| Branch | Build | Coverage | PyPI | Gitter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Master | 
|
|||
| Develop |
A django ModelAdmin mixin which adds advanced filtering abilities to the admin.
Mimics the advanced search feature in VTiger, see here for more info
For release notes, see Changelog
- Django >= 1.9 (Django 1.9 - 3.0 on Python 2/3/PyPy3)
- django-braces >= 1.4, < 1.14.0
- simplejson >= 3.6.5, < 4
- Install from pypi:
pip install django-advanced-filters - Add
'advanced_filters'toINSTALLED_APPS. - Add
url(r'^advanced_filters/', include('advanced_filters.urls'))to your project's urlconf. - Run
python manage.py syncdborpython manage.py migrate(for django >= 1.7)
Extending a ModelAdmin is pretty straightforward:
from advanced_filters.admin import AdminAdvancedFiltersMixin
class ProfileAdmin(AdminAdvancedFiltersMixin, models.ModelAdmin):
list_filter = ('name', 'language', 'ts') # simple list filters
# specify which fields can be selected in the advanced filter
# creation form
advanced_filter_fields = (
'name',
'language',
'ts',
# even use related fields as lookup fields
'country__name',
'posts__title',
'comments__content',
)Adding a new advanced filter (see below) will display a new list filter named "Advanced filters" which will list all the filter the currently logged in user is allowed to use (by default only those he/she created).
Initially, each field in advanced_filter_fields is resolved into an
actual model field. That field's verbose_name attribute is then used as
the text of the displayed option. While uncommon, it occasionally makes
sense to use a custom name, especially when following a relationship, as
the context then changes.
For example, when a profile admin allows filtering by a user name as well as a sales representative name, it'll get confusing:
class ProfileAdmin(AdminAdvancedFiltersMixin, models.ModelAdmin):
advanced_filter_fields = ('name', 'sales_rep__name')In this case the field options will both be named "name" (by default).
To fix this, use custom naming:
class ProfileAdmin(AdminAdvancedFiltersMixin, models.ModelAdmin):
advanced_filter_fields = ('name', ('sales_rep__name', 'assigned rep'))Now, you will get two options, "name" and "assigned rep".
By default the mixin uses a template which extends django's built-in
change_list template. This template is based off of grapelli's fork
of this template (hence the 'grp' classes and funny looking javascript).
The default template also uses the superb magnificPopup which is currently bundled with the application.
Regardless of the above, you can easily write your own template which
uses context variables {{ advanced_filters }} and
{{ advanced_filters.formset }}, to render the advanced filter
creation form.
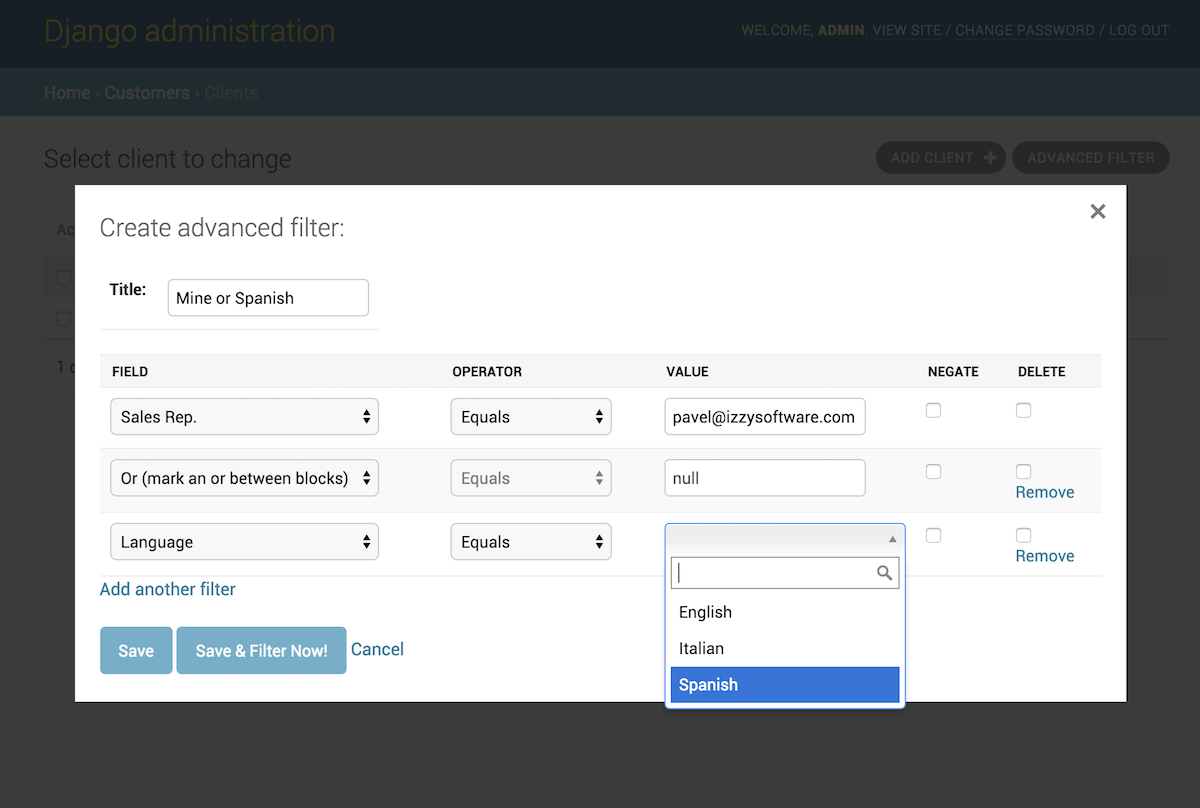
