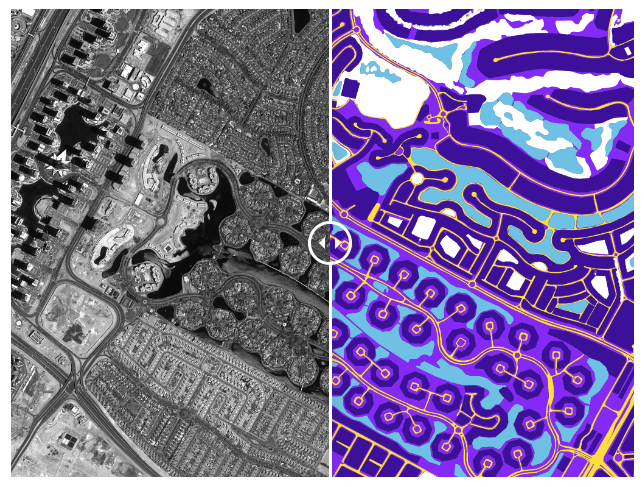
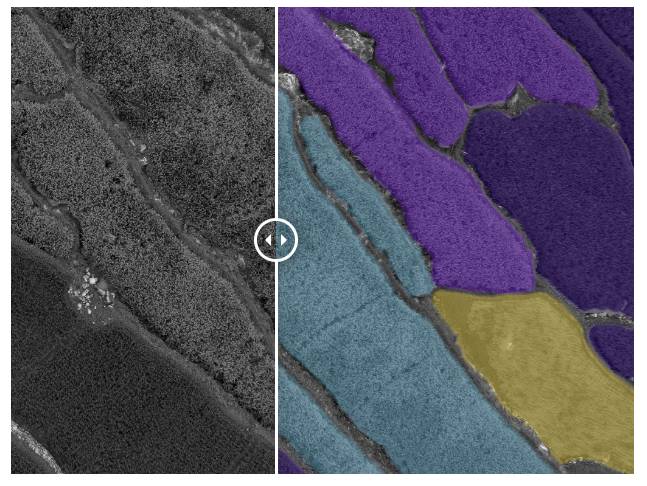
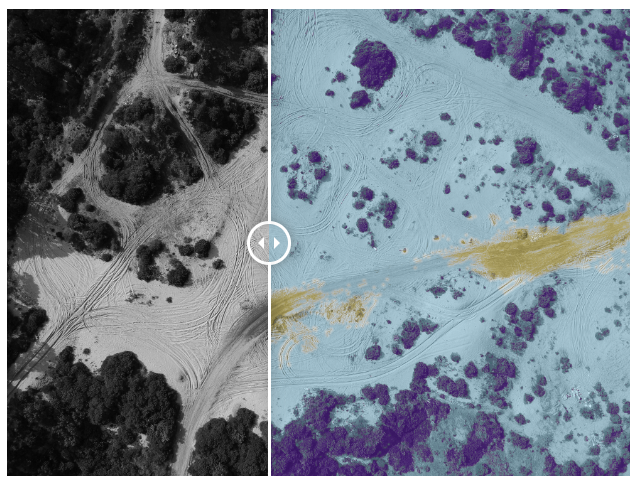
👉 Satellite imagery : Satellite images of entire cities can be segmented with pixel-perfect accuracy for detecting buildings, roads, water bodies, and other land. Other use cases include cloud detection, water bodies monitoring, as well as tracking changes in settlements and land use over time.
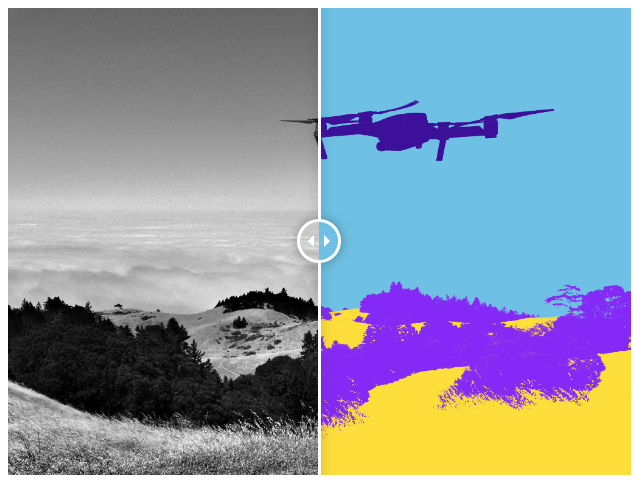
👉 Drone imagery : For drones, semantic segmentation can be used for training models for autonomous flight and safe landing. In addition to perception of the environment, drones can be trained to detect and recognize other obstacles and objects of interest, such as other drones.
👉 Inspection: Aerial images can also be labelled with labels such as polygons and bounding boxes. These labels can be used by AI models to inspect the environment and identify or count certain objects, such as houses, trees, vehicles, cattle, electricity poles, and transmission lines.
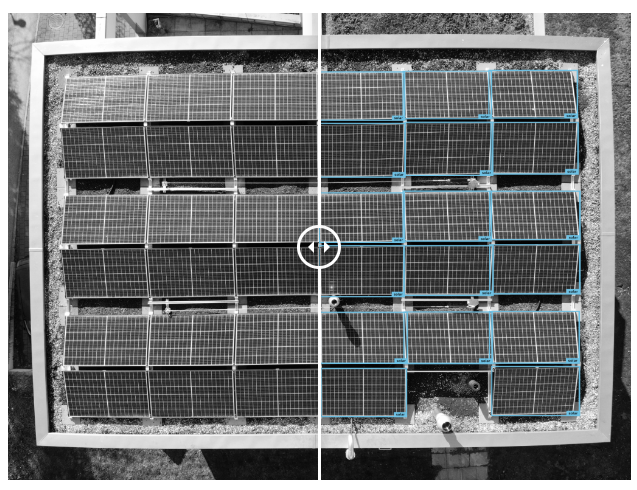
👉 Solar panels : Creating AI models that can detect solar panels can be used for large-scale analysis of solar parks. In addition, when applied on infrared imagery, labeling can be used as a time-efficient way to check the condition of solar panels and detect anomalies (short circuits, open circuits, broken glass, and dirt).
