Welcome to the Getting Started with Kubernetes workshop!
Complete the following sections to build a lab environment. The steps may look complicated, but they're not.
- Install
kubectlandgit - Sign-up to Linode ($100 free credit included)
- Create a Kubernetes cluster on Linode
- Connect to your Kubernetes cluster
- Clean-up
Install kubectl
Install git
-
MacOS:
brew install git -
Windows: Download the installation exe from here and follow the installation wizard.
You should quit and re-open your terminal.
Go to linode.com and complete your sign-up. This link includes $100 of free credit to pay for your cluster during the workshop.
You must be logged in to linode.com to complete the following steps.
- Select Kubernetes on the left-hand navigation pane
- Choose
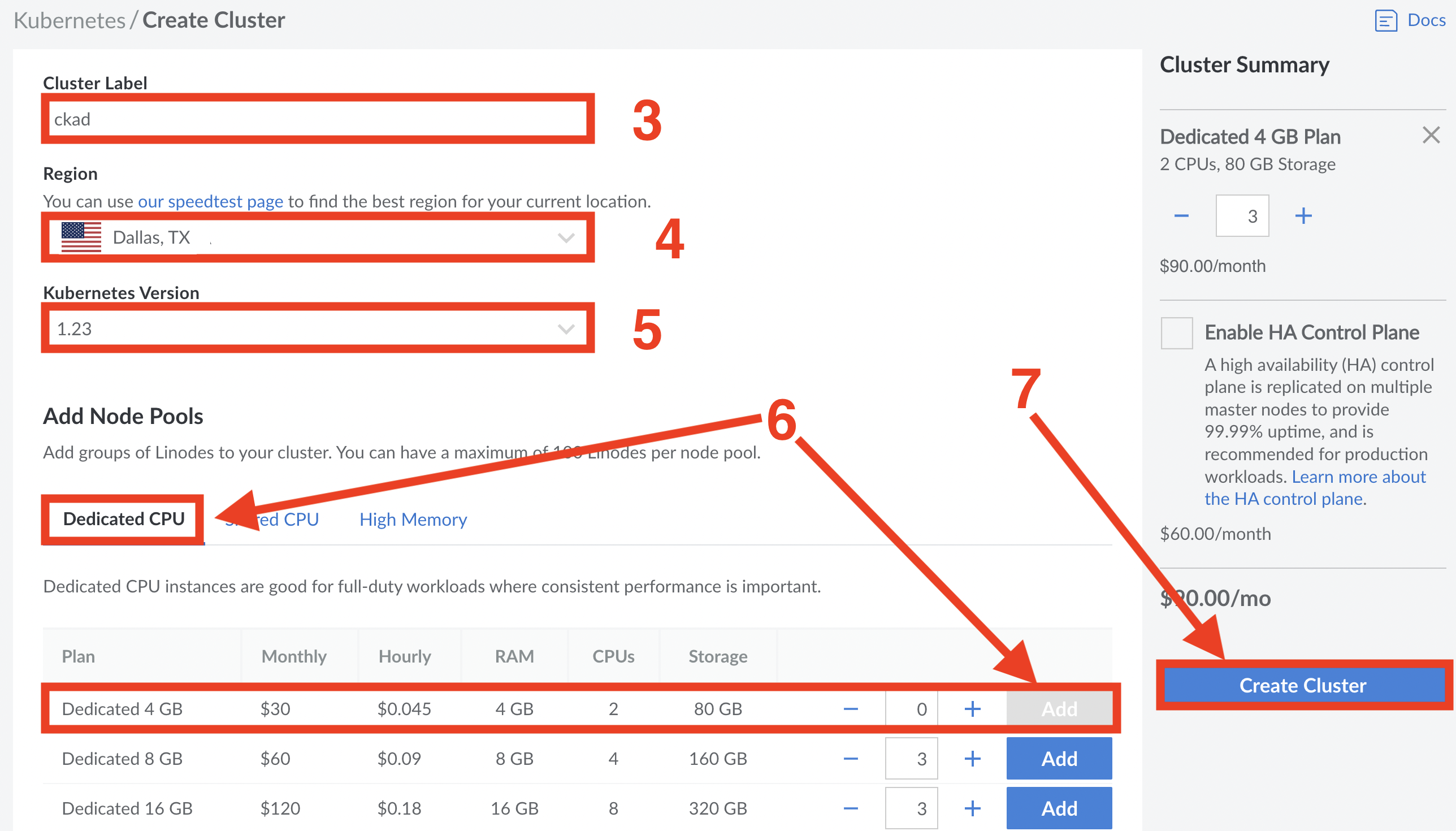
Create Clusterand set the following options - Cluster label: Give your cluster a name such as gsk
- Region: Dallas, TX
- Kubernetes Version: 1.23 (newer versions will also work)
- Add Node Pools: Click
Dedicated CPUand click the blueAddbutton at the end of the Dedicated 4 GB line (this will add 3 x 4GB nodes) - When your settings match the image below, click
Create Cluster
It may take a couple of minutes for your cluster to be ready.
You must be logged in to linode.com to complete the following steps.
- Click Kubernetes on the left-hand navigation pane
- Click the
Download kubeconfiglink for your cluster (the download will fail if your cluster is still being created) - Copy the downloaded file to the hidden
./kubefolder in your home directory- If you already have a file called
configin your hidden./kubefolder, rename the existing file toconfig.bkp - Rename the file you just downloaded from Linode and copied to your hidden
./kubefolder toconfig. Be sure the file is calledconfigand not something likeconfig.yml.
- If you already have a file called
- Open a terminal and type the following command. Your output should look similar
kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
lke76472-118784-634d2eb30838 Ready <none> 5m23s v1.23.6
lke76472-118784-634d2eb32f20 Ready <none> 5m21s v1.23.6
lke76472-118784-634d2eb354b1 Ready <none> 4m51s v1.23.6
Congratulations, you're connected to your Kubernetes cluster.
Run the following steps after the workshop is finished to shut down your lab and return to your pre-lab settings.
You must be logged in to Linode.com to complete these steps.
Delete your Kubernetes cluster
- Click
Kubernetesin the left navigation pane. Your cluster will be listed. - Click the
Deletebutton on the far right of your cluster and follow the prompts. If you have other clusters, be sure to delete the cluster used for the workshop. You may be prompted to type the name of your cluster as confirmation of the operation.
Delete other Linode resources
If you have other resources and clusters on Linode, be sure you only delete resources that were part of the workshop.
- Click
NodeBalancersand delete any NodeBalancers created as part of the lab. - Click
Volumesand clik the three dots to the far right of each volume created as part of the workshop. ChooseDeletefrom the list and follo the prompts.
Revert your kubeconfig
If you already had kubectl installed, you will need to revert to your saved kubeconfig file.
- Navigate to the hidden
./kubefolder in your home folder - Delete the file called
config - Rename the
config.bkpfile toconfig
Your kubeconfig is now reverted to it's pre-workshop configuration.