Self-Driving Car System Integration: Team Danya
Team
Hossam Ashtawy: hossam.ashtawy@gmail.com
Overview
This is the project repo for the final project of the Udacity Self-Driving Car Nanodegree: Programming a Real Self-Driving Car.
System Arcitecture
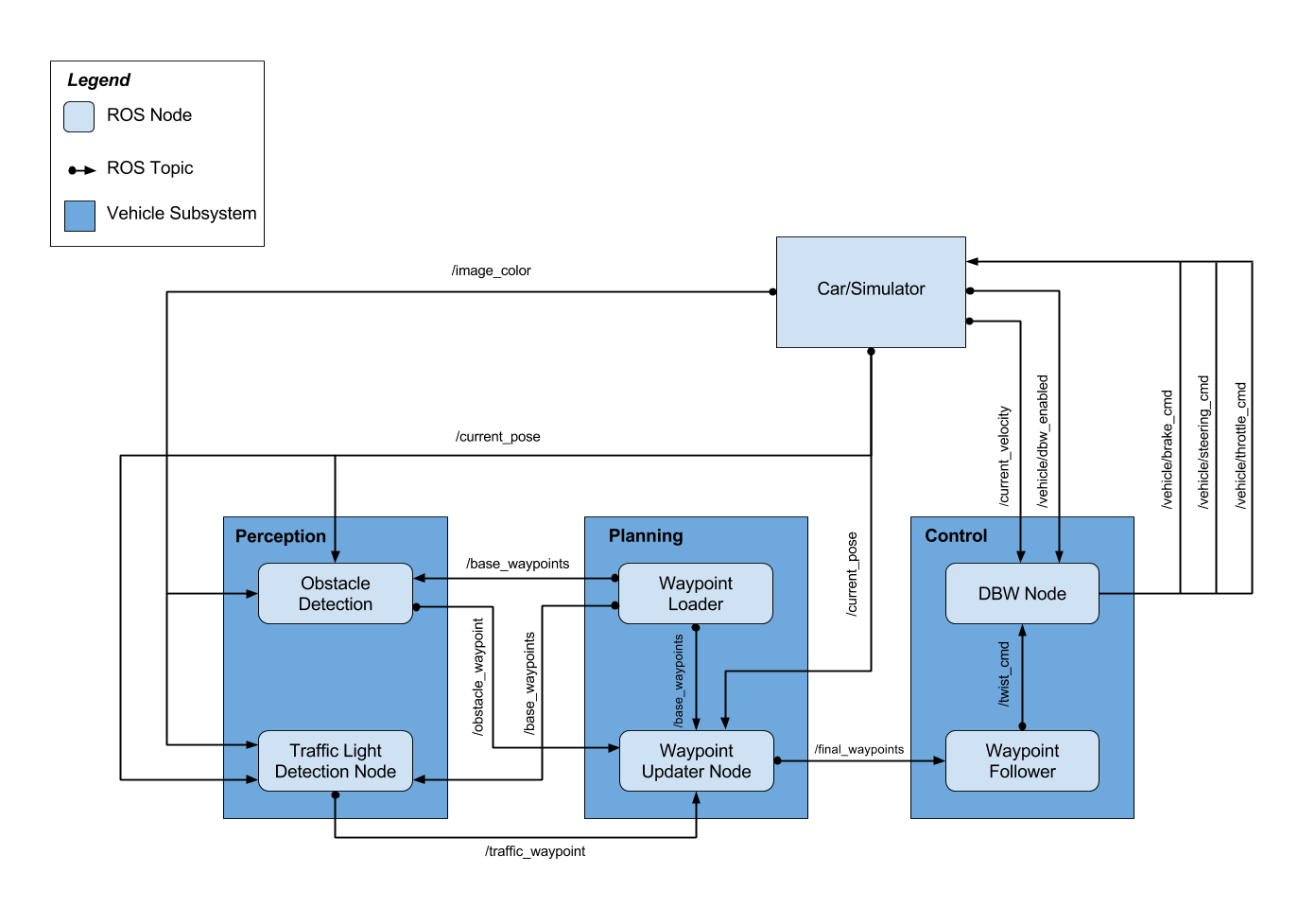
The following is a system architecture diagram showing the ROS nodes and topics used in the project. The ROS nodes and topics shown in the diagram are described briefly in the sections below, and more detail is provided for each node in the code.