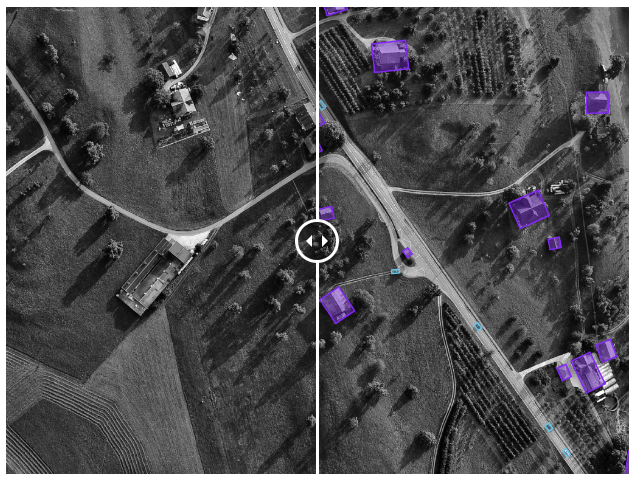
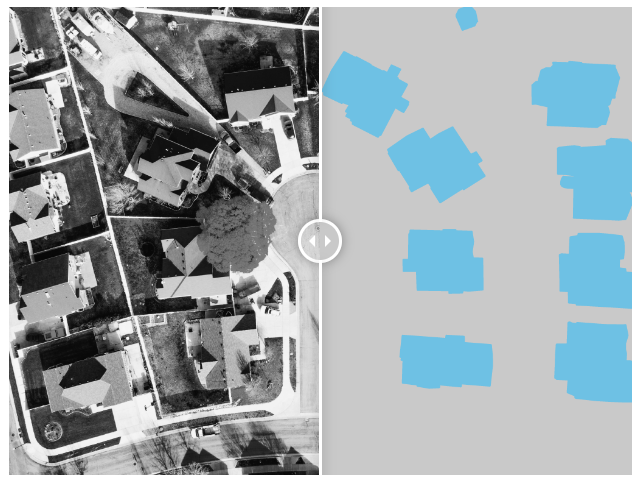
👉 Building footprint: The automatic extraction of building footprints from satellite imagery is vital for a variety of uses such as for city planning and logistical purposes. Precise building polygons on 2D images as well as 3D point cloud annotation of buildings can be used to verify outdated city maps.
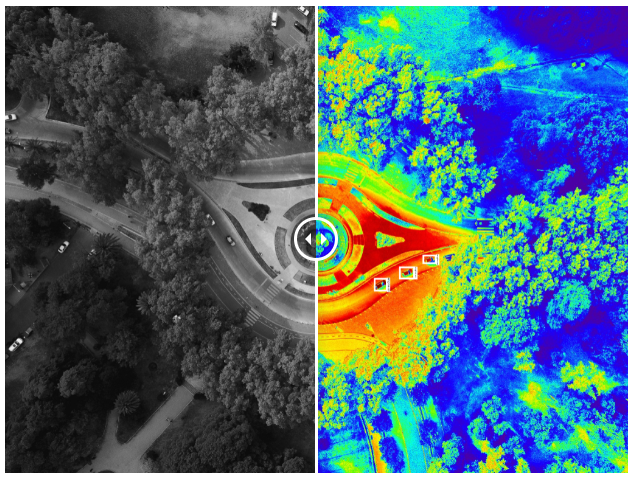
👉 Infrared imagery : By coupling RGB imagery with infrared channels, labeling can be performed to enhance standard detection models in a variety of settings, including night-time imagery, small object detection at sea or in complex settings, or better classification of crops based on their infrared profile.
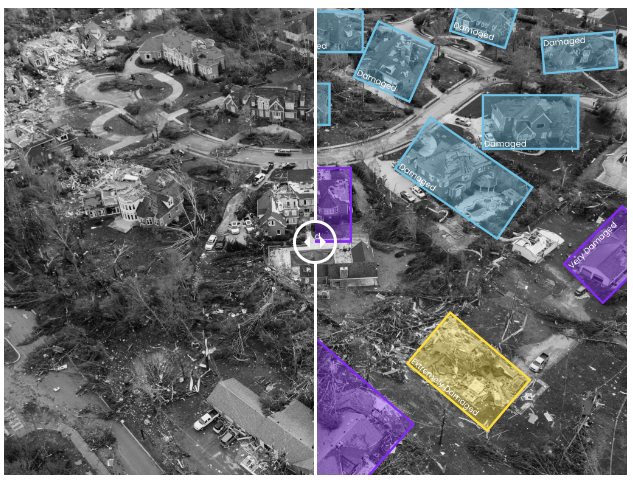
👉 Natural disasters : Labeled datasets can also be used to train AI models for smart disaster management. These models can be used to efficiently assess the extent of the damage without having to manually assess each incidence of damage, as well as identifying aid, rescue, and evacuation routes.
👉 Autonomous vehicles : With the future of the automotive industry moving towards autonomous vehicles, high-quality datasets are vital in creating safe and accurate models. Bounding boxes, polygons, full semantic segmentation, and cuboids drawn on 2D images are all techniques that can be used here.
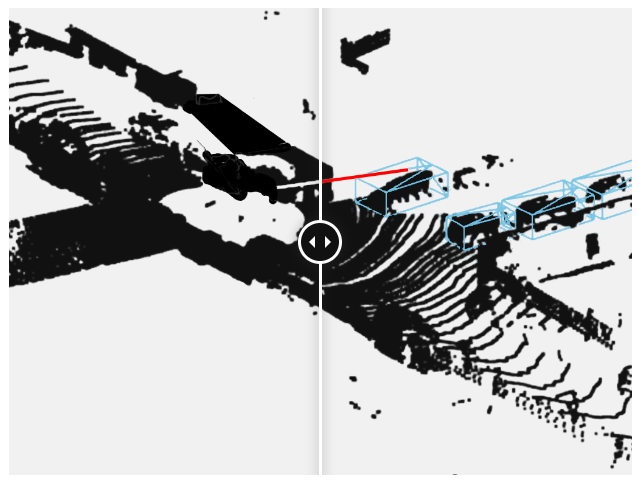
👉 LiDAR and sensor fusion : By labeling LIDAR point cloud data coupled with GPS and visual data, models can be trained for the perception of objects and events in three dimensions over time across different sensors. 3D cuboids and even voxel segmentation is used for these use cases.
