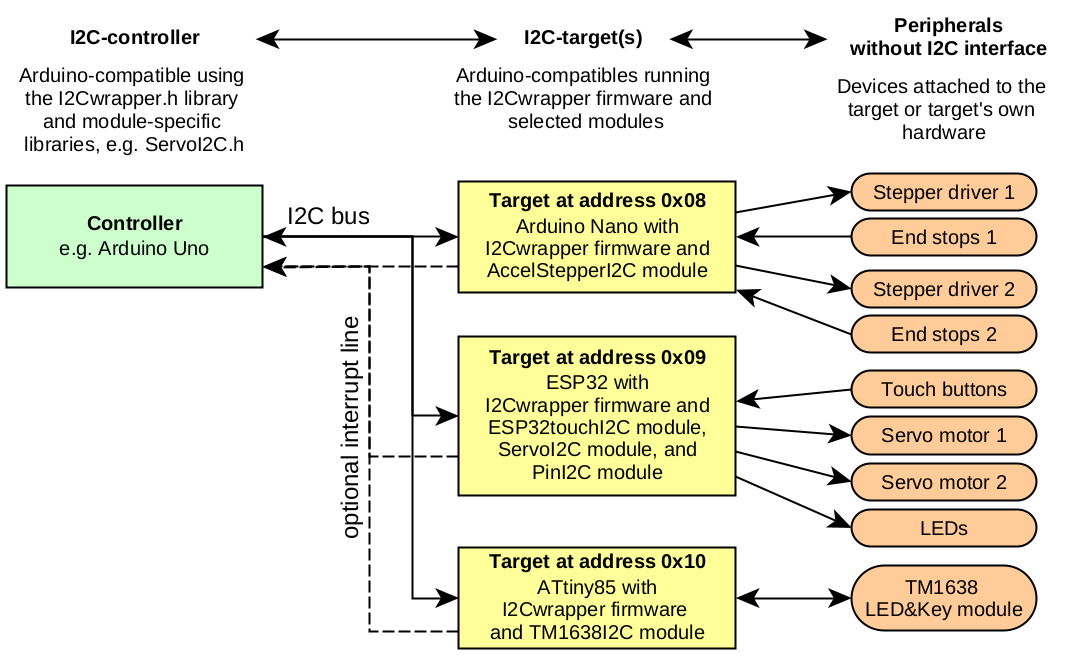
I2Cwrapper is a generic modular framework for Arduino I2C target devices(1) which runs on standard Arduinos, ESP8266, ESP32, and ATtiny platforms (see supported platforms). It allows you to easily control devices attached to the target or the target's own hardware via I2C. Typically, you can use it to integrate peripherals without dedicated I2C interface in an I2C-bus environment.
The I2Cwrapper core consists of an easily extensible firmware framework and a controller library. Together, they take care of the overhead necessary for implementing an I2C target device, while the actual target functionality is delegated to device-specific modules.
This is a possible example setup:
(1)I2Cwrapper uses the current I2C terminology which replaced master with controller, and slave with target.
Download I2Cwrapper on github.
The I2Cwrapper library and the module libraries are documented here.
See Usage for a quick start.
Currently, the following modules come shipped with I2Cwrapper in the firmware subfolder (see Available modules for more detailed information):
- AccelStepperI2C: Control up to eight stepper motors with acceleration control via Mike McCauley's AccelStepper library, and up to two end stops per stepper. Uses a state machine and an optional controller interrupt line to prevent I2C bus clogging.
- ServoI2C: Control servo motors via I2C just like the plain Arduino Servo library.
- PinI2C: Control the digital and analog in- and output pins of the target device via I2C, similar to an IO-expander. Works just like the plain Arduino pinMode(), digitalRead(), etc. commands.
- ESP32sensorsI2C: Read an ESP32's touch sensors, hall sensor, and (if available) temperature sensor via I2C. Uses the optional controller interrupt line to inform the controller about a touch button press.
