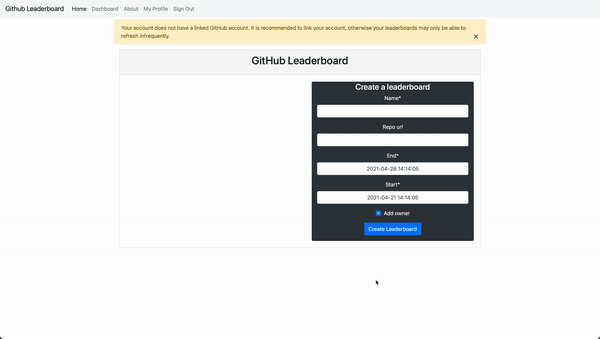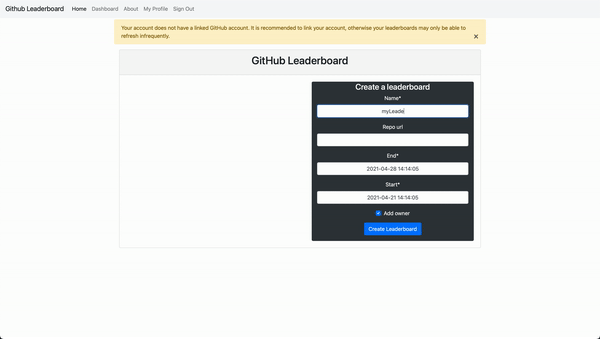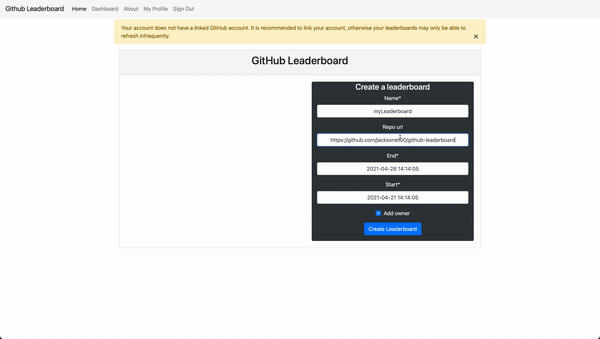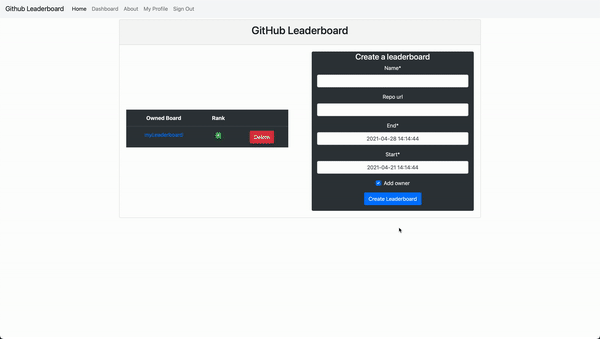
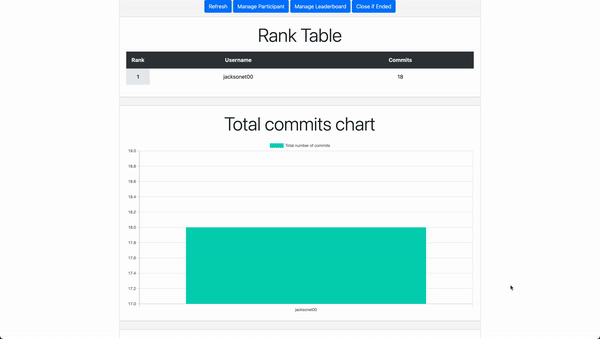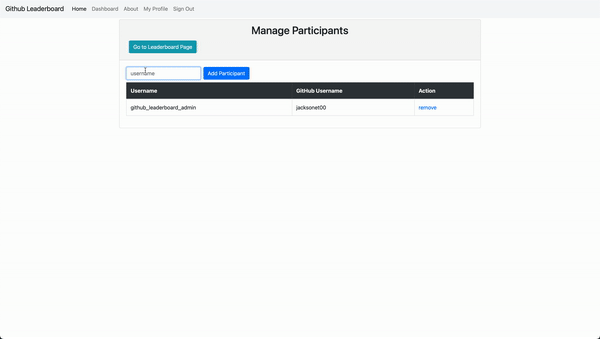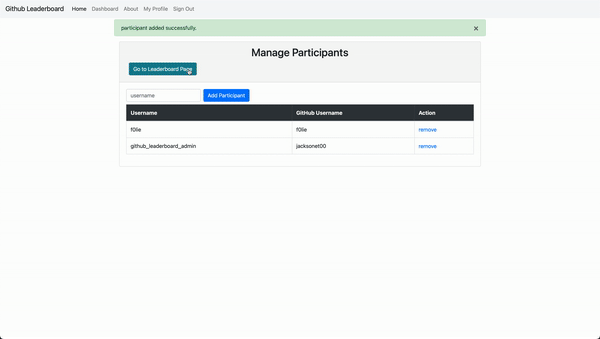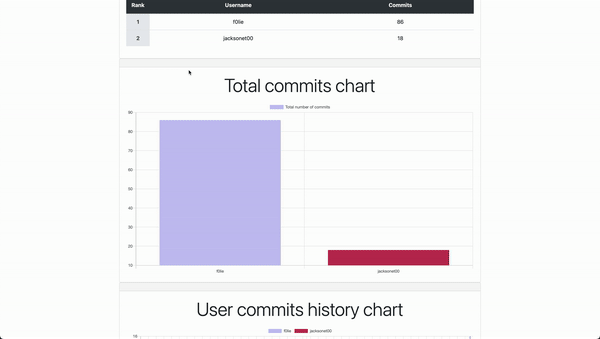
This Django website allows people to login with their Github accounts, pull commits from Github repos, and rank users by the number of commits.
