This notation provides an upper bound on the growth rate of a function.
It describes the limiting behavior of a function when the argument tends to a particular value or infinity.
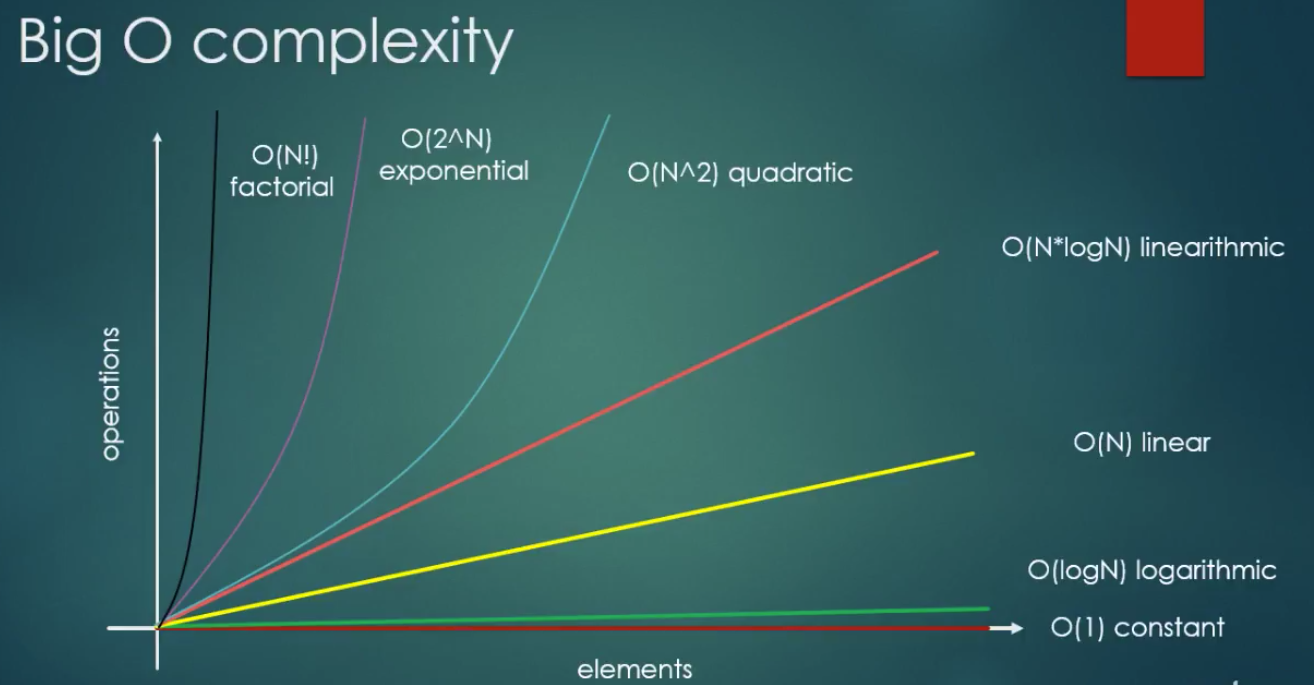
Time complexities
f(n) = c
Example: swap two numbers;
- O(logN) - Search in a sorted array with binary search;
- O(N) - Search for a max element in an unsorted array;
- O(N*logN) - Mergesort, quicksort, heapsort;
- O(N^2) - bubble sort
- O(2^N) - Travelling salesman problem with dynamic programming;
- O(N!) - Traveling salesman problem with brute force search;
Try to reduce algorithms complexity to linear or logarithmic time complexity.
Each node is composed of data and a reference to the next node in the sequence.
Time complexity based on activities:
- LinkedList (Dynamic data structures)
- Indexing: O(n)
- Insert at the beginning: O(1)
- Wast space: O(n) since we also store the reference to the next element.
- ArrayList
- Indexing: O(1)
- Insert at the beginning: O(n) we have to reallocate every other element in memory
- Wast space: 0
Use linked lists to inser/remove elements or if the list size changes frequently.
Use arrays if you need random access to the elements.
Linked lists allocate memory in run-time
Store items with different sizes whereas arrays assume all elements have the same size.
Nodes must be read in a sequencial order.
Difficult to reverse traversing. To do so we would have to implement doubly linked list.