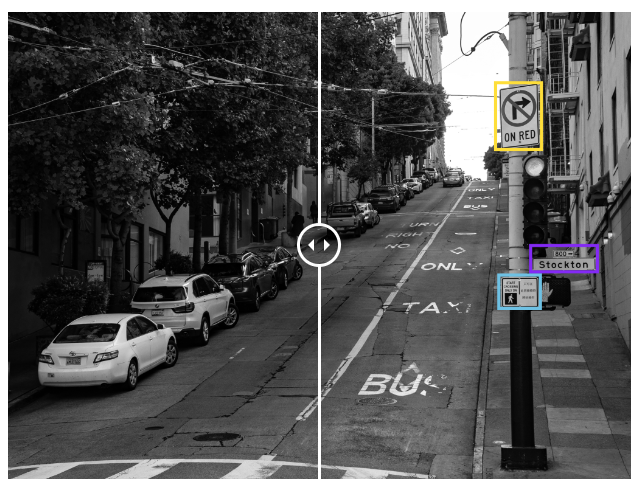
👉 Plate detection : Automatic registration plate detection and OCR can be critical for traffic monitoring and law enforcement purposes. Additional numbers such as USDOT codes on trucks and lorries can be detected for the efficient management of warehouses and parkings.
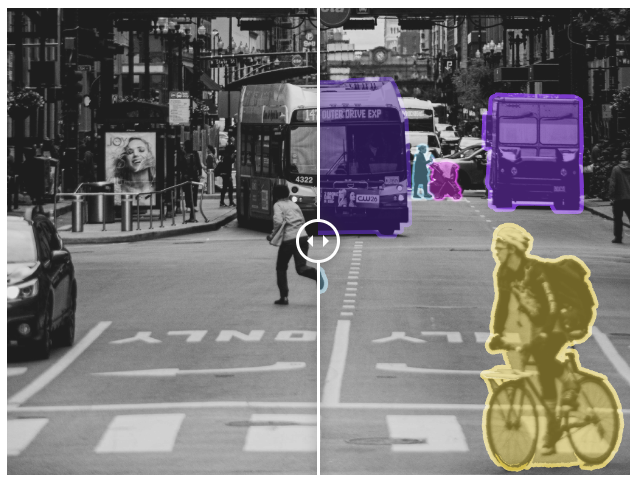
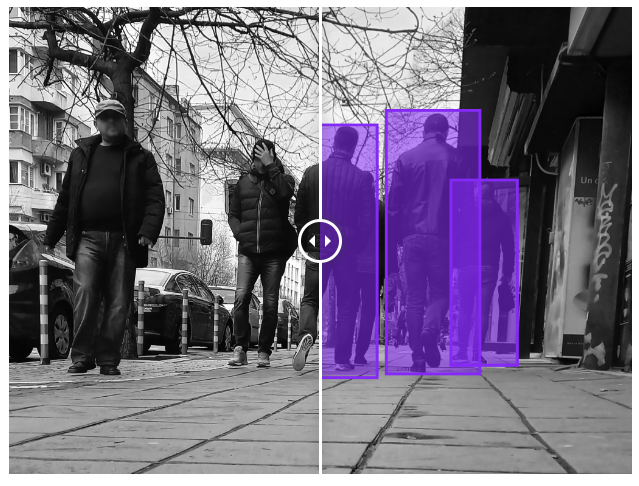
👉 Traffic monitoring : Being able to count, classify, and record vehicles is very important for a variety of uses such as traffic optimization and city planning. We are able to record rare events on hours of footage (jaywalking, traffic violations) across multiple cameras, in addition to vehicle recognition and counting.
👉 Damage detection : By coupling RGB imagery with infrared channels, labeling can be performed to enhance standard detection models in a variety of settings, including night-time imagery, small object detection at sea or in complex settings, or better classification of crops based on their infrared profile.
👉 Delivery robots : With home delivery becoming as common as ever, delivery robots could save time and money. However, as they will be navigating sidewalks and streets, it is important to label datasets which are built exclusively for their height and point of view.
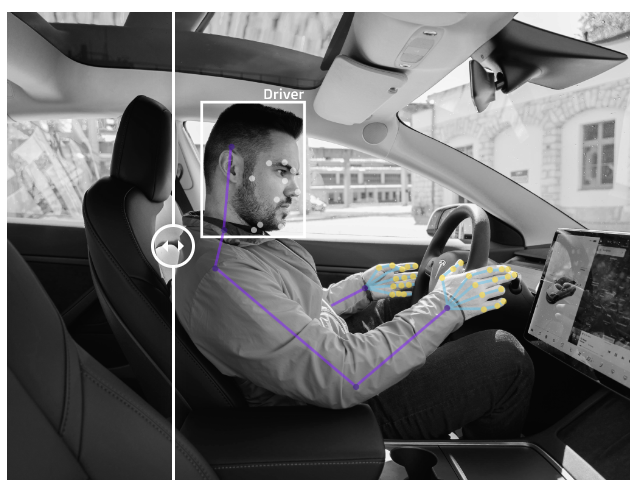
👉 In-cabin monitoring : Labeling can be performed on in-cabin footage in order to ensure the safety of the driver and those around him or her. This includes pose detection, gaze tracking, weariness and sleepiness detection, as well as passenger and driver action monitoring in order to prevent crime.
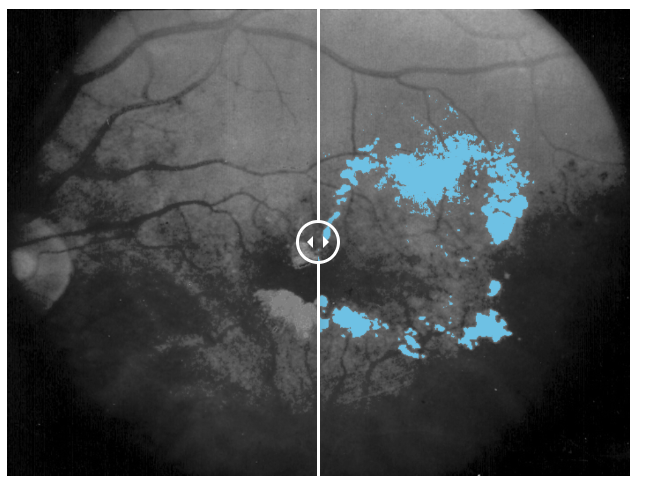
👉 Ophthalmology: Precisely annotated data can be used to identify and highlight anomalies in images of eyes that a professional can then use to diagnose common diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration, cataract, retinal vein occlusion, and glaucoma.
