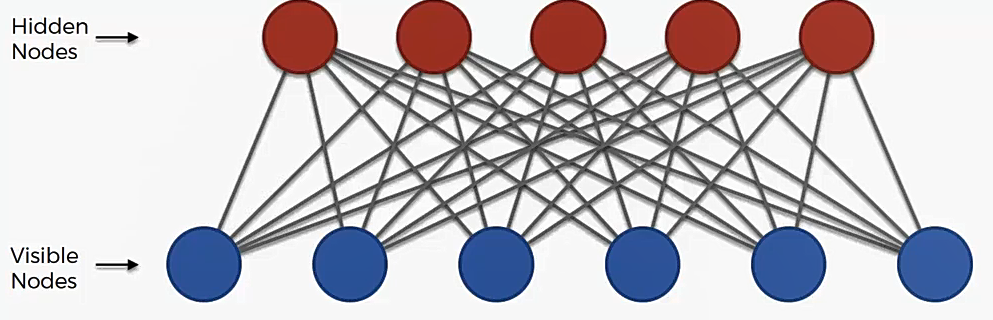
This repository is an implementation of Restricted Boltzmann Machine in Pytorch and Tensorflow.
- python 3.9
- Tensorflow == 2.11.0
- torch == 1.13.1
- pandas == 1.5.3
- numpy == 1.24.2
- mlxtend == 0.21.0
- sklearn == 1.1.1
- matplotlib == 3.6.3
from RBM import RBM
rbm = RBM(nv=len(training_set[0]), nh=64, k=5, lr=0.01)
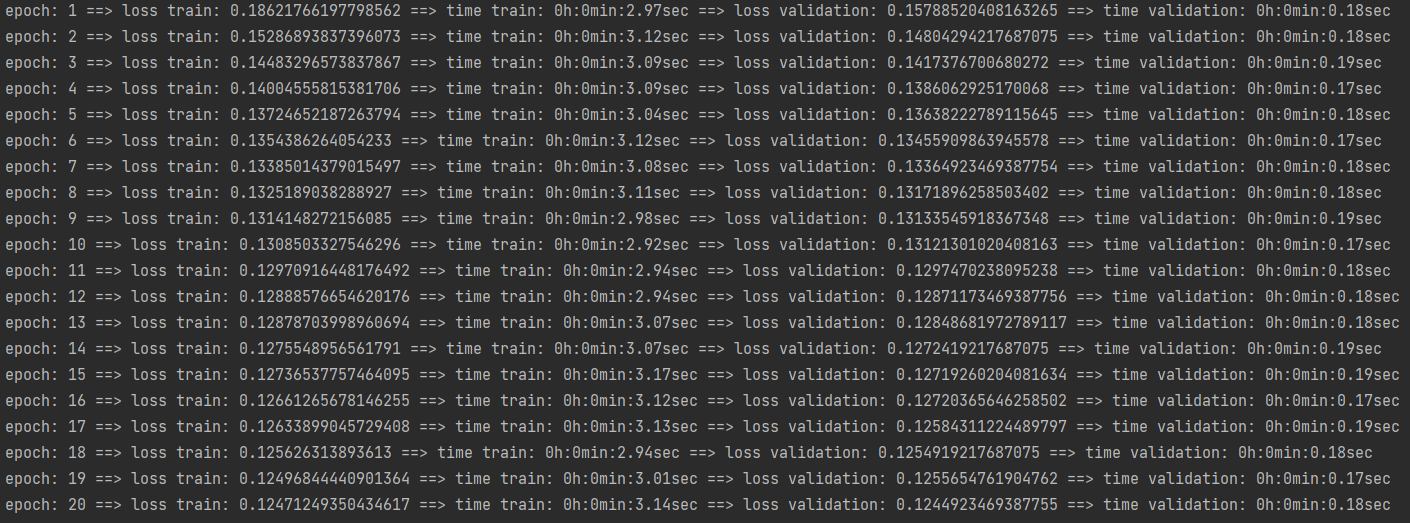
rbm.fit(training_set, batch_size=128, epoch=40, verbose=1, validation_data=validation_set)
predicted = rbm.predict(test_set, verbose=1)import pandas as pd
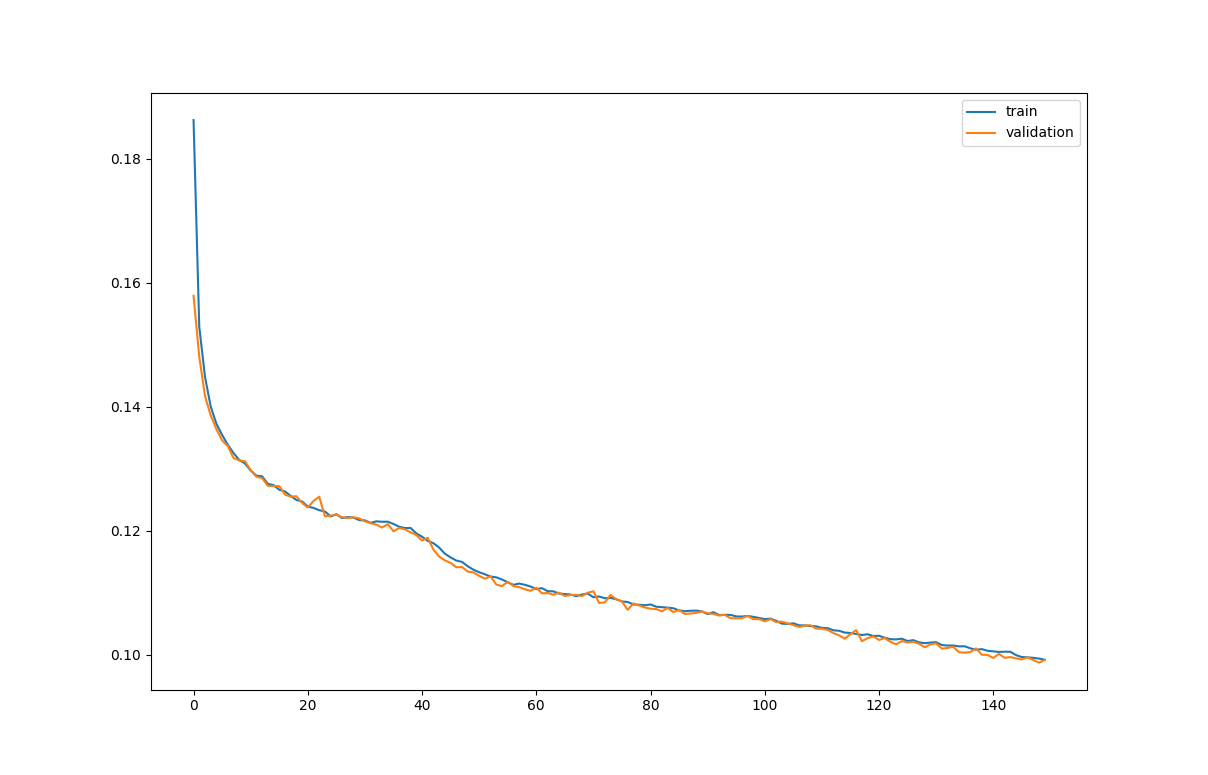
