For this task 2 VMs are used:
- an Ubuntu VM (192.168.3.200)
- Kali Linux VM (192.168.3.153)
For installing suricata (and suricata debugger) in the Ubuntu VM the following commands are executed in order:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:oisf/suricata-stable
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
sudo apt install suricata suricata-dbg
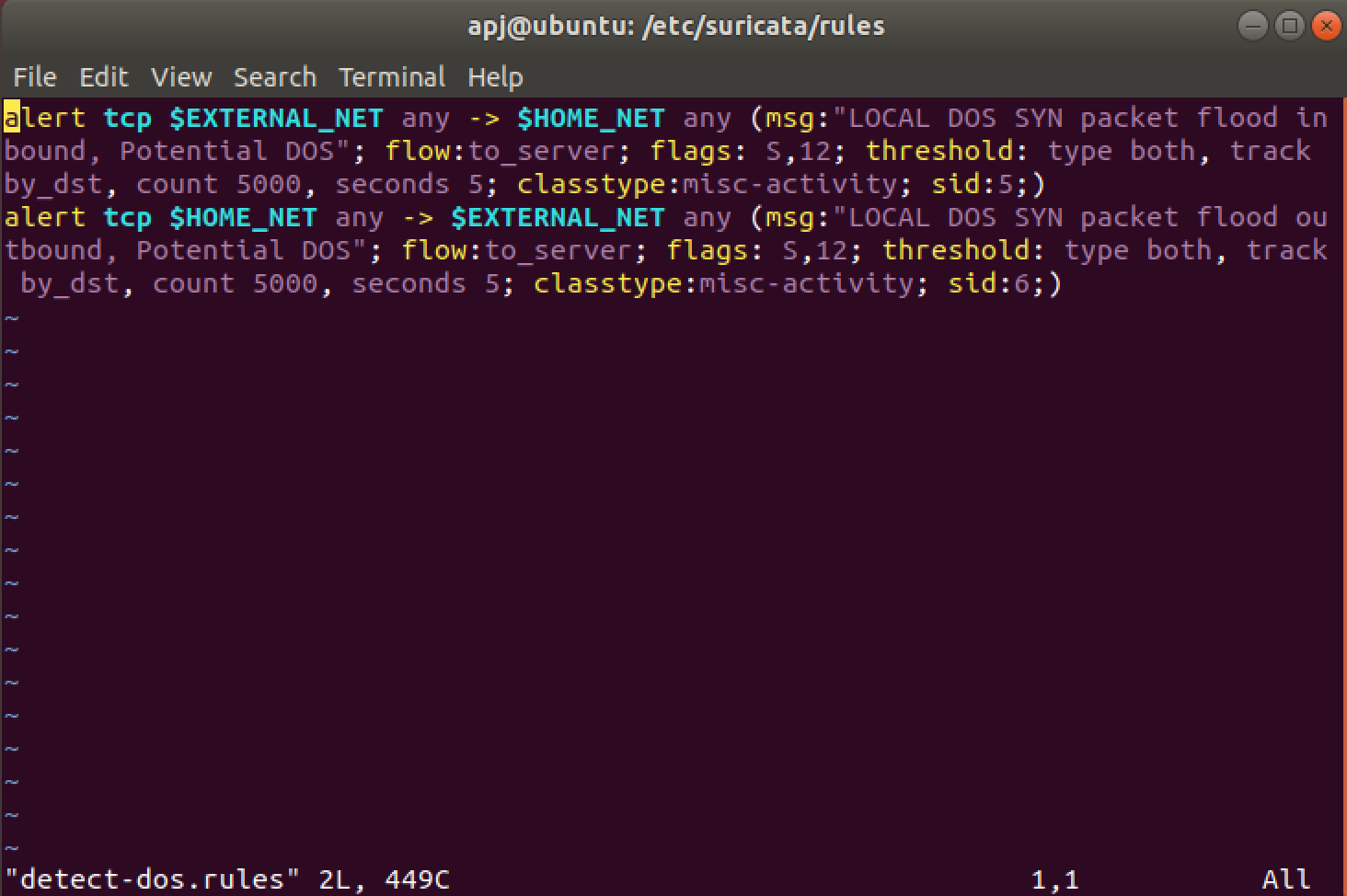
For this a file detect-dos.rules is created with the following contents:
alert tcp $EXTERNAL_NET any -> $HOME_NET any (msg:"LOCAL DOS SYN packet flood inbound, Potential DOS"; flow:to_server; flags: S,12; threshold: type both, track by_dst, count 5000, seconds 5; classtype:misc-activity; sid:5;)
alert tcp $HOME_NET any -> $EXTERNAL_NET any (msg:"LOCAL DOS SYN packet flood outbound, Potential DOS"; flow:to_server; flags: S,12; threshold: type both, track by_dst, count 5000, seconds 5; classtype:misc-activity; sid:6;)
The file is placed in the directory /etc/suricata/rules. The file includes 2 rules that are used to alert SYN flood attack. The common parameters in the rules are the actions:
-
alertwhich alerts when the conditions in the rule are met. -
tcpthe protcol that rule focuses on. -
$EXTERNAL_NET&$HOME_NETare set of ip addresses specified in the file/etc/suricata/suricata.yaml. -
msgparameter has the content which shows up during the alert. -
flagscontains S for SYN packet. -
thresholdparameter is set to both, which includes:- threshold to set a minimum threshold for a rule before it generates alerts.
