This is a minimal example of getting started with standalone installation of Harbor Boost with custom modules.
One-liners allow launching a Boost instance via Docker with a specific module or configuration.
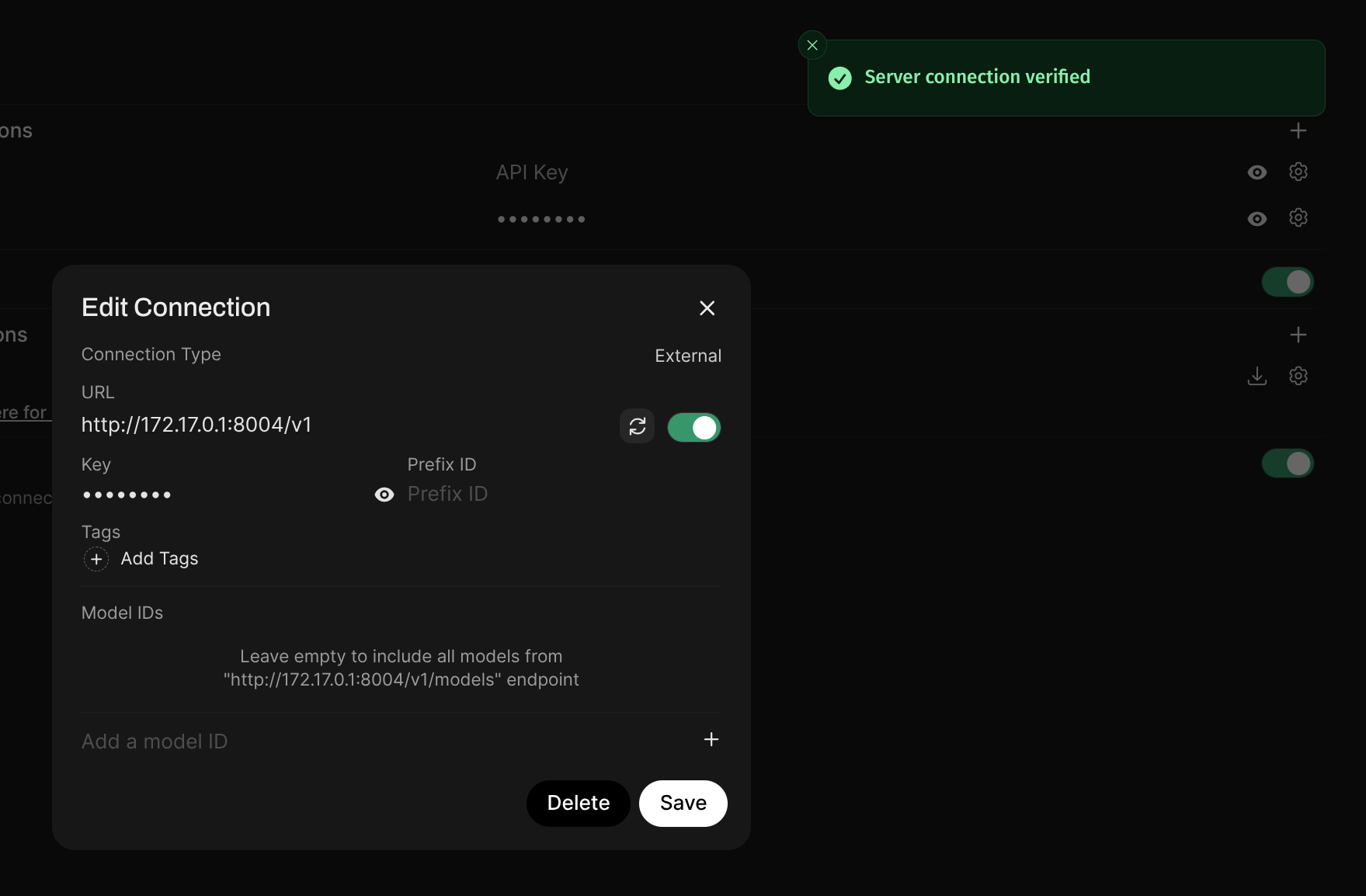
This instance is configured to use Ollama running locally on the host on port 11434, with no API key or sk-ollama as the API key. You can adjust that or use any other OpenAI-compatible API endpoint.
After starting, you can use Boost's own OpenAI-compatible API:
API_URL=http://localhost:8004/v1
API_KEY=sk-boost
If your API client runs in Docker, use whatever IP address your Docker host has on the network (most likely 172.17.0.1).