- TM1638lite: Read buttons from and control the single and seven-segment LEDs of up to four TM1638 modules like the ubiquitous LED&Key module via I2C. Uses Danny Ayers' TM1638lite library.
While the setup for these modules differs from their respective non-I2C counterparts, usage after setup is very similar, so that adapting existing code for I2C remote control is pretty straightforward.
If there are no intrinsic resource conflicts, modules can be selected in any combination at compile time for a specific target (see below for details). It is easy to add new modules with help of the provided templates.
v0.3.0 introduced additional feature modules. They don't act as interfaces to some peripheral, but can be used to add functionality to the target, such as an I2C-status LED, or implementing different methods of retrieving the target's own I2C address, e.g. from hardware pins or flash memory/EEPROM.
The I2Cwrapper framework consists of four basic components. The first two drive the I2C target device:
- A firmware framework for the target device, implemented in the
firmware.inosketch. It provides the basic I2C target functionality:- onReceive() and onRequest() interrupt service routines (ISRs) which listen and react to the controller's transmissions,
- a command interpreter which processes the controller's commands received by onReceive() (in traditional I2C hardware this is equivalent to register writes and reads),
- an output Buffer which allows the target to prepare a reply which will be sent upon the next onRequest() event,
- transmission error control with CRC8-checksums,
- different ways for setting the target's I2C address: fixed address; EEPROM stored; and
(not implemented yet)read from hardware pins, - a controller interrupt mechanism which modules can use to alert the master proactively,
- triggering a target reset (i.e. re-initialization to initial state).
- Firmware modules which implement the actual functionality of the target device, e.g. controlling stepper and/or servo motors, or reading sensors.
- Modules exist as separate include files, e.g.
ServoI2C_firmware.h, and are selected for compilation via thefirmware_modules.hfile. - Modules don't have to worry about the I2C overhead but can concentrate on what's important: interpreting and reacting to the controller device's commands and requests.
- A module's main job is to interpret and react to commands passed to them from the controller through the firmware framework.
- Modules can "inject" their code at different places in the firmware (e.g. setup, main loop, command interpreter), so that there is a high degree of flexibility.
- Modules exist as separate include files, e.g.
The other two basic components are for the I2C controller's side:
- The I2Cwrapper class, provided by the
I2Cwrapper.hlibrary.- Controller sketches use an object of type I2Cwrapper to represent the target device which handles all low level communication tasks like CRC8 checksums, error handling etc.
- It also provides basic functions for target device management like changing its I2C address, setting an interrupt pin, or making it reset.
- Controller libraries for each module, e.g.
ServoI2C.h.- Controller libraries use I2Cwrapper objects to talk to the target device (like the
ServoI2Cclass inServoI2C.h). - They implement an interface for the respective target functionality, which transmits function calls to the target device, and receives the target's reply, if the command was asking for it.
- In the simplest case, they closely mimick the interface of an existing library (like Arduino
Servo.h) which is used on the target's side to drive the actual hardware.
- Controller libraries use I2Cwrapper objects to talk to the target device (like the
- Arduinos aren't perfect I2C target devices. Not all Arduino hardware platforms have dedicated I2C hardware, which entails possible performance issues (see Supported platforms).
- The Arduino's Wire library doesn't support clock stretching in a way which allows the target to finish reacting to the previous command if it hasn't done so yet before the transmission occurred. That's why it's important to make sure that the target is not flooded with commands or requests with too little time to handle them. I2Cwrapper provides an adjustable minimum delay between transmissions to handle that problem.
- No serialization protocol is used at the moment, so the implementation is machine dependent in regard to the endians and sizes of data types. Modules will have to take care that transmitted commands and requests will transmit defined amounts of bytes by using typeguards for ambiguously sized datatypes like int.
- Modules use one byte command codes (similar to conventional I2C-registers) for each distinct function call to the target. At the moment, no mechanism is in place to prevent newly developed modules from reusing codes already used by another module or by one of the I2Cwrapper core functions. Note that this will only lead to problems if two conflicting modules are used concurrently by a target device. The I2Cwrapper documentation has a list of code ranges used by the currently available modules. Strictly reserved ranges are 0-9 and 240-255.