- limit to make sure system does not get flooded with alerts.
Here the alert will be generated if there are more than 5000 TCP SYN packets incoming within the next 5 seconds
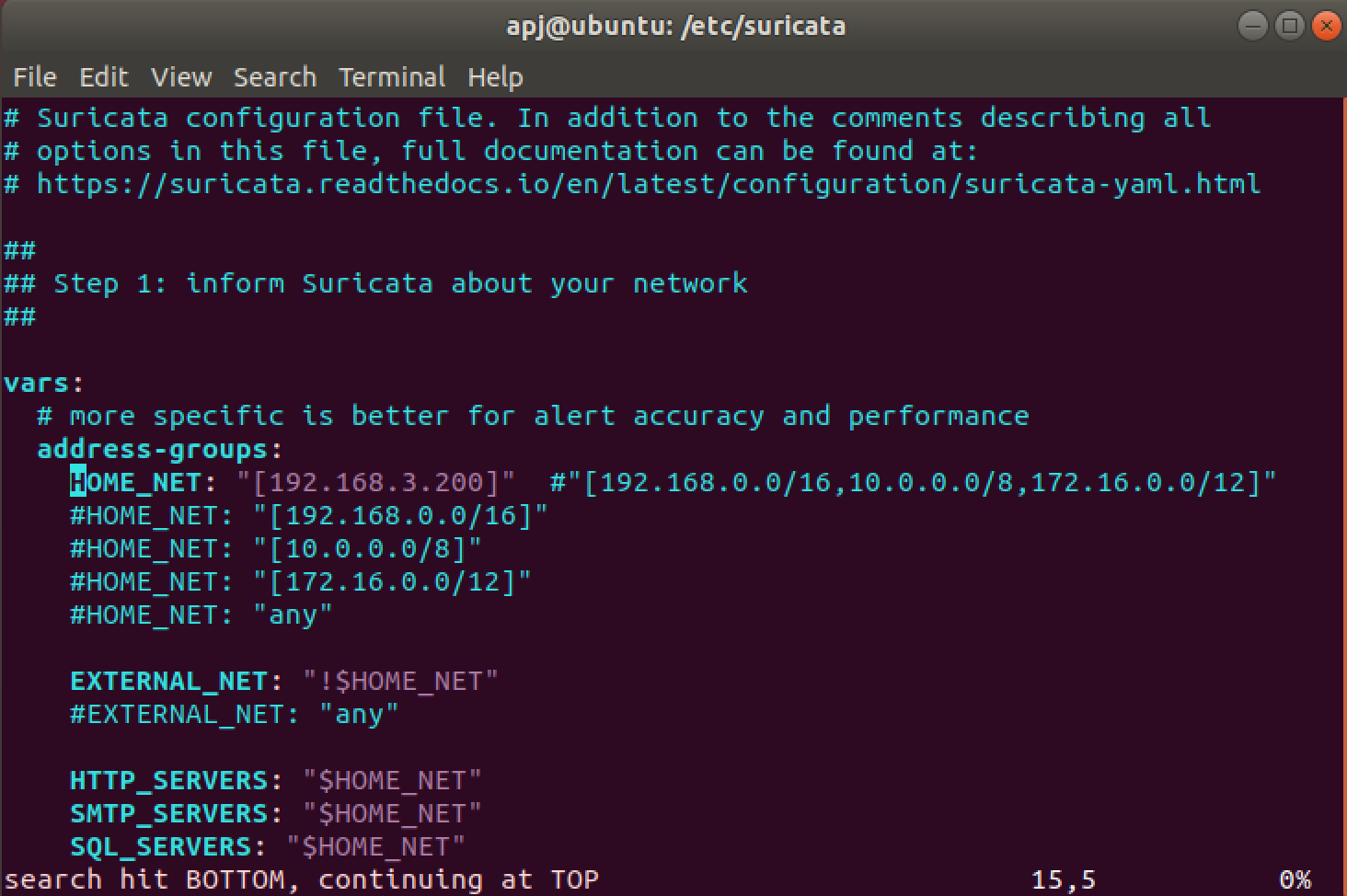
The contents of the suricata.yaml file is updated as follows:
The value of HOME_NET is updated with the IP address of the Ubuntu VM:
