aos8-iot-server-example-azure
Overview
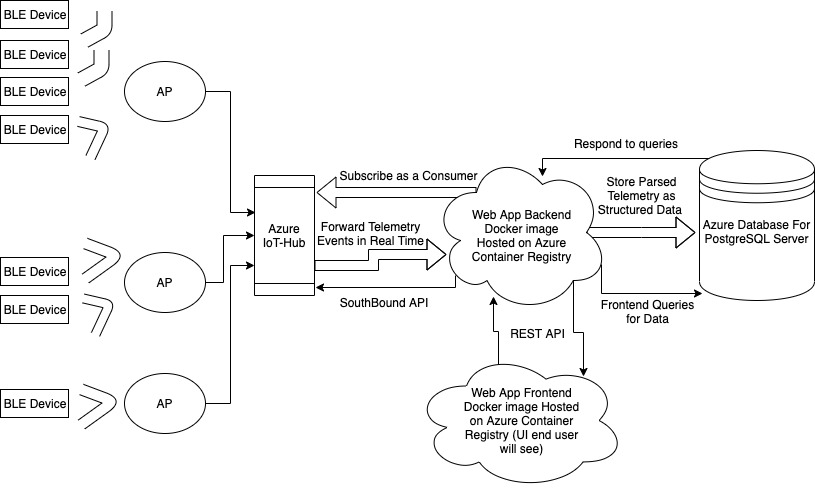
This project is a detailed yet simple to use demo application meant to provide a starting template for Aruba Partners and individuals who want to learn how to:
- Connect to Azure IoT Hub instances to ingest telemetry from IoT devices (Aruba NorthBound API)
- Breakdown (parse) telemetry received from IoT Hub and store parsed information into a structured, scalable, and optimized database
- Visualize and present telemetry directly from IoT Hub in different intuitive UI components
- View live telemetry using websockets
- Demonstrate how to control IoT devices using Aruba SouthBound API in an interactive manner
Architecture
Software Used
- node.js
- Express
- Microsoft Azure Database for PostgreSQL
- Microsoft Azure IoT-Hub
- Vue.js
- Bulma
- Dygraphs
- Timescale DB
Tutorial: Run Web App on Azure
Pre-requisites
- Install/update to latest version Azure CLI and Docker engine
- Please make sure that azure cli and docker engine are installed and/or updated to the most recent version
- Azure CLI installation: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli
- Docker engine: https://docs.docker.com/get-docker/
- An active Azure subcription is required
- Ensure Docker Engine is running
Setup using Azure Portal and Command Line
-
Create azure database for postgres server
- NOTE: telemetry scale requirements might affect web app functionality if there is a resource constraint on the server (see: troubleshooting) See: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/postgresql/single-server/concepts-limits
- Login to azure portal
- search for and click on resource "Azure Database for PostgreSQL servers"
- select create
- select the create button on the 'Single Server' panel (flexibile server has not been tested with app)
- Fill out basic settings
- create a new resource group or use an existing
- Pick a name for your server
- Select desired location (a location nearest to you)
- admin username and password
- all other settings can remain on default (storage + compute should be edited based on costs and needs)
- Select review+create
- after resource has deployed, select go to resource
- Under settings > connection security > Firewall Rules
- click on Add 0.0.0.0 - 255.255.255.255 (or just add your IP address / any IP address you wish to give access to your db)
- Select Save to preserve your changes. You get a notification once the change is saved.
- Log in to database using psql (a default database called "postgres" is created automatically) using a terminal of choice or azure cloud shell
- Information about the database that are needed to log into the database can be found under the 'overview' tab
- psql --set=sslmode=require --host=.postgres.database.azure.com --port=5432 --username=@ --dbname=postgres
- enter the password for the admin username you created earlier
- you can now use your postgres database with postgres queries / commands as needed
-
Installing TimescaleDB on existing Azure database for PostGres
- To install TimescaleDB, you need to include it in the server's shared preload libraries. A change to Postgres's shared_preload_libraries parameter requires a server restart to take effect. You can change parameters using the Azure portal or the Azure CLI.
