WARNING
Please read the guide before you start using AVD Quickstart Containerlab. Make sure that you understand the consequences of running Containerlab, cEOS-lab and various scripts provided with this repository on your machine. The components of the lab may change your system settings as they will have super user privileges. While this repository was tested on a number of machines without doing any harm, have a plan B. You are responsible for your lab machine, not the contributors.
"With su power comes great responsibility" (c)/ _ \ \_\_(_)_/_/ _/ /o\ \_ / \
For M1 MacBooks owners:
Sorry. Not yet supported.
The AVD Quickstart repository is a collection of Arista EOS labs based on Containerlab that you can build on any machine with Docker in a few minutes. The ultimate target of this repository is to provide a portable Arista lab collection for everyone. This collection can be used to learn and test certain Arista EOS features and in certain cases even build configs for production environment with the excemption of hardware features.
Some labs provided in this repository can be used with CloudVision Portal VM that must be deployed separately. But all labs that are not focused on CVP features can be used without such VM as it is quite resource intensive and can not be deployed on an avarage laptop for example.
WARNING: if CVP VM is part of the lab, make sure that it's reachable and credentials configured on CVP are matching the lab.
The initial lab list provided in this repository is focused on learning and testing AVD. Some labs can be easily adjusted to your needs using simplified CSV and YAML inputs.
Currently following labs are available:
- AVD repository to build EVPN MLAG network
- AVD repository to build EVPN Active-Active network
A machine with Docker CE or Docker Desktop is required. Following operating systems were tested:
- Ubuntu LTS Server
- MacOs (on x86 laptops only) The lab is expected to run on any major Linux distribution. Please test and contribute by reporting and/or fixing possible issues.
Hardware requirements depend on the number of containers deployed. Please read Containerlab Scalability with cEOS section before deploying a large topology. For a small topology of 10+ cEOS containers 8 vCPUs and 10 GB RAM are recommended.
WARNING: Please make sure that your host has enough resorces. Otherwise Containerlab can enter "frozen" state and require Docker restart.
To install Docker on a Linux machine, check this guide. To get Docker Desktop, check docker.com.
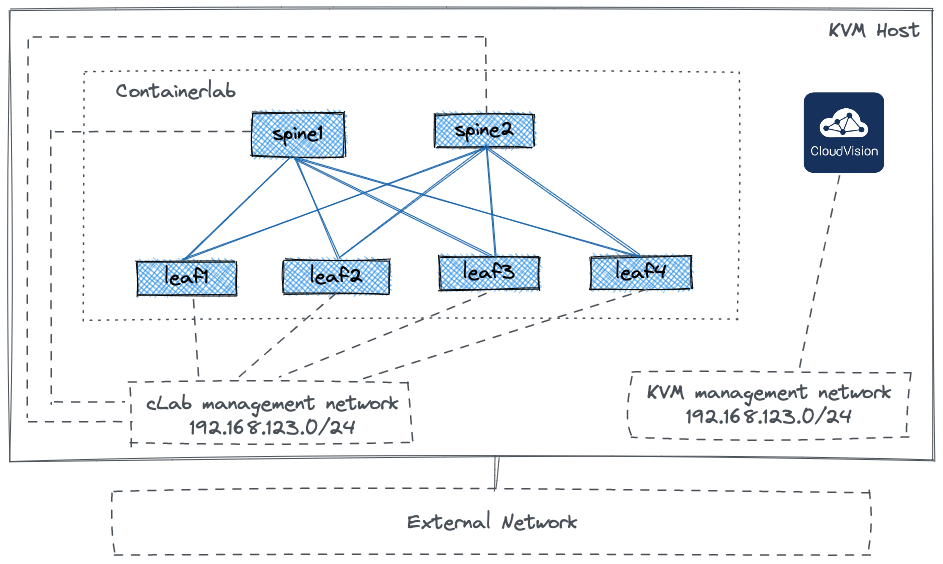
If you are planning to deploy Containerlab on a dedicated Linux host, you can also install and configure KVM and deploy CloudVision Portal as a virtual machine. To install KVM, check this guide or any other resource available on internet. Once KVM is installed, you can use one of the following repositories to install CVP:
- ISO-based KVM installer - currently not available on Github and distributed under NDA only. That will be fixed later.
- CVP KVM deployer
- CVP Ansible provisioning
It is also possible to run CVP on a dedicated host and a different hypervisor as long as it can be reached by cLab devices.
NOTE: to use CVP VM with container lab it's not required to recompile Linux core. That's only required if you plan to use vEOS on KVM for you lab setup.
