- [1] How To Apply For a CMS Computing Account
- [2] How to Connect To Your Lxplus Area
- [3] CMS Data Analysis
- [4] How to Request a Grid Certificate
- [5] How to Request an EOS Space for Users
How to request a computing account for a new student.
- Go to
https://cms.cern.ch/iCMS/jsp/secr/reg/regCMS.jspand fill the form.
- Email: any email you're mostly using: hotmail, gmail etc. you'll contact with the CMS secretariat from this email address.
- Name: Your family name (surname)
- First Name: your name
- Institute: Cukurova University
- Institute Representative: Isa Dumanoglu
- Activity: (Should be CMS User, not sure)
- Click on
Ask CMS secretariatbutton.
- Activity: HCAL
- Activity Detail: Data Analysis with CMS data
After the form, you'll receive an email with your HRPersonID as:
Dear XX YY (ADANA-CUKUROVA),
You are now registered in CMS as 'Non-Doctoral Student' from your institute (ADANA-CUKUROVA) .
You will use the HRPersonID number in the next mail.
When you receive the mail above, send an email to cms.people@cern.ch as below.
Mail Subject : CERN Account
Dear Sir / Madame,
I'm now registered in CMS as 'Non-Doctoral Student' from my institute (ADANA-CUKUROVA). Could you provide my "Username" and "Initial Password", please.
Thank You.
Surname, Name
HRpersonId:
For Step-1: They will ask you to upload a copy of your ID (english) or passport to the system.
For Step-2: Also they'll ask you to fill another form that your team leader (Isa Dumanoglu for CU) will approve your account.
After these steps, they should send you your username. Probably they'll not send your initial password. You'll get an email as:
Welcome to CERN. Your Primary Account was automatically created.
Name: XXX YYY
Login: xxxxx
Email: your initial email address (hotmail, gmail etc.)
For the initial password, you should send another email to service-desk@cern.ch as:
Mail Subject: CMS Account Activation & Initial Password
Dear CERN People,
My account "xxxxx" is now added to the CMS (zh) group, however it's currently disabled. Could you activate my account and send my initial password, please?
Thank you.
Best regards,
Surname, Name
HRpersonId :
They'll activate your account and send you an email including your initial password. Please follow the required actions section in your mail and change your account and EDH passwords in 3 days.
ps. these steps can be changed partly but more or less the process is the same.
For more information: https://twiki.cern.ch/twiki/bin/view/CMSPublic/WorkBookGetAccount
Step-1: Login to your lxplus area:
For Windows: Download & install:
- Putty (putty-64bit-0.74-installer.msi) or newer version: https://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/latest.html
- Xming: https://sourceforge.net/projects/xming/
- Winscp: https://winscp.net/eng/download.php
ps. lxplus6 is an old version and lxplus.cern.ch will direct you to latest version. (picture is old)
Host name: username@lxplus.cern.ch
Port: 22
Connection Type: SSH
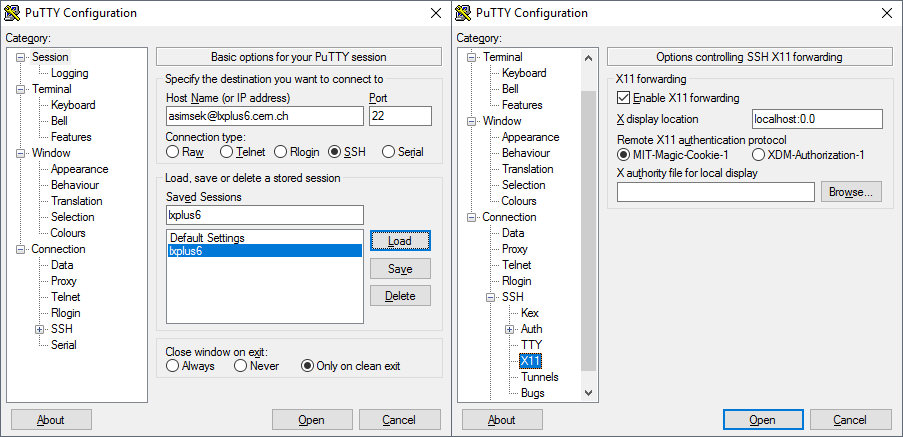
Saved Sessions: lxplus
- Save the settings.
- Go to: Connections >> SSH >> X11
- Enable X11 forwarding
- X display location: localhost:0.0
go back to Session tab on left side (first category), and save the session again (to save the ssh settings to your profile). Now you can double click on it or click to load while its selected.
This will open a terminal window and use your new cern account password. (you'll not see any character while you typing your password. Hold the backspace for a while if you type your password wrong). It's same with you email. (Btw, to see your e-mails: https://mmm.cern.ch/owa/). Now you're able to use your lxplus account. (list your folders with ls -lhtr when you login and use private folder for your analysis. cd private)
ps. open xming and you should see the icon on right bottom:
For Mac & Linux:
- Download & Install: XQuartz -- https://www.xquartz.org/
- Open a new terminal window
- type
ssh -Y username@lxplus.cern.chand hit enter - type your new cern account password and hit enter. (you'll not see any character while you typing your password. Hold the backspace for a while if you type your password wrong).
- Now you're able to use your lxplus account. (list your folders with ls -lhtr when you login and use private folder for your analysis. cd private)
- ls -- lists your files
- ls -lhtr -- list your files (newer at bottom)
- mv filename1 filename2 -- moves a file (i.e. gives it a different name, or moves it into a different directory.
- cp filename1 filename2 -- copies a file
- rm filename -- removes a file. It is wise to use the option rm -i, which will ask you for confirmation before actually deleting anything.
- diff filename1 filename2 -- compares files, and shows where they differ
- chmod options filename -- lets you change the read, write, and execute permissions on your files. For example, chmod o+r filename will make the file readable for everyone, and chmod o-r filename will make it unreadable for others again.
- mkdir dirname -- make a new directory
- cd dirname -- change directory. You basically 'go' to another directory, and you will see the files in that directory when you do 'ls'.
- cd -- without arguments, will let you to go home directory.
- cd .. -- this command will get you one level up from your current position.
- pwd -- tells you where you currently are.
- vi filename.xxx -- vi is a text editor for your scripts. when you open the editor you can activate insert mode with pressing i on your keyboard and you can press esc to deactivate. You can see the current mode on left-bottom side. To save the file you can press esc first, they type :w and hit to enter. To quit from vi editor press esc first, type :q and hit enter. If you want to quit without saving your changes, press esc first, type :q! and hit enter. If you would like to save & exit, press esc first, type :wq hit enter.
ps: If you are working on Windows (Putty Terminal), you should use the arrow keys (up, down, left, right) on your keyboard instead of mouse scrolling to navigate on the document that you opened with the vi editor. Also, the text or code block selected in the Putty terminal (Windows) will be copied to the clipboard and you can paste an item you copied with a right mouse click.
