Welcome to the Vertex AI Document Discovery repository! This comprehensive guide will walk you through setting up a Python pipeline for intelligent document discovery using Google Cloud's Vertex AI Search. Follow these steps to create powerful search applications with ease.
Before getting started, ensure you have the following:
- Python 3.6 or later
- Git
- Google Cloud Platform account with a project set up and Vertex AI API enabled
Make sure you have permissions to create service accounts and manage API keys within your GCP project.
Let's set up your local development environment and configure dependencies.
-
Clone the Repository: In your terminal, execute the following command:
git clone https://github.com/arunpshankar/VertexAI-Document-Discovery.git cd VertexAI-Document-Discovery
-
Create a Virtual Environment: Isolate project dependencies by creating a Python virtual environment:
-
For macOS/Linux:
python3 -m venv .VertexAI-Document-Discovery source .VertexAI-Document-Discovery/bin/activate -
For Windows:
python3 -m venv .VertexAI-Document-Discovery .VertexAI-Document-Discovery\Scripts\activate
-
-
Upgrade pip and Install Dependencies: Ensure pip is up-to-date and install project dependencies:
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip pip install -r requirements.txt
-
Update Your PYTHONPATH:
Ensure your Python interpreter recognizes the project directory as a module location.
-
For macOS/Linux:
export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:.
-
For Windows (use
setinstead ofexport):set PYTHONPATH=%PYTHONPATH%;.
-
-
Configure Service Account Credentials 🔑
-
Create a directory to store your Google Cloud service account key securely:
mkdir credentials
-
Generate a Service Account Key from the Google Cloud Console, then move the downloaded JSON file to the
credentialsdirectory, renaming it tokey.json.
-
Now, your environment is set up for intelligent document discovery with Vertex AI Search. Let's proceed with configuring your Google Cloud project settings, enabling APIs, and running the provided Python scripts to automate your search applications.
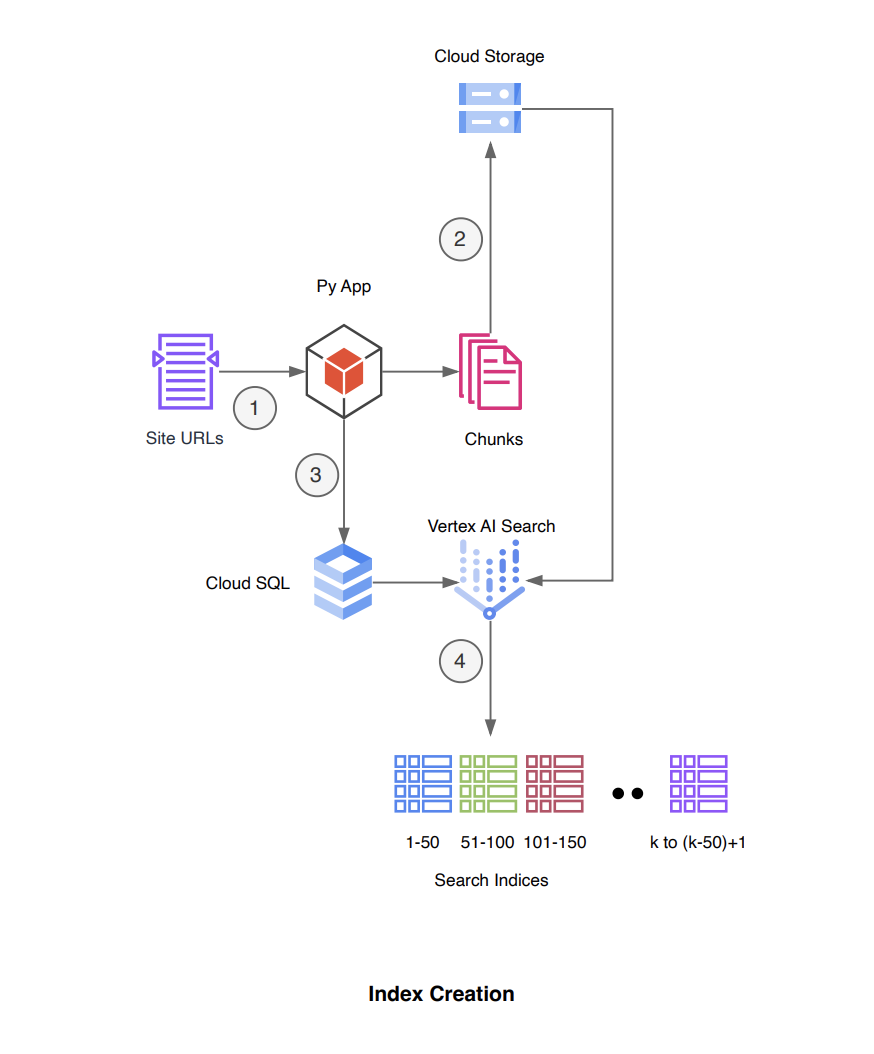
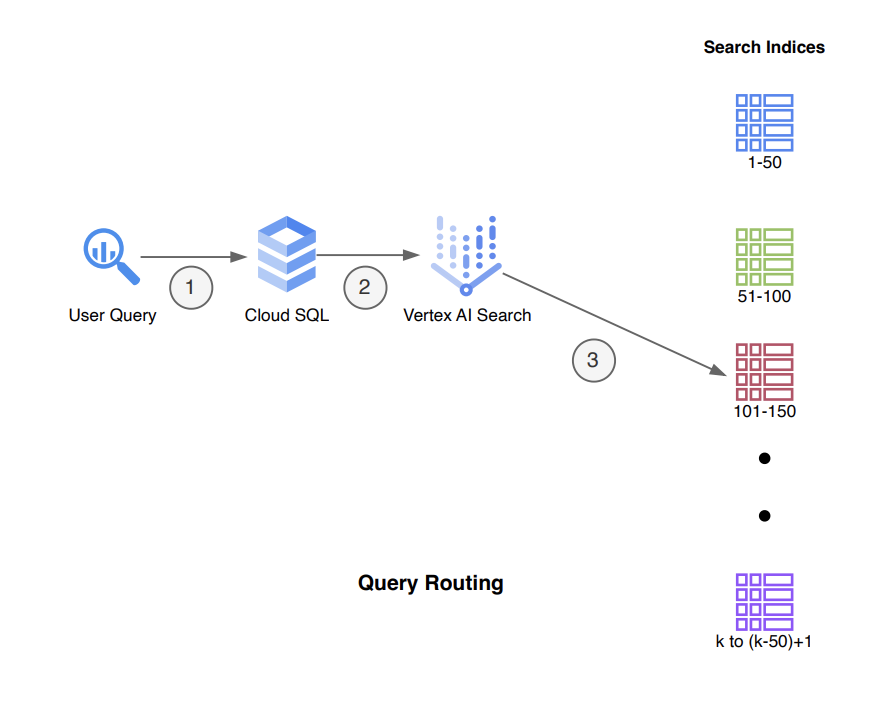
The architecture incorporates two primary workflows: index creation and query routing, optimized for handling a large number of site URLs by partitioning them into manageable chunks.
Ensure the following requirements are met before proceeding:
- Service Account Key is downloaded and stored in the
credentialsfolder, renamed tokey.json. - Cloud SQL Admin API is enabled within your GCP project.
