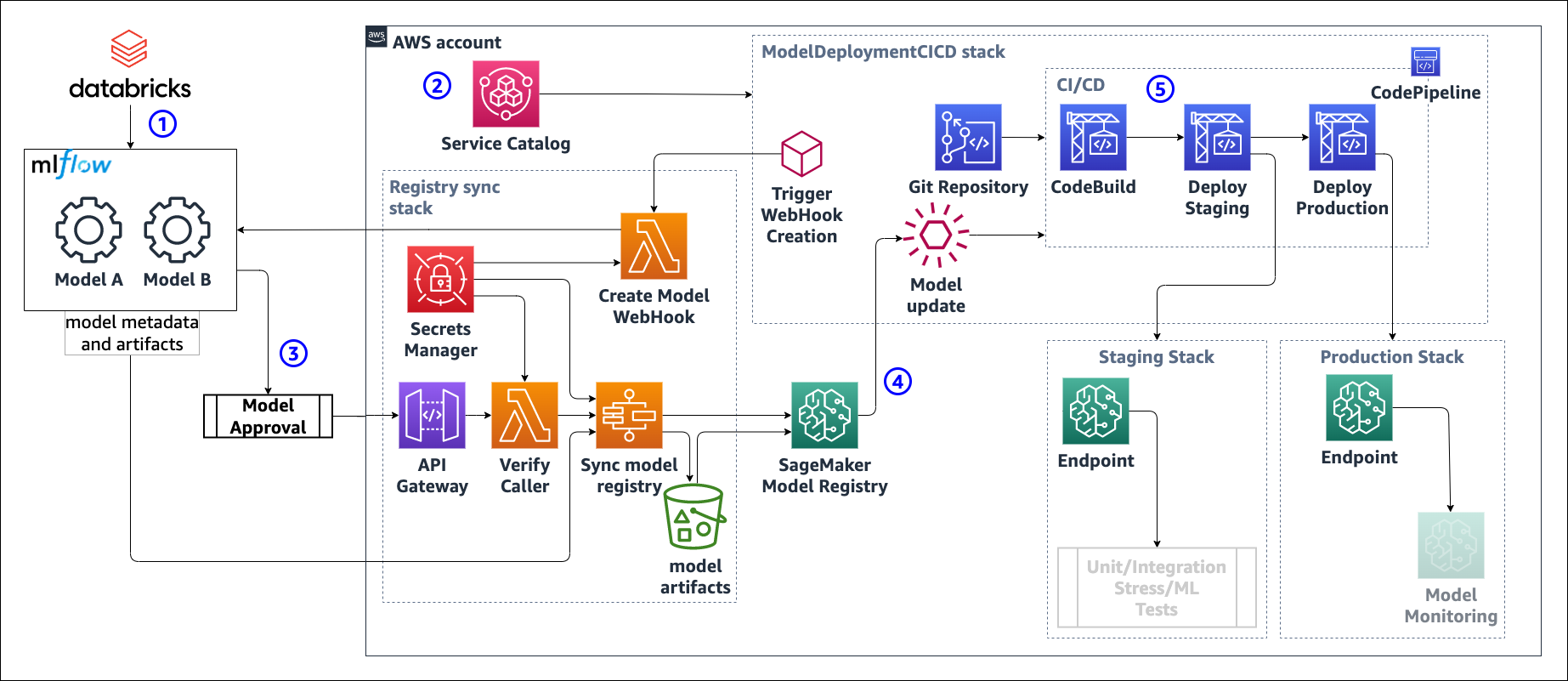
This repository demonstrates how to automate and scale the deployment of models from MLflow model registry to an Amazon SageMaker Endpoint.
The code is provided as an example, and it isn't intended to use in a production environment without a review of all configurations and code to comply with any security requirements.
The deployment of this sample will create resources outside of AWS free tier, please review the Running Costs section of this document.
Deploying models registered with MLflow Model registry to Amazon SageMaker real-time endpoints in a programmatic, repeatable, and automatic fashion.