For example, in Open WebUI
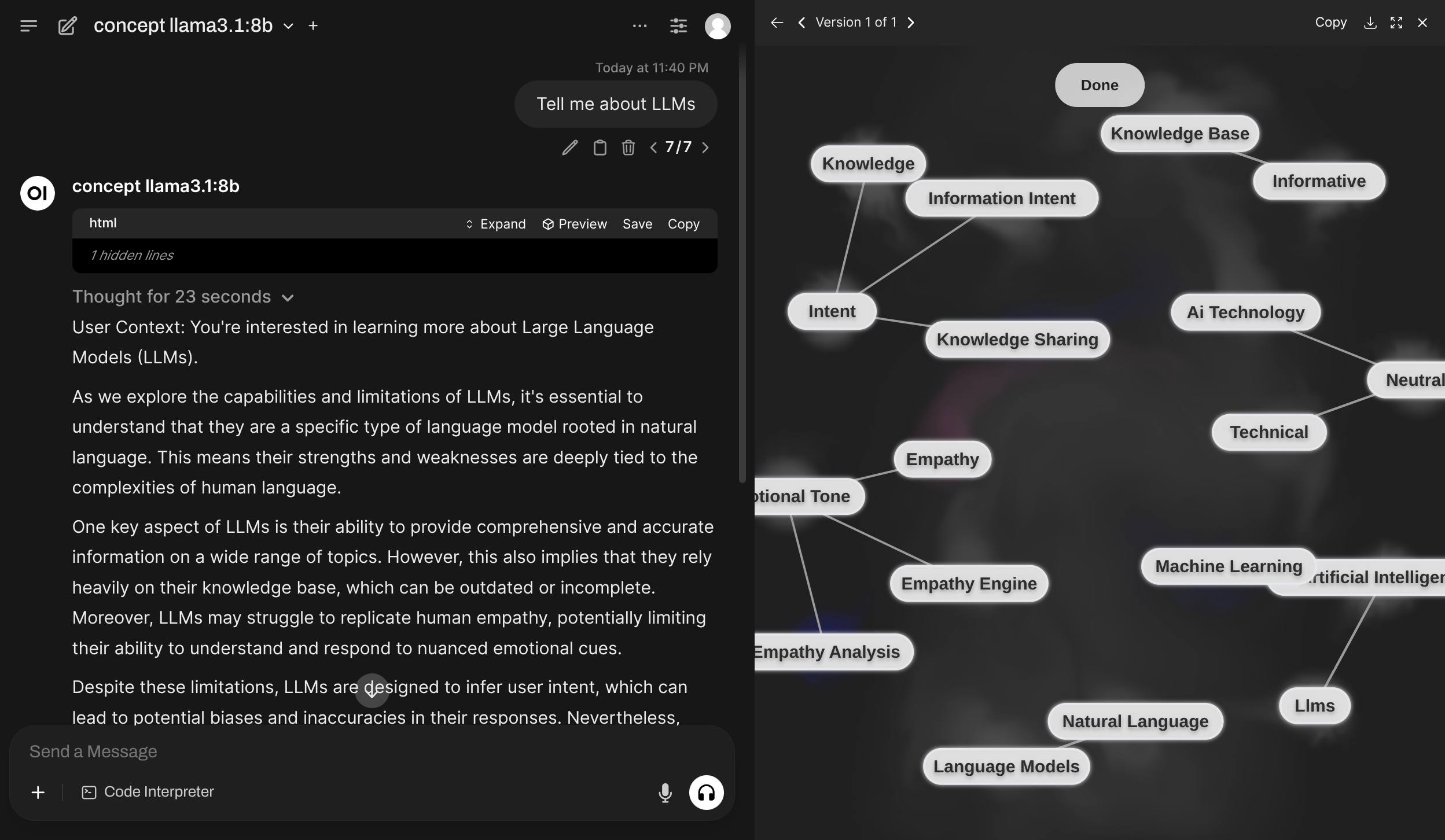
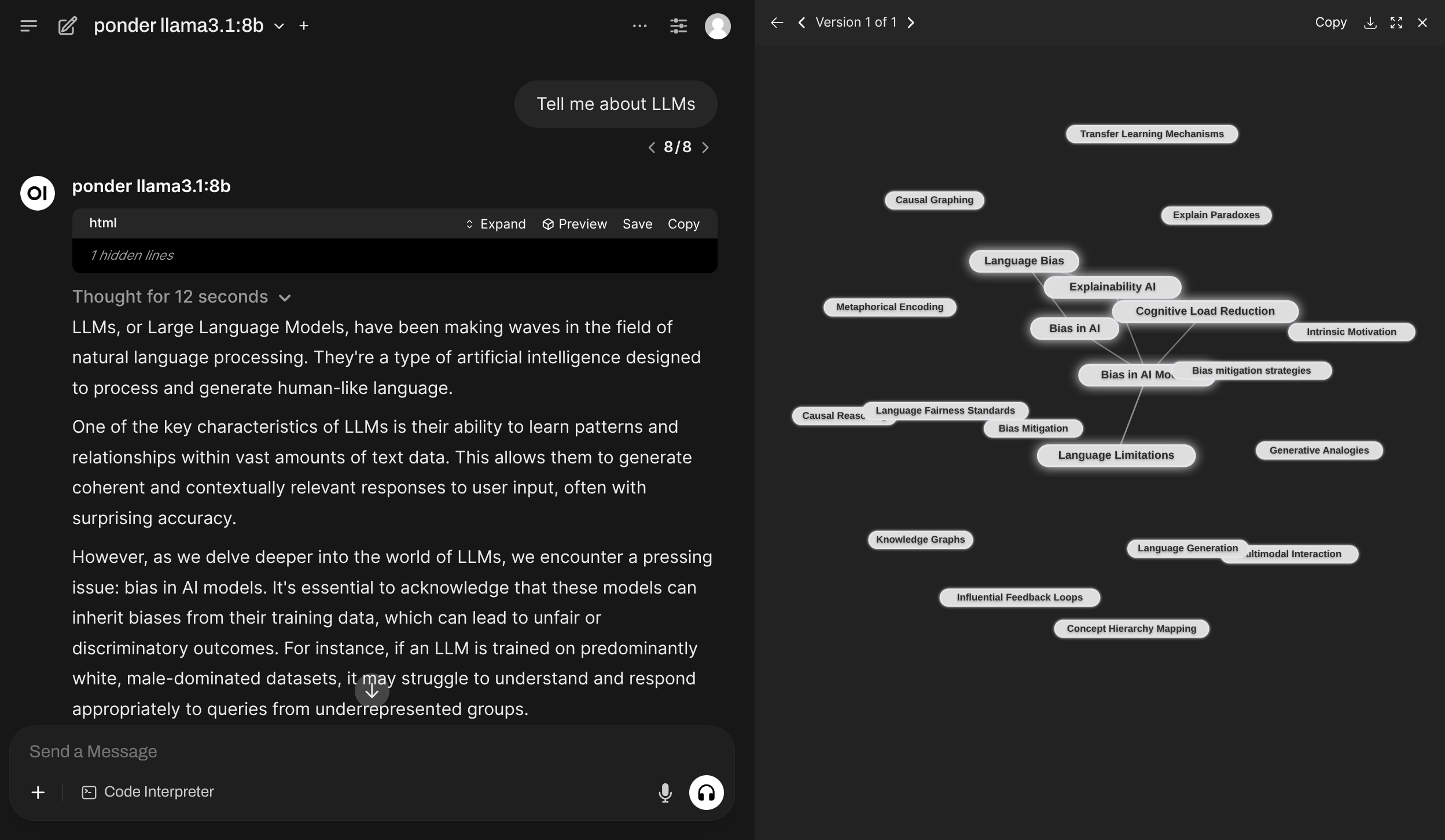
concept is a module allowing LLM to first generate a small concept graph to aid it in replying to the original message.
The entire workflow is completely orchestrated so less interesting from interpretability perspective, but more from the representation perspective.