The lab setup diagram:
The AVD Quickstart lab is not supported on M1 MacBooks right now.
Prerequisites to stat AVD Quickstart on MacOS:
- It is recommended to use cEOS-lab 4.28.0F or higher. Earlier cEOS-lab versions require cgroup v1 support. But default, latest Docker Desktop only supports cgroup v2. To enable cgroup v1 support in Docker Desktop, you can uncomment corresponding line in
MacOS_set_DockerDesktop.shscript before executing it withmake prepare_macoscommand. - Docker Desktop must have access to a number directories to run AVD Quickstart environment. Some locations do not even exist on MacOS, but can exist inside the container. That means, they must be present in Docker Desktop settings, but it's not possible to add them via GUI.
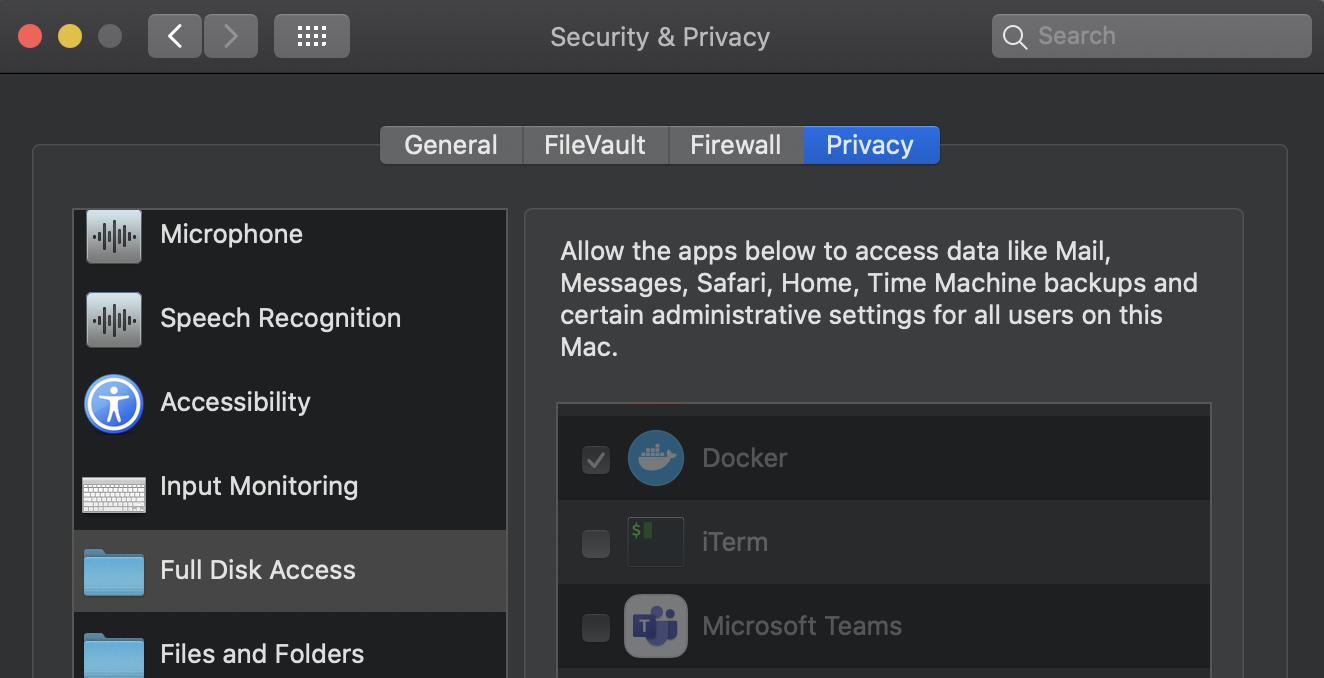
make prepare_macoswill add these directories to Docker Desktopsettings.jsonand install required tools withbrew. This tool requires Homebrew to be installed first. - Allow full disk access fo Docker Desktop in
System Preferences>Security & Privacy. You can limit that to specific directories, but full disk access is preferred for simplicity.
make prepare_macosscript is based on the code mentioned in this Docker Desktop for Mac issue on Github. With some modifications to allow access to certain directories and install missing tools.
- 0.1
- initial release with many shortcuts
- 0.2
- Fix bugs.
- Improve lab topology.
- Improve lab workflow.
- Add EVPN AA scenario.
- 0.3
- The lab now only requires Docker. Containerlab installation is not required and will be running inside provided Docker container.
