The Secure Pet Store sample is an application built in Java for AWS Lambda. It uses Amazon API Gateway to expose the Lambda function as HTTP endpoints and uses Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Amazon Cognito to retrieve temporary credentials for a user and authorize access to its APIs with.
- First, create an Amazon Cognito identity pool. The identity pool should only allow Custom authentication providers.
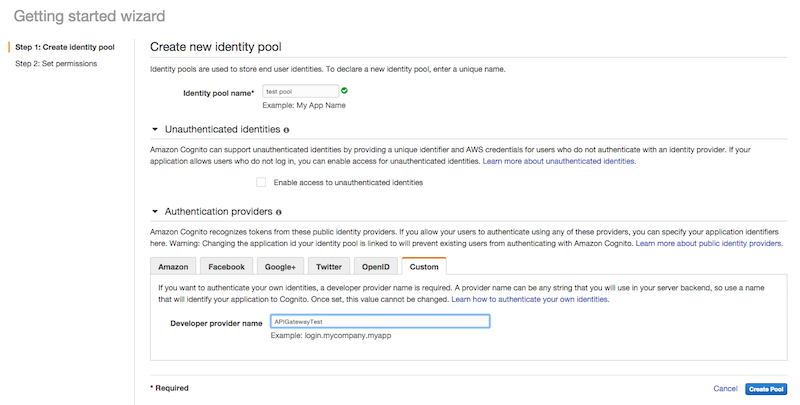
- The next step in the identity pool creation process sets up the IAM roles. For the time being simply click Allow to create the identity pool.
- Now that we have created the Cognito Identity Pool we need to setup the DynamoDB tables. The application requires 2 DynamoDB tables: one for the users and one for the pets. The annotated objects for users and pets are
com.amazonaws.apigatewaydemo.model.pet.Petandcom.amazonaws.apigatewaydemo.model.user.Userin the app source code. - The table for the users should have only a
Hash Keyof typestringcalled username. - The pets table also has only a
Hash Keyof typestringcalled petId.
The application needs to be modified to reflect the resource names created above. After adapting the configuration you package the application and deploy it as an AWS Lambda function with the necessary execution role.
- Configure the application to utilize the correct Cognito Identity Pool and DynamoDB tables. The app reads the configuration from static variables declared in the
CognitoConfigurationandDynamoDBConfigurationin thecom.amazonaws.apigatewaydemo.configurationpackage. Open the 2 classes and set the correct values on the properties.
| Class | Property | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CognitoConfiguration | IDENTITY_POOL_ID | The unique identifier for the Cognito Identity Pool. This values is available in the Amazon Cognito console. |
| CognitoConfiguration | CUSTOM_PROVIDER_NAME | The name of the developer provider specified during the Identity Pool creation process. You can access this value from the edit identity pool page. |
| DynamoDBConfiguration | USERS_TABLE_NAME | The name of the DynamoDB table created to store usernames and passwords |
| DynamoDBConfiguration | PET_TABLE_NAME | The name of the DynamoDB table created to store the pets |
-
Now that the application is configured you can build it and package it for AWS Lambda using Maven. Open a terminal and navigate to the application folder, then run
mvn package. This will create a target directory and inside it a file calledapi-gateway-secure-pet-store-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar. -
We will create an AWS Lambda function that needs access to the resources created above. Create a new role in AWS Identity and Access Management with the following policies:
Trust Policy for the AWS Lambda execution role:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "Service": "lambda.amazonaws.com" }, "Action": "sts:AssumeRole" } ] }
Policy for the AWS Lambda execution role:
```json
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"cognito-identity:GetOpenIdTokenForDeveloperIdentity"
],
"Resource": [
"<COGNITO_IDENTITY_POOL_ARN>"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"dynamodb:GetItem",
"dynamodb:PutItem",
"dynamodb:Scan",
"dynamodb:UpdateItem"
],
"Resource": [
"<DYNAMODB_PETS_TABLE_ARN>",
"<DYNAMODB_USERS_TABLE_ARN>"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:*"
],
"Resource": [
"*"
]
}
]
}
- Open the AWS Lambda console and create a new function. Skip the blueprint selection page and go straight to the Configure Function step. In this screen give your function a name and select Java 8 as runtime. AWS Lambda will ask you to upload a ZIP file for your function. You can upload the Jar file created by the maven process directly.
- As a Handler for your function enter
com.amazonaws.apigatewaydemo.RequestRouter::lambdaHandler. - Use the execution role created in the previous step.
