Ce repo peut servir de support pour présenter un ou plusieurs meetup(s). Le parcours est le suivant...
- "CSR" Client Side Rendering : React en tant que lib SPA standard
- "RSC" React Server Components : exécution de composants React uniquement côté serveur
- "SSG" Static Site Generation : exécution de composants React pendant le build
- "ISR" Incremental Static Regeneration : re-génération de composants à la demande
- "SSR" Server Side Rendering : pre-rendering côté serveur puis exécution (hydration) côté client
- "SSRF" Server Side Request Forgery : une faille de sécurité corrigée récemment dans Next.JS
Ce travail est basé principalement sur deux sources :
- https://demystifying-rsc.vercel.app/
- https://www.assetnote.io/resources/research/digging-for-ssrf-in-nextjs-apps
Important
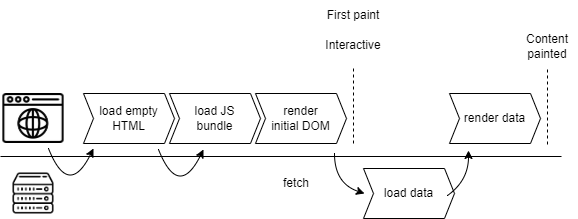
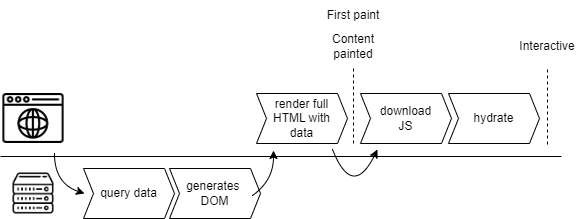
CSR (Client-Side Rendering): React code is delivered to the browser, which generates content that is inserted into the DOM.