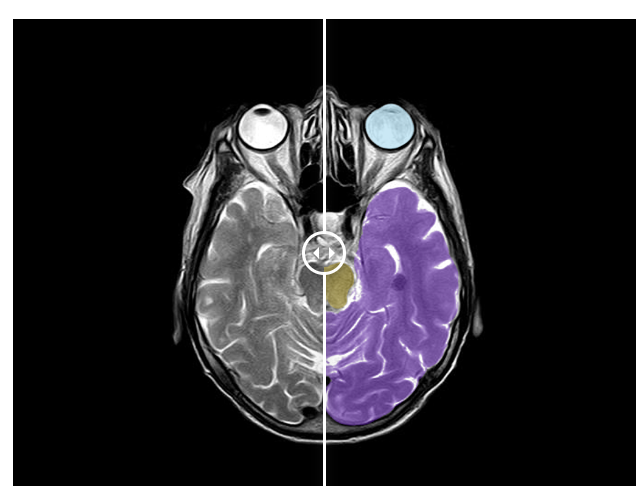
👉 Radiology : Computer vision can save radiologists’ time and make the entire process of diagnosing conditions more efficient. Through precise 2D annotation of DICOM imagery or 3D annotation of CT and MRI scans using advanced tools, our teams can help to segment and detect any organ or anomaly.
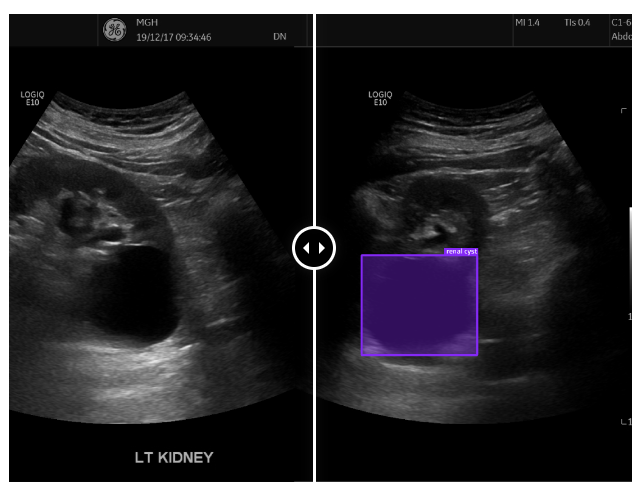
👉 Ultrasound : Ultrasound video can be annotated with bounding boxes, polygons, or full segmentation, in order to train models for locating the correct plane, identifying organs, calculating many of the standard measurements, and detecting tumors or lesions.
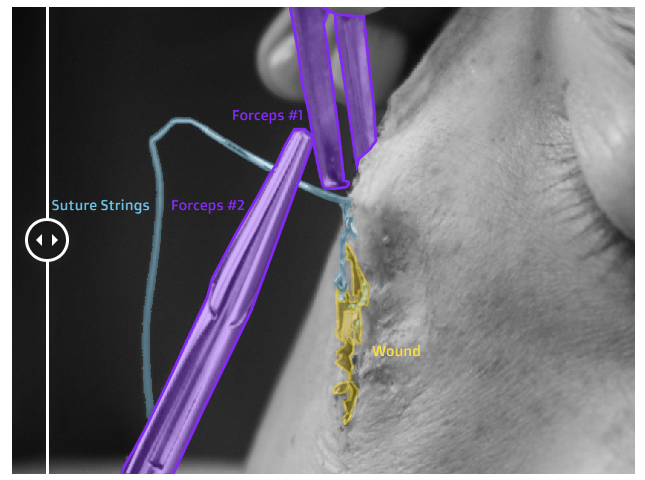
👉 Robotic surgery : In order to make robotic surgery safer and more efficient, AI models can be trained on images and videos with labels which identify the types of tools used, either with polygons or keypoints, as well as track their movement using interpolation across frames.
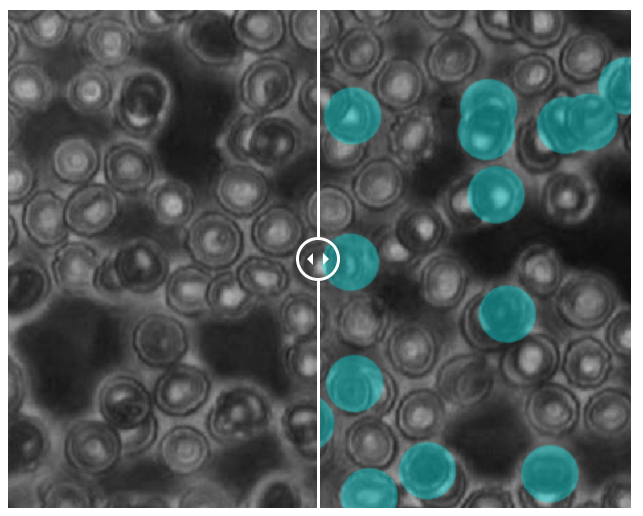
👉 Pathology : The analysis of bodily fluids like blood, or tissue samples from biopsies, can be automated at scale using labeled data. We can provide not only precise segmentation of different cells but also batch classification based on size, anomaly, structure, and other parameters.
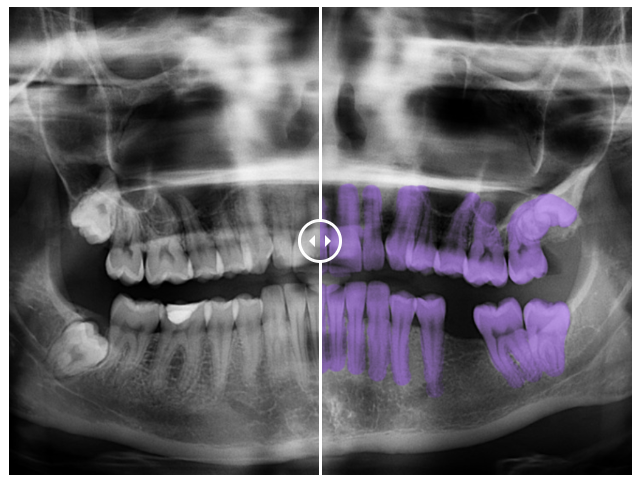
👉 Dentistry : From teeth, cavity, and gum segmentation on Xrays and dental surgery videos, to full 3D maxillofacial segmentation of different bone structures, our expert annotators can prepare any type of data which is needed for the purposes of AI applied in dentistry.
