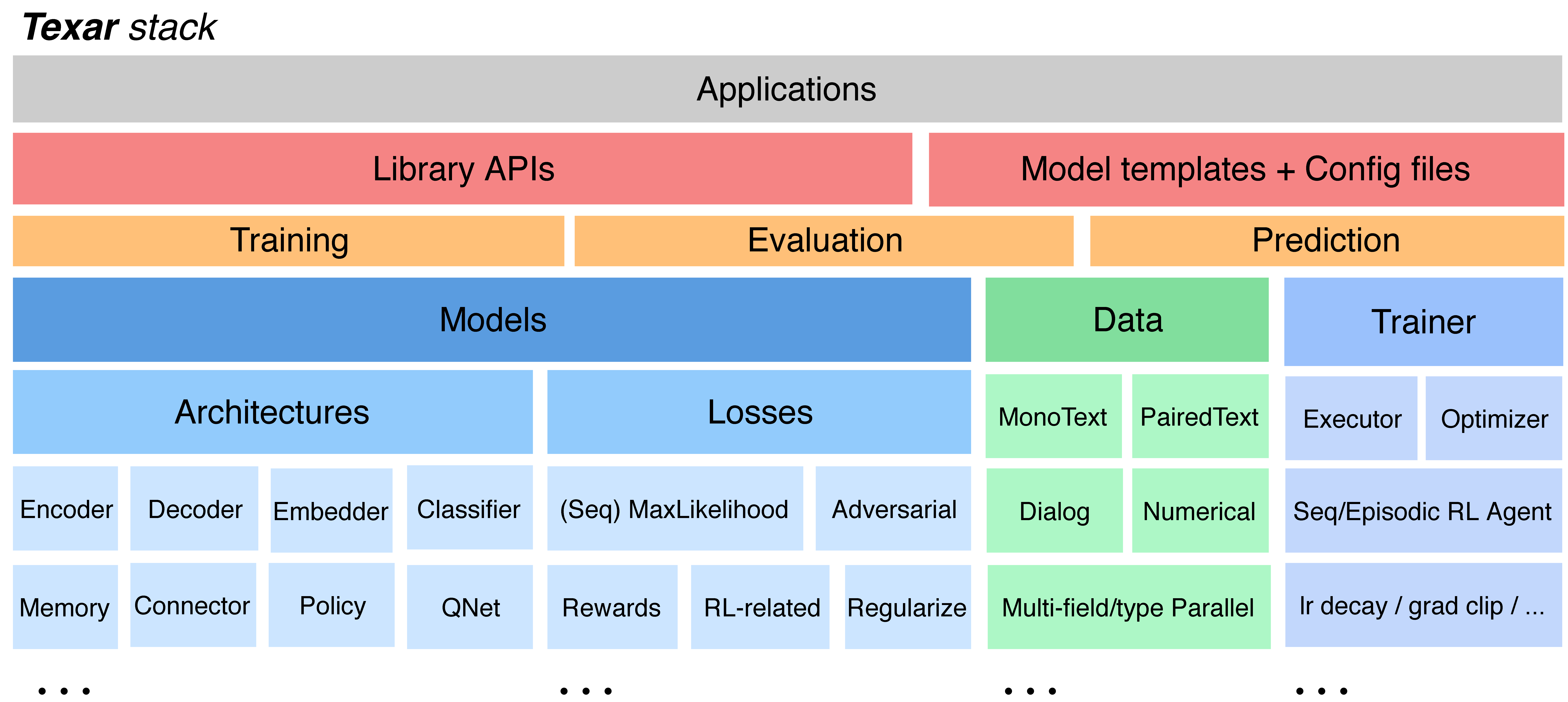
Texar-PyTorch is a toolkit aiming to support a broad set of machine learning, especially natural language processing and text generation tasks. Texar provides a library of easy-to-use ML modules and functionalities for composing whatever models and algorithms. The tool is designed for both researchers and practitioners for fast prototyping and experimentation. Texar-PyTorch was originally developed and is actively contributed by Petuum and CMU in collaboration with other institutes. A mirror of this repository is maintained by Petuum Open Source.
Texar-PyTorch integrates many of the best features of TensorFlow into PyTorch, delivering highly usable and customizable modules superior to PyTorch native ones.
- Two Versions, (Mostly) Same Interfaces. Texar-PyTorch (this repo) and Texar-TF have mostly the same interfaces. Both further combine the best design of TF and PyTorch:
- Interfaces and variable sharing in PyTorch convention
- Excellent factorization and rich functionalities in TF convention.
- Versatile to support broad needs:
- data processing, model architectures, loss functions, training and inference algorithms, evaluation, ...
- encoder(s) to decoder(s), sequential- and self-attentions, memory, hierarchical models, classifiers, ...