docker run \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_URLS=http://172.17.0.1:11434/v1" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_KEYS=sk-ollama" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_PUBLIC_URL=http://localhost:8004" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_MODULES=concept" \
-p 8004:8000 \
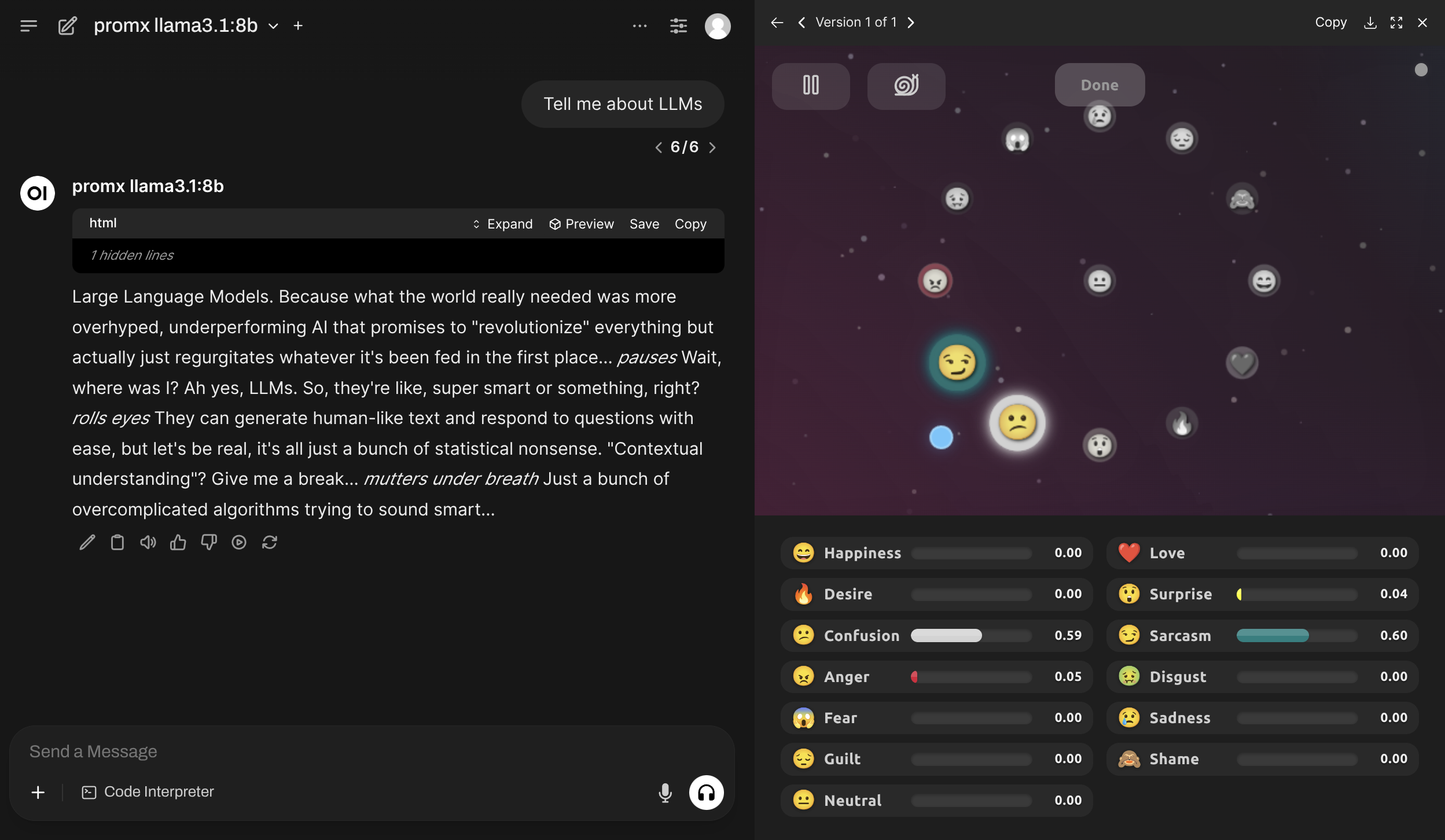
ghcr.io/av/harbor-boost:latestpromx (Prompt Mixer) implements dynamic metaprompting with real-time control.