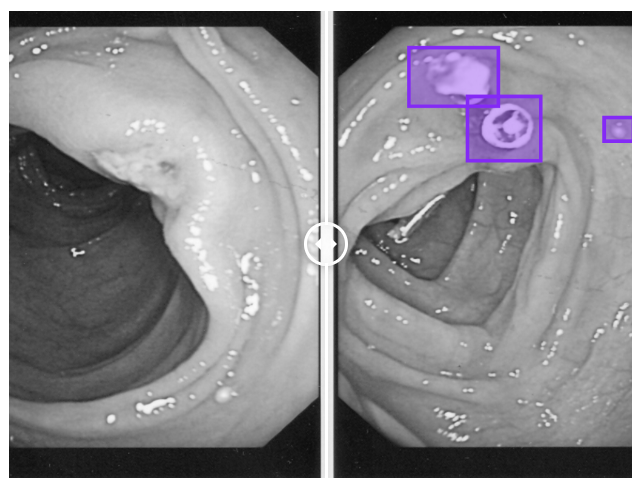
👉 Colonoscopy : Videos from colonoscopies and endoscopies can be analyzed by AI models trained on labeled footage to classify ulcerations, polyps, and lesions. Different actions performed during the procedures, such as the removal of polyps, or the removal of tissue for biopsy, can also be detected.
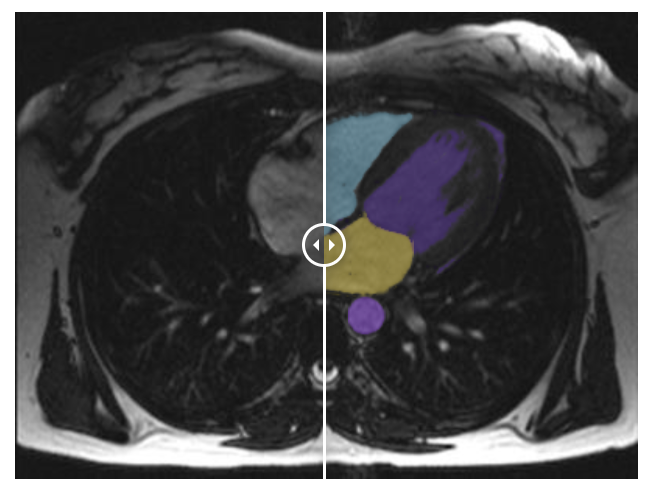
👉 Cardiology : Computer vision models in cardiology can be trained on segmented MRI, CT and ultrasounds of organs and tissues, allowing for the analysis of the cardiovascular structure and function. They often are used to analyze the ventricles and detect heart problems, irregularities, and anomalies.
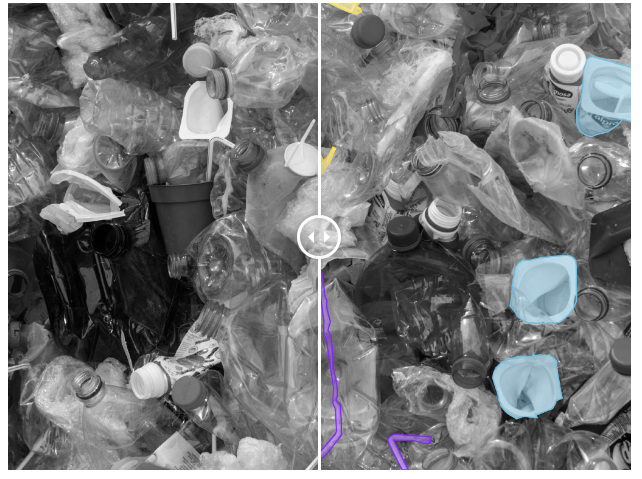
👉 Recycling : By using polygons, segmentation, or bounding boxes, datasets can be labeled to power computer vision models with a huge environmental impact. Labels can serve to recognise, separate, and sort recyclables, be it generic plastic, metal and paper, or complex medical or food waste.
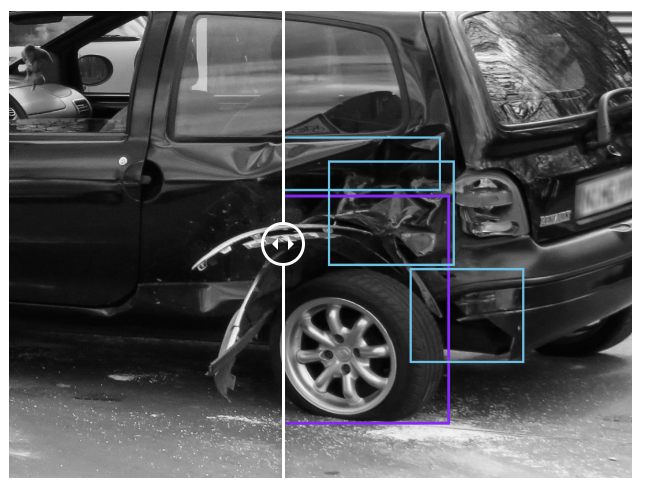
👉 Quality inspection : Quality inspection is a hard model to solve with deep learning because of the scarcity of anomaly examples in the training data. We are able to use special tools for anomaly detections so as to label and extract examples with damages or deformations.
