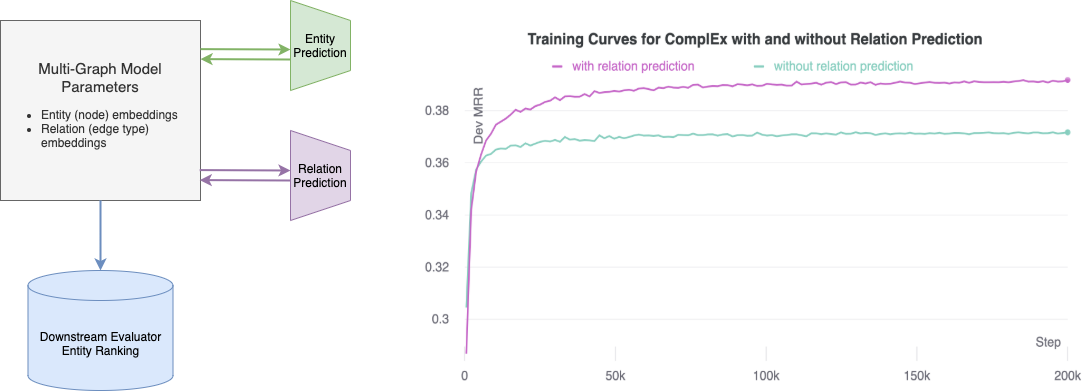
This repo contains the code accompanying the paper: “Relation Prediction as an Auxiliary Training Objective for Improving Multi-Relational Graph Representations”. We found that incorporating relation prediction into the 1vsAll objective yields a new self-supervised training objective for knowledge base completion (KBC), which results in significant performance improvement (up to 9.9% in Hits@1) by adding as little as 3–10 lines of code. Unleash the true power of your KBC models with the relation prediction objective!
The codebase also comes with SoTA results on several KBC datasets. Echoing previous research, we find that traditional factorisation-based models, e.g. ComplEx, DistMult and RESCAL, can outperform more recently proposed models when trained appropraitely. For most cases, we find the 1vsAll + Relation Prediction objective to be very effective and require less tweaking than more sophisticated architectures.
- 01/02/2022 Pretrained ComplEx embeddings on obgl-biokg/ogbl-wikikg2 are released. Check out them here
- 16/12/2021 Pretrained ComplEx embeddings on FB15K-237/WN18RR/CoDEx-M/CoDEx-S are released. Check out them here
- 01/12/2021 Hyper-parameters on CoDEx, ogbl-biokg and ogbl-wikikgv2 are released here
We attempt to include as many results as possible for recent knowledge graph completion datasets and release the hyper-parameters to foster easy reproduction. Feel free to create an issue if you want to suggest additional datasets for us to include.
Currently, we have results on the OGB link property prediction dataset ogbl-biokg, ogbl-wikikg2, codex, Aristo-v4, FB15K237, and WN18RR. All training was done on a single 16GB GPU except for ogbl-wikikg2 which was run on a 32GB GPU.
| Model | Params | Using RP? | MRR | Hits@1 | Hits@3 | Hits@10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ComplEx (50dim)1 | 250M | No | 0.3804 | - | - | - |
| ComplEx (250dim)1 | 1B | No | 0.4027 | - | - | - |
| ComplEx (25dim, ours) | 125M | No | 0.5161 | 0.4576 | 0.5310 | 0.6324 |
| ComplEx (25dim, ours) | 125M | Yes | 0.5192 | 0.4540 | 0.5394 | 0.6483 |
| ComplEx (50dim, ours) | 250M | No | 0.6193 | 0.5503 | 0.6468 | 0.7589 |
| ComplEx (50dim, ours) | 250M | Yes | 0.6392 | 0.5684 | 0.6686 | 0.7822 |
| ComplEx (100dim, ours) | 500M | No | 0.6458 | 0.5750 | 0.6761 | 0.7896 |
| ComplEx (100dim, ours) | 500M | Yes | 0.6509 | 0.5814 | 0.6800 | 0.7923 |
Note that the training of 50/100 dim takes about 3 days and that additional training time will likely lead to better results. We currently use only one 32GB GPU. Acceleration on multiple GPUs will be considered in the future.