HOME_NET: "[192.168.3.200]"
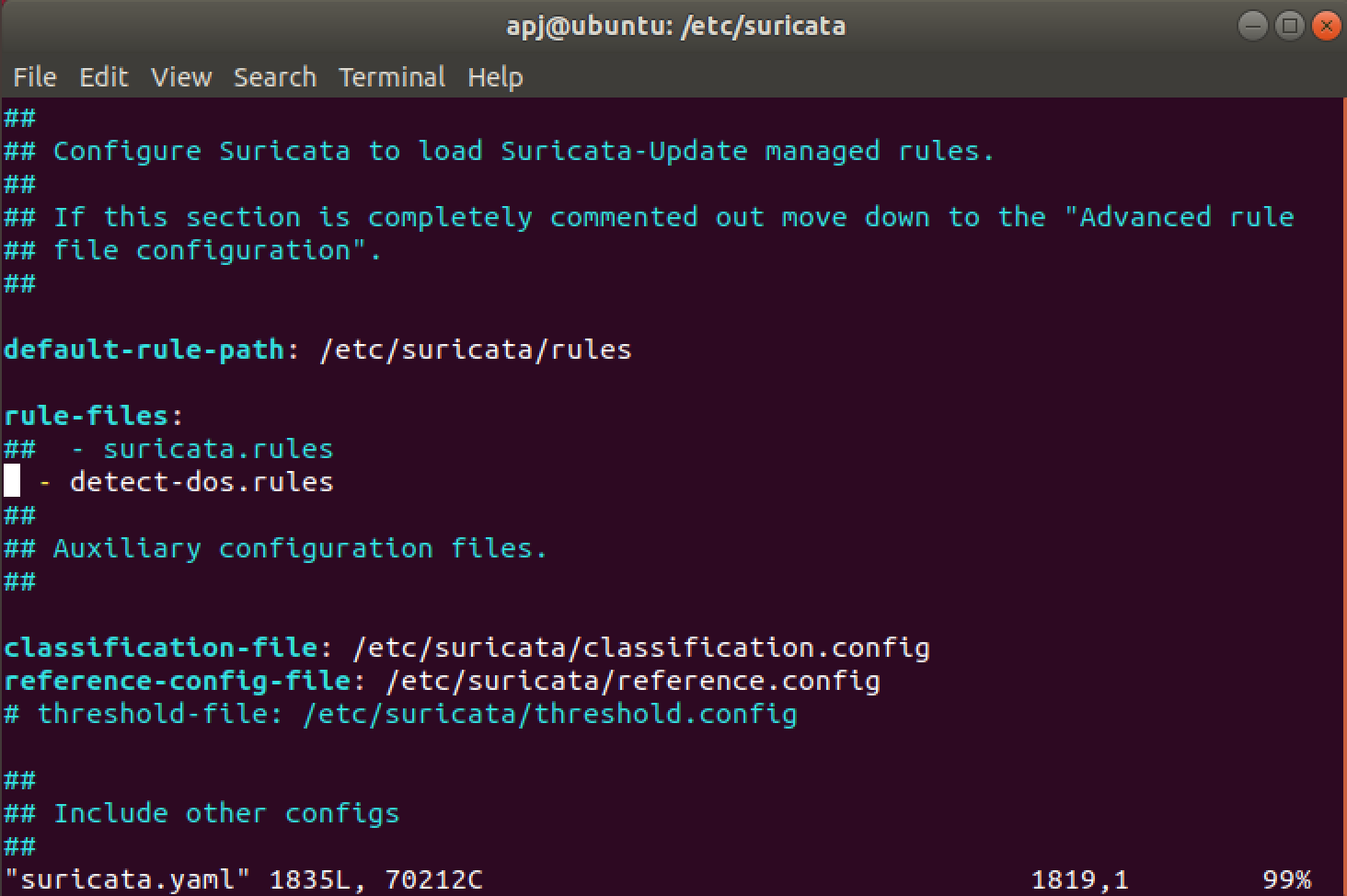
The newly created rule file which was placed in the appropriate directory is added to the rule-files list:
rule-files:
- detect-dos.rules
NOTE: if the rule-files is pointing to a different directory update rule-files location with /etc/suricata/rules.