- The I2C buffer size used by I2Cwrapper objects defaults to 20 bytes. The CRC checksum takes 1 byte, the command header for transmissions from controller to the target take 2 bytes. That leaves 17 bytes as maximum parameter payload for commands and 19 bytes for target responses. A more flexible approach is planned for a future release. Note for ATtiny: depending on the Wire library selected by ATtinyCore, the maximum usable buffer size might even be smaller, see supported platforms)
See the How to add new modules section if you are interested in writing a new module and implementing your own target device.
Install I2Cwrapper from the Arduino library manager. You'll find an I2Cwrapper examples folder in the usual menu after successful installation.
If you haven't done so yet, you'll also have to install the libraries needed by the modules you want to use, e.g. AccelSteppper, TM1638lite, etc. the usual way from the Arduino library manager.
If you've used the AccelStepperI2C library (not the module) before, please uninstall it (i.e. delete it from the Arduino library folder) or else you'll end up with include conflicts.
- Open firmware.ino from the examples menu of the Arduino editor, you'll find it in the the I2Cwrapper submenu. It will open multiple tabs, among them one for each available module in the firmware subfolder.
- Go to the
firmware_modules.htab and select the modules you want by (un)commenting them. For a first test, start with the PinI2C module, it is the simplest and doesn't need any extra hardware. - You can save a local copy of the firmware. Don't forget, though, that your local copy won't be updated in future releases which might result in conflicts after a library upgrade.
- Compile and upload to your target device.
The target device is now ready. To test it, you can use one of the example sketches:
- (optional, only tested for Linux) Open a completely new instance of the Arduino environment from your start menu. That way, you can connect target and controller devices at the same time without the need to change USB ports for uploading and serial output.
- Depending on the module(s) you selected, load one of the examples from the example folder and upload it to your controller device. Use
Pin_control.inofor a first test with thePinI2Cmodule. - Configure and upload the example sketch or your own controller sketch to another Arduino-like which will act as I2C-controller.
- Connect the I2C bus of both devices (SDA, SCL, and GND). Don't forget I2C pullups and, and if needed, level-shifters. Also, connect V+ <-> V+ to power one board from the other, if needed.
- Open the controller sketch's serial output and run the controller sketch.
Have a look at the examples for details.
Simply include the controller libraries for the module(s) you compiled into your target firmware (e.g. ServoI2C.h) and use them as shown in the documentation and example sketches of the respective modules.
Many functions take target pin numbers as an argument, e.g. when you define an interrupt pin with I2Cwrapper::setInterruptPin(). If controller and target devices run on different hardware platforms (e.g. ESP8266 and ATtiny85), you'll have to be careful that the controller addresses the target's side pins correctly. Pin constants like A0, D1, LED_BUILTIN etc. might not be known at the controller's side or, even worse, might represent a different pin number. In this case it is recommended to use the raw pin numbers. They are defined in the respective platform's pins_arduino.h file, or can easily be found out by running Serial.println(A0); etc. on the target platform.
If I2C transmission problems occur, any command sent to the I2C target could fail and every return value could be corrupted. Depending on context, this could lead to severe consequences, e.g. with uncontrolled stepper motor movements. That's why I2Cwrapper transmits each command and response with a CRC8 checksum. To find out if a controller's command or a target's response was transmitted correctly, the controller can check the following:
- If
I2Cwrapper::sentOKis false, the previous function call was not properly transmitted. - If
I2Cwrapper::resultOKis false, the data returned from the previous function call is invalid.
The library keeps an internal count of the number of failed transmissions, i.e. the number of cases that sentOK and resultOK came back false. If the controller doesn't want to check each transmission separately, it can use one of the following methods at the end of a sequence of transmissions, e.g. after setup and configuration of the target, or at the end of some program loop:
uint16_t I2Cwrapper::sentErrors()- number of falsesentOKeventsuint16_t I2Cwrapper::resultErrors()- number of falseresultOKeventsuint16_t I2Cwrapper::transmissionErrors()- sum of the above
The respective counter(s) will be reset to 0 with each invocation of these methods.