| Model | Params | Using RP? | MRR | Hits@1 | Hits@3 | Hits@10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ComplEx 2 | 188M | No | 0.8095 | - | - | - |
| ComplEx (ours) | 188M | No | 0.8482 | 0.7887 | 0.8913 | 0.9536 |
| ComplEx (ours) | 188M | Yes | 0.8494 | 0.7915 | 0.8902 | 0.9540 |
| Model | Using RP? | MRR | Hits@1 | Hits@3 | Hits@10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ComplEx 3 | No | 0.465 | 0.372 | 0.504 | 0.646 |
| ComplEx (1000dim, ours) | No | 0.472 | 0.378 | 0.508 | 0.658 |
| ComplEx (1000dim, ours) | Yes | 0.473 | 0.375 | 0.514 | 0.663 |
| Model | Using RP? | MRR | Hits@1 | Hits@3 | Hits@10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ComplEx 3 | No | 0.337 | 0.262 | 0.370 | 0.476 |
| ComplEx (1000dim, ours) | No | 0.351 | 0.276 | 0.385 | 0.492 |
| ComplEx (1000dim, ours) | Yes | 0.352 | 0.277 | 0.386 | 0.490 |
| Model | Using RP? | MRR | Hits@1 | Hits@3 | Hits@10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ComplEx 3 | No | 0.294 | 0.237 | 0.318 | 0.400 |
| ComplEx (1000dim, ours) | No | 0.342 | 0.275 | 0.374 | 0.470 |
| ComplEx (1000dim, ours) | Yes | 0.345 | 0.277 | 0.377 | 0.473 |
| Model | Using RP? | MRR | Hits@1 | Hits@3 | Hits@10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ComplEx | No | 0.487 | 0.441 | 0.501 | 0.580 |
| ComplEx | Yes | 0.488 | 0.443 | 0.505 | 0.578 |
| Model | Using RP? | MRR | Hits@1 | Hits@3 | Hits@10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ComplEx | No | 0.366 | 0.271 | 0.401 | 0.557 |
| ComplEx | Yes | 0.388 | 0.298 | 0.425 | 0.568 |
| Model | Using RP? | MRR | Hits@1 | Hits@3 | Hits@10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ComplEx | No | 0.301 | 0.232 | 0.324 | 0.438 |
| ComplEx | Yes | 0.311 | 0.240 | 0.336 | 0.447 |
| Dataset | #Pred (including reciprocal predicates) | #Ent | Model | Hyper-parameters | Download Link | #Params | File Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB15K-237 | 474 | 14,541 | ComplEx(1000dim, ours) | HPs | Link | 30M | 115MB |
| WN18RR | 22 | 40,943 | ComplEx(1000dim, ours) | HPs | Link | 82M | 313M |
| CoDEx-M | 102 | 17,050 | ComplEx(1000dim, ours) | HPs | Link | 34M | 131M |
| CoDEx-S | 84 | 2,034 | ComplEx(1000dim, ours) | HPs | Link | 4M | 17M |
| ogbl-biokg | 102 | 93773 | ComplEx(1000dim, ours) | HPs | Link | 188M | 717M |
| ogbl-wikikg2 | 1070 | 2500604 | ComplEx(50dim, ours) | HPs | Link | 250M | 955M |
Note that we also learn the embeddings for reciprocal predicates as they are reported to be helpful (Dettmers et al., 2018, Lacroix et al., 2018).
Edit preprocess_datasets.py and specify the dataset you want to run on, either
datasets = ['ogbl-wikikg2']
or
datasets = ['ogbl-biokg']
Then run preprocess_datasets.py as follows
mkdir data/
python preprocess_datasets.py
After preprocessing is complete, a model can be trained by running main.py. For example, to train ComplEx on ogbl-biokg, use the following command
python main.py --dataset ogbl-biokg --model ComplEx --score_rel True --rank 1000 --learning_rate 1e-1 --batch_size 500 --optimizer Adagrad --regularizer N3 --lmbda 0.01 --w_rel 0.25 --valid 1
and to train a ComplEx on ogbl-wikikg2, use the following command on a GPU with 32GB memory
python main.py --dataset ogbl-wikikg2 --model ComplEx --score_rel True --rank 50 --learning_rate 1e-1 --batch_size 250 --optimizer Adagrad --regularizer N3 --lmbda 0.1 --w_rel 0.125 --valid 1
You should obtain training curves similar as the figures below.