- maximum likelihood learning, reinforcement learning, adversarial learning, probabilistic modeling, ...
- Fully Customizable at multiple abstraction level -- both novice-friendly and expert-friendly.
- Free to plug in whatever external modules, since Texar is fully compatible with the native PyTorch APIs.
- Modularized for maximal re-use and clean APIs, based on principled decomposition of Learning-Inference-Model Architecture.
- Rich Pre-trained Models, Rich Usage with Uniform Interfaces. BERT, GPT2, XLNet, etc, for encoding, classification, generation, and composing complex models with other Texar components!
- Clean, detailed documentation and rich examples.
A code example that builds and trains a Conditional GPT2 model (e.g., for machine translation and text summarization):
import texar.torch as tx
from texar.torch.run import *
# (1) Modeling
class ConditionalGPT2Model(nn.Module):
"""An encoder-decoder model with GPT-2 as the decoder."""
def __init__(self, vocab_size):
super().__init__()
# Use hyperparameter dict for model configuration
self.embedder = tx.modules.WordEmbedder(vocab_size, hparams=emb_hparams)
self.encoder = tx.modules.TransformerEncoder(hparams=enc_hparams)
self.decoder = tx.modules.GPT2Decoder("gpt2-small") # With pre-trained weights
def _get_decoder_output(self, batch, train=True):
"""Perform model inference, i.e., decoding."""
enc_states = self.encoder(inputs=self.embedder(batch['source_text_ids']),
sequence_length=batch['source_length'])
if train: # Teacher-forcing decoding at training time
return self.decoder(
inputs=batch['target_text_ids'], sequence_length=batch['target_length'] - 1,
memory=enc_states, memory_sequence_length=batch['source_length'])
else: # Beam search decoding at prediction time
start_tokens = torch.full_like(batch['source_text_ids'][:, 0], BOS)
return self.decoder(
beam_width=5, start_tokens=start_tokens,
memory=enc_states, memory_sequence_length=batch['source_length'])
def forward(self, batch):
"""Compute training loss."""
outputs = self._get_decoder_output(batch)
loss = tx.losses.sequence_sparse_softmax_cross_entropy( # Sequence loss
labels=batch['target_text_ids'][:, 1:], logits=outputs.logits,
sequence_length=batch['target_length'] - 1) # Automatic masking
return {"loss": loss}
def predict(self, batch):
"""Compute model predictions."""
sequence, _ = self._get_decoder_output(batch, train=False)
return {"gen_text_ids": sequence}
# (2) Data
# Create dataset splits using built-in data loaders
datasets = {split: tx.data.PairedTextData(hparams=data_hparams[split])
for split in ["train", "valid", "test"]}
model = ConditionalGPT2Model(datasets["train"].target_vocab.size)
# (3) Training
# Manage the train-eval loop with the Executor API
executor = Executor(
model=model, datasets=datasets,
optimizer={"type": torch.optim.Adam, "kwargs": {"lr": 5e-4}},
stop_training_on=cond.epoch(20),
log_every=cond.iteration(100),
validate_every=cond.epoch(1),
train_metric=("loss", metric.RunningAverage(10, pred_name="loss")),
valid_metric=metric.BLEU(pred_name="gen_text_ids", label_name="target_text_ids"),
save_every=cond.validation(better=True),
checkpoint_dir="outputs/saved_models/")
executor.train()
executor.test(datasets["test"])Many more examples are available here.
Texar-PyTorch requires:
python == 3.6or3.7torch >= 1.0.0. Please follow the official instructions to install the appropriate version.
After torch is installed, install Texar from PyPI:
pip install texar-pytorchTo use cutting-edge features or develop locally, install from source:
git clone https://github.com/asyml/texar-pytorch.git
cd texar-pytorch
pip install .
To use tensorboard support with Executor, please install tensorboardX with the following command
pip install tensorboardX
If you use Texar, please cite the tech report with the following BibTex entry:
Texar: A Modularized, Versatile, and Extensible Toolkit for Text Generation
Zhiting Hu, Haoran Shi, Bowen Tan, Wentao Wang, Zichao Yang, Tiancheng Zhao, Junxian He, Lianhui Qin, Di Wang, Xuezhe Ma, Zhengzhong Liu, Xiaodan Liang, Wanrong Zhu, Devendra Sachan and Eric Xing
ACL 2019
@inproceedings{hu2019texar,
title={Texar: A Modularized, Versatile, and Extensible Toolkit for Text Generation},
author={Hu, Zhiting and Shi, Haoran and Tan, Bowen and Wang, Wentao and Yang, Zichao and Zhao, Tiancheng and He, Junxian and Qin, Lianhui and Wang, Di and others},
booktitle={ACL 2019, System Demonstrations},
year={2019}
}