For more: http://mally.stanford.edu/~sr/computing/basic-unix.html
Log-in to your lxplus account and go to your private folder.
cd private
mkdir CMSDataAnalyzerStudy
cd CMSDataAnalyzerStudy
echo $0echo $0command will show your shell type. Use one of the following command lines appropriate for your shell type.
ps: You need to
sourcethe following script (cmsset_default.***) to be able to use thecmsenvcommand every time you make a new connection to Lxplus.
# for Bash User
source /cvmfs/cms.cern.ch/cmsset_default.sh
# for csh/tcsh user
source /cvmfs/cms.cern.ch/cmsset_default.cshCreate a new CMSSW version.
cmsrel CMSSW_10_2_5_patch1You'll see a warning as following:
WARNING: Release CMSSW_10_2_5_patch1 is not available for architecture slc7_amd64_gcc820.
Developer's area is created for available architecture slc7_amd64_gcc700.
This means, you need to change your architecture with the following command line.
echo $0echo $0 command will show your shell type. Use one of the following command lines appropriate for your shell type.
# for Bash User
export SCRAM_ARCH=slc7_amd64_gcc700
# for csh/tcsh user
setenv SCRAM_ARCH slc7_amd64_gcc700cd CMSSW_10_2_5_patch1/src
cmsenv
mkdir DataAnalyzer
cd DataAnalyzerps: cmsenv command is crutial for usage of all cms functions. Don't forget to use it before using the cms commands ( root, cmsRun, edmProvDump, edmDumpEventContent, etc. )
Create a new EDAnalyzer:
mkedanlzr DemoAnalyzer
cd DemoAnalyzer
scram b -j 4Now we need to change & add some code lines into plugins/DemoAnalyzer.cc . For the usage of vi editor, see basic linux commands section above.
ps: This tutorial & general CMS data analysis needs basic c++ and python knowledge. Also, you should be familiarized with the linux commands.
vi plugins/DemoAnalyzer.ccWe're defining the header files:
#find
//
// class declaration
//
#replace
//
// class declaration
//
#include "DataFormats/HcalDetId/interface/HcalDetId.h"
#include "DataFormats/HcalRecHit/interface/HcalRecHitCollections.h"
#include "DataFormats/HcalDigi/interface/HBHEDataFrame.h"
#include "DataFormats/HcalRecHit/interface/HBHERecHit.h"
#include "DataFormats/HcalDetId/interface/HcalSubdetector.h"
#include "Geometry/CaloGeometry/interface/CaloSubdetectorGeometry.h"
#include "Geometry/CaloGeometry/interface/CaloCellGeometry.h"Define the namespaces:
#find
using reco::TrackCollection;
#replace
using namespace std;
using namespace edm;
using namespace reco;Replace the token to analyze HCal-Barrel & HCal-EndCap:
#find
// ----------member data ---------------------------
edm::EDGetTokenT<TrackCollection> tracksToken_; //used to select what tracks to read from configuration file
#replace
// ----------member data ---------------------------
EDGetTokenT<HBHERecHitCollection> hbherechit_;Delete unnecessary part:
#find & Delete (with :)
:
tracksToken_(consumes<TrackCollection>(iConfig.getUntrackedParameter<edm::InputTag>("tracks")))Initialize the HBHE collection:
#find
//now do what ever initialization is needed
#replace
//now do what ever initialization is needed
hbherechit_ = consumes<HBHERecHitCollection>(iConfig.getParameter<edm::InputTag>("HBHERecHitCollection"));Get the data from root file by token:
#find
Handle<TrackCollection> tracks;
iEvent.getByToken(tracksToken_, tracks);
#replace
Handle<HBHERecHitCollection> hbhehits_;
iEvent.getByToken(hbherechit_, hbhehits_);Replace the track loop with HBHE loop:
#find
for(TrackCollection::const_iterator itTrack = tracks->begin();
itTrack != tracks->end();
++itTrack) {
// do something with track parameters, e.g, plot the charge.
// int charge = itTrack->charge();
}
#replace
const HBHERecHitCollection* hbhe_hits = hbhehits_.failedToGet () ? 0 : &*hbhehits_;
if (hbhehits_.isValid()) {
for (HBHERecHitCollection::const_iterator j=hbhe_hits->begin(); j!=hbhe_hits->end(); j++) {
// This for loop is looping in each event!
HcalDetId id = (*j).id();
int ieta= id.ieta();
float energy = (*j).energy();
cout << "ieta: " << ieta << " -- Energy:" << energy << endl;
}
}Now, you can press escto deactivate insert mode in vi editor and save&quit with typing :wq. (for more information see: basic linux commands)
Before the config file, we need to create another file which is necessary:
vi python/CfiFile_cfi.pyActivate the vi editor with pressing i on your keyboard and paste the following command lines:
import FWCore.ParameterSet.Config as cms
demo = cms.EDAnalyzer('DemoAnalyzer'
)press esc and type :wq to save&exit. (For more vi commands, please see: basic linux commands)
We need to create a config file in python folder and add some code lines into ConfFile_cfg.py file.
vi python/ConfFile_cfg.pyActivate the insert mode and add the following commands
import FWCore.ParameterSet.Config as cms
import datetime
import PhysicsTools.PythonAnalysis.LumiList as LumiList
from FWCore.ParameterSet.VarParsing import VarParsing
options = VarParsing ('python')
options.register('reportEvery', 1,
VarParsing.multiplicity.singleton,
VarParsing.varType.int,
"Report every N events (default is N=1000)"
)
options.register('process', '146908',
VarParsing.multiplicity.singleton,
VarParsing.varType.string,
"MC-simulated event type"
)
options.register('wantSummary', False,
VarParsing.multiplicity.singleton,
VarParsing.varType.bool,
"Print out trigger and timing summary"
)
options.parseArguments()
process = cms.Process("Test")
process.load('Configuration.StandardSequences.Services_cff')
process.load('SimGeneral.HepPDTESSource.pythiapdt_cfi')
process.load('FWCore.MessageService.MessageLogger_cfi')
process.load('Configuration.StandardSequences.GeometryRecoDB_cff')
process.load('Configuration.StandardSequences.MagneticField_AutoFromDBCurrent_cff')
process.load('CommonTools.RecoAlgos.HBHENoiseFilterResultProducer_cfi')
process.load("RecoJets.Configuration.CaloTowersES_cfi")
process.load("Configuration.StandardSequences.RawToDigi_Data_cff")
process.load("RecoLocalCalo.Configuration.hcalLocalReco_cff")
# report every #1 hit! You can change it to any number you like.
process.MessageLogger.cerr.FwkReport.reportEvery = 1
# How many event you want to analyze. To analyze all events change 1000 with -1
process.maxEvents = cms.untracked.PSet( input = cms.untracked.int32(1000) )