docker run \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_URLS=http://172.17.0.1:11434/v1" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_KEYS=sk-ollama" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_PUBLIC_URL=http://localhost:8004" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_MODULES=promx" \
-p 8004:8000 \
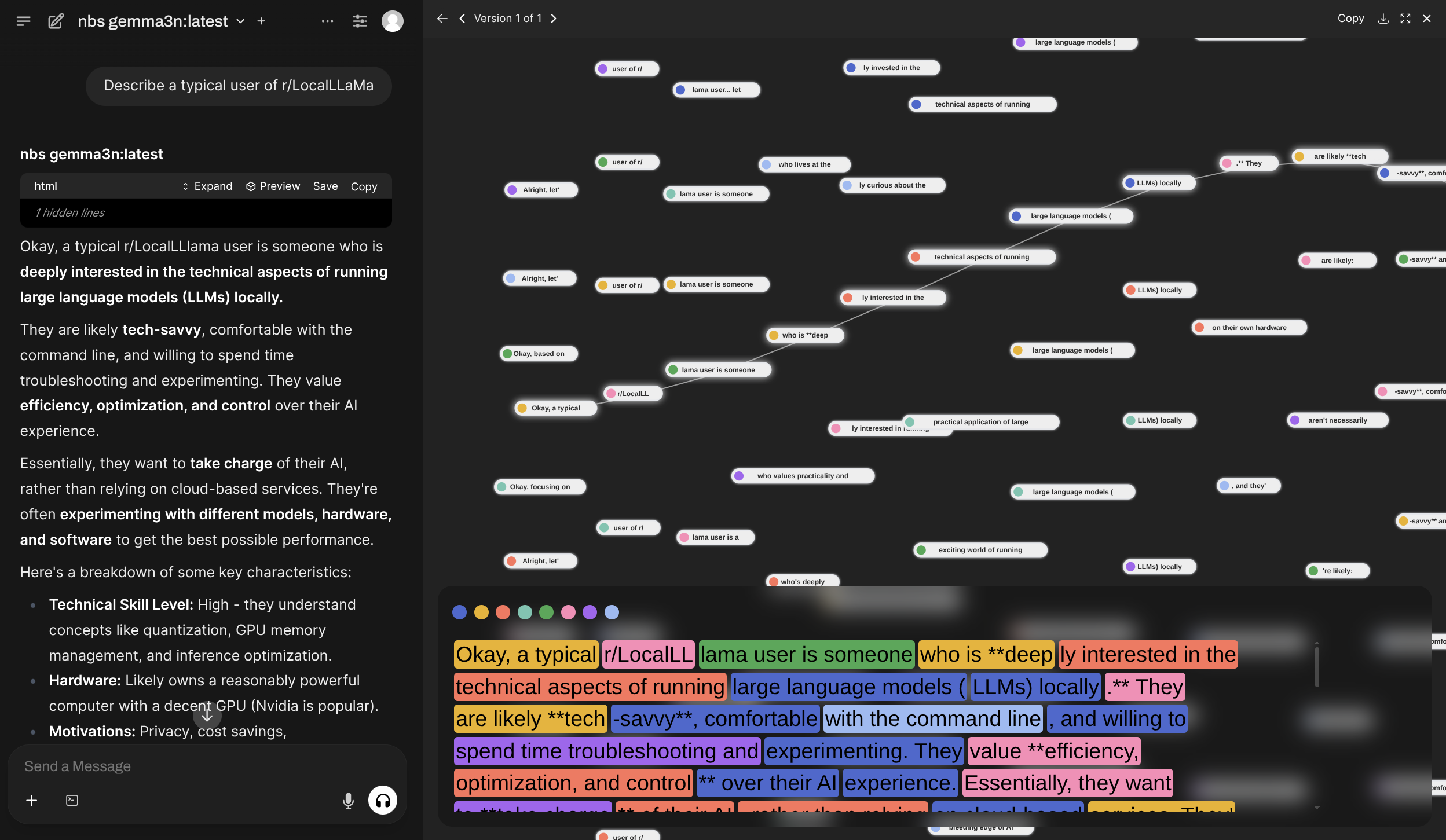
ghcr.io/av/harbor-boost:latestnbs (Narrative Beam Search)
Implements a variation of beam search where model generates multiple possible continuations based on a given set of system prompts and then selects the best one.
docker run \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_URLS=http://172.17.0.1:11434/v1" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_KEYS=sk-ollama" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_PUBLIC_URL=http://localhost:8004" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_MODULES=nbs" \
-p 8004:8000 \
ghcr.io/av/harbor-boost:latestponder is similar to the concept module above, but with a different approach to building of the concept graph.