Each advanced filter has only a couple of required fields when constructed with the form; namely the title and a formset (consisting of a form for each sub-query or rule of the filter query).
Each form in the formset requires the following fields: field,
operator, value
And allows the optional negate and remove fields.
Let us go over each of the fields in a rule fieldset.
The list of all available fields for this specific instance of the
ModelAdmin as specific by the `advanced_filter_fields
property. <#integration-example>`__
OR is an additional field that is added to every rule's available
fields.
It allows constructing queries with OR statements. You can use it by creating an "empty" rule with this field "between" a set of 1 or more rules.
Query field suffixes which specify how the WHERE query will be
constructed.
The currently supported are as follows: iexact, icontains,
iregex, range, isnull, istrue and isfalse
For more detail on what they mean and how they function, see django's documentation on field lookups.
The value which the specific sub-query will be looking for, i.e the
value of the field specified above, or in django query syntax:
.filter(field=value)
A boolean (check-box) field to specify whether this rule is to be negated, effectively making it a "exclude" sub-query.
Similarly to other django formsets, used to remove the selected line on submit.
The AdvancedFilterAdmin class (a subclass of ModelAdmin) is
provided and registered with AdvancedFilter in admin.py module.
The model's change_form template is overridden from grapelli's/django's standard template, to mirror the add form modal as closely as possible.
Note: currently, adding new filters from the ModelAdmin change page is not supported.
TODO: write a few words on how serialization of queries is done.
Since version 1.0, AdvancedFilter are tightly coupled with a specific model
using the model field and the app_label.Name template.
On creation, model is populated based on the admin changelist it's created
in.
This change has a few benefits:
- The mixin can be used with multiple
ModelAdminclasses while performing specific query serialization and field validation that are at the base of the filter functionality. - Users can edit previously created filters outside of the
context of a changelist, as we do in the
`AdvancedFilterAdmin<#editing-previously-created-advanced-filters>`__. - Limit the
AdvancedListFiltersto limit queryset (and thus, the underlying options) to a specified model.
The GetFieldChoices view is required to dynamically (using javascript)
fetch a list of valid field choices when creating/changing an
AdvancedFilter.
- Add permission user/group selection functionality to the filter form
- Allow toggling of predefined templates (grappelli / vanilla django admin), and front-end features.
- Support more (newer) python/django versions