process.source = cms.Source("PoolSource",
fileNames = cms.untracked.vstring( *(
# Add your root files here! (don't forget to add comma for the end of each line!)
'file:/eos/cms/store/user/asimsek/Run2018E/023F1B34-4E2E-A343-8E2C-09C411E86530.root',
#'file:/afs/cern.ch/cms/Tutorials/TWIKI_DATA/TTJets_8TeV_53X.root',
)
)
)
# Give any output name you like ( it's better to end with .root )
OutputFileNames = "Results2018.root"
process.TFileService = cms.Service("TFileService",
fileName = cms.string(OutputFileNames)
)
process.options = cms.untracked.PSet(
wantSummary = cms.untracked.bool(options.wantSummary),
allowUnscheduled = cms.untracked.bool(True),
#SkipEvent = cms.untracked.vstring('ProductNotFound')
)
from Configuration.AlCa.autoCond import autoCond
process.load("Configuration.StandardSequences.FrontierConditions_GlobalTag_condDBv2_cff")
# You can change the global tag here but you need to find spesific global tag for each dataset, run number or root files.
process.GlobalTag.globaltag = '101X_dataRun2_Express_v8'
process.demo = cms.EDAnalyzer('DemoAnalyzer',
HBHERecHitCollection = cms.InputTag("hbhereco"),
)
process.p = cms.Path(process.demo)For the Global Tag: https://twiki.cern.ch/twiki/bin/view/CMSPublic/SWGuideFrontierConditions?redirectedfrom=CMS.SWGuideFrontierConditions#Global_Tags_for_2018_data_taking
When you make any change in plugins/DemoAnalyzer.cc file, you need to re-compile the file:
cd $CMSSW_BASE/src/DataAnalyzer/DemoAnalyzer
cmsenv
scram b -j 4Now you can run your scripts with cmsRun command.
cmsRun python/ConfFile_cfg.pyYou should see some output including ieta and energy values of the #hits. It's very hard to understand the detector with infinite number of entries. We're using histograms to understand the numbers and detector. Now let's plot these numbers in a histogram.
vi plugins/DemoAnalyzer.ccDefine the header files:
#find
#include <map>
#replace
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <locale>And also:
#find:
#include "Geometry/CaloGeometry/interface/CaloCellGeometry.h"
#replace with:
#include "Geometry/CaloGeometry/interface/CaloCellGeometry.h"
#include "FWCore/ServiceRegistry/interface/Service.h"
#include "CommonTools/UtilAlgos/interface/TFileService.h"
#include "TH1.h"
#include "TH1D.h"We need to define histogram iteration to create histograms:
#find
// ----------member data ---------------------------
#replace
// ----------member data ---------------------------
map<string, TH1D*> histo1D;
map<string, TH1D*>::iterator histo1Diter;We need to define histograms in beginJob() class:
#find
DemoAnalyzer::beginJob()
{
}
#replace
DemoAnalyzer::beginJob()
{
cout<<"Begin Job"<<endl;
edm::Service<TFileService> fs;
histo1D["HEiEta"] = fs->make<TH1D>("HEiEta", "iEta vs Number Of Hits",60,-30,30);
histo1D["HEiEta"]->GetXaxis()->SetTitle("i#eta");
histo1D["HEiEta"]->GetYaxis()->SetTitle("Number of Hits");
histo1D["HERecHitEnergy"] = fs->make<TH1D>( "HERecHitEnergy", "HE: Energy Distibution",300,0,300);
histo1D["HERecHitEnergy"]->GetXaxis()->SetTitle("GeV");
histo1D["HERecHitEnergy"]->GetYaxis()->SetTitle("Number of Hits");
}Let's comment the cout with adding // on the beginning of the line and add the commands for the filling histograms:
#find
cout << "ieta: " << ieta << " -- Energy:" << energy << endl;
#replace
//cout << "ieta: " << ieta << " -- Energy:" << energy << endl;
if(id.subdet() == HcalEndcap){
histo1D["HEiEta"]->Fill(ieta);
histo1D["HERecHitEnergy"]->Fill(energy);
}Save the file and quit with pressing escand typing :wq.
Now let's make necessary changes in plugins/BuildFile.xml file:
vi plugins/BuildFile.xml#find
<use name="FWCore/Framework"/>
<use name="FWCore/PluginManager"/>
<use name="FWCore/ParameterSet"/>
<use name="DataFormats/TrackReco"/>
<flags EDM_PLUGIN="1"/>
#replace
<use name="FWCore/Framework"/>
<use name="FWCore/PluginManager"/>
<use name="FWCore/ParameterSet"/>
<use name="DataFormats/TrackReco"/>
<use name="CommonTools/UtilAlgos"/>
<flags EDM_PLUGIN="1"/>For more statistic, we need to set -1 for the maxEvents in python/ConfFile_cfg.py file.
vi python/ConfFile_cfg.py#find
process.maxEvents = cms.untracked.PSet( input = cms.untracked.int32(1000) )
#replace
process.maxEvents = cms.untracked.PSet( input = cms.untracked.int32(-1) )save&quit with pressing esc and typing :wq.
Since we made changes in cc file (plugins/DemoAnalyzer.cc), we need to re-compile:
cd $CMSSW_BASE/src/DataAnalyzer/DemoAnalyzer
cmsenv
scram b -j 4Let's run it again with cmsRun:
cmsRun python/ConfFile_cfg.pyYou should see some text as below:
=============================================
MessageLogger Summary
type category sev module subroutine count total
---- -------------------- -- ---------------- ---------------- ----- -----
1 fileAction -s file_close 1 1
2 fileAction -s file_open 2 2
type category Examples: run/evt run/evt run/evt
---- -------------------- ---------------- ---------------- ----------------
1 fileAction PostGlobalEndRun
2 fileAction pre-events pre-events
Severity # Occurrences Total Occurrences
-------- ------------- -----------------
System 3 3
dropped waiting message count 0
Now you can check your results:
ps: Please make sure Xming app is open on your computer before using the following commands.
root -l Results2018.rootThis will activate the root with your result file.
