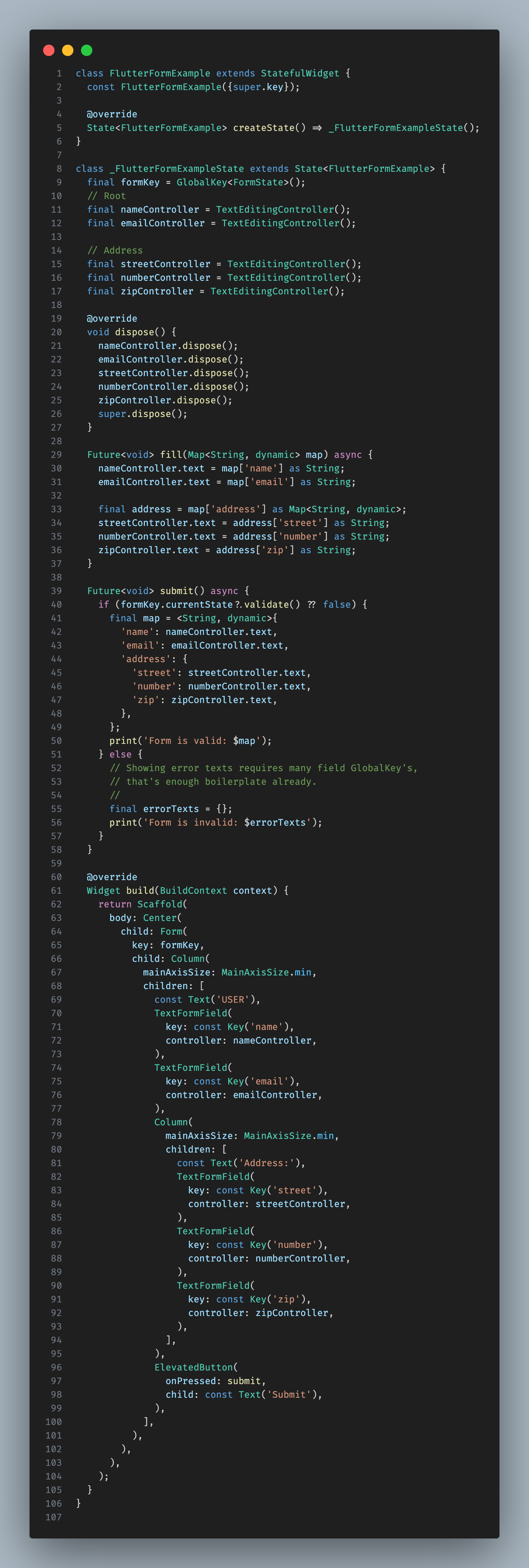
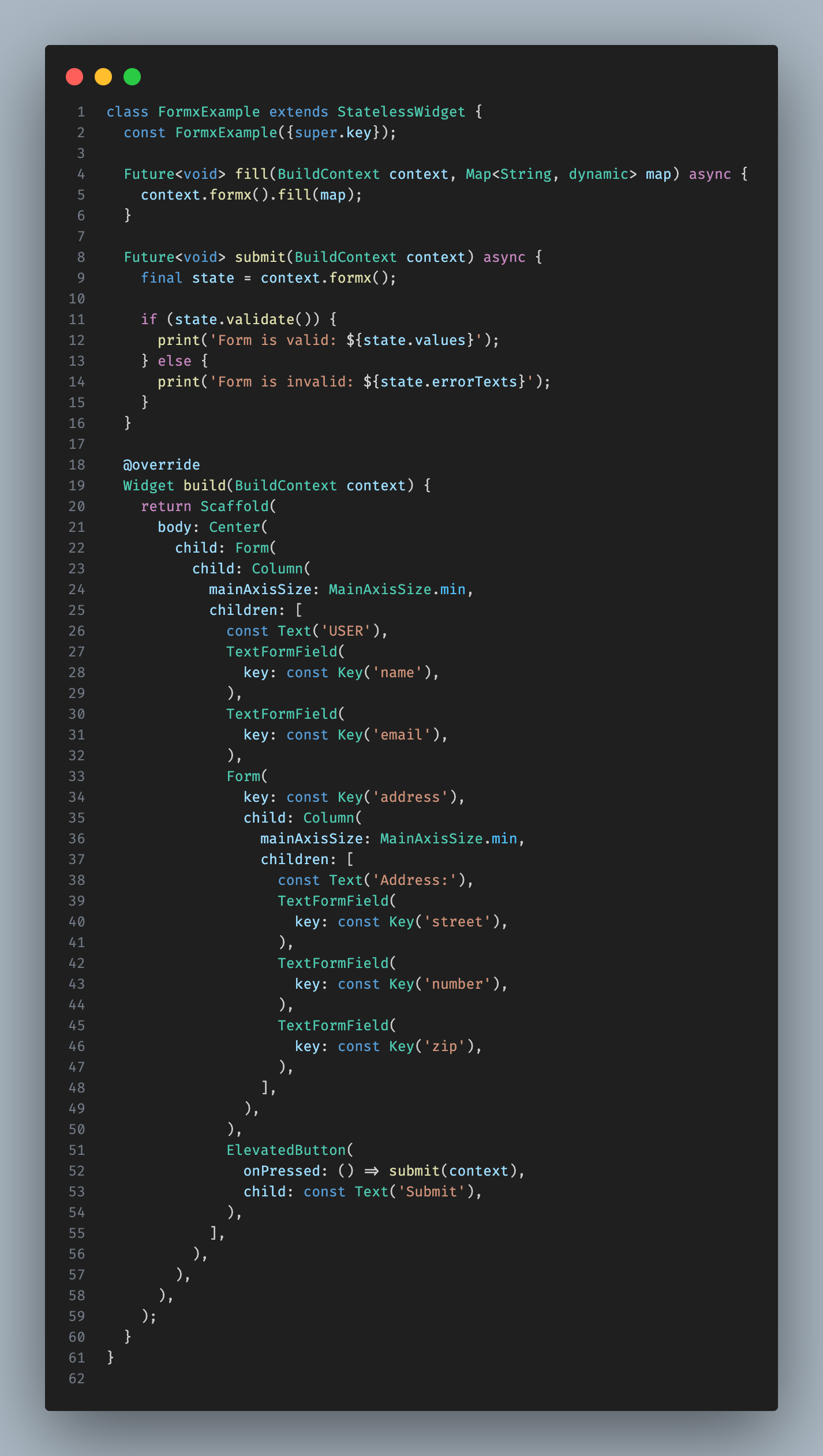
BuildContext.formx([String? key]) automatically retrieves the appropriate FormState for you, though you can specify a key if necessary.
final state = context.formx();
final addressState = context.formx('address');
final email = context.field('email').value;Alternatively, use Formx.of(context) for a traditional approach without visitors.
⚠️ Be careful, as using it will also rebuild the widget tree on any field change, just asForm.of(context).
.rawValues, a structuredMapwith all raw [FormField.value] of the form..values, same asrawValues, but with global [FormxOptions] applied..customValues(), same asrawValues, but with explicit options applied..initialValues, a structuredMapwith all the initial values of the form..hasInteractedByUser, whether any nested [FormFieldState.hasInteractedByUser]..hasError, whether any nested [FormFieldState.hasError]..isValid, whether all nested [FormFieldState.isValid]..invalids, a list with all invalid field keys, regardless if validated..errorTexts, a flatMapwith all nested [FormFieldState.errorText]..fill(Map<String, dynamic> values), to fill the form with values.
FormxState is an inline-class that redeclares some of the FormState methods:
.validate([List<String>? keys]).save([List<String>? keys]).reset([List<String>? keys])
These methods function identically to their original counterparts but extend their effects to nested forms. Using FormState.validate only validates the top-level form, whereas FormxState.validate also validates any nested forms.
You have the option to specify a list of keys with these methods to target specific forms or fields for validation, saving, or resetting.
