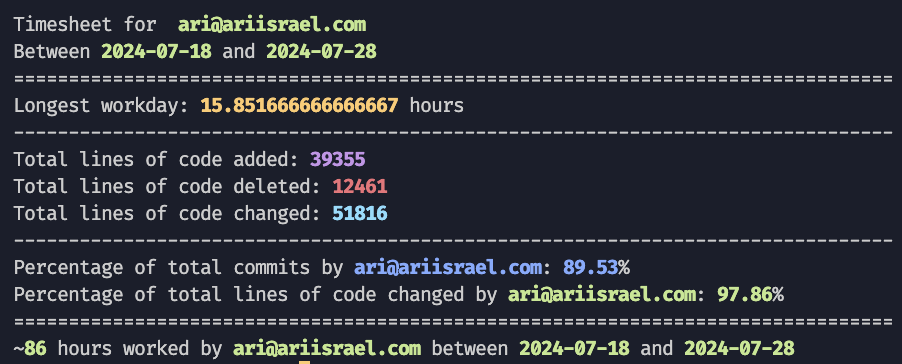
This script fetches commits from a specified GitHub repository and analyzes workdays based on commit activity. It calculates the total hours worked each day and within a specified date range.
- Node.js (v20 or later)
- npm
- A GitHub personal access token
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/ariisrael/timesheet.git cd timesheet -
Install dependencies:
npm install
-
Create a
.envfile in the root of the project:touch .env
-
Open the
.envfile and add the following environment variables**:GITHUB_OWNER=gosabo GITHUB_REPO=web GITHUB_USER_EMAILS=github_email_for_timesheet_user@example.com GITHUB_TOKEN=your_personal_access_token START_DATE=2024-07-19 END_DATE=null # null means today, or specify a date like 2024-07-20 TIME_BETWEEN_COMMITS=10 # hours between commits to consider a new work day
Replace
your_personal_access_tokenandyour_github_email@example.comwith your actual GitHub personal access token and GitHub email. -
Add
.envto.gitignoreto ensure it is not committed to version control:echo ".env" >> .gitignore
To run the script and analyze the commits:
npm startGITHUB_OWNER: The GitHub username or organization that owns the repository.GITHUB_REPO: The name of the repository.GITHUB_TOKEN: Your GitHub personal access token. You can generate this token from your GitHub account settings underDeveloper settings>Personal access tokens.GITHUB_USER_EMAILS: The GitHub email(s) of the user for whom you are generating a timesheet, separated by commas.START_DATE: The start date for the analysis (e.g.,2024-07-19).END_DATE: The end date for the analysis (e.g.,2024-07-20). Usenullfor today.TIME_BETWEEN_COMMITS: The number of hours between commits to consider a new workday (default: 10).USE_CACHED_COMMITS: Use commits inallCommits.jsononce you hit the GitHub API once to avoid ratelimit.
- Go to GitHub: Log in to your GitHub account and navigate to
Settings. - Developer settings: Scroll down to
Developer settings. - Personal access tokens: Click on
Personal access tokens. - Generate new token: Click the
Generate new tokenbutton. - Set token scopes: Select the scopes for the token. For reading repository data, you typically need the
reposcope. - Generate token: Click
Generate token. - Copy the token: Make sure to copy the token immediately, as you won't be able to see it again.
- Ensure your
.envfile is correctly configured with your GitHub credentials. - The script calculates workdays based on the time between commits. If the time between commits exceeds a specified number of hours (default: 10), it is considered a new workday.
- Modify the
START_DATEandEND_DATEconstants in the script to specify the date range for analysis.
This project is licensed under the MIT License.