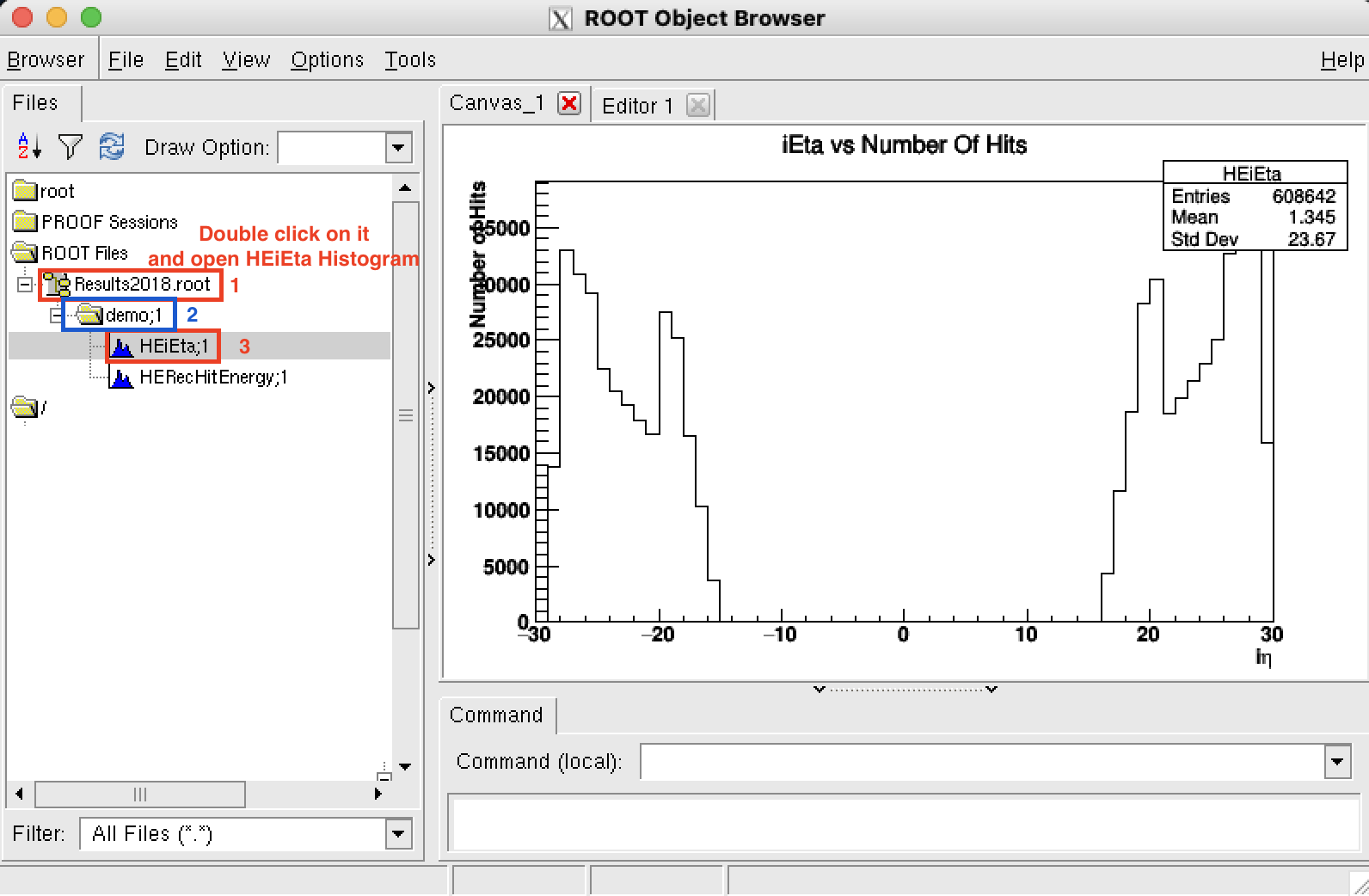
Open a TBrowser to see the results:
TBrowser bps: Argument b is an arbitrary argument and you can change it if the b does not work. (ie. TBrowser c)
This command line will open a new browser window:
When you see the browser, (be patient, it can be slow) double click on your root file Results2018.root on the left side, then demo and HEiEta histogram to see the results on the right side.
To save the plot as pdf or png, click the File on top and click on save as. Give a name and click on save button. Now you can close the TBrowser and check the pdf or png file in your directory. To do that, you need to quit from root with typing .q and press enter. Then use the ls -lhtr command to list your directory.
To display your png or pdf file use display command:
display FileName.pngps. display shows both png and pdf. You can also use
evincecommand for only pdfs. The usage is same, just replacedisplaywithevince.
So far, we have only accessed the data in the HBHE Reco collection. In order to access different collections, we first need to dump our root file with the edmDumpEventContent command.
ps:
cmsenvcommand is crutial for usage of all cms functions. Don't forget to use it before using the cms commands (root,cmsRun,edmProvDump,edmDumpEventContent, etc. ) You can useedmDumpEventContentcommand under the/CMSSW_10_2_5_patch1/src/DataAnalyzer/DemoAnalyzer/folder where you can seepluginsandpythonfolders withlscommand.
source /cvmfs/cms.cern.ch/cmsset_default.sh
cmsenvLet's use one of our root file
023F1B34-4E2E-A343-8E2C-09C411E86530.rootwith theedmDumpEventContentcommand. Note that we add> Run2018E_Collections.txtat the end to write all output to a txt file.
edmDumpEventContent /eos/cms/store/user/asimsek/Run2018E/023F1B34-4E2E-A343-8E2C-09C411E86530.root > Run2018E_Collections.txtThis command will list you all module names to a txt file. We can open the txt file with vi editor:
vi Run2018E_Collections.txtYou will now see a list like the one below:
Type Module Label Process
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GlobalObjectMapRecord "hltGtStage2ObjectMap" "" "HLT"
edm::TriggerResults "TriggerResults" "" "HLT"
trigger::TriggerEvent "hltTriggerSummaryAOD" "" "HLT"
FEDRawDataCollection "rawDataCollector" "" "LHC"
BXVector<GlobalAlgBlk> "gtStage2Digis" "" "RECO"
BXVector<GlobalExtBlk> "gtStage2Digis" "" "RECO"
BXVector<l1t::CaloTower> "caloStage2Digis" "CaloTower" "RECO"
BXVector<l1t::EGamma> "caloStage2Digis" "EGamma" "RECO"
BXVector<l1t::EGamma> "gtStage2Digis" "EGamma" "RECO"
.
.
.
