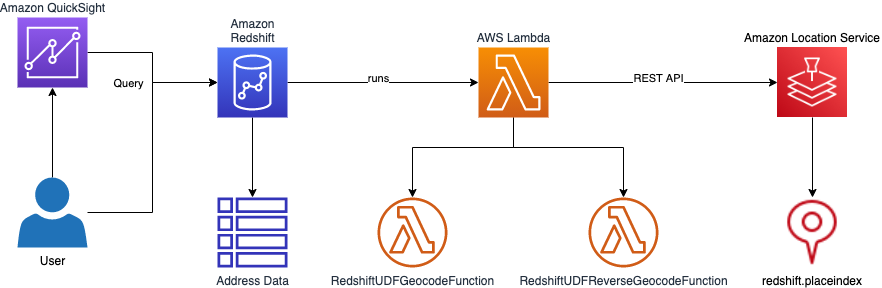
This repository contain the code necessary to deploy Amazon Redshift Lambda-based User Defined Functions (UDF) to allow a user to call Amazon Location Service APIs, such as geocoding and reverse geocoding, as part of SQL queries.
As a pre-requisite, create a new Amazon Location Service place index if you don't have already one you use. Follow the instructions in Create a place index resource.
You can launch the code provided in this repository directly in you AWS account using the lauch button below:
This CloudFormation template uses a Custom Resource to copy lambdas from a central repository and install it in your account as described here. The template has the following parameters:
- OriginBucketName: The S3 bucket from where you are copying the lambda functions from. Should be kept unchanged (unless you know what are you doing).
- OriginKeyPrefix: The S3 bucket prefix that contains the lambda functions. Should be kept unchanged (unless you know what are you doing).
- PlaceIndex: A pre-existing place index. You need to create one before applying this template.
- Create a new RedShift cluster if you don't have one already. Follow the instructions in Getting started with Amazon Redshift.
- Attach the IAM roles RedshiftGeocodeFunctionRole and RedshiftReverseGeocodeFunctionPolicy created by this CloudFormation template to your cluster. You can add a role to a cluster or view the roles associated with a cluster by using the Amazon Redshift Management Console, CLI, or API. For more information, see Associating an IAM Role With a Cluster in the Amazon Redshift Cluster Management Guide.
- Connect to your database
- Open an Editor and execute the instructions in the file create-geocoding-udf.sql. This will give the required permissions and create public external function pointing to out lambda. Don't forget to replace the placeholder with your AWS account it.
- To test the geocoding, create a new table and populate it with data as below:
create table places(address varchar (200));
insert into places values
('Domagkstraße 28'),
('Marcel-Breuer-Straße 12');- Execute a query using the newly created lambda as in:
select address,
json_extract_path_text(geocode_address(address, '[48.192087, 11.617126]','["DEU"]'), 'Label') as full_address
from places; - To test the reverse geocoding, create another table and populate it with data as below:
create table places_pos(
latitude decimal(18, 15),
longitude decimal(18,15)
);
insert into places_pos values (7.37951000000003, 51.38240000000007);- And execute a query using the newly created lambda as in:
select latitude, longitude,
reverse_geocode_position(latitude, longitude)
from places_pos; See CONTRIBUTING for more information.
This library is licensed under the MIT-0 License. See the LICENSE file.