code for MOONLIT: Momentum-contrast and Large-kernel for Multi-fine-grained Deraining
pip install -r requirements.txt
We recommend to install mmcv-full by downloading mmcv-full*.whl from the official mmcv-full website. Please note that mmcv-full==1.53.
train:
python train.py --batch_size 10 --net_name 'resnet'
batch_size can be set to 3, 10 or 100, meaning that the raind streaks are fine-grained into 3, 10 and 100 classes.
net_name can be set to 'resnet' or 'vit', meaning that the encoder of UMRC uses Resnet200-2x or ViT-L.
The best model has been uploaded to experiment/exp0/best_epoch.pth.
test:
python test.py
You can change line 21 of test.py to change the trained model.
The derained image will be saved as restored.jpg
Deep learning-based methods have achieved excellent performance in image-deraining tasks. Unfortunately, most existing deraining methods incorrectly assume a uniform rain streak distribution and a fixed fine-grained level. And this uncertainty of rain streaks will result in the model not being competent at repairing all fine-grained rain streaks. In addition, some existing convolution-based methods extend the receptive field mainly by stacking convolution kernels, which frequently results in inaccurate feature extraction. In this work, we propose momentum-contrast and large-kernel for multi-fine-grained deraining network (MOONLIT). To address the problem that the model is not competent at all fine-grained levels, we use the unsupervised dictionary contrastive learning method to treat different fine-grained rainy images as different degradation tasks. Then, to address the problem of inaccurate feature extraction, we carefully constructed a restoration network based on large-kernel convolution with a larger and more accurate receptive field. In addition, we designed a data enhancement method to weaken features other than rain streaks in order to be better classified for different degradation tasks. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world deraining datasets show that the proposed method MOONLIT achieves the state-of-the-art performance on some datasets.
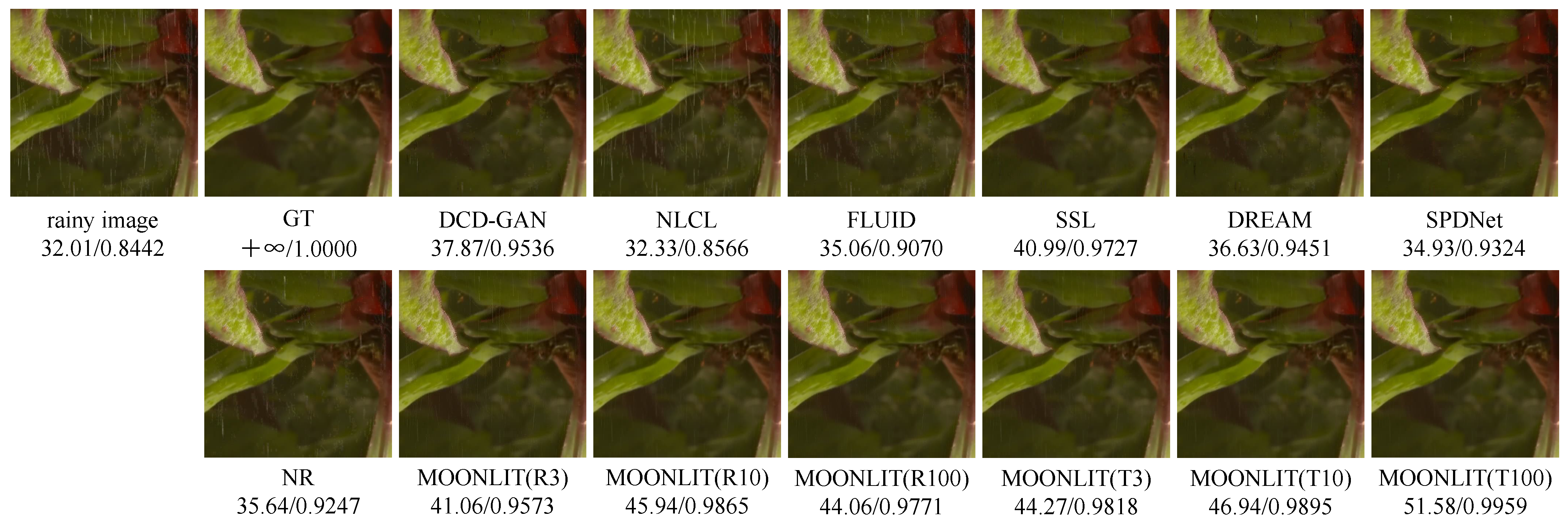 Comparison of selected results of MOONLIT with 8 SOTA methods on the SPA-DATA dataset
Comparison of selected results of MOONLIT with 8 SOTA methods on the SPA-DATA dataset