.
edm::SortedCollection<EcalRecHit,edm::StrictWeakOrdering<EcalRecHit> > "ecalRecHit" "EcalRecHitsEB" "RECO"
edm::SortedCollection<EcalRecHit,edm::StrictWeakOrdering<EcalRecHit> > "ecalRecHit" "EcalRecHitsEE" "RECO"
.
.
.
edm::SortedCollection<HBHERecHit,edm::StrictWeakOrdering<HBHERecHit> > "hbheprereco" "" "RECO"
edm::SortedCollection<HBHERecHit,edm::StrictWeakOrdering<HBHERecHit> > "hbhereco" "" "RECO"
edm::SortedCollection<HBHERecHit,edm::StrictWeakOrdering<HBHERecHit> > "reducedHcalRecHits" "hbhereco" "RECO"
edm::SortedCollection<HFPreRecHit,edm::StrictWeakOrdering<HFPreRecHit> > "hfprereco" "" "RECO"
edm::SortedCollection<HFRecHit,edm::StrictWeakOrdering<HFRecHit> > "hfreco" "" "RECO"
edm::SortedCollection<HFRecHit,edm::StrictWeakOrdering<HFRecHit> > "reducedHcalRecHits" "hfreco" "RECO"
edm::SortedCollection<HORecHit,edm::StrictWeakOrdering<HORecHit> > "horeco" "" "RECO"
edm::SortedCollection<HORecHit,edm::StrictWeakOrdering<HORecHit> > "reducedHcalRecHits" "horeco" "RECO"
edm::SortedCollection<ZDCDataFrame,edm::StrictWeakOrdering<ZDCDataFrame> > "castorDigis" "" "RECO"
edm::SortedCollection<ZDCDataFrame,edm::StrictWeakOrdering<ZDCDataFrame> > "hcalDigis" "" "RECO"
edm::SortedCollection<ZDCRecHit,edm::StrictWeakOrdering<ZDCRecHit> > "zdcreco" "" "RECO"
.
.
.
.
vector<reco::CaloJet> "ak4CaloJets" "" "RECO"
vector<reco::CaloMET> "caloMet" "" "RECO"
.
.
vector<reco::Muon> "muons" "" "RECO"
vector<reco::Muon> "muonsFromCosmics" "" "RECO"
.
.
vector<reco::PFJet> "ak4PFJets" "" "RECO"
vector<reco::PFJet> "ak4PFJetsCHS" "" "RECO"
.
.
The second column defines the module name. We'will use the module name as an input tag in our configuration file.
For "HB & HE" analysis:
hbhereco
For "HF" analysis:
hfreco
For "HO" analysis:
horeco
For "calo-jets":
ak4CaloJets
For "pf-jets":
ak4PFJets
For "HCAL Noise" analysis:
hcalnoise
Here is a couple example for you to show how to implement collections to your configuration file.
vi python/ConfFile_cfg.py## Find
process.demo = cms.EDAnalyzer('DemoAnalyzer',
HBHERecHitCollection = cms.InputTag("hbhereco"),
)
## Replace
process.demo = cms.EDAnalyzer('DemoAnalyzer',
HBHERecHitCollection = cms.InputTag("hbhereco"),
HBHEPreRecHitCollection = cms.untracked.InputTag("hbheprereco"),
HcalDigisCollection = cms.untracked.InputTag("hcalDigis"),
PFJetCollection = cms.untracked.InputTag("ak4PFJets"),
CaloJetCollection = cms.untracked.InputTag("ak4CaloJets"),
CaloMETCollection = cms.untracked.InputTag("caloMet"),
HORecHitCollection = cms.untracked.InputTag("horeco"),
VertexCollection = cms.untracked.InputTag("offlinePrimaryVertices"),
TriggerRecord = cms.untracked.InputTag("gtDigis"),
rbxnoise =cms.untracked.InputTag("hcalnoise"),
)After adding the collections to your configuration file, don't forget to call it in your DemoAnalyzer.cc script under the plugin folder.
Let's add hfreco collection to our DemoAnalyzer.cc script as an example:
vi plugin/DemoAnalyzer.cc#Find
//edm::EDGetTokenT<TrackCollection> tracksToken_; //used to select what tracks to read from configuration file
EDGetTokenT<HBHERecHitCollection> hbherechit_;
#Add Underneath
EDGetTokenT<HFRecHitCollection> hfrechit_;#Find
//now do what ever initialization is needed
hbherechit_ = consumes<HBHERecHitCollection>(iConfig.getParameter<edm::InputTag>("HBHERecHitCollection"));
#Add Underneath
hfrechit_ = consumes<HFRecHitCollection>(iConfig.getParameter<edm::InputTag>("HFRecHitCollection"));#Find
Handle<HBHERecHitCollection> hbhehits_;
iEvent.getByToken(hbherechit_, hbhehits_);
#Add Underneath
Handle<HFRecHitCollection> hfhits_;
iEvent.getByToken(hfrechit_, hfhits_);Now we can reach to the HF collection by creating a hit loop as we did for the HBHE collection.
#Find
const HBHERecHitCollection* hbhe_hits = hbhehits_.failedToGet () ? 0 : &*hbhehits_;
#Add Overneath
const HFRecHitCollection* hf_hits = hfhits_.failedToGet () ? 0 : &*hfhits_;
if (hfhits_.isValid()) {
for (HFRecHitCollection::const_iterator j=hf_hits->begin(); j!=hf_hits->end(); j++) {
HcalDetId id = (*j).id();
int ieta= id.ieta();
int iphi= id.iphi();
int depth = id.depth();
float energy = (*j).energy();
float time = (*j).time();
int auxwd = (*j).aux();
histo1D["HFiEta"]->Fill(ieta);
histo1D["HFRecHitEnergy"]->Fill(energy);
}
}
Now initialize the histograms in beginJob()class.
#Find
histo1D["HERecHitEnergy"] = fs->make<TH1D>( "HERecHitEnergy", "HE: Energy Distibution",300,0,300);
histo1D["HERecHitEnergy"]->GetXaxis()->SetTitle("GeV");
histo1D["HERecHitEnergy"]->GetYaxis()->SetTitle("Number of Hits");
#Add Underneath
histo1D["HFiEta"] = fs->make<TH1D>("HFiEta", "iEta vs Number Of Hits",90,-45,45);
histo1D["HFiEta"]->GetXaxis()->SetTitle("i#eta");
histo1D["HFiEta"]->GetYaxis()->SetTitle("Number of Hits");
histo1D["HFRecHitEnergy"] = fs->make<TH1D>( "HFRecHitEnergy", "HF: Energy Distibution",300,0,300);
histo1D["HFRecHitEnergy"]->GetXaxis()->SetTitle("GeV");
histo1D["HFRecHitEnergy"]->GetYaxis()->SetTitle("Number of Hits");After saving the DemoAnalyzer.cc file with :wq , we run the following command to compile our script.