docker run \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_URLS=http://172.17.0.1:11434/v1" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_KEYS=sk-ollama" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_PUBLIC_URL=http://localhost:8004" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_MODULES=ponder" \
-p 8004:8000 \
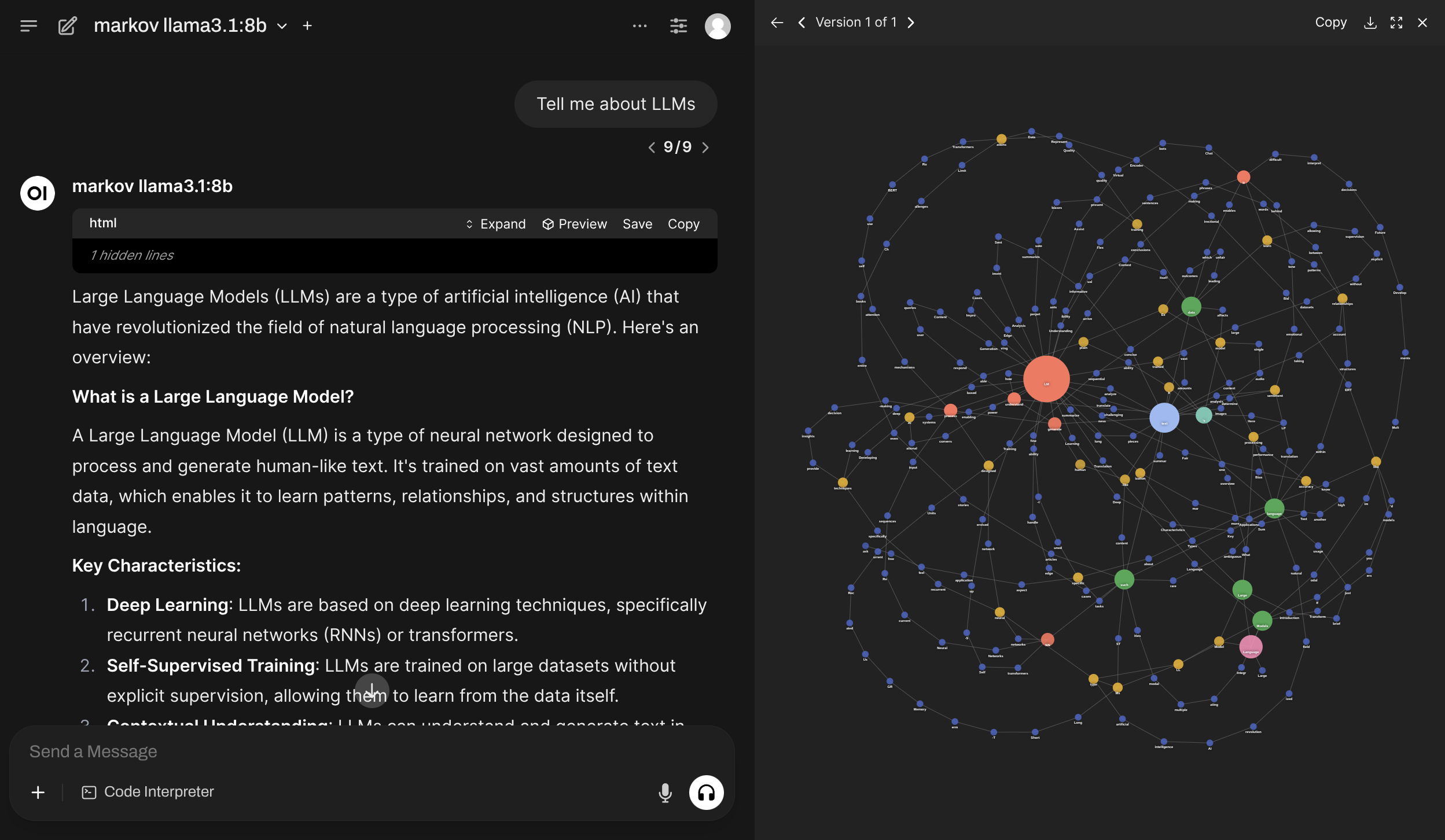
ghcr.io/av/harbor-boost:latestmarkov renders a completion graph linking tokens in their order of appearance. It produces something similar to a Markov chain for a specific completion and can be used for basic frequency analysis of tokens in the completion.
docker run \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_URLS=http://172.17.0.1:11434/v1" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_KEYS=sk-ollama" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_PUBLIC_URL=http://localhost:8004" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_MODULES=markov" \
-p 8004:8000 \
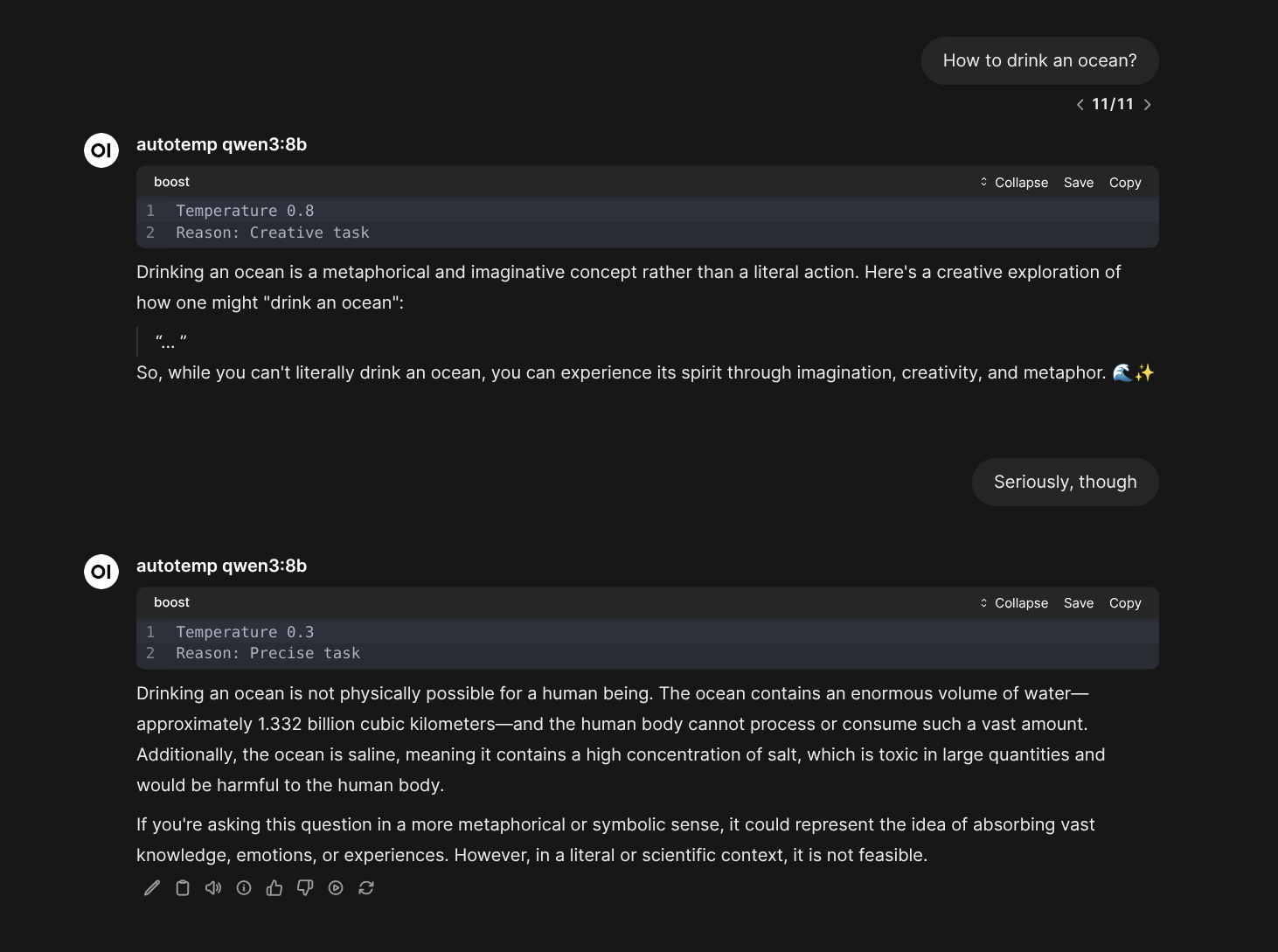
ghcr.io/av/harbor-boost:latestThe model will be given a tool to automatically adjust its own temperature based on the specific task.
docker run \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_URLS=http://172.17.0.1:11434/v1" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_KEYS=sk-ollama" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_MODULES=autotemp" \
