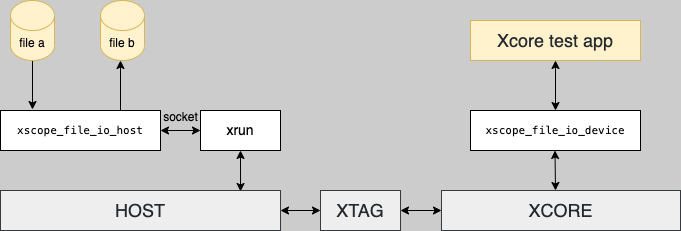
This library allows a program on the xCore to access binary files on the host machine via xscope.
Currently it supports:
- Arbitrary number (32 currently) of read or write files (not read/write)
- “wb” or “rb” file access mode only
- 6-8MBytes/s Device to Host speed
- Up to 1MBytes/s Host to Device speed (on tools 15.0.4)
This compares to around 2kBytes/s for fileio over JTAG supported using xrun --io.
pip install -e . or pip install .
To compile firmware code, add src_xcore to your source dirs and include dirs.
Ensure you use the config.xscope included in src_xcore.
If running on a Windows host, you will have to build the host endpoint yourself; the resulting executable
xscope_host_endpoint.exe must be placed in the host directory. The specific commands will vary depending
on your build system, but you can use cmake to generate build files for your build system using the -G
option, eg. cmake -G"NMake Makefiles" .
The host-side interface is written in Python. To run an xcore binary with access to xscope fileIO, use:
xscope_fileio.run_on_target(adapter_id, firmware_xe, use_xsim=False)
This can be combined with xtagctl e.g.:
with xtagctl.acquire("XCORE-AI-EXPLORER") as adapter_id:
xscope_fileio.run_on_target(adapter_id, device_xe)
Source and header files for device code are found in src_xcore
void xscope_io_init(chanend_t xscope_end); unsigned xscope_fileio_is_initialized(void); xscope_file_t xscope_open_file(char* filename, char* attributes); //NOTE MAXIMUM n_bytes_to_read of 64kB on Linux http://bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=18528 size_t xscope_fread(xscope_file_t *xscope_io_handle, uint8_t *buffer, size_t n_bytes_to_read); void xscope_fwrite(xscope_file_t *xscope_io_handle, uint8_t *buffer, size_t n_bytes_to_write); void xscope_fseek(xscope_file_t *xscope_io_handle, int offset, int whence); int xscope_ftell(xscope_file_t *xscope_file); void xscope_close_all_files(void);
The device side application requires a multi-tile main since it uses the xscope_host_data(xscope_chan); service to communicate with the host, which requires this. See examples for XC and C applications for how to do this.
You will also need a copy of config.xscope in your firmware directory. This
enables xscope in the tools and sets up the xscope probes used by fileio for communicating with the host app. You
can find a copy in xscope_fileio/config.xscope xscope_fileio/config.xscope.txt which you should rename to config.xscope.
Note currently missing from fileio api:
fprintf, fscanf
The run_on_target function calls xrun --xscope-port with the binary and specified target adapter,
and simultaneously launches a host application to communicate xscope data to/from
the xrun process via sockets. The host application responds to xscope_fileio API calls
in the firmware code, reading/writing to the host file system.
The call to run_on_target returns when the firmware exits.