Application is deployed at Heroku.
The project is setup with cookiecutter and docker so follow this link. The following instructions is the bare minimal to get things running. Important configuration instructions is included in the link.
Important locations are config which contains top level information about Django like routing for homepage and
installed apps. requirements contain the Python packages that Docker uses. compose is for
Docker. github_leaderboard contains all the Django files that you would modify.
This runs pre-commit before you commit with flake8 and black autoformatting. If you have flake8 errors, the code will fail to commit.
python -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
pip install pre-commit
pre-commit install-
Build the docker containers
docker-compose -f local.yml build
-
If in production, we can easily change things by running the production setting files.
docker-compose -f production.yml build
-
Save the dependency to the requirements file. Note we have two different files
local.txtandproduction.txtfor the two environments. Remember to add the right dependency to the right file# Local dependency echo "<DEPENDENCY_NAME>==<VERSION_NUMBER>" >> requirements/local.txt # Production dependency echo "<DEPENDENCY_NAME>==<VERSION_NUMBER>" >> requirements/production.txt
-
Add the dependency to Django by modifying the
INSTALLED_APPSarray within theconfig/settings/local.pyorconfig/settings/production.pyfile
-
Running the local setup. This runs both Django and Postgres.
docker-compose -f local.yml up
-
If in production, we can run it easily as well. This runs additional things for running things in production environment.
docker-compose -f production.yml up
- Ensure server is running
- Add a superusername with the
manage.pyas detailed below. Since you are running local Postgres instances, you add your own superuser identity. - Visit
localhost:8000/adminand login with that.
-
Update schema
-
Ensure server is not running
-
Create migrations for new schema
docker-compose -f local.yml run --rm django python manage.py makemigrations
-
Migrate database
docker-compose -f local.yml run --rm django python manage.py migrate
If typing out the docker command is a pain, just alias
with alias docker_django="docker-compose -f local.yml run --rm django python manage.py"
-
Create a new superuser
docker-compose -f local.yml run --rm django python manage.py createsuperuser
-
Log in through the admin panel
docker-compose -f local.yml run --rm django pytestFollow this guide mostly. Scroll to the bottom half that explains adding github oath application.
Do not use localhost for things. It breaks github redirect.
-
Go your
Githubaccount and go toSettings/Developer Settings -
Go to
OAuth Appsand click toNew OAuth App -
Change
Application nameto something likeGit Leaderboards. ChangeHomepage urltohttp://0.0.0.0:8000. ChangeAuthorization callback URLtohttp://0.0.0.0:8000/accounts/github/login/callback.Clearly you can change all of this for the production environment. Do not add an additional
/to the end of callback url or you will get an error. -
Save your
Cilent IDandSecret Key. You need this for the Django app. -
Go to admin page at
http://0.0.0.0:8000/adminor the production url. -
Go to
Sitesand add yourDomain NameandDisplay Nameto match your settings.Domain Namecould be0.0.0.0:8000andDisplay Namecould be w/e for local development. -
Go to
Social Applicationand click onadd. -
Select the
Providerand change toGithub. Add theGithub LeaderboardtoName -
Add your
Cilent IDandSecret Keyfrom when you savedGithub Leaderboard
Follow this guide. Ignore the settings to add AWS because we host staticfiles from the server itself using WhiteNoise.
Note that git push heroku master should be git push heroku main.
Django provides a default User table in the database which automatically integrates with authorization and the admin
panel. We will use this User for our app, but extend it to add additional functionality such as GitHub info and roles.
These users are represented by the ExtendedUser class which has a One-to-One relationship with the default User.