Graphs
Definition
-
A graph can be defined as group of vertices and edges that are used to connect these vertices. A graph can be seen as a cyclic tree, where the vertices (Nodes) maintain any complex relationship among them instead of having parent child relationship.
-
A graph G can be defined as an ordered set G(V, E) where V(G) represents the set of vertices and E(G) represents the set of edges which are used to connect these vertices.
-
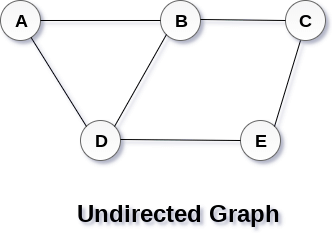
A Graph G(V, E) with 5 vertices (A, B, C, D, E) and six edges ((A,B), (B,C), (C,E), (E,D), (D,B), (D,A)) is shown in the following figure.
Directed and Undirected Graph
-
In an undirected graph, edges are not associated with the directions with them. An undirected graph is shown in the above figure since its edges are not attached with any of the directions. If an edge exists between vertex A and B then the vertices can be traversed from B to A as well as A to B.
-
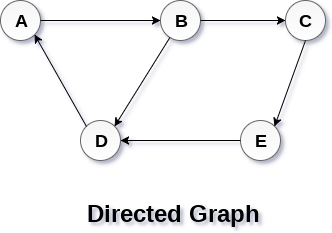
In a directed graph, edges form an ordered pair. Edges represent a specific path from some vertex A to another vertex B. Node A is called initial node while node B is called terminal node.
Terminologies
-
Path
A path can be defined as the sequence of nodes that are followed in order to reach some terminal node V from the initial node U without repeating any nodes.
-
Cycle
A cycle can be defined as the path which has no repeated edges or vertices except the first and last vertices.
-
Walk
Start from vertex, end with a vertex. Edges should be alternate and no repetition. Open walk start and end with different vertex. Closed walk start and end with same vertex.
-
Degree
A degree of a node is the number of edges that are connected with that node. A node with degree 0 is called as isolated node.