cd 1-csr-load-data
npm start
Important
After the page has been loaded for the first time, navigating to other pages on the same website uses JavaScript to re-render parts of the page without requiring a full page refresh.
cd 2-csr-router
npm start
Important
React components which are written to run only on the server, rather than in the browser.
cd 3-rsc-load-data
npm run build
npm run start
Important
Components are executed only on the server. The default behavior is static rendering: components are executed at build time.
cd 4-rsc-router
npm run build
npm run start
Important
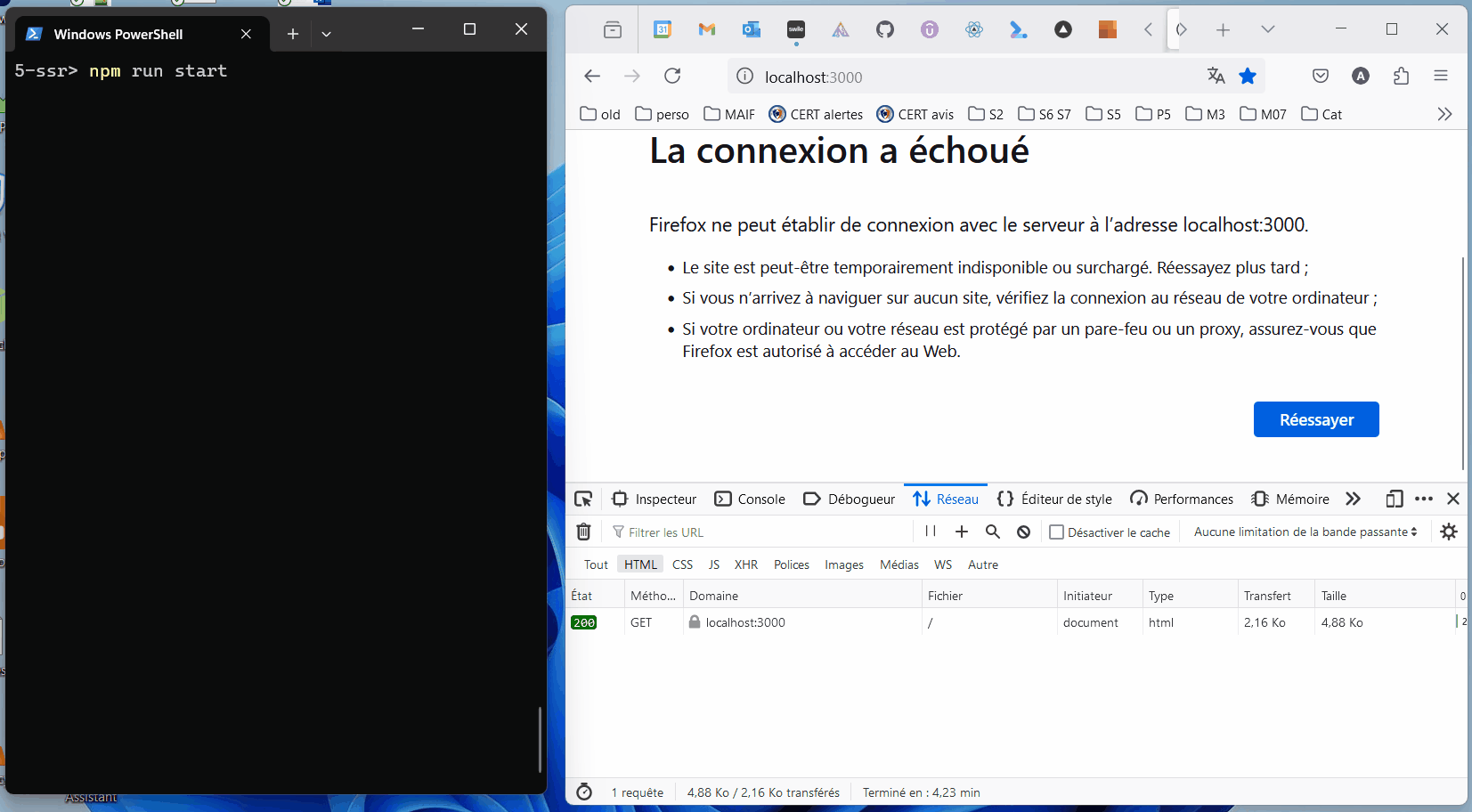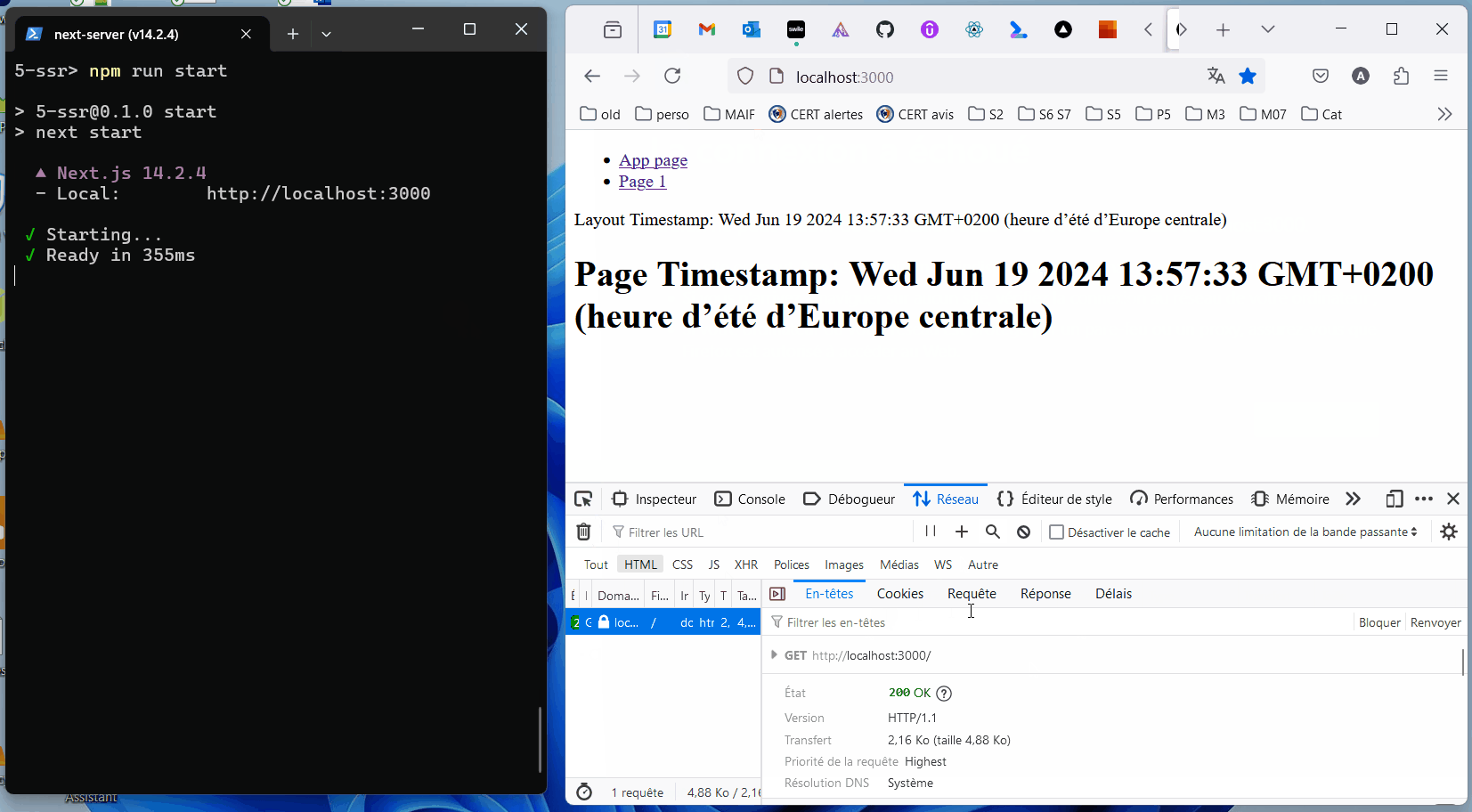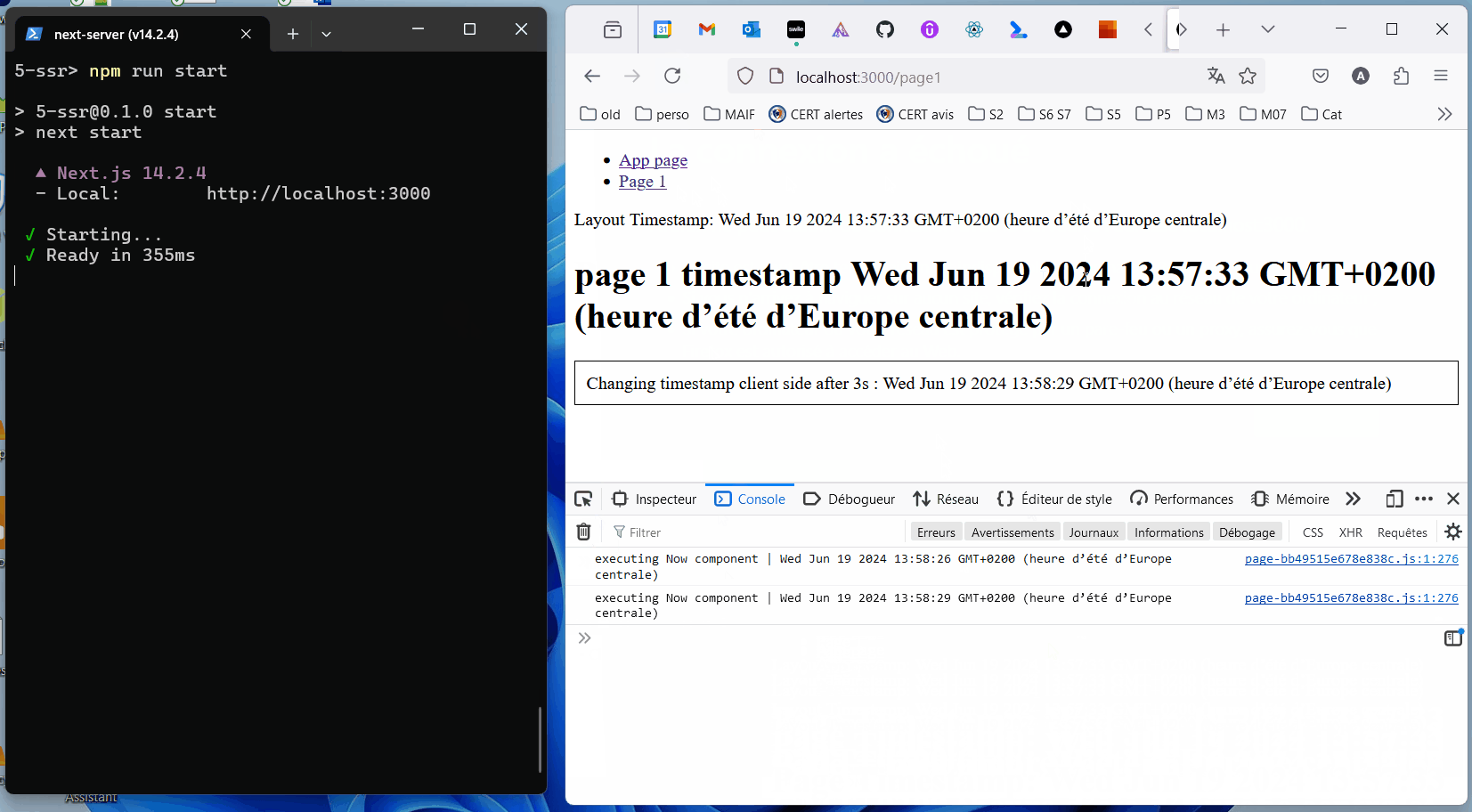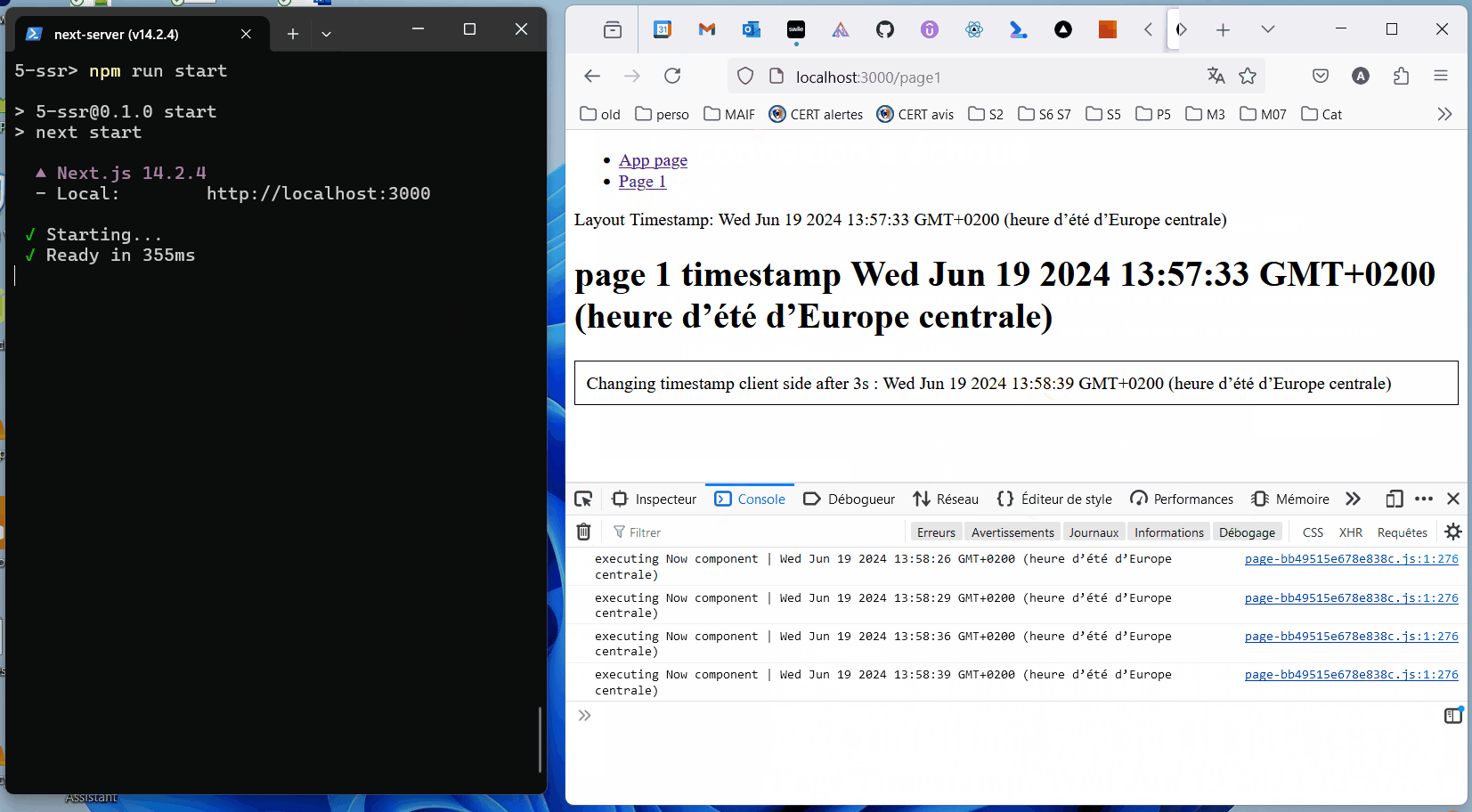
SSR means prerendering client components on the server. React code runs at the time it is requested. The result may be cached for future requests.
Best practice: define 'use client'; components as far down the component tree as possible.
