Repository to reproduce the analyses in the paper “Diurnal temperature range as a key predictor of plants’ elevation ranges globally”.
Simply use the main.R file to run all the analyses performed in the
manuscript.
You can run multiple models automatically using a set of for loops.
For example:
# global-scale analyses
model <- load_model(scope = "global")
for (expr in c(~dtr, ~ts, ~past_dmat)) {
for (elevation_span in ELEV_SPANS) {
for (exclusion_zone in EXCLS) {
mdl_data <- compile_mdl_data(
trs,
clim_data = trs_bioclim,
elevation_span = elevation_span,
exclusion_zone = exclusion_zone,
singleton_thr = SINGLETON_THR,
std_elev_grad = TRUE,
average = TRUE,
std_from = "top",
cols = c("location", "sp_range", "land_type"),
expr = expr
)
run_jags(
mdl_data,
model = model,
n.iter = JAGS_ITER,
n.thin = JAGS_THIN,
n.chains = JAGS_CHAINS,
n.burnin = JAGS_BURN_IN,
save = TRUE,
path = glue("data/jags/{model$scope}-scale/")
)
gc() # to free up RAM
}
}
}Note that the expr parameter in compile_mdl_data() takes a
formula for the global-scale analyses and a character string for
the local-scale analyses.
A list of the different models ran in the manuscript can be found below.
Once the models have finished running, use:
results.Rto plot model estimates and get model statisticsmdl_diagnostics.Rto perform model diagnostics
- Global-scale analyses:
- main models:
~dtr,~ts,~past_dmat - land type:
~dtr * land_type,~ts * land_type,~past_dmat * land_type - climate-related interactions:
~dtr * ap,~dtr * mat,~past_dmat * past_map
- main models:
- Local-scale analyses:
"dtr","ts"
Run the following line to make the required data set to reproduce the analyses on Gilchrist’s hypothesis.
trs_dtr_lower_third <- filter(trs, bio2 <= max(bio2, na.rm = TRUE) / 3)Run the ~past_dmat model using the trs_dtr_lower_third data set.
model <- load_model(scope = "global")
for (elevation_span in ELEV_SPANS) {
mdl_data <- compile_mdl_data(
trs_dtr_lower_third,
clim_data = trs_bioclim,
elevation_span = elevation_span,
exclusion_zone = EXCL_DEFAULT,
singleton_thr = SINGLETON_THR,
std_elev_grad = TRUE,
average = TRUE,
std_from = "top",
cols = c("location", "sp_range", "land_type"),
expr = ~past_dmat
)
run_jags(
mdl_data,
model = model,
n.iter = JAGS_ITER,
n.thin = JAGS_THIN,
n.chains = JAGS_CHAINS,
n.burnin = JAGS_BURN_IN,
save = TRUE,
path = "data/jags/global-scale/gilchrist hypothesis/"
)
}Use the GlobalAnalyses class to plot model estimates:
gh <- GlobalAnalyses$new("data/jags/global-scale/gilchrist hypothesis")
gh$regressions(
vars = "past_dmat",
facet_cols = "elevation_span",
labels = "∆ mean annual temperature (0-1980) (°C)"
)
gh$posterior_distributions(
vars = "past_dmat",
yvar = "elevation_span",
facet = FALSE,
reverse = TRUE,
scales = .6
)Climate data are already provided in the trs.csv data set.
If you would like to perform GIS analyses again, proceed as follows:
- Open
TRS.Rprojand execute the following function in the console:TRS.utilities::setup_gis(). The function will create all the required directories to store SRTM and climate-related data. - Download bioclim and
digital elevation data (as
.tif) as well as PaleoView. See here for instructions to generate past climate data. - Save each file in the appropriate folder (see file tree below).