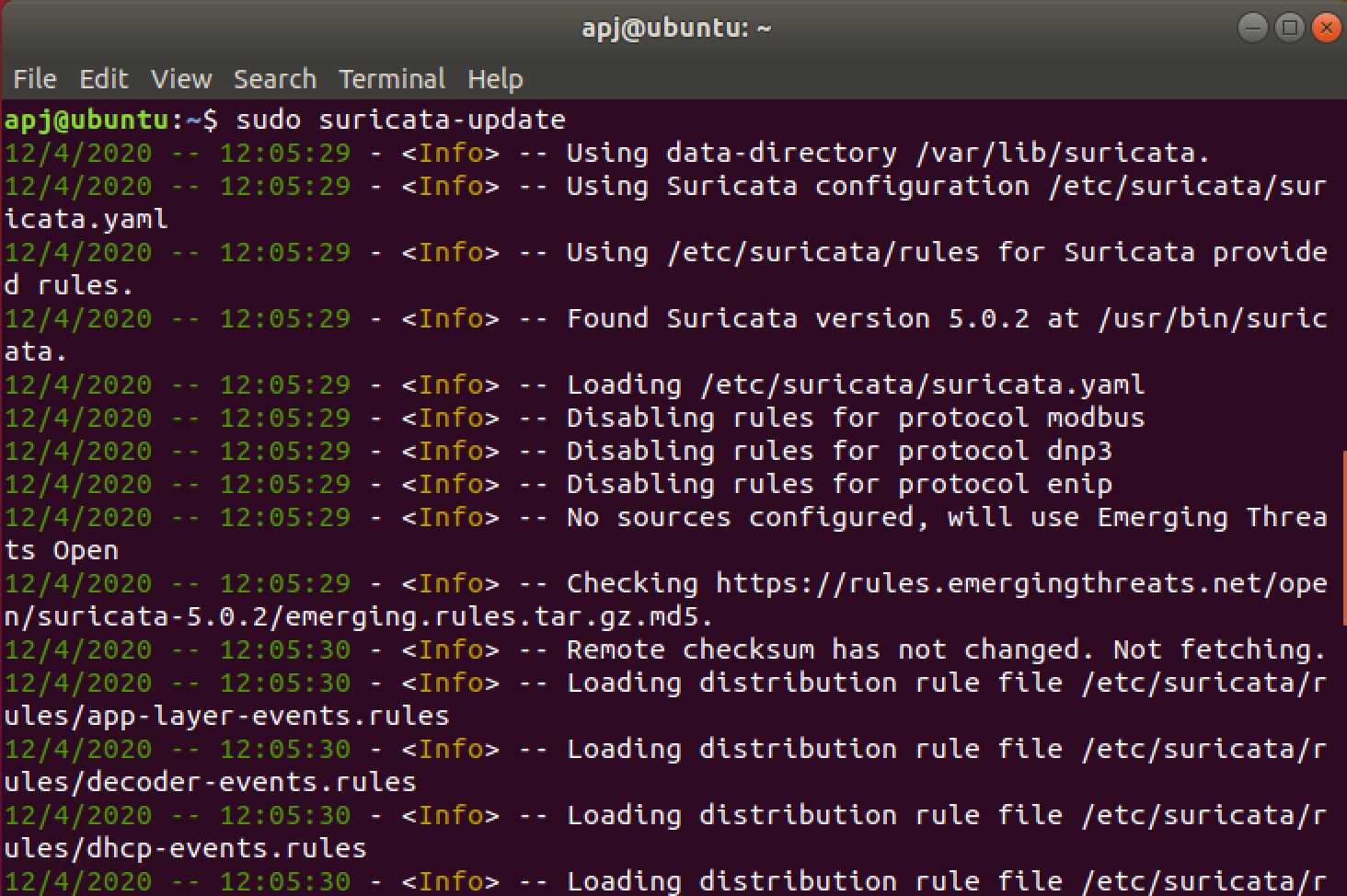
Once this is done rules are updated within Suricata with the command:
suricata-update
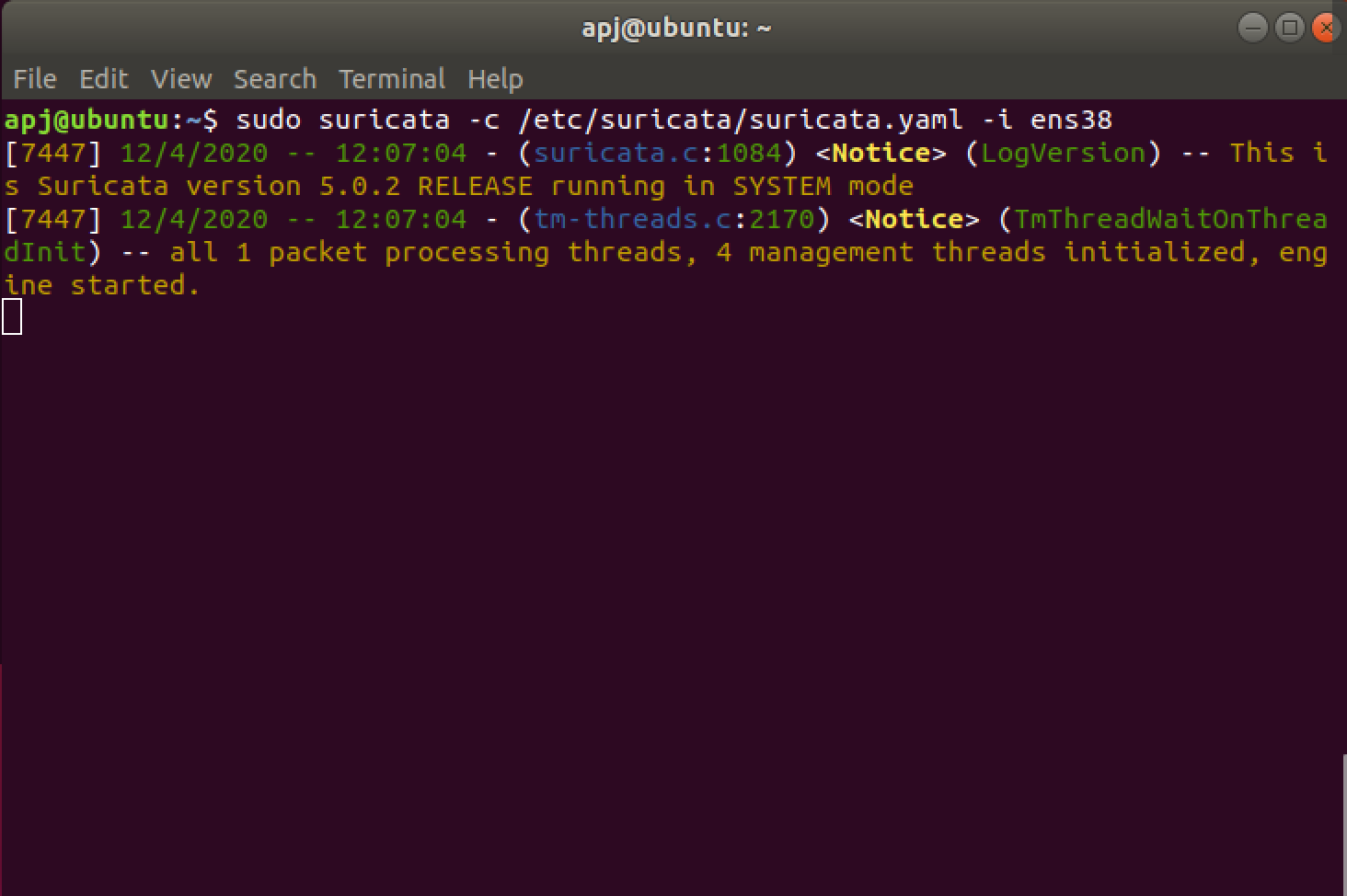
Now the IDS is executed with the following command:
suricata -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml -i ens33
NOTE: The interface on which the IDS should be listening is provided with -i flag. Also no warning or error should come up regarding the rules while running the IDS.