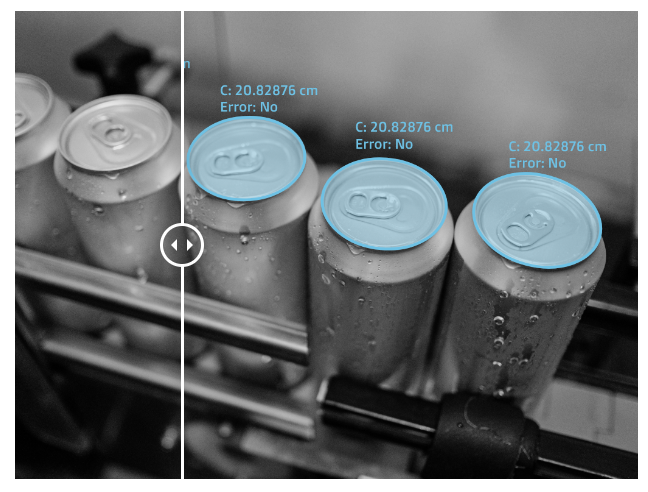
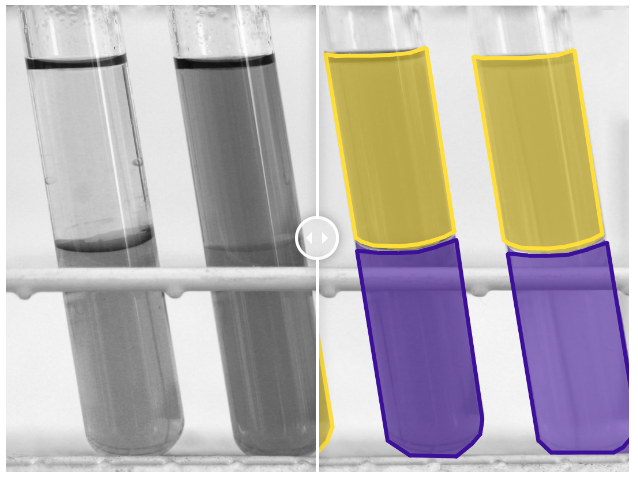
👉 Liquid estimation : Whether you are dealing with chemicals, petrol, bodily fluids or other types of liquids, AI models can be trained to perform automatic volume estimations after a centrifuge. This requires labeling the surfaces and phase boundaries of each liquid using a polyline or a polygon.
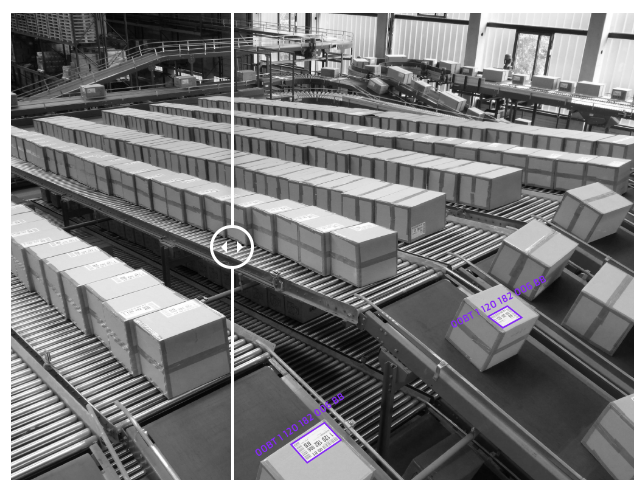
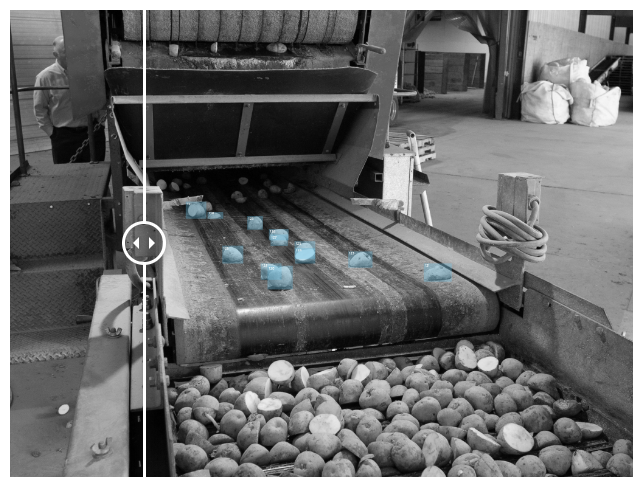
👉 Conveyor belt analysis : Through computer vision models, data from conveyor belts can be analysed for a variety of purposes. Through either image or video annotation with object tracking, annotated data can be used to train models for counting the number of products, classifying their type, or detecting fallen or stuck ones.
👉 Logistics: Logistics and warehouse management can be streamlined through AI in several different ways: automatic object location tracking, barcode and label detection and OCR, picking and sorting of products… and all of this can be achieved through correctly labeled data.
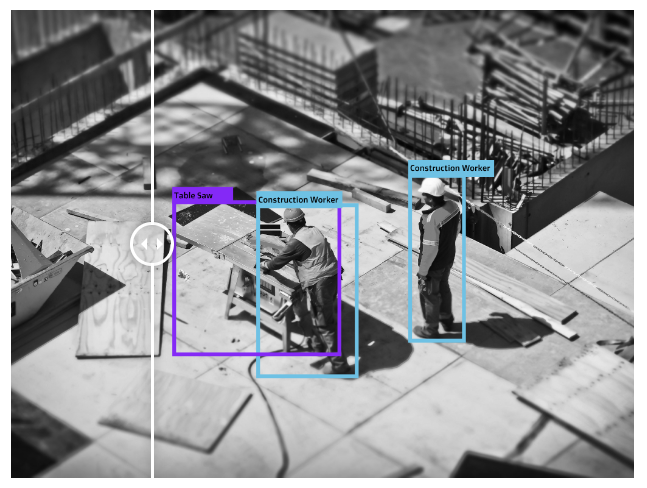
👉 Construction : In construction, datasets can be labeled to track worker movement and activity on sites, to monitor progress, as well as for highlighting potentially dangerous situations. These may be simple bounding boxes but they will require going through a very large amount of data.
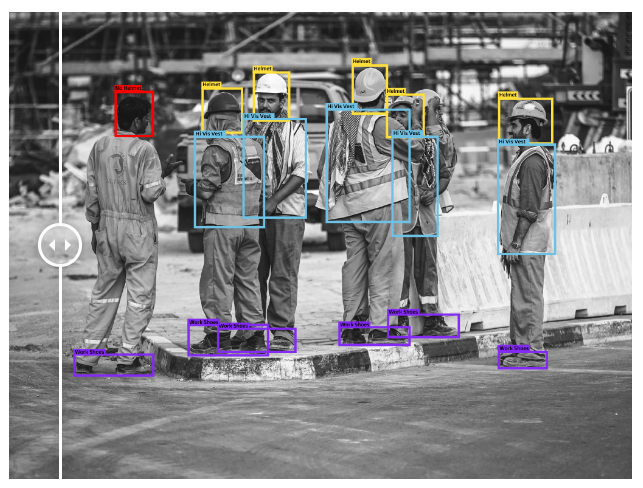
👉 PPE detection: Wearing personal protective equipment at work, especially at construction sites or in hospitals, is crucial for safety. The monitoring process can be automated through bounding box detection and classification not only of different types of equipment but also of incorrectly worn items.