- When building container with
make build, UID and GID will be updated using intermediate container similar to the container used by VSCode devcontainers. - The Dockerfile can be used as VSCode devcontainer or standalone.
- The lab environment is now supported and tested on MacOS. x86 MacBooks only.
- Dynamic aliases in the container for quick access to lab devices.
This section is explaining basic AVD quickstart lab workflow.
- Clone AVD quickstart repository to your lab host:
git clone https://github.com/arista-netdevops-community/avd-quickstart-containerlab.gitOr use your favorite IDE (like VSCode) for that. - It is recommended to remove git remote as changes are not supposed to be pushed to the origin:
git remote remove origin - Change to the lab directory:
cd avd-quickstart-containerlab. IDE should do that for you automatically. - Before running the lab it is recommended to create a dedicated git branch for you lab experiments to keep original branch clean.
- Check makefile help for the list of commands available:
make help
petr@nuc10i7:~/avd-quickstart-containerlab$ make help
avd_build_cvp build configs and configure switches via eAPI
avd_build_eapi build configs and configure switches via eAPI
avd_snapshot build configs and configure switches via eAPI
avd_validate build configs and configure switches via eAPI
build Build docker image
clab_deploy Deploy ceos lab
clab_destroy Destroy ceos lab
clab_graph Build lab graph
clean Remove all containerlab files and directories
help Display help message
inventory_evpn_aa onboard devices to CVP
inventory_evpn_mlag onboard devices to CVP
onboard onboard devices to CVP
prepare_mac_os Prepare Docker Desktop on MacOS for cEOS-based Containerlab
rm Remove all containerlab files and directories
run run docker image, if the image is not present - build it first- If cEOS image does not exist on your host yet, download it from arista.com and import. For example:
docker import <path-to-you-download-location>/ cEOS-lab-4.27.0F.tar ceos-lab:4.27.0F. The image tag must match the parameters defined in the lab files, for exampleCSVs_EVPN_AA/clab.ymlorCSVs_EVPN_MLAG/clab.yml. - Use
make buildto buildavd-quickstart:latestcontainer image. If that was done earlier and the image already exists, you can skip this step. If you are using VSCode devcontainer, VSCode will do that for you automatically. - (Optional) If VSCode devcontainer is used, the container will start automatically. Otherwise you can start it manually in the interactive mode by entering
make run. You can also skip this steps and execute all commands listed below directly on your host. They will run inside a non-interactive container in that case. - Build lab inventory with
make inventory_evpn_aa(EVPN Active-Active scenario) ormake inventory_evpn_mlag(EVPN MLAG scenario). This will create a directory with all files required to build the lab. - Review the inventory generated by AVD quickstart. Optional: you can git commit the changes.
- Run
make clab_deployto build the containerlab. Wait until the deployment will finish. - If you are working with
avd-quickstart:latestcontainer in the interactive mode, you can add aliases to connect to the lab devices quickly:add_aliases. This will allow you to connect to any lab device by typing it's short hostname. For example,leaf1will SSH to the switch with the corresponding hostname. You can list generated aliases withaliascommand. This can be especially useful on MacOS, as/etc/hostsfile can not be changed by Containerlab due to system integrity check restrictions.
- If CVP VM is used in the lab, onboard cLab switches with
make onboard. Once the script behind this shortcut wil finish, devices will appear in the CVP inventory. - To build EVPN configuration and deploy it on the lab switches, you can execute corresponding Ansible AVD playbook with
make avd_build_eapi(deploy directly) ormake avd_build_cvp(deploy via CVP if it's present in the lab) shortcut. That will executeplaybook/fabric-deploy-eapi.ymlorplaybook/fabric-deploy-cvp.ymlplaybooks. If the configuration is delivered via CVP, don't forget to execute the tasks generated by the playbook. - Once the configs are deployed, you can SSH to any switch using corresponding alias and type any show commands to check the lab state. Verify that hosts can ping each other.
- To test Ansible AVD post-validation role, use
make avd_validate. The playbook itself is located atplaybooks/validate-states.yml. This will generate corresponding reports in the lab directory. - You can also collect as snapshot (series of pre-defined show commands) with
make avd_snapshot. - You can optionally git commit the changes and start playing with the lab. Use CSVs to add some VLANs, etc. for example. Re-generate the inventory and check how the AVD repository data changes.
- Execute
make clab_destroyto destroy the containerlab. - Execute
make rmormake cleanto delete the generated AVD inventory.
under construction, coming soon