Opinionated implementation of the Jakarta JSON binding API. It is not spec compliant and requires explicit configuration with annotations rather than relying on naming conventions or the Java Beans specification.
Why explicit configuration? Because I want to maximize the freedom of being able to refactor your code as
required without fear of breakage. If the application relies on naming conventions there is a much higher chance of
something breaking when refactoring. It also clearly communicates intent when a method is annotated with
@JsonbProperty("name")
that it will be included in the JSON output rather than just seeing a method called getName().
There is also the possibility to designate @JsonbProperty as "methods annotated with this are used" which can improve
the feedback your IDE can provide instead of potentially falsely marking it as unused.
Java 17. This library uses reflection so your classes used for (de-)serialization must therefore be at least opened in their module definition.
Write your application against the Jakarta JSON binding API. Make Donkey available during runtime, and it will be used as the provider. An implementation of Jakarta JSON processing must also be available during runtime.
Donkey comes with an annotation processing module located at io.github.asvanberg:donkey-apt.
It is highly recommended using this module as it increases serialization performance.
If you are building a modular application you have to explicitly configure the annotation processor by adding the
artifact coordinates to the Maven compiler configuration using annotation processor paths.
You also need to add requires static io.github.asvanberg.donkey.apt to module-info.java.
Non-modular apps requires no extra configuration besides adding the provided dependency.
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.asvanberg</groupId>
<artifactId>donkey</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.asvanberg</groupId>
<artifactId>donkey-apt</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>requires io.github.asvanberg.donkey;
requires static io.github.asvanberg.donkey.apt
When serializing objects only public methods annotated with @JsonbProperty
and whose value
is explicitly set will be included in the JSON.
Empty Optional and null values will not be included in the JSON output unless @JsonbProperty#nillable
is set to true.
When deserializing objects they must have a constructor or static method annotated with @JsonbCreator
and all parameters must be annotated with @JsonbProperty and have an explicit value set.
null in JSON will only be deserialized into String, Optional, or @JsonbCreatorobjects, other types will fail.
- (De-)serialization of the following;
- Primitives (and wrappers)
Stringjava.time.{Instant, LocalDate, LocalTime, LocalDateTime, OffsetDateTime}(using their respective ISO formats)List<E>,Set<E>, andCollection<E>Map<String, E>Optional(and primitive specializations)- Enums
java.net.URIjava.util.UUID- Other types (including records) are treated as annotated objects according to the above paragraphs
@JsonbDateFormat(Instantonly supports the special case TIME_IN_MILLIS)- Type-level
@JsonbTypeAdapter - Configured
JsonbAdapters - Locale configuration which is relevant for certain date formats
Using Donkey 1.4.0 (with annotation processing) and Yasson 2.0.4.
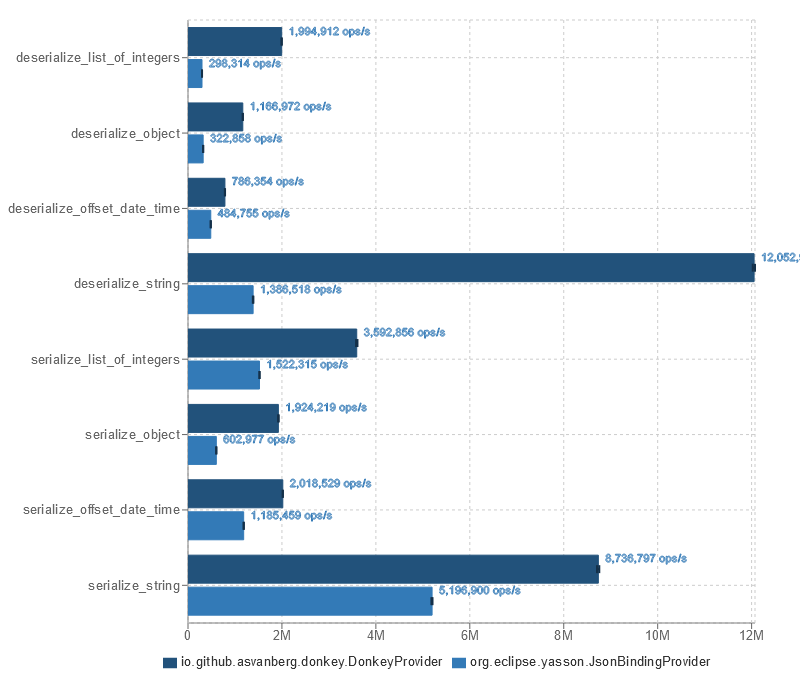
mvnw -f benchmark/pom.xml clean package
java -jar benchmark/target/benchmarks.jar
