A flowtrace is a persisted record of the execution of an Flow-based Programming (FBP) or dataflow program.
It is used for retroactive (after-the-fact) debugging; to locate, understand and fix bugs.
The concept is analogous to a 'stacktrace' or 'core dump' for imperative code.
This project will define a data format to store traces in, and provide debugging tools for working with these traces.
Minimally useful
- NoFlo has support for creating flowtraces, from noflo-nodejs 0.6 and noflo-runtime-msgflo 0.2.2
- Several commandline tools exist for working with flowtraces
- Note: File format not 100% finalized
- Some not-yet-useful timeline UI prototypes exist
See braindump and UI notes for ideas/plans.
First make sure you have Node.js with NPM installed.
To install locally in a project. Recommended.
npm install flowtrace
export PATH=./node_modules/.bin:$PATH
To install globablly on your system
npm install -g flowtrace
flowtrace-show reads a flowtrace, and renders a human-friendly log output from it.
./bin/flowtrace-show mytrace.flowtrace.json
Example output:
-> IN repeat CONN
-> IN repeat DATA hello world
-> IN stdout CONN
-> IN stdout DATA hello world
-> IN repeat DISC
-> IN stdout DISC
When used in a terminal, supports colors.
flowtrace-replay reads a flowtrace, and then acts as a live FBP runtime. That means it can be used with
any FBP IDEs/client which support the FBP runtime protocol.
flowtrace-replay mytrace.flowtrace.json
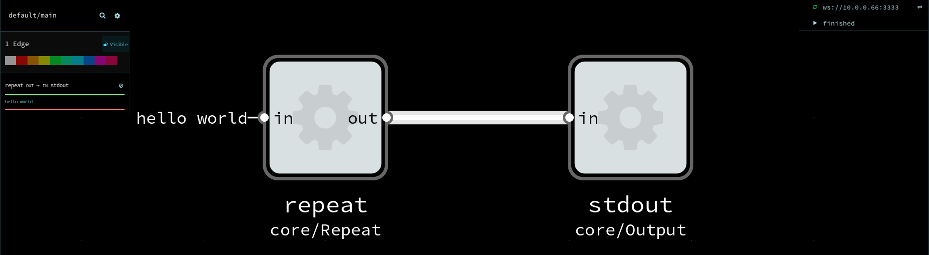
By default this will open Flowhub in your browser, automatically connect and show you the graph. To replay the data press the play button. You should then see the data flowing through edges.
You can specify which --ide to use, and disable automatic opening of browser with -n.
flowtrace-replay --ide http://localhost:8888 -n
You can also set the --host and --port. See --help for all options.