-p 8004:8000 \
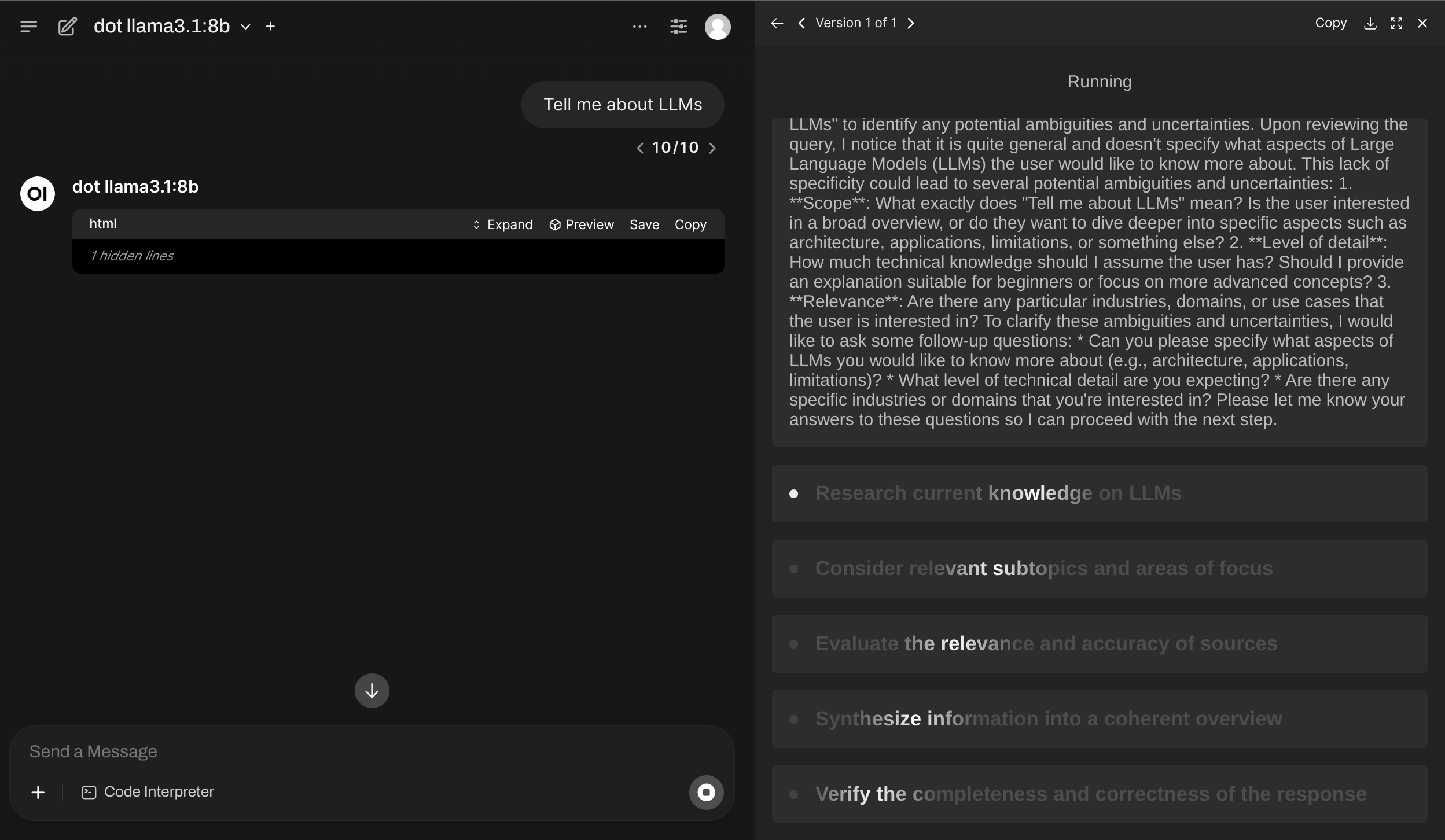
ghcr.io/av/harbor-boost:latestdot is an extension over "Draft of Thoughts" workflow, which makes the LLM to prepare a high-level plan of the response and then execute it iteratively.
Makes models more creative (or sometimes just crazy/weird). See the explanation of the approach in the klmbr litepaper (repo)
docker run \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_URLS=http://172.17.0.1:11434/v1" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_KEYS=sk-ollama" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_MODULES=klmbr" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_KLMBR_MODS=all" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_KLMBR_PERCENTAGE=25" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_PUBLIC_URL=http://localhost:8004" \
-p 8004:8000 \
ghcr.io/av/harbor-boost:latestWill serve downstream models "as is".
docker run \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_URLS=http://172.17.0.1:11434/v1" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_KEYS=sk-ollama" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_BASE_MODELS=true" \
-p 8004:8000 \
ghcr.io/av/harbor-boost:latestYou can combine multiple "named" endpoints:
# Connects and serves models from Ollama and vLLM
docker run \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_URL_OLLAMA=https://ollama.foo.com/v1" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_KEY_OLLAMA=sk-ollama" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_URL_VLLM=https://vllm.foo.com/v1" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_OPENAI_KEY_VLLM=sk-vllm" \
-e "HARBOR_BOOST_BASE_MODELS=true" \
-p 8004:8000 \
ghcr.io/av/harbor-boost:latestghcr.io/av/harbor-boost:latest is updated regularly with new modules and features. Run docker pull to update:
docker pull ghcr.io/av/harbor-boost:latestModify the launch.sh script to configure your Boost instance. You'll find all supported environment variables documented in the Boost Wiki.
# 1. Clone the repository
git clone git@github.com:av/boost-starter.git
# 2. Move to the repository
cd boost-starter
# 3. Launch boost
./launch.shYou'll find pre-included example module in the boost_modules directory with a sample workflow that avoids invoking an LLM altogether and replies with "Hello, boost!" to any message.
ID_PREFIX = 'example'
async def apply(chat, llm):
await llm.emit_message('Hello, boost!')You can further modify/add files in the boost_modules directory to include your custom modules. See the custom modules guide to learn more.