You should note that after every change in the
DemoAnalyzer.ccfile, you must compile it with scram.
scram b -j 8Now we also need to define the collection (module name) to our config file:
vi python/ConfFile_cfg.py#Find
HBHERecHitCollection = cms.InputTag("hbhereco"),
#Add Underneath
HFRecHitCollection = cms.InputTag("hfreco"),Now, Let's run with the following command line and see the results as we did before with the root -l Results2018.rootcommand and using TBrowser b.
cmsRun python/ConfFile_cfg.pyCongratulations!! From now, you can easily analyze the CMS data.
You need to get your Grid Certificate in order to access the CERN data and some CERN websites that requiring this certificate. Such as; CMS DAS.
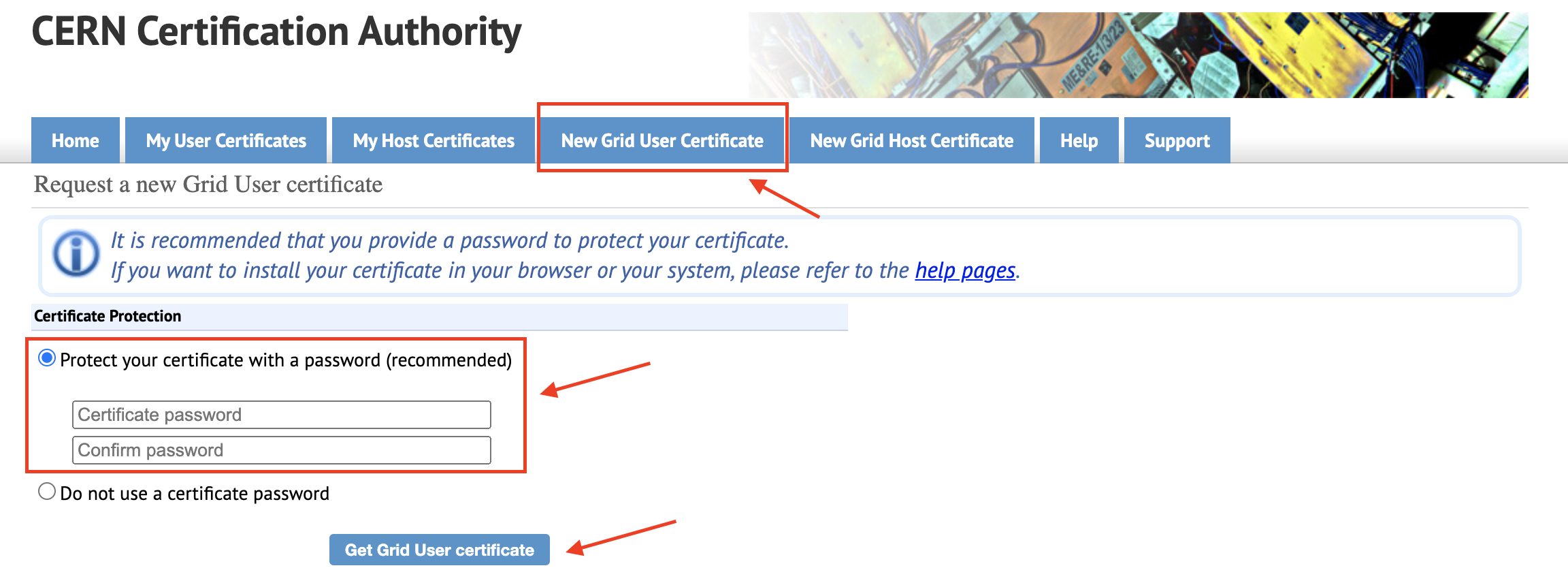
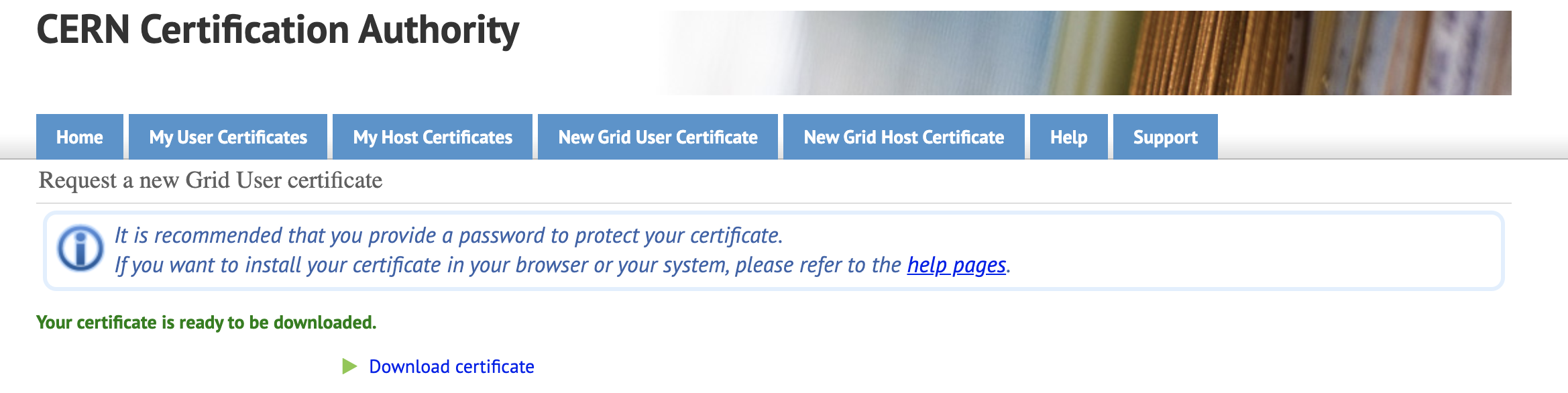
You need to go to the following link to request a CERN Grid Certificate. Type a new Grid Certificate password that you'll NOT forget. Because you'll use that password when you want to reach the CERN data. Click on "Get Grid User certificate" button.
https://ca.cern.ch/ca/user/Request.aspx?template=EE2User
Click on "Download Certificate" label and download your certificate to your computer.