- Register a version of the model in mlflow model registry.
- Create the CI/CD pipeline to deploy an MLflow model using the product in Service Catalog, providing the model name.
- In MLflow, set the stage of the model to either
StagingorProduction - A webhook triggers a step function to sync MLflow registry with Amazon SageMaker Model Registry. The step function
- repackages the model artifact into a format suitable for SageMaker deployments
- stores the new artifact in an S3 bucket
- create the model package for registering, including a reference to the docker image to be used for deployment (currently only tensorflow implemented)
- Any change in the Model Package Group associated with the mlflow model triggers a run of the CI/CD pipeline using EventBridge
- The CI/CD deploys staging and production endpoints according to the metadata of all the model version registered in the Model Registry.
The project uses CDK pipelines to create the deployment pipeline, offering the flexibility to reshape the deployment to integrate with a variety of processes and governance requirements.
- Store the credentials for programmatic access to mlflow model registry, either as a User name/password or as application token, into AWS Secrets Manager in the same region where the stack is to be deployed
- Create a CodeCommit repository in the same region where the stack is to be deployed
- [Optional] An Amazon SageMaker Studio domain in the same region where the stack is to be deployed. Studio offers a convenient environment visualize model in SageMaker model registry and the associated endpoints.
Clone the repository into a local directory, and setup a new remote pointing at the CodeCommit repository.
Deploy the project with
cdk deploy \
--parameters SecretName=<name of the secret> \
--parameters RepositoryName=<name of the repository>
Common issues:
- the account/region needs to bootstrap CDK. See CDK- Bootstrapping
- need to specify the profile and/or the environment for CDK to have sufficient permissions and to deploy into the correct account/region. See CDK - Permissions
Once the CDK deployment is completed (you can verify also in the CloudFormation console), you should find a CodePipeline called MLflow-MLOps in progress. This is a self-mutating pipeline, it is expected it might run multiple times and change its configuration.
A successful execution of the pipeline results in two CloudFormation stacks: ModelRepack-ModelSyncStack and ServiceCatalogProduct-ScProductStack. ModelRepack-ModelSyncStack contains
- StepFunction with corresponding Lambda functions
- Api Gateway with REST endpoint to receive webhook invocations
- S3 bucket
sagemaker-mlflow-<region>-<account>to store model artifacts - a Secret in Secret manager, used to authenticate the webhook invocations.
The deployment creates a new portfolio in Service Catalog called MLflow-MLOps. To create a model deployment pipeline, grant the the relevant End User access to the portfolio following the documentation.
Authorized IAM users/roles can provision the Deploy-MLflow-model from service catalog. The provisioning requires as input parameter, model_name. This must match the model name in MLflow model registry for the automatic model synchronization to work.
The product provisions
- a CodeCommit repository called
sagemaker-mlflow-<model_name>-deployment - a self-mutating CDK pipeline in CodePipeline, called
sagemaker-mlflow-<model_name>-pipeline - an S3 bucket necessary to support the CDK pipeline. The name of the bucket is generated automatically
- a webhook in mlflow model registry configured to monitor status changes in the model named
<model_name> - an EventBridge Rule monitoring SageMaker Model Registry for any changes in ModelGroups with name
<model_name>
The CDK pipeline will execute and, if it doesn't encounter any error, it will create two CloudFormation Stacks: ProductionStack-ModelDeploy and StagingStack-ModelDeploy. Both stacks should be empty.
After registering a model in MLflow model registry, transition the model version of interest to either Staging or Production.