pd.DataFrame(rbm.total_losses).plot()import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
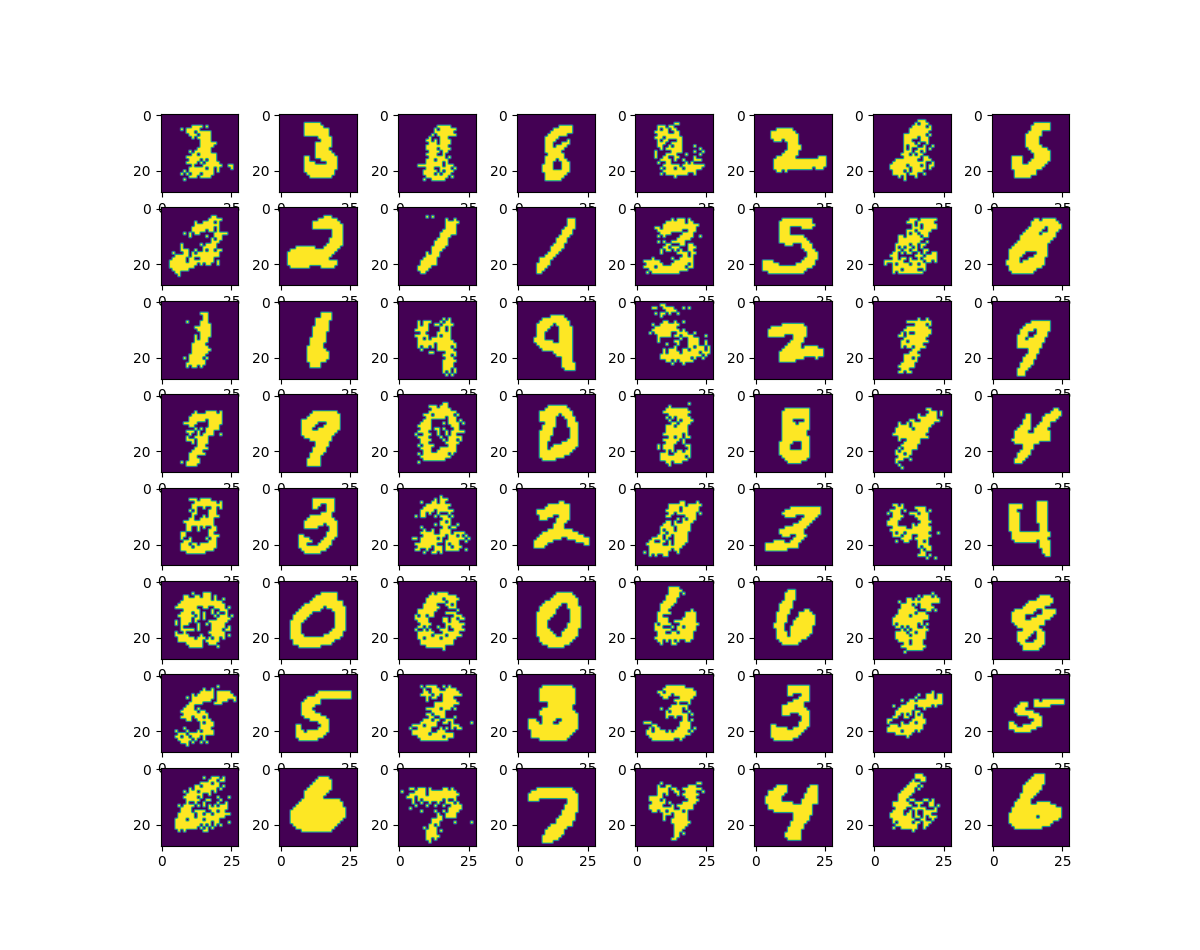
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
for i in range(1, 33):
plt.subplot(8, 8, i * 2 - 1)
plt.imshow(predicted[i].reshape(28, 28))
plt.subplot(8, 8, i * 2)
plt.imshow(test_set[i].reshape(28, 28))
plt.show()import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# visualize tensorflow weights
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
for i in range(1, 65):
plt.subplot(8, 8, i)
plt.imshow(rbm.W[i-1].numpy().reshape(28, 28))
# visualize torch weights
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
for i in range(1, 65):
plt.subplot(8, 8, i)
plt.imshow(rbm.W[i-1].reshape(28, 28))
plt.show()This repository is released under Apache License V2. To develop, publication and use it, please follow the terms of this license.
Please cite this paper if you use this code in your research project.
@article{
title={An introduction to restricted Boltzmann machines.},
author={A Fischer, C Igel},
journal={Progress in Pattern Recognition, Image Analysis, Computer Vision, and Applications: 17th Iberoamerican Congress, CIARP 2012, Buenos Aires, Argentina, September 3-6, 2012. Proceedings 17},
pages={14-36},
year={2012},
publisher={Springer}
}