See the Error_checking.ino example for further illustration.
In v0.3.0 an I2C state machine was introduced to explicitly handle irregular sequences of events, e.g. a receiveEvent() happening while a requestEvent() was expected. It's main aim is to always keep the target in a responsive state and prevent it from sending bogus data. So even if errors occur, at least the target should remain responsive. See I2C state machine.svg for details on the state machine's flow of states.
To keep the controller from having to constantly poll the target device for some new event (e.g. an input pin change) over I2C, the controller can use the I2Cwrapper::setInterruptPin() function to tell the target to use one if the target pins as an interrupt line. The target's modules may use it if they want to inform the controller about some new event. Of course, an additional hardware line connecting this target pin and a free, interrupt-capable controller pin is needed to use the interrupt mechanism.
The controller will have to implement an interrupt service routine (ISR) to listen to the respective controller pin. After having received an interrupt, it must call I2Cwrapper::clearInterrupt() to clear the target's interrupt state and find out about the reason that caused the interrupt.
Interrupt reasons are specific for a module. A module can send an interrupt to the controller with the triggerInterrupt() function which is provided by the firmware.ino framework. It can provide additional information on the interrupt reason and the target device's (sub)unit that caused the interrupt.
See the example Interrupt_Endstop for further illustration.
If a controller sends commands too quickly or requests a target device's response too quickly after having sent a command, the target might not have finished processing the previous command and will not be ready to react appropriately. Usually, it should not take more than very few microseconds for the target to be ready again, yet particularly when serial debugging is enabled for the target it can take substantially longer.
That's why I2Cwrapper makes sure that a specified minimum delay is kept between each transmission to the target, be it a new command or a request for a reply. The default minimum delay of 20 ms is chosen deliberately conservative to have all bases covered and for many not time-critical applications there is no need to lower it. However, depending on debugging, target device speed, target task execution time, bus speed, and the length of commands sent, the default can be adjusted manually to be considerably lower with the I2Cwrapper::setI2Cdelay() function. Typically, 4 to 6 ms are easily on the safe side.
At the moment, you'll have to use your own tests to find an optimal value. A self-diagnosing auto-adjustment feature is planned for a future release.
(new in v0.3.0, experimental)
Alternatively, the controller can use the I2Cwrapper::autoAdjustI2Cdelay(uint8_t maxLength, uint8_t safetyMargin, uint8_t startWith) function to make an educated guess for the shortest, yet still reasonably safe I2C delay value in a given environment. It will be based on a number of simulated test transmissions to and from the target device. It can be supplemented by an additional safety margin (default: 2 ms) and factor in the maximum command length to be used (default: max length allowed by buffer).
See Adjust_I2Cdelay.ino for some in-depth experiments. An everyday use example used in a setup() function could look like this (from Error_checking.ino):
Serial.print("I2C delay set to ");
Serial.print(wrapper.autoAdjustI2Cdelay()); // uses default safetyMargin of 2ms and max. length transmissions
Serial.print(" ms (default was ");
Serial.print(I2CdefaultDelay); Serial.println(" ms)");or simply
wrapper.autoAdjustI2Cdelay();To chose which modules are supported by an I2C target device, edit the firmware_modules.h file accordingly.
The AccelStepperI2C module provides access to up to eight stepper motors over I2C. It uses Mike McCauley's AccelStepper library and additionally supports two end stops per stepper and the I2Cwrapper interrupt mechanism. Think of it as a more accessible and more flexible alternative to dedicated I2C stepper motor controller ICs like AMIS-30622, PCA9629 or TMC223 with some extra bells and whistles. Use it with your own hardware or with a plain stepper driver shield like the Protoneer CNC GRBL shield (recent V3.51 or V3.00 clone).