Here's the sequence of events:
- the stage transition triggers the webhook
- the webhook triggers the execution of the the step function
- Step function
- the step function compares the state of the model version in mlflow model registry with the corresponding model package in SageMaker Model Registry. The matching is based on the model
run_id. - If necessary the step function repackages the model artifact into a
tar.gzfile compatible with deployment using SageMaker Frameworks images. The model packages are stored in the dedicated S3 bucketsagemaker-mlflow-<region>-<account> - Register new models packages, updates the model metadata, or delete model packages in SageMaker Model Registry
- the step function compares the state of the model version in mlflow model registry with the corresponding model package in SageMaker Model Registry. The matching is based on the model
- The EventBridge rule detects changes in the SageMaker Model Registry Model Group and triggers the execution of the model deployment CI/CD pipeline
- The CI/CD pipeline deploys the models to SageMaker endpoints using the Model Packages in SageMaker Model Registry and the configuration in
inference.yaml - Once the CI/CD pipeline execution is completed, the Staging and Production stacks should contain the corresponding endpoints. The endpoint(s) name(s) from the output panel of the CloudFormation stacks.
The template does not include any test for the endpoint or model monitoring. These can be added by modifying the relevant code in the CodeCommit repository.
As of September 2022, a sample breakdown of the estimated running cost of the solution is as follows, before considering AWS Free Tier.
-
Amazon API Gateway - the sample deploys 1 REST endpoint to receive the change of state from the selected models in mlflow model registry. Assuming few hundreds model transitions per month, the cost will be much less than $0.10. Amazon API Gateway Pricing
-
AWS Step Functions - every change of state of a selected model in mlflow model registry triggers the execution of a Step Function. Assuming 1000 executions per month, the cost will be much less than $
0.10. AWS Step Functions Pricing -
AWS Lambda Functions - there are two classes of Lambda functions in the sample:
- functions used supporting the creation of custom resources as part of the CloudFormation deployments. These are executed rarely, and the accrued cost is negligible.
- functions used in the model registry synchronization as part of the Step Function.
Assuming 1000 executions per month, the cost will be much less than $
0.10. AWS Lambda Pricing -
AWS Secrets Manager - the solution requires a secret per model group, plus one secret for holding the credentials to access mlflow. Assuming 5 models groups in operation, and 1000 API calls to access the relevant secrets, monthly cost is around $
2.40. AWS Secrets Manager Pricing -
AWS CodePipeline - the solution deploys one Pipeline for the CICD of the solution itself, and one Pipeline for each model group that is operationalized. Assuming 5 models groups in operation, the expected monthly cost is $5. AWS CodePipeline pricing
-
AWS CodeBuild - all the Code Pipelines run CodeBuild jobs with the default
general1.smallinstances. Assuming 100 CICD executions per month, the expected cost is less than $4. AWS CodeBuild pricing -
Amazon SageMaker
- Amazon SageMaker Model Registry - free of charge, but there are costs associated with Storage in Amazon S3 for the model artifact, and Amazon ECR for any custom Docker image
- Amazon SageMaker hosting - the cost and the units of billing depends on the choice of endpoint configuration. The default values used in the sample are
- Staging models versions: 1 x
ml.m5.largeinstance, $0.144/h in Singapore region - Production model versions: Serverless Inference with 1024 MB of memory. Assuming a processing time per request of 150 ms, the cost for 10,000 requests is around $0.03 in Singapore Region.
- Staging models versions: 1 x
To avoid incurring into unnecessary costs, it is recommended to delete the endpoints when not in use.
This can be achieved by deleting the Cloudformation Stacks ProductionStack-ModelDeploy and StagingStack-ModelDeploy. A more elegant alternative is to change the state of the model(s) in MLflow Model registry to None or Archived. This in turn will remove the models from SM Model Registry and trigger the CodePipeline, resulting in the deletion of the endpoints.
Terminate the corresponding provisioned product using ServiceCatalog. This should send a delete request to the corresponding CloudFormation template. Even after deletion of the CloudFormation template, the pipeline artifact S3 bucket will persist, and it will need to be deleted manually.
Delete the ModelRepack-ModelSyncStack and ServiceCatalogProduct-ScProductStack CloudFormation Stacks.
- Delete
MlflowMlopsStackCloudFormation stack - Delete the secret in AWS SecretManager and the CodeCommit repository
- Empty the model artifact bucket. If there are still model registered in SageMaker Model Registry originally synchronized from mlflow model registry, removing the model artifacts will make it impossible to deploy these models.