This application has 3 sub-programs:
sreis used to find potential 'Hive' performance issues caused by small files and excessive partitions.u3is used to review 'Hive 1/2' environments for Hive3 upgrade planning.cliis an hdfs interactive client. It is a core part of thehive-sreapplication, so we've exposed the shell here via thehive-sre-cliexecutable.perfis used to check the throughput of a JDBC connection.
| Sub-Program | Database | Version | Tested | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
u3 |
MySql | 5.6 | Limited | Recommend upgrading 5.7. This is the lower MySql supported env for HDP |
| 5.7 | Yes | |||
| 5.7 | Yes | |||
| 8.0 | No | Not supported by HDP | ||
| MariaDb | 10.1 | No, but should work as 10.2 does | ||
| 10.2 | Yes | |||
| Postgresql | 9.6 | No, but should work | ||
| 10 | Yes | Field Tested, May still be a few rough edges | ||
| 11 | No, but should work at 10 does | |||
| Oracle | 12 | Yes | Field Tested, May still be a few rough edges | |
sre |
MySql | 5.6 | Limited | Recommend upgrading 5.7. This is the lower MySql supported env for HDP |
| 5.7 | Yes | |||
| 5.7 | Yes | |||
| 8.0 | No | Not supported by HDP | ||
| MariaDb | 10.1 | No, but should work as 10.2 does | ||
| 10.2 | Yes | |||
| Postgresql | 9.6 | No, but should work | ||
| 10 | Yes | Field Tested, May still be a few rough edges | ||
| 11 | No, but should work at 10 does | |||
| Oracle | 12 | Yes | Field Tested, May still be a few rough edges |
Ensure you have the database appropriate driver in the ${HOME}/.hive-sre/aux_libs directory.
I've tried to match supported DB's for HDP 2.6.5 and 3.1.x as much as I could.
USE THE PRE-BUILT BINARY!!! You won't have the necessary dependencies to build this from scratch without downloading and building the 'Hadoop Cli'.
Don't Build, Download the LATEST binary here!!!
On the edgenode:
- Remove previous install directory
rm -rf hive-sre-install - Expand the tarball
tar zxvf hive-sre-dist.tar.gz.This produces a child
hive-sre-installdirectory. - Two options for installation:
- As the root user (or
sudo), runhive-sre-install/setup.sh. This will install thehive-srepackages in/usr/local/hive-sreand create symlinks for the executables in/usr/local/bin. At this point,hive-sreshould be available to all user and in the default path. - As the local user, run
hive-sre-install/setup.sh. This will install thehive-srepackages in$HOME/.hive-sreand create symlink in$HOME/bin. Ensure$HOME/binis in the users path and runhive-sre.
- As the root user (or
DO NOT RUN hive-sre from the installation directory.
If you install both options, your environment PATH will determine which one is run. Make note of this because an upgrade may not be reachable.
This will create and install the hive-sre and hive-sre-cli applications to your path.
Try it out on a host with default configs (if kerberized, get a ticket first):
hive-sre-cli
OR
hive-sre
See the config docs for details.
To ease the launch of the application below, configure these core environment variables.
hive-sre sre -db priv_dstreev -cfg /tmp/test.yaml -o ./sre-out`
The output is a set of files with actions and error (when encountered). The files maybe txt files or markdown. You may want to use a markdown viewer for easier viewing of those reports. The markdown viewer needs to support github markdown tables .
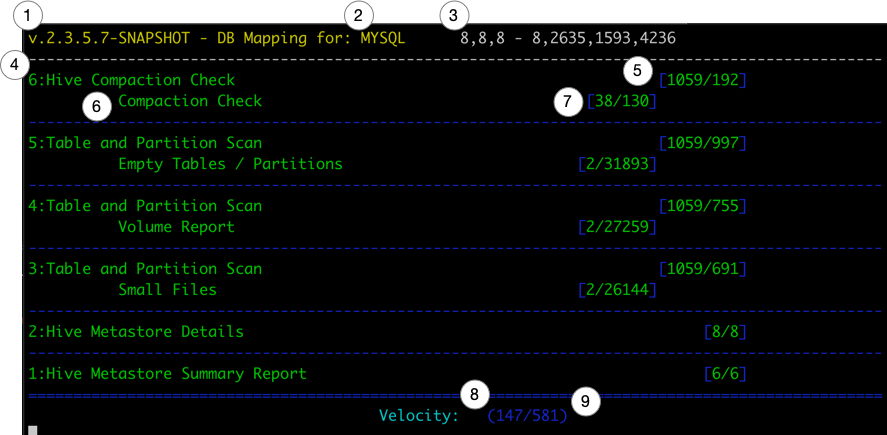
Only active processes will show up in the UI. The UI will refresh every second and display the current details below.
There are several 'processes' that are defined in u3. Each process will run 1 or more 'sub-processes'. The counters lists in the UI are specific to the 'process' and 'sub-processes' in that section.
The number of concurrent processes is controlled by the parallelism variable in the configuration yaml defined above.
hive-sreversion information- Metastore RDBMS Type
- Thread Status
a,b,c - d,e,f,j- (a) Core Pool Size
- (b) Largest Pool Size
- (c) Max Pool Size
- (d) Active Thread Count
- (e) Completed Thread Tasks
- (f) Remaining Thread Queue
- (j) Total Task Count
- Procedure Name
- Procedure Counts
[Total/Completed]Totalis the full count of all tasks for that processCompletedis the number of tasks this procedure has completed.
- Procedure Check - Child of Procedure
- Procedure Check Counts -
errors/successes - Velocity - Total Time in Seconds process has been running.
- Velocity - The average number of Tasks completed per second since job started.
- Note that not all Tasks are equal. Task times vary based on the content of the cluster and area being inspected. And can largely be effected by Namenode performance.
- Sorting results for loc_scan..
sort -k 1 --field-separator="|" loc_scan_missing_dirs.md > loc_scan_missing_dirs_sorted.txt