- Using the Azure portal:
- Select your Azure Database for PostgreSQL server.
- On the sidebar, select Server Parameters.
- Search for the shared_preload_libraries parameter.
- Select TimescaleDB.
- Select Save to preserve your changes. You get a notification once the change is saved.
- After the notification, restart the server to apply these changes
- Log in to database using psql
- psql --set=sslmode=require --host=.postgres.database.azure.com --port=5432 --username=@ --dbname=postgres
- enter the password for the admin username you created earlier
- Create the timescaledb extension:
- CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS timescaledb CASCADE;
-
Real Time Telemetry
- Log in to database using psql:
- psql --set=sslmode=require --host=.postgres.database.azure.com --port=5432 --username=@ --dbname=postgres
- enter the password for the admin username you created earlier
- Create a trigger on each row added (the app uses websockets and a postgres listener for the event below for live telemetry features)
-
CREATE FUNCTION notify_trigger() RETURNS trigger AS $$ DECLARE BEGIN PERFORM pg_notify('new_azurepgmsg', row_to_json(NEW)::text); RETURN new; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
-
CREATE TRIGGER ble_table_trigger AFTER INSERT ON tsdatahypertable FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE PROCEDURE notify_trigger();
-
- Log in to database using psql:
-
Set Up IoT Devices, Azure IoT Hub, and Azure DPS (your Azure IoT Solution)
- see: documentation/Azure IoTHub Integration User Guide.pdf
- see: documentation/Azure IoT Central Integration User Guide.pdf
-
Deploy to Azure
- Create a .env file locally in project root (ex: echo -e "IotHubConnectionString='xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx'\nEventHubConsumerGroup='xxxxxxxxx'\nDBHOST='xxxxxx.postgres.database.azure.com'\nDBUSER='xxxxxxx@xxxxxxx'\nDBPASSWORD='xxxxxxx'\nDATABASE='xxxxxxx'" > .env ) format: IotHubConnectionString='xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx' EventHubConsumerGroup='xxxxxxxxx' DBHOST='xxxxxx.postgres.database.azure.com' DBUSER='xxxxxxx@xxxxxxx' DBPASSWORD='xxxxxxx' DATABASE='xxxxxxx'
- Build backend image
- From project root run:
- docker build --file=backend/Dockerfile -t .
- From project root run:
- Register the backend image in Azure Container Registry:
- login to azure
- az login (NOTE: tenant id will be one of the fields in the JSON object that is returned, you can optionally use this for later steps)
- OPTIONAL: create a new resource group
- az group create --name myResourceGroup --location westus
- create backend azure container registry
- az acr create --resource-group myResourceGroup --name --sku Basic
- Login to registry
- TOKEN_BE=$(az acr login --name --expose-token --output tsv --query accessToken)
- Authorize Azure
- docker login .azurecr.io --username 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000 --password $TOKEN_BE
- Tag image
- docker tag .azurecr.io/:v1
- Push to registry
- docker push .azurecr.io/:v1
- login to azure
- Deploy web app
- OPTIONAL: create a new resource group
- az group create --name myResourceGroup --location westus
- create web app azure container registry
- az acr create --resource-group myResourceGroup --name --sku Basic
- Login to registry
- TOKEN_FE=$(az acr login --name --expose-token --output tsv --query accessToken)
- Authorize Azure
- docker login .azurecr.io --username 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000 --password $TOKEN_FE
- Modify Docker Yaml file
- under project root, open the file "docker-compose.yml" with an editor of your choice
- modify the value of image (under services > app-frontend > image)
- change "webappfrontendacr.azurecr.io/app-frontend" to .azurecr.io/app-frontend
- optionally change "app-frontend" to a different image name if desired
- modify the value of image (under services > app-backend > image)
- change "webappbackendacr.azurecr.io/ao8-iot-server-example-azure_app-backend:v1" to .azurecr.io/:v1 (from the previous steps)
- docker compose up
- docker-compose up --build -d
- push docker images
- docker-compose push
- login to azure
- Find tenant id (tenant id is also returned in JSON object from the az login command that was previously run)
- log into azure portal
- Select Azure Active Directory.