The original AccelStepper needs the client to constantly 'poll' each stepper by invoking one of the run() commands (run(), runSpeed(), or runSpeedToPosition()) at a frequency which mustn't be lower than the stepping frequency. Over I2C, this would clutter the bus, put limits on stepper speeds, and be unstable if there are other I2C devices on the bus, particularly with multiple steppers and microstepping.
To solve this problem, AccelStepperI2C implements a state machine in the target device's main loop for each connected stepper which makes the target do the polling locally on its own.
All the controller has to do is make the appropriate settings, e.g. set a target with AccelStepperI2C::moveTo() or choose a speed with AccelStepperI2C::setSpeed() and then start the target's state machine (see example below) with one of
AccelStepperI2C::runState(): will pollrun(), i.e. run to the target with acceleration, and stop the state machine upon reaching itAccelStepperI2C::runSpeedState(): will pollrunSpeed(), i.e. run at constant speed until told otherwise (seeAccelStepperI2C::stopState()), orAccelStepperI2C::runSpeedToPositionState(): will pollrunSpeedToPosition(), i.e. run at constant speed until the target has been reached.
AccelStepperI2C::stopState() will stop any of the above states, i.e. stop polling. It does nothing else, so the controller is solely in command of target, speed, and other settings.
Up to two end stop switches can be defined for each stepper. If enabled and the stepper runs into one of them, it will make the state machine (and the stepper motor) stop.
Of course, this is most useful in combination with AccelStepperI2C::runSpeedState() for homing and calibration tasks at startup. See Interrupt_Endstop.ino example for a use case.
I2Cwrapper's interrupt mechanism can be used to inform the controller that the AccelStepperI2C state machine's state has changed. Currently, this will happen when a set target has been reached or when an endstop switch was triggered. See Interrupt_Endstop.ino example for a use case.
- The original
run(),runSpeed(), orrunSpeedToPosition()functions are implemented, but it is not recommended to use them. The idea of these functions is that they are called as often as possible which would cause constant I2C traffic. The I2C protocol was not designed for this kind of load, so use the state machine instead. If you feel you must use the original ones, take it slow and see if your setup, taking other I2C devices into consideration, allows you to increase the I2C bus frequency. Even then you shouldn't poll as often as possible (as AccelStepper usually expects you to), but adjust the polling frequency to your max. stepping frequency, so that the I2C bus still has some room to breathe. - Naturally, you cannot declare your own stepping functions with the constructor [2/2] variant.
Steppers can exert damaging forces, even if they are moving slow. If in doubt, set up your system in a way that errors will not break things, particularly during testing:
- Place your end stops in a non-blocking position so that they are activated in a by-passing way but do not block the way themselves. That way you still have time to stop things manually if they fail.
- To be really safe, put emergency stops which shut down the target in a final end position. Currently there is no dedicated pin mechanism for that, so just use the target's reset pin instead.
- Always keep a manual emergency stop at hand or make it easy to cut the power quickly.
- And again, do check for transmission errors in critical situations (see error handling).
Controls servo motors via I2C. Works literally just like the plain Arduino Servo library. See Servo_Sweep.ino example.
Read and control the digital and analog input and output pins of the target device via I2C. Can replace a dedicated digital or analog port expander like MCP23017, PCF8574, PCF8591, or ADS1115. Can be used like the plain Arduino digitalRead(), analogWrite()etc. commands. See Pin_control.ino example.
Read an ESP32's touch sensors, hall sensor, and (if it works) temperature sensor via I2C. Can use the optional I2Cwrapper interrupt mechanism to inform the controller about a touch button press. See ESP32sensors.ino example.
The TM1638 chip uses an SPI bus interface to control matrices of buttons and LEDs. If you want to unify your bus environment in a given project or need to save pins, it can be useful to be able to control it via I2C. To implement an I2Cwrapper module, I chose Danny Ayers' TM1638lite library as it came with the most straightforward and burden-free implementation in comparison with the more popular choices. Apart from the setup, it can be used just like the original. Interrupt mechanism support for key presses is planned but not implemented yet. See the TM1638lite.ino example for more details.