| ogbl-biokg | ogbl-wikikg2 |
|---|---|
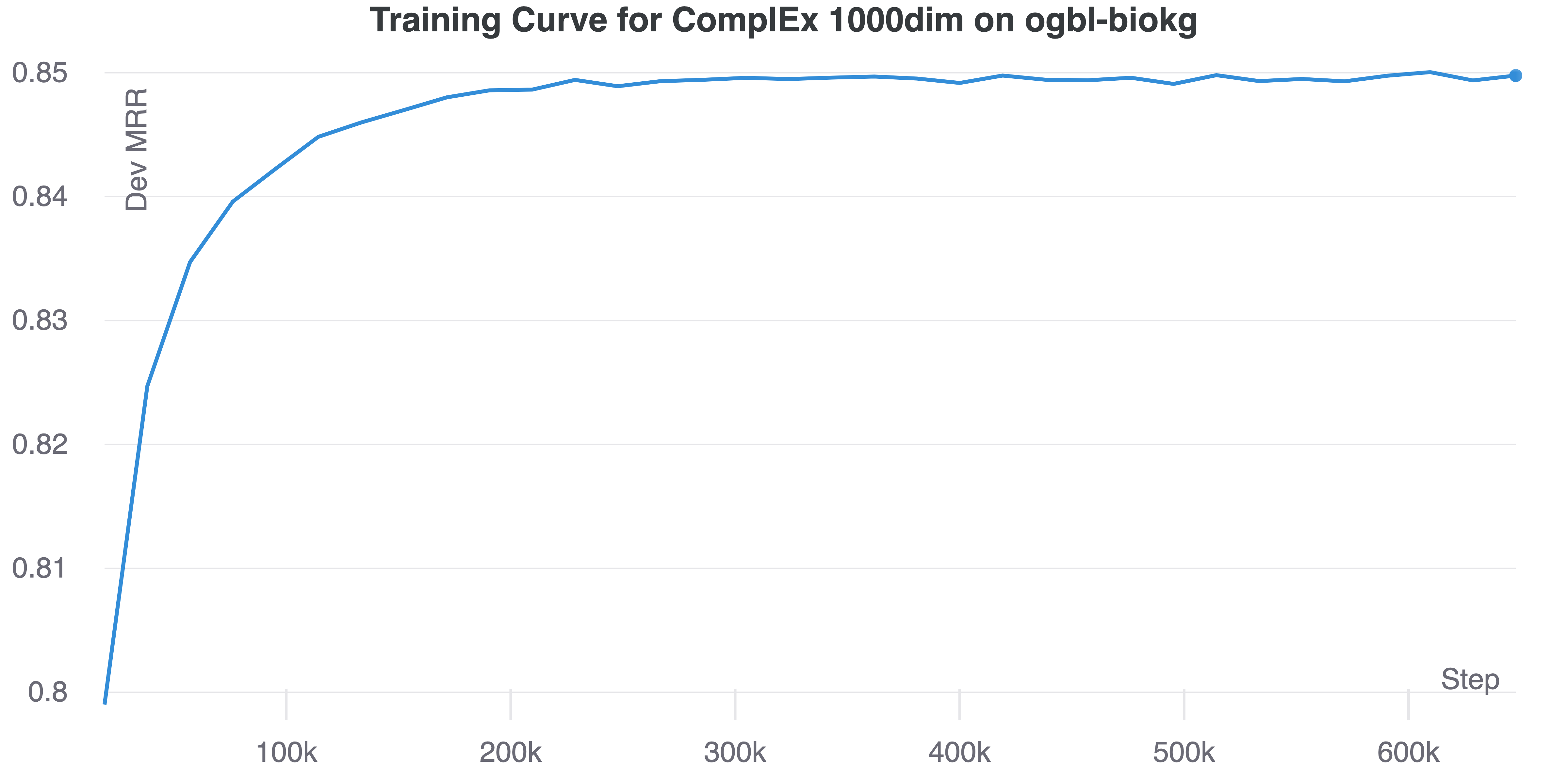 |
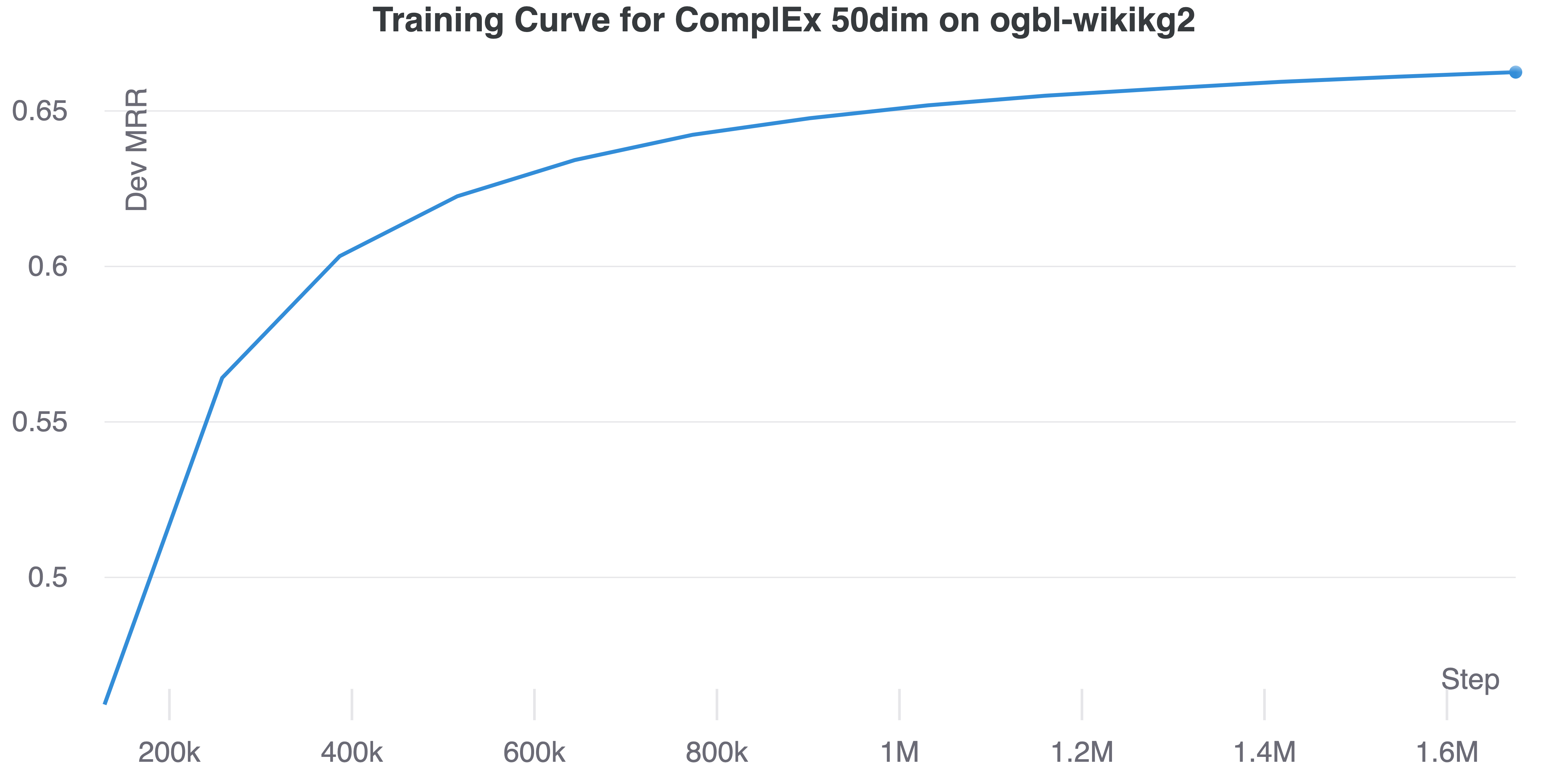 |
- Download the datasets and place them under
src_data. - Name the file containing training triplets as
train, validation triplets asvalidand test triplets astest. The folder should look like this
src_data/FB15K-237/train # Tab separated file, each row should be like `head relation tail`
src_data/FB15K-237/valid # Tab separated file, each row should be like `head relation tail`
src_data/FB15K-237/test # Tab separated file, each row should be like `head relation tail`
- After downloading the datasets, the preprocessing is quick and can be completed within a few minutes. First, edit
preprocess_datasets.pyand specify the dataset you want to run on, e.g.
datasets = ['custom_graph']
then run
mkdir data/
python preprocess_datasets.py
You can download together UMLS, Nations, Kinship, FB15K-237, WN18RR from here and aristo-v4 from here. You can also download some datasets separately on WN18RR and FB15K-237.
Use the option score_rel to enable the auxiliary relation prediction objective. Use the option w_rel to set the weight of the relation prediction objective.
For example, the following command trains a ComplEx model with with the auxiliary relation prediction objective on FB15K-237