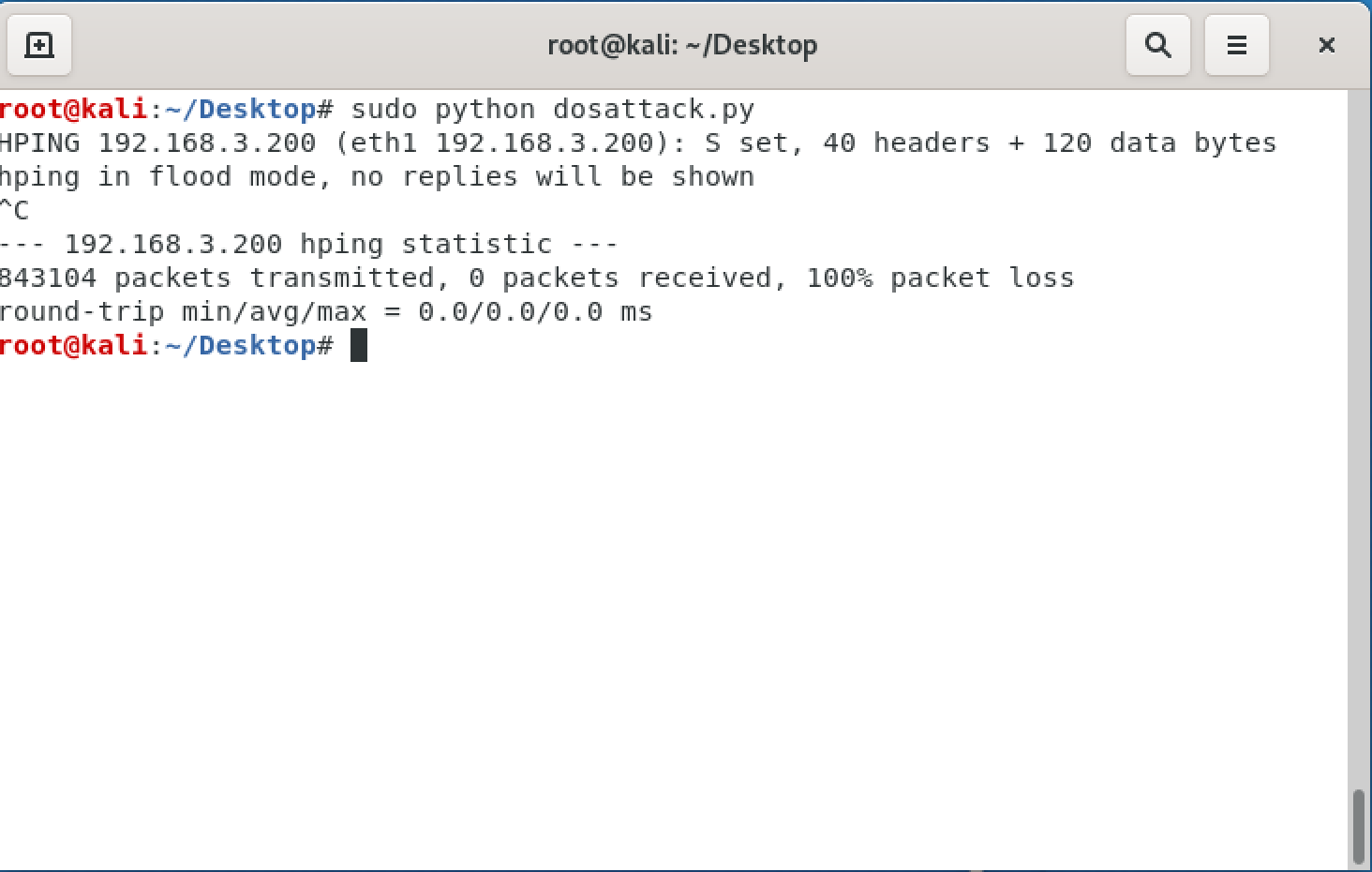
Now the DOS attack is conducted from the Kali Vm using the python script dos_attack.py which utilizes the hping3 network utlity to generate and flood TCP SYN packet to the target IP address (the IP address can be updated by changing the file contents).