(new in v0.3.0)
Feature modules extend or modify the firmware with additional features. As they don't act as interfaces to some peripheral, as the normal modules do, they do not necessarily include a matching controller library. To set them apart from normal modules, their filename starts with an underscore character ("_xxx_firmware.h").
Including the _statusLED_firmware.h in firmware_modules.hwill make the target's built in LED (LED_BUILTIN) flash briefly when an external interrupt (receiveEvent or requestEvent) is coming in. Alternatively, it can be modified to flash each time the I2C state machine changes its state (see Error handling). Meant for diagnostic purposes to see if the target device is still alive and active. Doesn't need a controller library, just comment it out in firmware_modules.hto disable it. It could easily be extended to have more than one status LED for a more differentiated status display.
To make the target device use a different I2C address than the default (0x08), you can include one (and only one) of the following feature modules:
_addressFixed_firmware.h: use a fixed I2C address for the target other than the default_addressFromPins_firmware.h: make the target read its I2C address from a given set of input pin states (jumper bridges, DIP switches etc.) at startup_addressFromFlash_firmware.h: make the target read its I2C address from non volatile memory (EEPROM, flash memory) and store a new changed address upon the controller's command.
If you want to add your own modules and implement your own I2C target device, you can use the templates provided in the templates subfolder.
template_I2C.handtemplate_I2C.cpp- controller library templates. Their main function is to define an interface for the target's functionality and the related command codes (see limitations). Each function is implemented so that the function's command code and parameters are transmitted to the target with the help of the I2Cwrapper library.- Often, the header file
template_I2C.hwill very closely resemble the header file of the library which you are addressing on the target device's side. - The implementation
template_I2C.cpp, however, looks quite different: It will do nothing else but "wrap" each function's arguments into a command, transmit it to the target, and, optionally, receive the target device's reply.
- Often, the header file
template_I2C_firmware.h- Target firmware templates. Here, the most important part is injecting code into the command interpreter (theprocessMessage()function) which will "unwrap" the controller function's command codes and arguments, react adequately, and, optionally, prepare a reply.
Refer to the documentation within the templates' source code and to the existing modules for more details and illustration.
All transmissions to the target device have a three byte header followed by an arbitrary number of zero or more parameter bytes:
- [0] CRC8 checksum
- [1] command code: Modules and the I2Cwrapper core use their own unique command code ranges (see Limitations for end users, though), so that the command code will decide which module or if the I2Cwrapper library itself will interpret the command.
- [3] unit addressed: If a target module enables I2C access to more than one instance of some hardware, e.g. multiple stepper or servo motors, the unit can be used to differentiate them. It is up to each module to decide if and how the unit is interpreted. Modules which don't need them because there is only one instance of their respective hardware (like e.g. the
PinI2Cmodule), can just ignore the unit and will have to live with the one byte wasted bandwidth per transmission.
Since v0.3.0 dropped the hardware reset (it's considered bad practice), each module now needs to provide proper cleanup code in the (6) reset event section. This code needs to free all allocated resources and reset all hardware used by the module. The goal is to put all resources used by the module, and only(!) those, into the state they were after bootup, so that a controller can make sure it finds a clean slate when it starts to use the target by sending a reset command.
The following platforms will run the target firmware and have been (more or less) tested. Unfortunately, they all have their pros and cons:
ATmega328 based Arduinos come with I2C hardware support which should make communication most reliable and allows driving the I2C bus at higher frequencies. With only 16MHz CPU speed not recommended for high performance situations.
The ESP8266 has no I2C hardware. The software I2C may not work stable at the default 80MHz CPU speed, make sure to configure the CPU clock speed to 160MHz. Even then, it might be necessary to decrease the bus speed below 100kHz for stable bus performance, start as low as 10kHz if in doubt. Apart from that, expect a performance increase of ca. 10-15x vs. plain Arduinos due to higher CPU clock speed and better hardware support for math calculations.
