@localfirst/relay is a tiny service that helps local-first applications connect with peers on
other devices. It can run in the cloud or on any device with a known address.
Deploy to: Glitch | Heroku | AWS | Google | Azure | local server
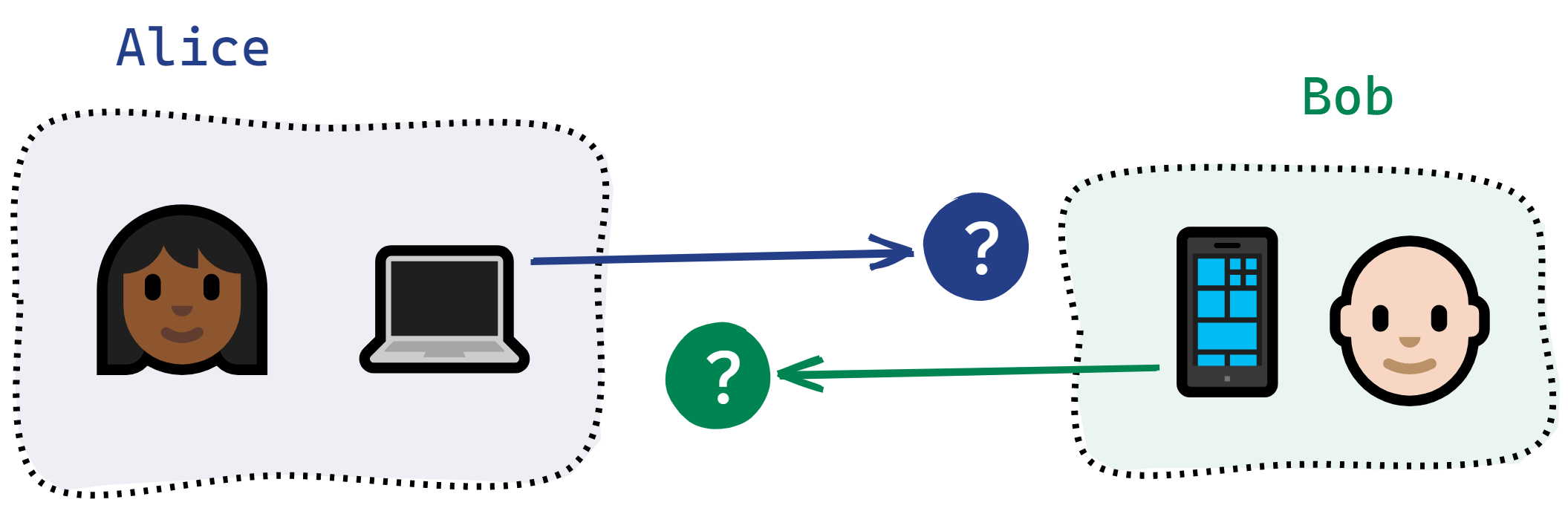
Getting two end-user devices to communicate with each other over the internet is hard. Most devices don't have stable public IP addresses, and they're often behind firewalls that turn away attempts to connect from the outside. This is a connection problem.
Even within a local network, or in other situations where devices can be reached directly, devices that want to communicate need a way to find each other. This is a problem of discovery.
This service offers a solution to each of these two problems.
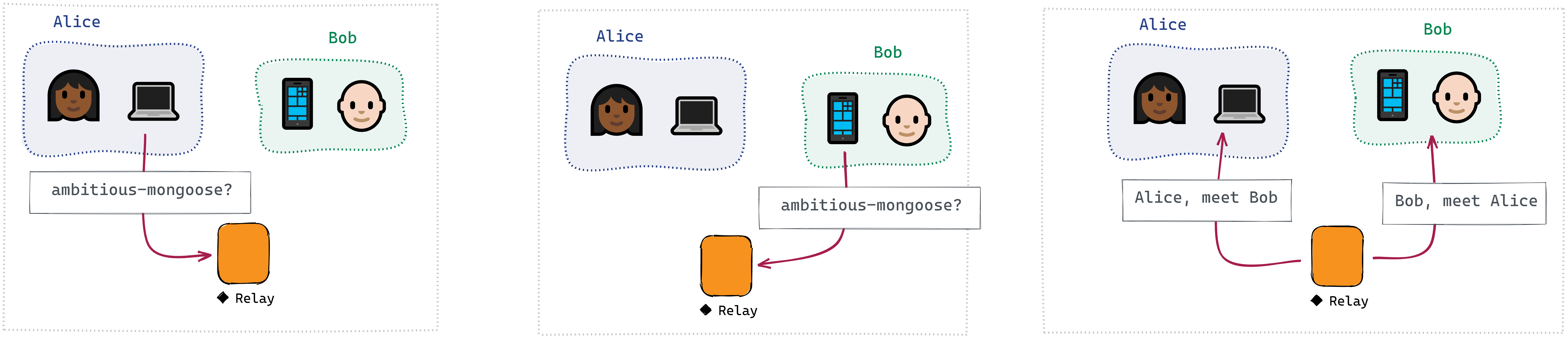
Alice can provide one or more document documentIds that she's interested in. (A document documentId is a unique ID
for a topic or channel — it could be a GUID, or just a string like ambitious-mongoose.)
