
num_samples = 100
x = np.random.uniform(-10, 10, num_samples)
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, num_samples)
y = m_gt * x + b_gt + noise
num_iterations = 1000
batch_size = 10
learning_rate = 0.001
m, b = regression_sgd(x, y, num_samples, num_iterations, batch_size, learning_rate)
file = Path('test_plot_regression.png')
plot_regression(file, x, y, prediction=(m, b), groundtruth=(m_gt, b_gt))
assert file.exists()