The ESP 32 has no I2C hardware. I2C is stable at the default 240MHz, but officially cannot run faster than 100kHz. Also, the target implementation is awkward. It might be more susceptible for I2C transmission errors, so timing is critical. Apart from that, expect a performance increase of ca. 15-20x vs. plain Arduinos due to higher CPU clock speed and better hardware support for math calculations.
Depending on the specific model, ATtinys can have software only I2C, full hardware I2C, or something in between. SpenceKonde's fantastic ATTinyCore comes with fully transparent I2C support which chooses the appropriate Wire library variant automatically. Note, though, that these might bring restrictions with them like a smaller I2C buffer size of 16 in the case of USI implementations (e.g. ATtiny85), which will decrease the maximum number of parameter bytes of I2Cwrapper commands to 13.
Using ATTinyCore, I2Cwrapper firmware has been successfully tested on ATtiny85 (Digispark) and ATtiny88 (MH-ET-live) boards. Mileage with the available firmware modules may vary, though. Currently, only Pinl2C and TM1638liteI2C will run without changes. See the respective comment sections in the Pin_Control.ino and TM1638lite.ino examples for testing purposes. Of course, ATtinys are relatively slow and have limited memory. The firmware alone, without any modules enabled, currently uses 44% of a Digispark's usable 6586 bytes of flash memory, with the PinI2C module enabled it's 54%.
This is a simplified version of the Pin_control.ino example sketch for addressing a target device running the I2Cwrapper firmware with the PinI2C module enabled.
/*
PinI2C Pin control demo
(c) juh 2022
Reads a digital and an analog input pin and mirrors their values on a
digital and a PWM-capable output pin.
Needs PinI2C.h module enabled in the target's firmware_modules.h.
*/
#include <Wire.h>
#include <PinI2C.h>
uint8_t i2cAddress = 0x08;
I2Cwrapper wrapper(i2cAddress); // each target device is represented by a wrapper...
PinI2C pins(&wrapper); // ...that the pin interface needs to communicate with the controller
// Arduino Uno/Nano example pins
const uint8_t dPinIn = 12; // any pin; connect switch against GND and +V (or use only GND and INPUT_PULLUP below)
const uint8_t dPinOut = 13; // any pin; connect LED with resistor or just use 13 = LED_BUILTIN on Uno/Nano
const uint8_t aPinIn = 14; // needs analog pin; 14 = A0 on Uno/Nano; connect potentiometer against GND and +V
const uint8_t aPinOut = 6; // needs PWM pin; 6 is PWM-capable on Uno/Nano; connect LED with resistor, or multimeter
void setup()
{
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(115200);
if (!wrapper.ping()) {
Serial.println("Target not found! Check connections and restart.");
while (true) {};
}
wrapper.reset(); // reset the target device for a clean slate
pins.pinMode(dPinIn, INPUT); // INPUT_PULLUP will also work
pins.pinMode(dPinOut, OUTPUT);
pins.pinMode(aPinIn, INPUT);
pins.pinMode(aPinOut, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
pins.digitalWrite(dPinOut, pins.digitalRead(dPinIn));
pins.analogWrite(aPinOut, pins.analogRead(aPinIn)/4);
Serial.print("Digital input pin = "); Serial.print(pins.digitalRead(dPinIn));
Serial.print(" | Analog input pin = "); Serial.println(pins.analogRead(aPinIn));
delay(500);
}This is an example for addressing a target device running the I2Cwrapper firmware with (at least) the AccelStepperI2C module enabled.
/*
AccelStepperI2C Bounce demo
(c) juh 2022
This is a 1:1 equivalent of the AccelStepper Bounce.pde example
https://www.airspayce.com/mikem/arduino/AccelStepper/Bounce_8pde-example.html
*/
#include <Wire.h>
#include <AccelStepperI2C.h>
uint8_t i2cAddress = 0x08;
I2Cwrapper wrapper(i2cAddress); // each target device is represented by a wrapper...