If Bob is interested in the same documentId or documentIds, each will receive an Introduction message with the
other's userName. They can then use that information to connect.
Alice can request to connect with Bob on a given document documentId. If we get matching connection requests from Alice and Bob, we pipe their sockets together.
From this monorepo, you can run this server as follows:
$ yarn startYou should see something like thsi:
yarn run v1.22.4
$ yarn workspace @localfirst/relay start
$ node dist/start.js
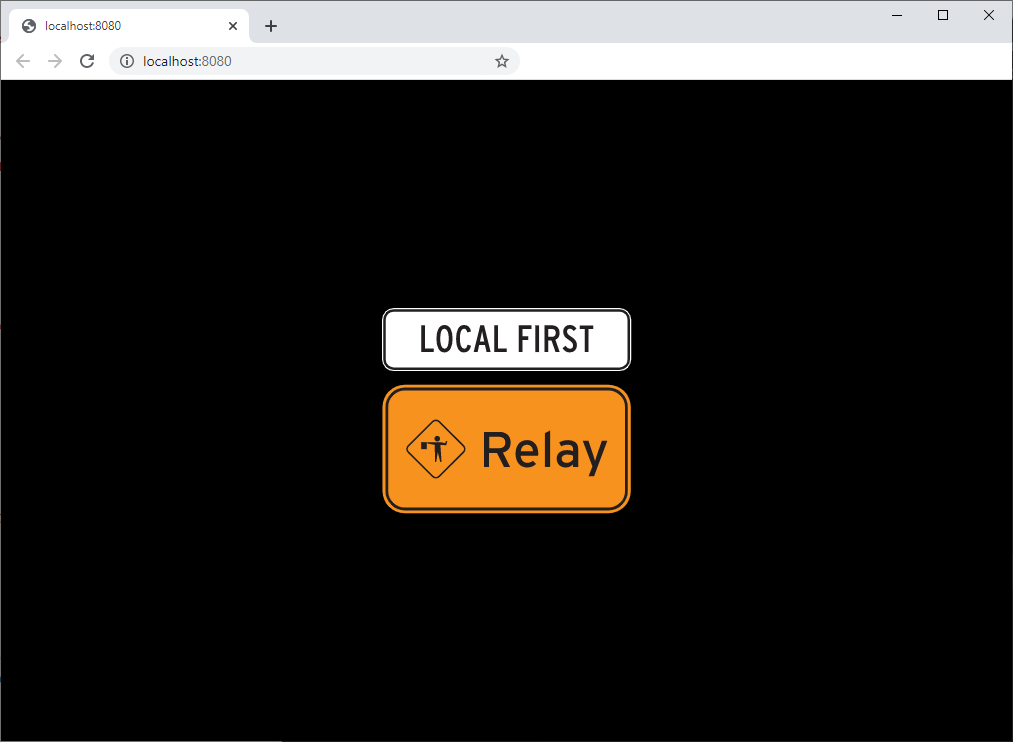
🐟 Listening at http://localhost:8080You can visit that URL with a web browser to confirm that it's working; you should see something like this:
The recommended way to stand one of these up is to use the relay-deployable repo, which is optimized for deployment.
See instructions for deploying to: Glitch | Heroku | AWS | Google | Azure | local server
@localfirst/relay-client, included in this repo, is a lightweight client library designed to be used with this server.