You can redeclare any FormState to a FormxState by using FormxState(formState) type extension.
.setErrorText(String? errorText), sets the field errorText programmatically. RequiresValidator.
You can use Formx.options to modify FormState.values output.
trimremoves leading and trailing whitespaces.unmaskremoves all [MaskTextInputFormatter] masks.nonNullremoves allnullvalues.nonEmptyMapsremoves all empty maps.nonEmptyStringsremoves all empty strings.nonEmptyIterablesremoves all empty iterables.dateAdapterto format date inFormState.values.
By default, all options are enabled, except for [nonEmptyIterables].
To get the unmodified values, use
FormState.rawValues.
To understand how masks are applied, see mask_text_input_formatter library, also exported by this package.
A shortcut for GlobalKey<FormFieldState<T>> that allows you to control the form fields directly. Additionally, you can modify the field behavior, with:
.adapterto format the field value..unmaskto (un)mask the field value, regardless of the form global options.
TextFormField(
key: FieldKey('phone', unmask: true),
),
TextFormField(
key: FieldKey('age', adapter: (value) => value?.toInt()),
),You can also use extension modifiers:
TextFormField(
// Use `text()` as this is a TextFormField.
key: const Key('phone').text().toInt().unmasked();
),Looking for a way to create validators declaratively? The Validator class provides a readable and declarative approach to defining validation rules for your Dart applications.
TextFormField(
validator: Validator<String>(
isRequired: true,
test: (value) => value.isEmail,
),
),For the one-liners, the modifiers allows you to chain your validators.
TextFormField(
validator: Validator().required().email(),
),You can also easily create custom validators:
extension CustomValidators on Validator<T> {
Validator<T> myValidator([String? requiredText]) {
return test((value) => /* your logic here */, requiredText);
}
}// You can set a default `requiredText`/`invalidText` for all validators:
Validator.defaultRequiredText = 'This field is required';
Validator.defaultInvalidText = 'This field is invalid';
// You can also modify the errorText of a validator:
Validator.translator = (key, errorText) => errorText; // good for translations
// And disable them all:
Validator.disableOnDebug = true; // only works on debug mode.test(bool Function(T value) test).number(bool Function(num value) test).datetime(bool Function(DateTime value) test).required.email.url.phone.creditCard.cpf.cnpj.date.alpha.numeric.alphanumeric.hasAlpha.hasNumeric.hasAlphanumeric.hasUppercase.hasLowercase.hasSpecialCharacter.minLength(int length).maxLength(int length).minWords(int words).maxWords(int words).minNumber(num number).maxNumber(num number).isAfter(DateTime date).isBefore(DateTime date)
Formx comes bundled with a set of built-in validators and sanitizers, which you can use to validate and sanitize your form fields.
.isPhone.isCpf.isCnpj.numeric(returns the numbers).alpha(returns the letters).alphanumeric(returns numbers/letters).hasAlpha.hasNumeric.hasAlphanumeric.hasUppercase.hasLowercase.hasSpecialCharacters.equalsIgnoreCase(String)
Additionally exports string_validator library. See it for complete list of extensions.
.indentedfor a map view that indents when printed..indentedTextfor getting an indented text..deepMap()for mapping nested maps..clean()for values that arenullor empty string/iterable/map..cleaned()for a new map with allnullor empty values removed.
Deeply recases all your map keys:
.camelCase"camelCase".constantCase"CONSTANT_CASE".sentenceCase"Sentence case".snakeCase"snake_case".dotCase"dot.case".paramCase"param-case".pathCase"path/case".pascalCase"PascalCase".headerCase"Header-Case".titleCase"Title Case"
Additionally exports recase library. See it for complete list of extensions.
.keepAliveusually needed for building forms with [PageView.children]..expandedusually needed for building forms with [Column.children] or [Row.children].
Contributions to formx are welcome! Whether it's bug reports, feature requests, or pull requests, all "forms" of collaboration can help make formx better for everyone.