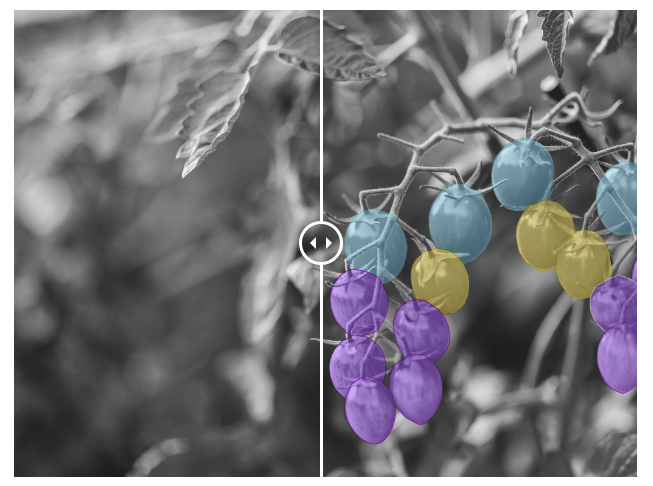
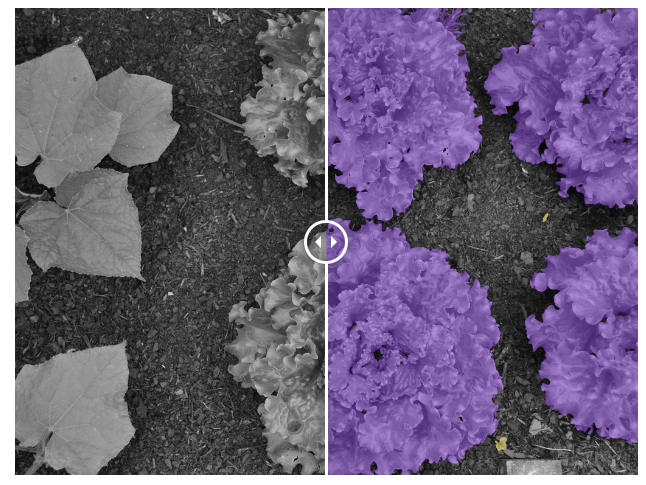
👉 Crop detection : Fields in different geographies might vary greatly and a lot of training data is needed in order to detect and classify crops correctly. In addition to bounding box and polygon labeling, instance segmentation can be applied in order to count exactly the number of leaves or fruits of each plan
👉 Weed detection : Detecting weeds in a precise way is necessary in order to optimize the use of chemicals such as herbicides and to avoid affecting crops. Weeds can be detected by using bounding boxes or, for even better precision, polygons or semantic/instance segmentation.
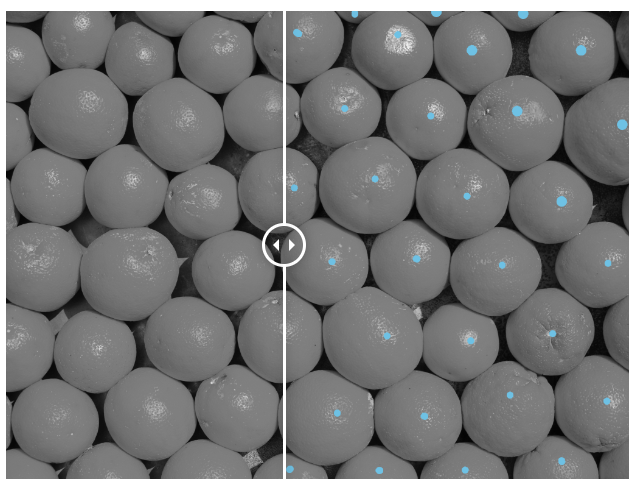
👉 Fruit counting: Using keypoints or bounding boxes, computer vision models can be trained on datasets of produce where each instance/fruit is labelled. By using this data, fruit counting and classification can be done automatically at scale.
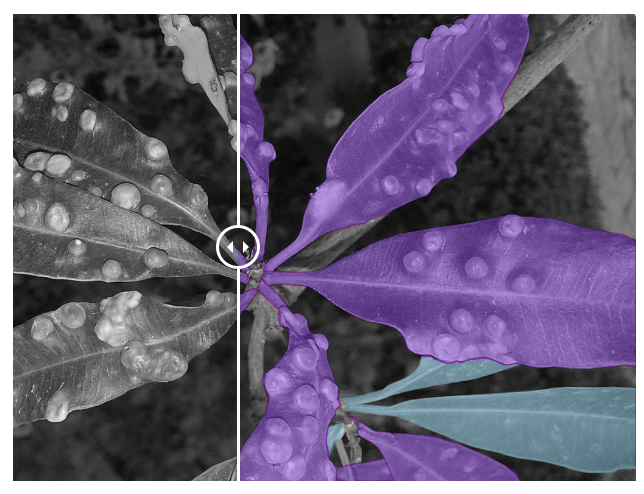
👉 Health monitoring: By using labeled data, machine learning models can be trained to detect and even diagnose a diseased plant at scale. This can be done in various ways such as labeling the diseased plants with bounding boxes or polygons or segmenting the diseased parts and the healthy parts separately.
👉 Growth analysis: Precision agriculture needs a lot of data about plant growth stage and yield in order to apply water and fertilizer in a targeted way. This requires the labeling of each crop with information about its growth stage and status (e.g. water stress, nitrogen stress, etc).
👉 Soil analysis: With labeled data, often aerial and sometimes even satellite images, computer vision models can be trained to classify the soil in an area. This can be useful for example in searching for fertile land, or tracking the effects of deforestation and erosion.
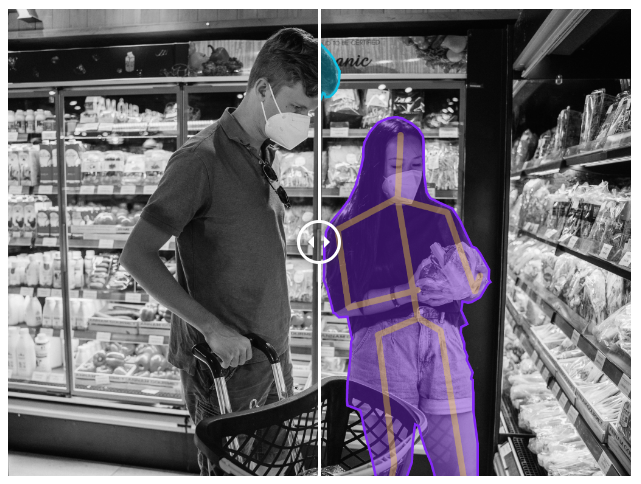
👉 Shopper tracking : Analyzing the behaviour of customers in a store is essential for making cashier-free shops a reality. The labeling can consist of skeleton keypoints for movement detection, action tracking on video frames, as well as product localization and intention detection.