You don't strictly need to use this client - you could interact directly with the server the way we do in the server tests - but it automates the business of accepting invitations when they're received.
The client keeps track of all peers that the server connects you to, and for each peer it keeps track of each documentId (aka discoveryKey, aka channel) that you're working with that peer on.
client = new Client({ userName: 'alice', url: 'myrelay.somedomain.com' })
.join('ambitious-mongoose')
.on('peer.connect', ({ documentId, userName, socket }) => {
// `socket` is a WebSocket
// send a message
socket.write('Hello! 🎉')
// listen for messages
socket.on('data', message => {
console.log(`message from ${userName} about ${documentId}`, message)
})
})⚠ This server makes no security guarantees. Alice and Bob should probably:
- Authenticate each other, to ensure that "Alice" is actually Alice and "Bob" is actually Bob.
- Encrypt all communications with each other.
The @localfirst/auth library can be used with this relay service. It provides peer-to-peer authentication and end-to-end encryption, and allows you to treat this relay (and the rest of the network) as untrusted.
The following documentation might be of interest to anyone working on
@localfirst/relay-client, or replacing it with a new client. You don't need to know any of this to interact with this server if you're using the included client.
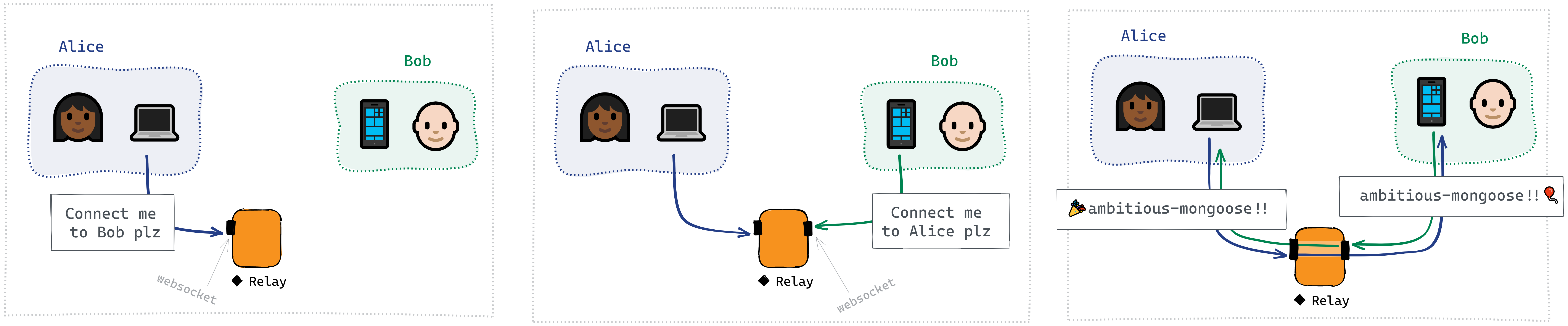
This server has two WebSocket endpoints: introduction and connection.
-
I connect to this endpoint, e.g.
wss://myrelay.somedomain.com/introduction/alice. -
:localIdis my unique client identifier. -
Once a WebSocket connection has been made, I send an introduction request containing one or more document IDs I'm interested in joining:
{ type: 'Join', join: ['ambitious-mongoose', 'frivolous-platypus'], // documents I have or am interested in }
-
If another peer is connected to the same server and interested in one or more of the same documents IDs, the server sends me an introduction message:
{ type: 'Introduction', userName: 'bob', // the peer's userName documentIds: ['ambitious-mongoose'] // documents we're both interested in }
-
I can now use this information to request a connection to this peer via the
connectionendpoint:
Once I've been given a peer's ID, I make a new connection to this endpoint, e.g.
wss://myrelay.somedomain.com/connection/alice/bob/ambitious-mongoose.
:localIdis my unique client identifier.:remoteIdis the peer's unique client identifier.:documentIdis the document ID.
If and when the peer makes a reciprocal connection, e.g.
wss://myrelay.somedomain.com/connection/bob/alice/ambitious-mongoose, the server pipes their sockets
together and leaves them to talk.
The client and server don't communicate with each other via the connection endpoint; it's purely a
relay between two peers.
MIT
Inspired by https://github.com/orionz/discovery-cloud-server
Formerly known as 🐟 Cevitxe Signal Server. (Cevitxe is now @localfirst/state)