- Cloud SQL Client role is granted to the IAM principal.
- Configuration details such as database credentials are populated in
config.ymlunder the/configdirectory.
This process involves dividing a user input file, which contains site URLs, entity information, and other metadata, into chunks. Each chunk is then processed to create data stores and a search application, respectively, using other GCP services for support.
- Divide the input file into multiple files, each containing 50 URLs.
- Transfer the partitioned files to Google Cloud Storage.
- For each segment, input the associated entity, site URL, and other details into a Cloud SQL table, associating each entity with its batch number.
- Utilize the Vertex AI Search API to establish a datastore and a search application for each segment, distinguishing each datastore by its batch ID.
This workflow focuses on identifying the appropriate batch ID for a user query based on the entity information it contains and routing the query to the corresponding datastore.
- User submits a query including entity information and other details.
- Query the Cloud SQL table using the entity information to find the corresponding row that contains the batch ID.
- Use the batch ID to direct the API request to the relevant datastore, along with the user's query.
- Enable Cloud SQL Admin API: Run
gcloud services enable sqladmin.googleapis.comin your terminal. - Create a Database: Execute
gcloud sql databases create <db name> --instance=<instance_name>to create a new database within your Cloud SQL instance.
Within the src/run directory, you'll find three runners:
index_pipeline.py: Handles chunking of URLs, uploads to GCS, creates datastores and search apps, and updates the Cloud SQL table. This corresponds to workflow I previously discussed.query_pipeline.py: Tests query routing functionality based on the provided query. Also, it can be used to take a list of entities and run search requests in bulk, collect the PDF URLs, and download the PDFs to a local directory. Corresponds to workflow II.clean_pipeline.py: Cleans up resources by removing objects from Cloud Storage, entries from the Cloud SQL table, and deleting datastores and search apps.
Before executing the modules, update config.yml with relevant database details such as username, password, database name, and table name. Follow the outlined steps to create indexes and route queries efficiently, leveraging GCP's powerful cloud capabilities for your website's search functionality.
Happy coding! 🚀