- Once all the files are in their respective folders, use the
gis.Rscript to extract present and past climate data in each location. Output data will be stored in thegis/clim/extracted/subfolders.
gis
├── clim
│ ├── data
│ │ ├── past <- PaleoView-related folder
│ │ │ ├── base <- past climate data go here
│ │ │ └── var
│ │ │ ├── mean precipitation <- generated mean precipitation files go here
│ │ │ └── mean temperature <- generated mean temperature files go here
│ │ └── present <- present bioclim files go here
│ └── extracted
│ ├── past
│ └── present
└── srtm <- save SRTM tiles in the corresponding subfolders
├── Afghanistan
├── Alborz Mountains
├── Azores
├── Baekdudaegan Mountains
├── Bioko
├── Canary
├── Cantabria
├── Cape Verde
├── Chicauma
├── Colombian Andes
├── Crete
├── Cyprus
├── Denali
├── Drakensberg
├── Euboea
├── Golestan
├── Hawaii
├── Hengduan
├── Jamaica
├── Jaya
├── Kenya
├── La Amistad
├── Lazio
├── Mt Ararat
├── Mt Etna
├── Mt Kilimanjaro
├── Nanga Parbat
├── Nepal
├── Nevada Test Site
├── Owens Peak
├── Reunion
├── Santa Rosa Mountains
├── Sierra Nevada
├── Sierra San Pedro Martir
├── Socotra
├── South-Eastern Pyrenees
├── Swiss Alps
├── Tahoe
├── Taiwan
├── Tajikistan
├── Tasmania
├── Utah
├── Venezuelan Andes
└── Wind River Mountains
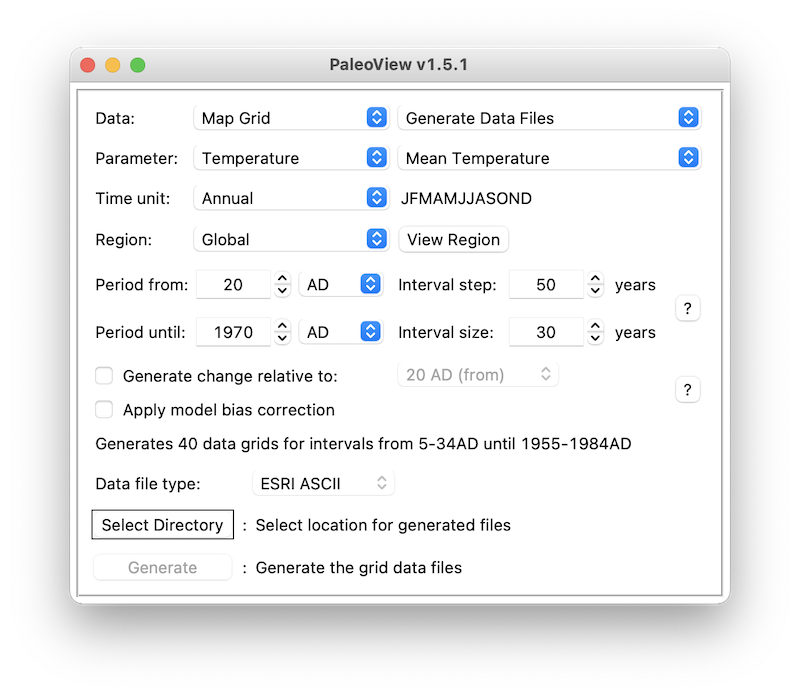
Open PaleoView and download the climate data (see chapter 2 of
PaleoView’s user
manual)
for mean temperature and precipitation. Configure the input data
location (see chapter 3 in the user manual). Run PaleoView with the same
settings as shown in the image below for temperature and
precipitation:
Below are the different R packages required to run the code in this repository:
- tidyverse
- TRS.utilities
- glue
- bayesplot (only for model diagnostics)
To install TRS.utilities, use:
# install.packages("pak")
pak::pak("arnaudgallou/TRS.utilities")In addition, you will need to have JAGS installed on your machine.