Important
"In React, “hydration” is how React “attaches” to existing HTML that was already rendered by React in a server environment. During hydration, React will attempt to attach event listeners to the existing markup and take over rendering the app on the client. In apps fully built with React, you will usually only hydrate one “root”, once at startup for your entire app."
https://react.dev/reference/react-dom/client/hydrateRoot
https://www.gatsbyjs.com/docs/conceptual/partial-hydration/
cd 5-ssr
npm run build
npm run start
Important
SSG (Static Site Generation) using the pages router: React code is run when you build your application, and the generated output is static.
cd 6-pages-router-ssg
npm run build
npm run start
Important
ISR (using pages router): "Next.js allows you to create or update static pages after you’ve built your site. Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR) enables you to use static-generation on a per-page basis, without needing to rebuild the entire site. With ISR, you can retain the benefits of static while scaling to millions of pages."
cd 7-pages-router-isr
npm run build
npm run start
"the data could become stale at request time"
https://vercel.com/blog/nextjs-server-side-rendering-vs-static-generation
https://react.dev/reference/rsc/server-actions
...
- Si on a accès à un serveur vulnérable mais pas au serveur cible directement (DMZ, FireWall...)
- Si on veut exécuter des requêtes en masquant sa propre origine
- ...
https://www.assetnote.io/resources/research/digging-for-ssrf-in-nextjs-apps
Conditions pour exploiter la CVE-2024-34351
- Une application basée sur Next.JS en version inférieure à la
14.1.1 - L'utilisation de la fonction redirect, avec un chemin absolu. Dans la démo, dans addTodo.js :
redirect(/blog/${inputValue});
Fonctionnement de la fonction redirect
Source : https://www.assetnote.io/resources/research/digging-for-ssrf-in-nextjs-apps
- La fonction Next.JS redirect ne renvoie pas une réponse HTTP 302 au navigateur.
Next.JS exécute la requête côté serveur, puis retourne le résultat au navigateur :
- Pour exécuter la requête, Next.JS doit construire l'URL à appeler.
Dans la démo, dans addTodo.js :
La fonction
redirect('/blog/123');construit l'URLhttp://207.154.209.99/blog/123. Pour construire cette URL, Next.JS récupère notamment le host207.154.209.99à partir du header HTTP de la requête initiale. - Next.JS commence par requêter l'URL avec un HTTP HEAD.
- Si la réponse retourne un header
Content-Type: text/x-component, alors Next.JS requête l'URL avec un HTTP GET.
Pour aboutir à un SSRF sur le serveur cible, il faut donc exécuter un autre serveur :
- qui écoute sur toutes les routes (query path)
- qui retourne un HTTP 200 avec un header
Content-Type: text/x-component, pour toute requête HEAD - qui retourne un HTTP 302 vers le serveur cible, pour toute requête GET
Dans /etc/nginx/sites-available/nextjs
Avant :
server {
listen 80 default_server;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade';
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
}
}
Après :
server {
listen 80;
server_name 207.154.209.99;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000;
proxy_set_header Host 207.154.209.99;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade';
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
}
}
Risque d'effet de bord...
https://nginxtutorials.com/nginx-proxy_set_header-directive/
https://github.com/vercel/next.js/security/advisories/GHSA-fr5h-rqp8-mj6g
"getStaticProps" is not supported in app/. Read more: https://nextjs.org/docs/app/building-your-application/data-fetching
Pages in the app directory are Server Components by default. This is different from the pages directory where pages are Client Components.
Upgrading to Next.js 13 does not require using the new App Router. You can continue using pages with new features that work in both directories
Si on veut comparer les performances de chargement pour les différentes solutions, on peut ajouter les metriques web core vital en console.log.
https://web.dev/articles/fcp?hl=fr
https://rsc-parser.vercel.app/
https://github.com/reactjs/rfcs/blob/main/text/0188-server-components.md#does-this-replace-ssr
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jEJEFAc8tSI
ISR using App router ?
In the Next.js App Router, all fetched data is now static by default, rendered at build time. However, this can be changed easily: Next.js extends the fetch options object to provide flexibility in caching and revalidating rules. You can use the {next: {revalidate: number}} option to refresh static data at set intervals or when backend changes occur (Incremental Static Regeneration), while the {cache: 'no-store'} option can be passed in the fetch request for dynamic data (server-side rendering).
https://www.telerik.com/blogs/current-state-react-server-components-guide-perplexed
https://github.com/reactjs/server-components-demo
https://dev.to/vteacher/let-s-make-a-web-application-with-react-server-components-5dmg
https://react.dev/blog/2024/04/25/react-19
https://react.dev/reference/rsc/server-components
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ePAPd9qzGyM
https://www.joshwcomeau.com/react/server-components/
https://nextjs.org/docs/pages/building-your-application/rendering/static-site-generation
https://nextjs.org/docs/pages/building-your-application/data-fetching/get-static-props
https://react.dev/reference/rsc/server-components#server-components-without-a-server