/ros/src/tl_detector/
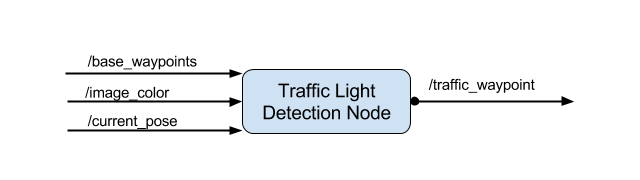
This package contains the traffic light detection node: tl_detector.py. This node takes in data from the /image_color, /current_pose, and /base_waypoints topics and publishes the locations to stop for red traffic lights to the /traffic_waypoint topic.
The /current_pose topic provides the vehicle's current position, and /base_waypoints provides a complete list of waypoints the car will be following.
You will build both a traffic light detection node and a traffic light classification node. Traffic light detection should take place within tl_detector.py, whereas traffic light classification should take place within ../tl_detector/light_classification_model/tl_classfier.py.
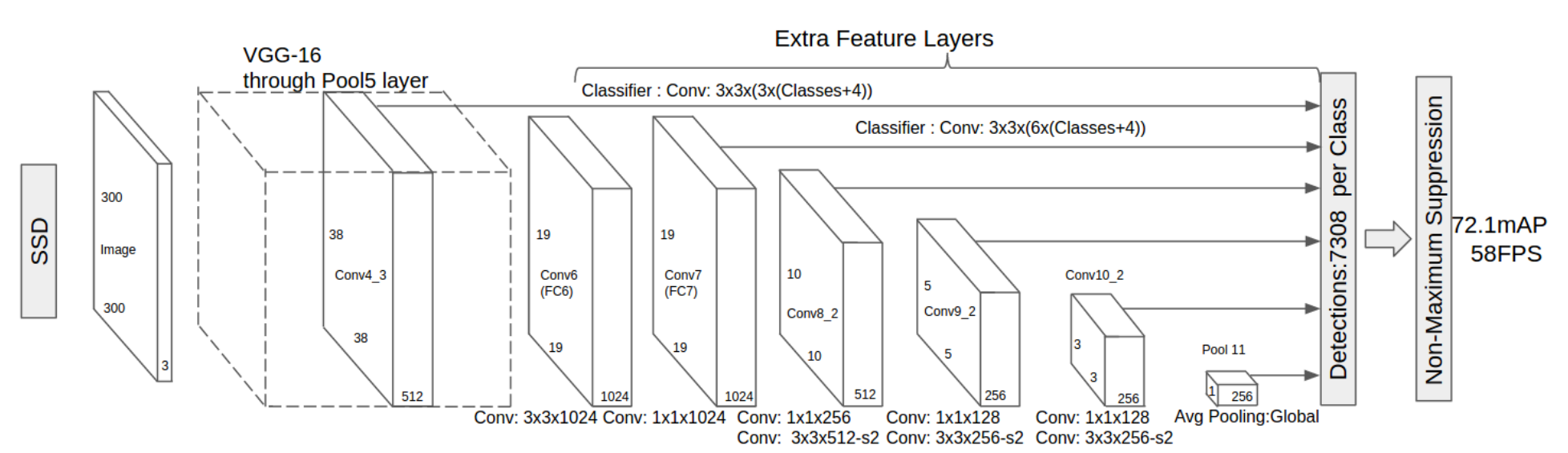
The classifier used in this project to detect the traffic light state is based on the model ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco from the model zoo of the TensorFlow Object Detection API. The model is pre-trained on the COCO dataset and then finetuned for traffic sign detection and classification on traffic lights dataset. The model's small inference time (<50ms) and high accuracy are the main reasons for choosing it to run in real time in the simulator and the car.
Image from Deep Learning for Object Detection: A Comprehensive Review
/ros/src/waypoint_updater/
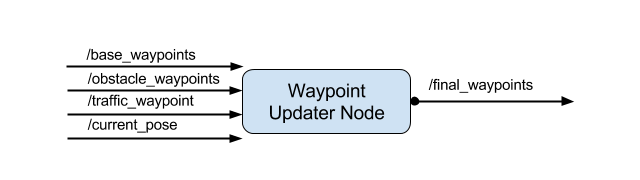
This package contains the waypoint updater node: waypoint_updater.py. The purpose of this node is to update the target velocity property of each waypoint based on traffic light and obstacle detection data. This node will subscribe to the /base_waypoints, /current_pose, /obstacle_waypoint, and /traffic_waypoint topics, and publish a list of waypoints ahead of the car with target velocities to the /final_waypoints topic.