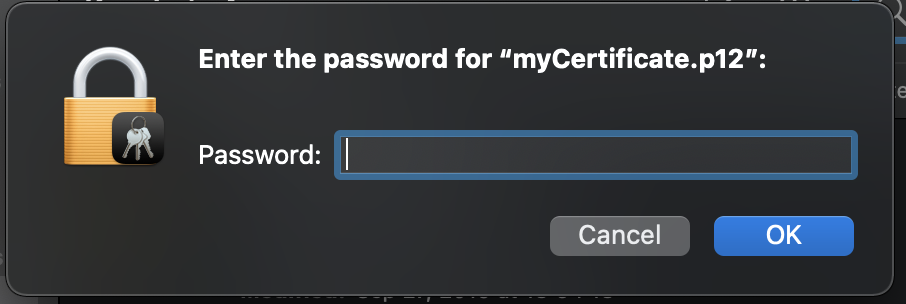
For Mac:
Double click on your certificate and use your fingerprint (touchID) of your Mac or type your macbook user password. Then, it'll ask your grid certificate password. Type the password that you set when you create the Grid Certificate and click "OK".
For Windows & Linux:
You need to add your certificate to your Mozilla Firefox or Chrome from settings of your browser. https://ca.cern.ch/ca/Help/?kbid=040110
For more information, please follow this link: https://ca.cern.ch/ca/Help/?kbid=024010
When you have a Grid Certificate, you have to register your certificate in the CMS Virtual Organisation (VO) in order to be authorized to use CMS resources.
You should note that you only need to register at your first time. When your certificate expires, you do not need to register for VO again.
If you succesfully added your Grid Certificate to your browser (Firefox, Chrome, etc.) please follow these steps:
- Click on this link to reach the VOMSAdmin server and submit the registration form: https://voms2.cern.ch:8443/voms/cms/user/home.action
- After submitting the form, you will get a confirmation email that contains a link that you need to click to confirm your registration. Find the link and click it.
Select cmsuser on the "Select your groups and group roles" part.
- Now, you need to wait for final confirmation that will be done by the VO administrators, wait up to a couple days especially on weekends.
- When they confirm your registration request, you will get a notification email.
- Finally, you can sign up the AUP using the link in that mail, or go directly to https://voms2.cern.ch:8443/voms/cms/aup/sign.action
For more information, please follow this twiki page: https://twiki.cern.ch/twiki/bin/view/CMSPublic/SWGuideLcgAccess
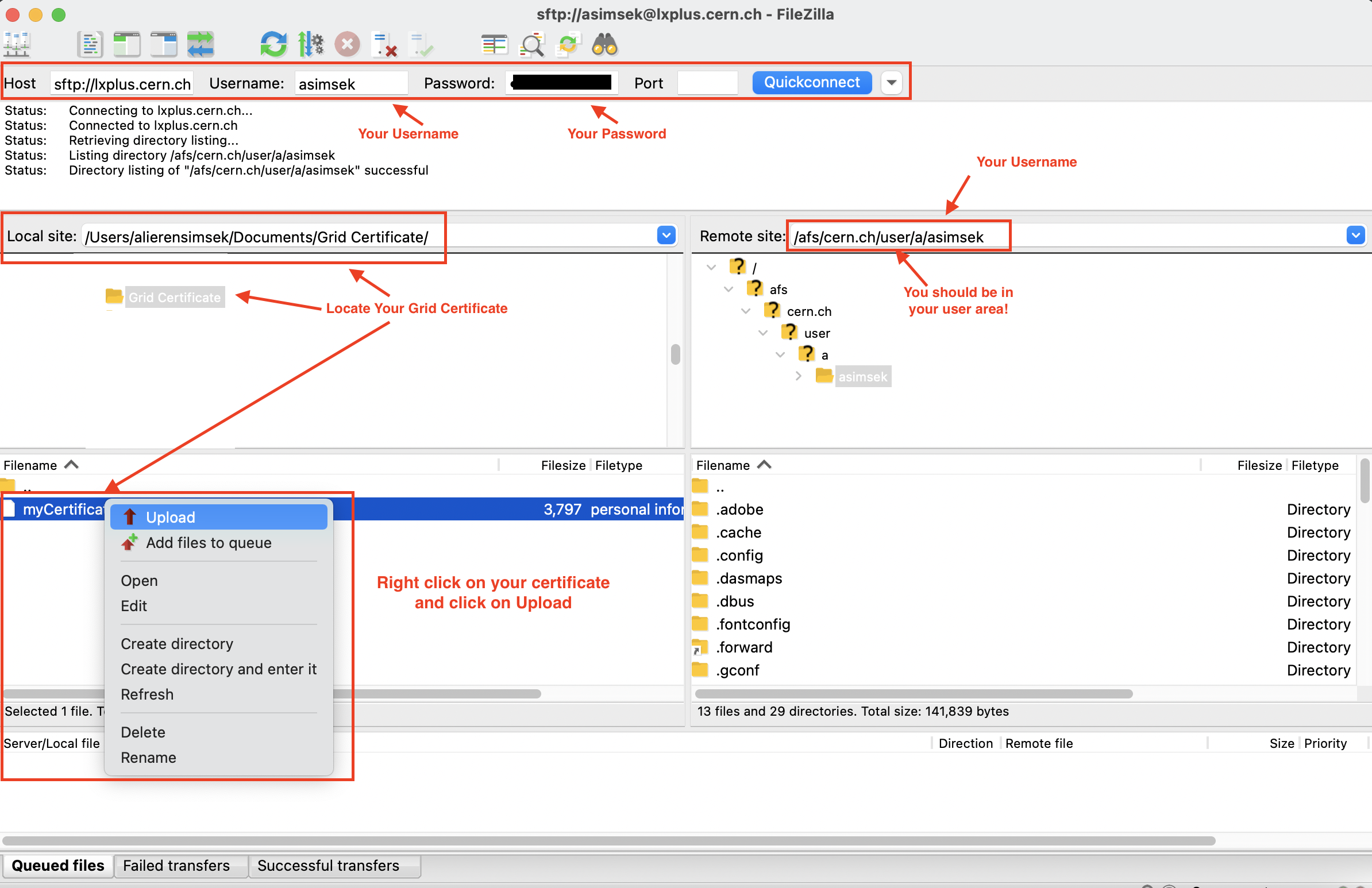
Now, let's upload your Grid Certificate to your lxplus area.
Download & install FileZilla app to your computer. After the installation is completed, run the application and connect your lxplus area as follows:
Then upload your Grid Certificate to your lxplus USER area as indicated in the picture below.