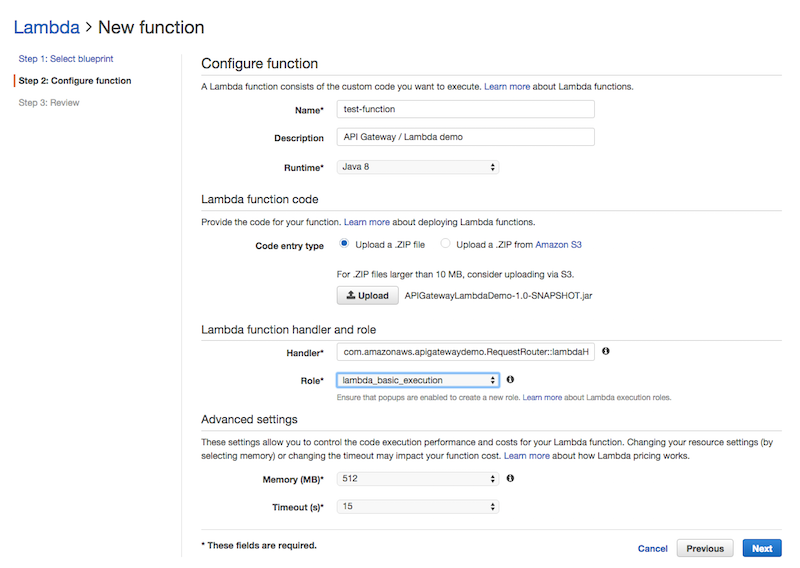
- Now that the Lambda function is ready we can setup the API structure in Amazon API Gateway. To easily create the entire API we are going to use the Swagger format and import this into Amazon API Gateway.
- Open the Swagger definition in the
src/main/resources/Swagger.yamlfile. Search the file forx-amazon-apigateway-integration. This tag defines the integration points between API Gateway and the backend, our Lambda function. Make sure that theurifor the Lambda function is correct, it should look like this:
arn:aws:apigateway:<YOUR REGION>:lambda:path/2015-03-31/functions/<YOUR LAMBDA FUNCTION ARN>/invocations
-
You can specify the role ARN in the
credentialsfield of the Swagger file, next to theurifield. The/petsmethods use a special role:arn:aws:iam::*:user/*. This tells API Gateway to invoke the Lambda function using the caller credentials. For the/usersand/login(the first 2 paths in the file) you will also have to specify the invocation role API Gateway should use to call the Lambda function. You can create a new invocation role for the/usersand/loginmethods from the Identity and Access Management (IAM) console with the following policies:Trust Policy for the AWS Lambda invocation role:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "Service": "apigateway.amazonaws.com" }, "Action": "sts:AssumeRole" } ] }
Policy for the AWS Lambda invocation role:
```json
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"lambda:InvokeFunction"
],
"Resource": [
"<LAMBDA_ARN>"
]
}
]
}
-
Copy the Role ARN from the Role Summary page, and paste it in the
credentialsfield of the/usersand/loginmethods of the Swagger file. -
Now that we have generated all resources for our API and we have all the ARNs, we should also modify the access policy of the Cognito Identity Pool to grant access to the Amazon API Gateway for authenticated users.
-
In the IAM console navigate to the roles list and open the authenticated role of your Cognito Identity Pool - the role is likely to be called Cognito_"IdentityPoolName"Auth_Role
-
Change the policy to:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "execute-api:Invoke" ], "Resource": [ "*" ] } ] }
* Once you have modified and saved the Swagger file to call the correct Lambda function and use your roles [create a new API in Amazon API Gateway](https://console.aws.amazon.com/apigateway/home?region=us-east-1#/apis/create) with the **Import from Swagger** feature.
* You should now be able to deploy and test your **API Gateway Secure Pet Store** API with Amazon API Gateway
# Setting up the iOS sample
## Introduction
The iOS sample application is located under the ```/src/main/resources/ios_sample folder```. It uses [CocoaPods](https://cocoapods.org/) to retrieve its dependencies and includes an iOS client SDK generated with API Gateway.
## Step by Step setup
* If you don't have [CocoaPods](https://cocoapods.org/) installed, follow the installation instructions on the website
* The first step is to copy the contents of the `ios_sample` folder to a new project directory.
* Open a terminal and navigate to the new project directory `cd /your/project/dir`
* To install the dependencies using CocoaPods run `pod install` from the terminal in the project folder
* Open the new `.xcworkspace` file created by CocoaPods in the project folder using XCode
* From XCode open the `PetTest/ClientSDK/PETLambdaMicroserviceClient.m` file
* On line 117 change the `*URLString` definition to match the url of your API deployment with Amazon API Gateway
## The AWSCredentialsProvider
In order to provide credentials to our SDK, and make calls to the Secure Pet Store backend, we have created a custom implementation of the `AWSCredentialsProvider` object. The `AWSCredentialsProvider` interface declares a single method, `(AWSTask *)refresh`. This method is called by the generated SDK whenever it needs credentials and is in charge of fetching a new set of temporary AWS credentials from your backend and storing them in its `_accessKey`, `_secretKey`, and `session_key` properties.
Our custom implementation is located under `PetTest/APIGSessionCredentialsProvider`. The refresh method uses the generated client to call the `login` method with a cached username and password. The login method from our backend verifies the credentials and responds with a set of temporary AWS credentials.