/ros/src/twist_controller/
Carla is equipped with a drive-by-wire (dbw) system, meaning the throttle, brake, and steering have electronic control. This package contains the files that are responsible for control of the vehicle: the node dbw_node.py and the file twist_controller.py, along with a pid and lowpass filter that you can use in your implementation. The dbw_node subscribes to the /current_velocity topic along with the /twist_cmd topic to receive target linear and angular velocities. Additionally, this node will subscribe to /vehicle/dbw_enabled, which indicates if the car is under dbw or driver control. This node will publish throttle, brake, and steering commands to the /vehicle/throttle_cmd, /vehicle/brake_cmd, and /vehicle/steering_cmd topics.
In addition to these packages you will find the following, which are not necessary to change for the project. The styx and styx_msgs packages are used to provide a link between the simulator and ROS, and to provide custom ROS message types:
- /ros/src/styx/ A package that contains a server for communicating with the simulator, and a bridge to translate and publish simulator messages to ROS topics.
- /ros/src/styx_msgs/ A package which includes definitions of the custom ROS message types used in the project.
- /ros/src/waypoint_loader/ A package which loads the static waypoint data and publishes to /base_waypoints.
- /ros/src/waypoint_follower/ A package containing code from Autoware which subscribes to /final_waypoints and publishes target vehicle linear and angular velocities in the form of twist commands to the /twist_cmd topic.
Please use one of the two installation options, either native or docker installation.
Native Installation
-
Be sure that your workstation is running Ubuntu 16.04 Xenial Xerus or Ubuntu 14.04 Trusty Tahir. Ubuntu downloads can be found here.
-
If using a Virtual Machine to install Ubuntu, use the following configuration as minimum:
- 2 CPU
- 2 GB system memory
- 25 GB of free hard drive space
The Udacity provided virtual machine has ROS and Dataspeed DBW already installed, so you can skip the next two steps if you are using this.
-
Follow these instructions to install ROS
- ROS Kinetic if you have Ubuntu 16.04.
- ROS Indigo if you have Ubuntu 14.04.
-
- Use this option to install the SDK on a workstation that already has ROS installed: One Line SDK Install (binary)
-
Download the Udacity Simulator.
Docker Installation
Build the docker container
docker build . -t capstoneRun the docker file
docker run -p 4567:4567 -v $PWD:/capstone -v /tmp/log:/root/.ros/ --rm -it capstonePort Forwarding
To set up port forwarding, please refer to the instructions from term 2
Udacity Workspace
Make sure you do the following to avoid errors related dbw mkz messages:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y ros-kinetic-dbw-mkz-msgs
cd /home/workspace/CarND-Capstone/ros
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src --rosdistro=kinetic -y
pip install --upgrade catkin_pkg_modulesUsage
- Clone the project repository
git clone https://github.com/udacity/CarND-Capstone.git- Install python dependencies
cd CarND-Capstone
pip install -r requirements.txt- Make and run styx
cd ros
catkin_make
source devel/setup.sh
roslaunch launch/styx.launch- Run the simulator
Real world testing
- Download training bag that was recorded on the Udacity self-driving car.
- Unzip the file
unzip traffic_light_bag_file.zip- Play the bag file
rosbag play -l traffic_light_bag_file/traffic_light_training.bag- Launch your project in site mode
cd CarND-Capstone/ros
roslaunch launch/site.launchRunning ROS bag on the Udacity Workspace
Navigate to a temporary storage folder, so as not to exceed the 2GB limit in /home/workspace.
- Download the [ros bag] (https://s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/udacity-selfdrivingcar/traffic_light_bag_file.zip) using wget and the download link and unzip the file:
cd /opt
wget <link_to_your_download>
unzip /opt/path/to/your/download.zip- Open a terminal and start roscore.
- Open another terminal and run rosbag play -l /opt/path/to/your.bag
- Click the "Go To Desktop" button.
- From the XWindows desktop, open terminator, and run rviz. You can change the RViz configuration to Udacity's .config file by navigating to /home/workspace/default.rviz from File > Open Config in RViz.
- Confirm that traffic light detection works on real life images