After you uploaded your certificate to your lxplus user area, open a new terminal window and connect to your lxplus area with:
ssh -Y yourUserName@lxplus.cern.ch
Then follow these commands:
cd ~
mkdir .globus
mv myCertificate.p12 .globus
cd ~/.globus
openssl pkcs12 -in myCertificate.p12 -clcerts -nokeys -out usercert.pem
openssl pkcs12 -in myCertificate.p12 -clcerts -nokeys -out $HOME/.globus/usercert.pem
openssl pkcs12 -in myCertificate.p12 -nocerts -out userkey.pem
chmod 400 userkey.pem
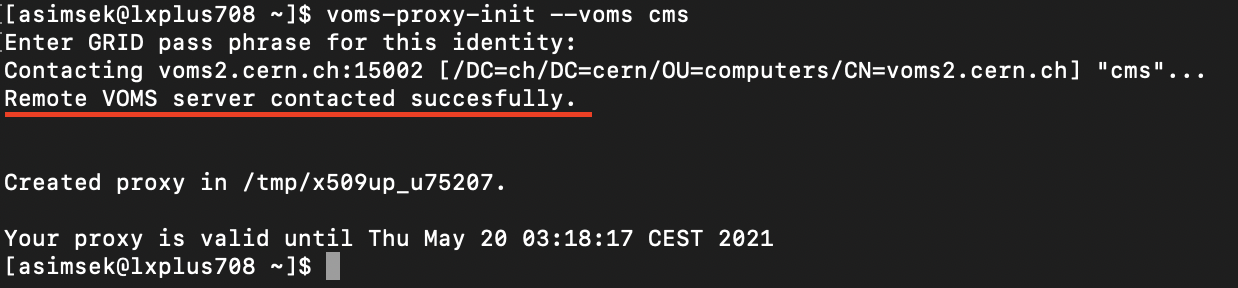
chmod 400 usercert.pemIf everything goes right, use the following command and see if you can create a proxy successfully.
voms-proxy-init --voms cmsYou should see a message as below indicating the VOMS connection is succesfull.
ps: Unless you complete the 2-step VO registration process, this command line will not open a proxy and will give you an error.
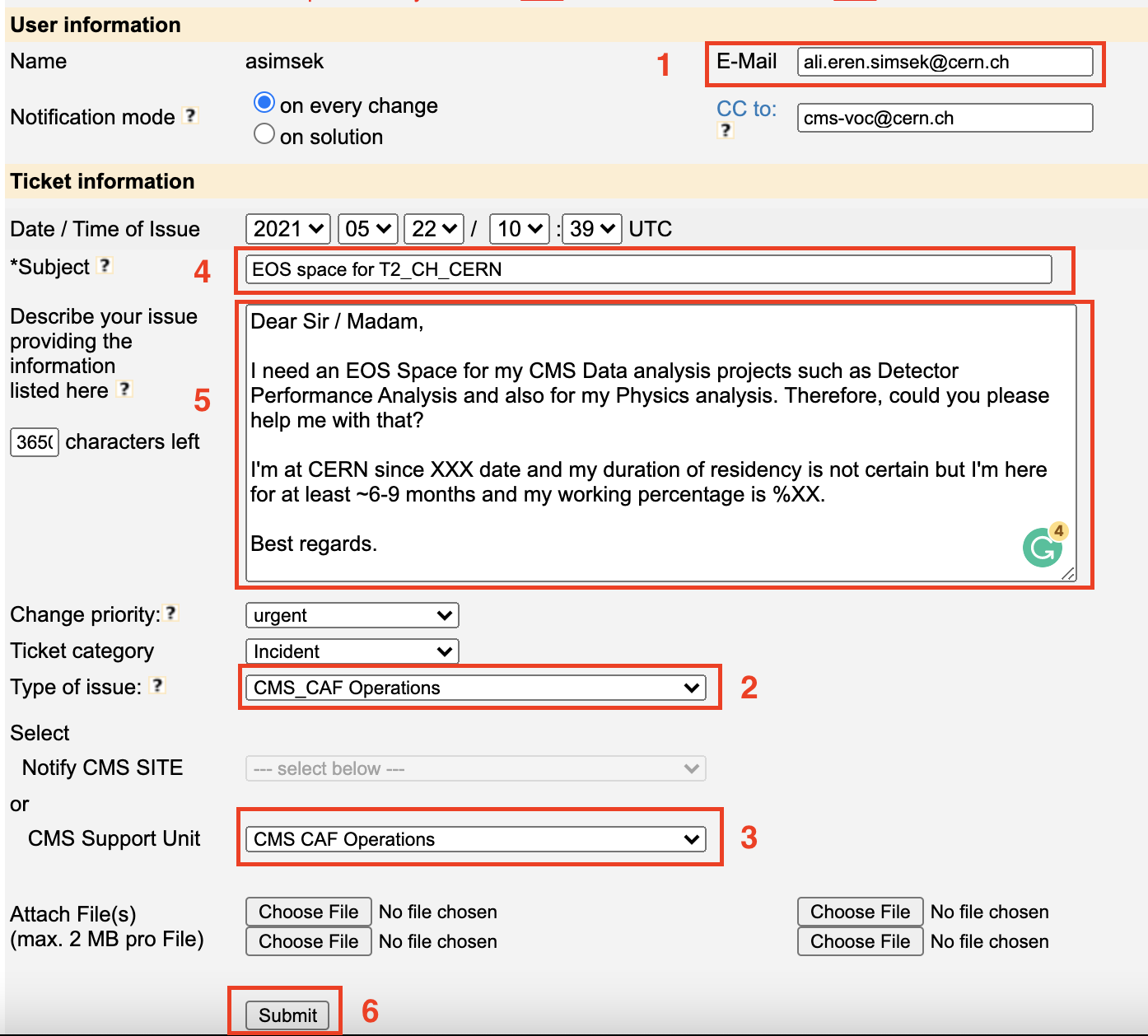
The CERN CMS T2 (EOS Space) is reserved for the CMS collaborators who are resident at CERN for more than 50% of their time for a period of at least a year. If you qualifiy for access to the the CERN CMS T2 you can gain access by submitting a GGUS ticket: (Open this link through your browser where you defined/add your Grid certificate.)
https://ggus.eu/?mode=ticket_cms
Please fill the form as shown below:
- Type of issue: CMS_CAF Operations
- CMS Support Unit: CMS_CAF Operations
- Subject: EOS space for T2_CH_CERN
- You should state in the ticket the start and the end date of your CERN residency, as well as the degree of residency (in %).
For more information: https://twiki.cern.ch/twiki/bin/viewauth/CMS/T2CHCERN#Right_of_access_to_CERN_CMS_T2 http://cp3.irmp.ucl.ac.be/downloads/RootTreeDescription.html
For more, please follow this twiki page: https://twiki.cern.ch/twiki/bin/view/CMSPublic/WorkBookWriteFrameworkModule?LOCALSHELL=bash