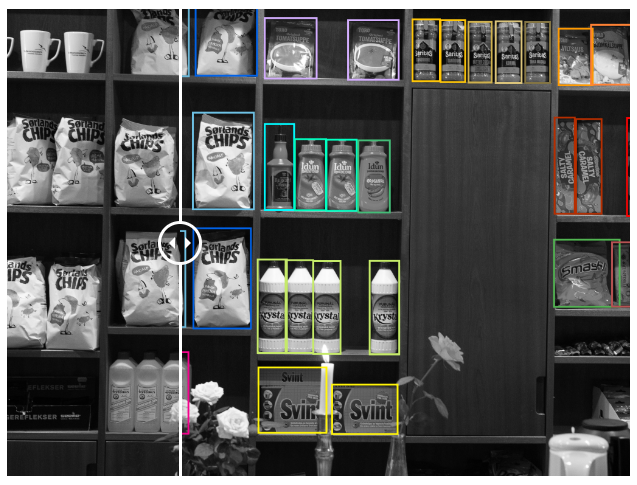
👉 Shelf analysis: Monitoring the stocks on shelves can be very useful for supplier logistics and inventory management. Product positioning can be analyzed using bounding boxes, including for the detection of empty spaces, as well as incorrectly placed or stacked products.
👉 Barcode analysis : While traditional barcodes have to be scanned once at a time, computer vision models can be trained on labeled data to recognise and process barcodes at scale. We can provide labeling for the entire barcode, as well as separate labels and transcription for each number.
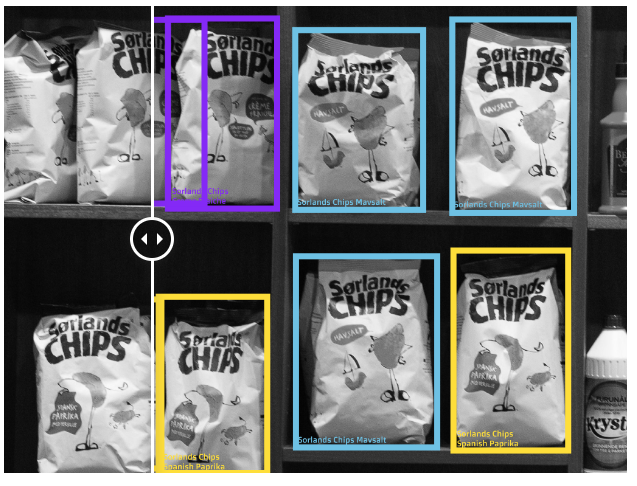
👉 Product recognition : Product recognition is a challenging task due to the enormous number of different products and the fact that many of them look similar. By using special tool add-ons for SKUs, our workforce can make sure each product is matched to its SKU, even if it’s one in a million.
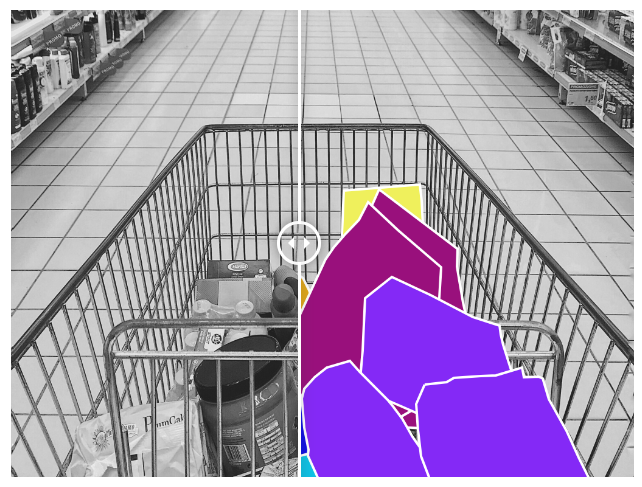
👉 Smart carts: The way people shop has never been easier. Smart carts equipped with cameras can be trained on labeled datasets in order to identify, classify, and record the contents even when there is occlusion – which is where bounding box annotation comes in handy.
👉 Logo detection: Logo applications can detect and identify logos in images or video for blurring purposes or for analyzing product placement. The task is not too simple because of the many potential logo permutations, or the appearance of unknown logos which have to be identified using reverse search.
👉 E-commerce: In order to classify products for search engines at scale, automatic tagging is needed for e-commerce applications. By tagging each product with the appropriate tags according to the search filters of the website, our annotators can make sure clients discover exactly what they want.
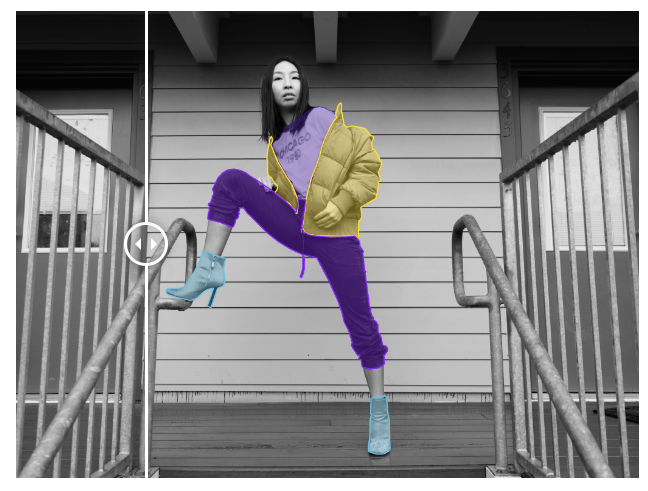
👉 Fashion: Fashion trends can be documented and analysed by training AI models to identify and classify various articles of clothing. The labeling taxonomy may get very complex, from garment type classification, to color, fabric, pattern, and other additional attributes for each item.
👉 Note : This Case Studies for Education purpose and for learning references only. All write reserved by original author mentioned in the references
✔️ Reference : https://humansintheloop.org/industries/