AccelStepperI2C stepper(&wrapper); // ...that the stepper needs to communicate with it
void setup()
{
Wire.begin();
// Wire.setClock(10000); // uncomment for ESP8266 targets, to be on the safe side
if (!wrapper.ping()) {
Serial.println("Target not found! Check connections and restart.");
while (true) {}
}
wrapper.reset(); // reset the target device
stepper.attach(); // Defaults to AccelStepper::FULL4WIRE (4 pins) on 2, 3, 4, 5
// attach() replaces the AccelStepper constructor, so it could also be called like this:
// stepper.attach(AccelStepper::DRIVER, 5, 6);
if (stepper.myNum < 0) { // stepper could not be allocated (should not happen after a reset)
while (true) {}
}
// Change these to suit your stepper if you want
stepper.setMaxSpeed(500);
stepper.setAcceleration(100);
stepper.moveTo(2000);
}
/* This is the recommended AccelStepperI2C implementation using the state machine.
* Note that the polling frequency is not critical, as the state machine will stop
* on its own. So even if stepper.distanceToGo() causes some I2C traffic, it will be
* substantially less traffic than sending each stepper step seperately (see below).
* If you want to cut down I2C polling completely, you can use the interrupt mechanism
* (see Interrupt_Endstop.ino example sketch).
*/
void loop()
{
stepper.runState(); // start the state machine with the set target and parameters
while (stepper.distanceToGo() != 0) { // wait until target has been reached
delay(250); // just to demonstrate that polling frequency is not critical
}
stepper.moveTo(-stepper.currentPosition());
}
/* This is the "classic" implementation which uses the original polling functions.
* It will work, at least in low performance situations, but will clog the I2C bus as
* each (attempted) single stepper step needs to be sent via I2C.
*/
void loopClassic()
{
if (stepper.distanceToGo() == 0)
stepper.moveTo(-stepper.currentPosition());
stepper.run(); // frequency is critical, each call will cause I2C traffic
}Find the I2Cwrapper library documentation here.
- Improve I2C buffer size handling, which is currently fixed. Either let the user decide on both sides (with parameter in I2Cwrapper constructor - already implemented - and command to target for changing the buffer size), or let the source decide on its own by using the preprocessor to determine the maximum value needed given the used modules (not sure if this will work).
- reintroduce diagnostics as a standalone feature module
- Interrupt mechanism support for TM1638liteI2C and PinI2Cmodule
- enable debugging for the firmware by feature module, instead of macro (completely eliminate the need to edit
firmware.ino) - New modules:
- SonarI2C module with support for 1 to n ultrasonic distance sensors
- InfraredI2C module with support for 1 to n infrared remote receivers
- TFT_I2C module based on (a subset of) Ucglib or Adafruit's GFX lib for SPI bus color TFTs
- DC motor control module
Self-adjusting I2C-delayDetermine I2C-address from hardware pinsMove I2C-address options (fixed, EEPROM, hardware pins) to modulesAttiny support (memory will be an issue, though)
Apart from its predecessor AccelStepperI2C, this is my first "serious" piece of software published on github. Although I've some background in programming, mostly in the Wirth-tradition languages, I'm far from being a competent or even avid c++ programmer. At the same time I have a tendency to over-engineer (not a good combination), so be warned and use this at your own risk. My current main interest is nor in programming, but in 3D printing, you can find me on prusaprinters, thingiverse, and youmagine. This library first saw the light of day as part of my StepFish project (also here).
Contact me at ftjuh@posteo.net.
Jan (juh)
This software is Copyright (C) 2022 juh (ftjuh@posteo.net)
I2Cwrapper is distributed under the GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE Version 2.
see releases page
Historical note: I2Cwrapper evolved from the AccelStepperI2C project. The latter is still available in the Arduino library manager even if its use is discouraged. I2Cwrapper is functionally fully equivalent to AccelSteperI2C if you simply select only the AccelSteperI2C and ServoI2C modules for compilation and ignore the other modules.