- Select Properties.
- Then, scroll down to the Tenant ID field. Your tenant ID will be in the box.
- docker login azure --tenant-id xxxxxxxx
- Find tenant id (tenant id is also returned in JSON object from the az login command that was previously run)
- create azure container instance docker context to host web app
- docker context create aci
- switch to newly created context
- docker context use
- start the application in Azure Container Instances
- docker compose up
- view IP address of running web app
- docker ps
- Visit web app at <IP_addr_from_docker_ps>:80
- Troubleshoot
- ensure schema was created corectly
- Log in to database using psql
- psql --set=sslmode=require --host=<your_env_dbhost>.postgres.database.azure.com --port=5432 --username=<your_env_dbuser> --dbname=<your_env_database>
- enter <your_env_dbpassword> when prompted
- run '\dt' and verify if the schema has been created
- check console logs for the frontend and backend for errors or unexpected behavior
- docker logs aos8-iot-server-example-azure_app-backend
- docker logs aos8-iot-server-example-azure_app-frontend
- if you see the error message
- psql: FATAL: remaining connection slots are reserved for non-replication superuser connections
- this means that the database resources are insufficient to handle the telemetry workload
- to solve: adjust the speed and scale at which telemetry is being sent to iothub OR increase constraints of postgres server
- ensure schema was created corectly
- Bring down web app
- run 'docker compose down' in project root (ensure that you are still using your acicontext for docker, see step 9)
- How to run web app again after making changes:
- recommended → run docker compose down before deploying again
- docker context use default; docker ps
- verify that both the frontend and backend images are still running
- if they are not, run
- docker push .azurecr.io/:v1
- docker-compose up --build -d
- docker-compose push
- docker context use
- After verifying images are running:
- docker compose up; docker ps
- OPTIONAL: create a new resource group
Tutorials
- IoT-Hub from node js:
- Starter code for web application: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/sql-api-nodejs-application
- Interact with Cosmos DB using Node JS: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/sql-api-nodejs-samples
- https://blog.baeke.info/2019/04/15/iot-with-azure-database-for-postgresql-and-timescaledb/
- Create azure for postgres using portal:
- send c2d messages: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/iot-hub/iot-hub-node-node-c2d
- Dockerize web app: https://milanwittpohl.com/projects/tutorials/Full-Stack-Web-App/dockerizing-our-front-and-backend
- Web app:
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/container-instances/tutorial-docker-compose
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/container-instances/container-instances-tutorial-prepare-acr
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/container-registry/#:~:text=Azure%20Container%20Registry%20allows%20you,container%20development%20and%20deployment%20pipelines
- https://docs.docker.com/cloud/aci-integration/
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/fundamentals/active-directory-how-to-find-tenant
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/container-registry/container-registry-authentication?tabs=azure-cli
- PostgreSQL:
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/tutorial-python-postgresql-app?toc=https%3A%2F%2Fdocs.microsoft.com%2Fen-us%2Fazure%2Fpostgresql%2Ftoc.json&bc=https%3A%2F%2Fdocs.microsoft.com%2Fen-us%2Fazure%2Fbread%2Ftoc.json&tabs=bash%2Cclone&pivots=postgres-flexible-server
- https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/power-iot-and-time-series-workloads-with-timescaledb-for-azure-database-for-postgresql/
- https://www.educative.io/blog/what-is-foreign-key-database
- Timescale DB:
- Cosmos DB Documentation
- Cosmos DB vs TimsescaleDB