python dos_attack.py
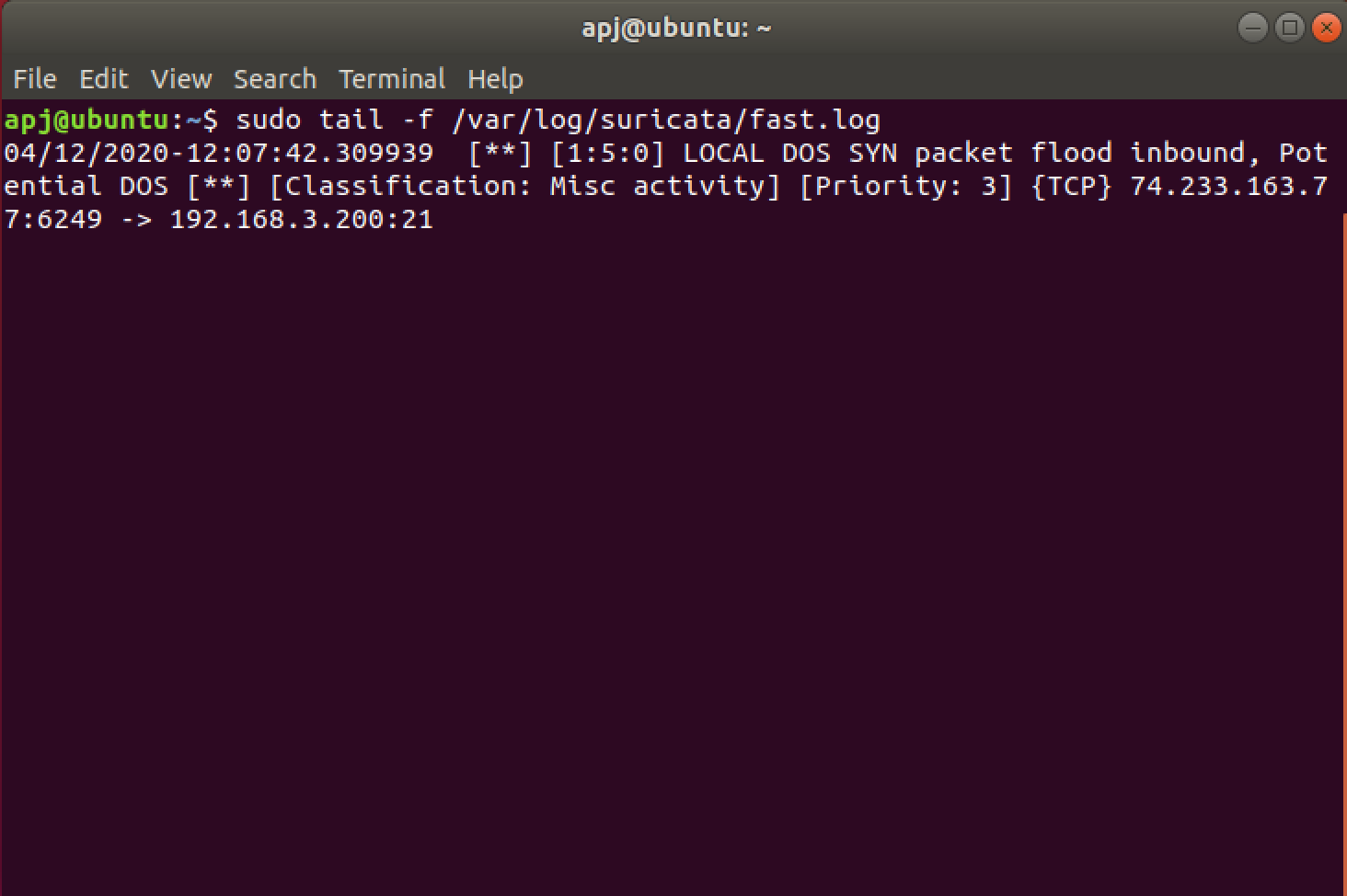
Now the IDS rules get triggered and suricata alerts that there is a possible DOS attack, this can be seen in the logs with the command:
sudo tail -f /var/log/suricata/fast.log
Hence suricata acted as an IDS and detected the DoS attack.