python main.py --dataset FB15K-237 --score_rel True --model ComplEx --rank 1000 --learning_rate 0.1 --batch_size 1000 --lmbda 0.05 --w_rel 4 --max_epochs 100
And the following command trains a ComplEx model without the auxiliary relation prediction objective on FB15K-237
python main.py --dataset FB15K-237 --score_rel False --model ComplEx --rank 1000 --learning_rate 0.1 --batch_size 1000 --lmbda 0.05 --w_rel 4 --max_epochs 100
- pytorch
- wandb
This repo is based on the repo kbc, which provides efficient implementations of 1vsAll for ComplEx and CP. Our repo also includes implementations for other models: TransE, RESCAL, and TuckER.
If you find this repo useful, please cite us
@inproceedings{
chen2021relation,
title={Relation Prediction as an Auxiliary Training Objective for Improving Multi-Relational Graph Representations},
author={Yihong Chen and Pasquale Minervini and Sebastian Riedel and Pontus Stenetorp},
booktitle={3rd Conference on Automated Knowledge Base Construction},
year={2021},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=Qa3uS3H7-Le}
}
This repo is CC-BY-NC licensed, as found in the LICENSE file.
Footnotes
-
The results are taken from OGB Link Property Prediction Leaderboard on ogbl-wikikg2. ↩ ↩2
-
The results are taken from OGB Link Property Prediction Leaderboard on ogbl-biokg. ↩
-
The results are taken from the awesome CoDEx repo. ↩ ↩2 ↩3