Table of Contents
Please see the blog post here for more information.
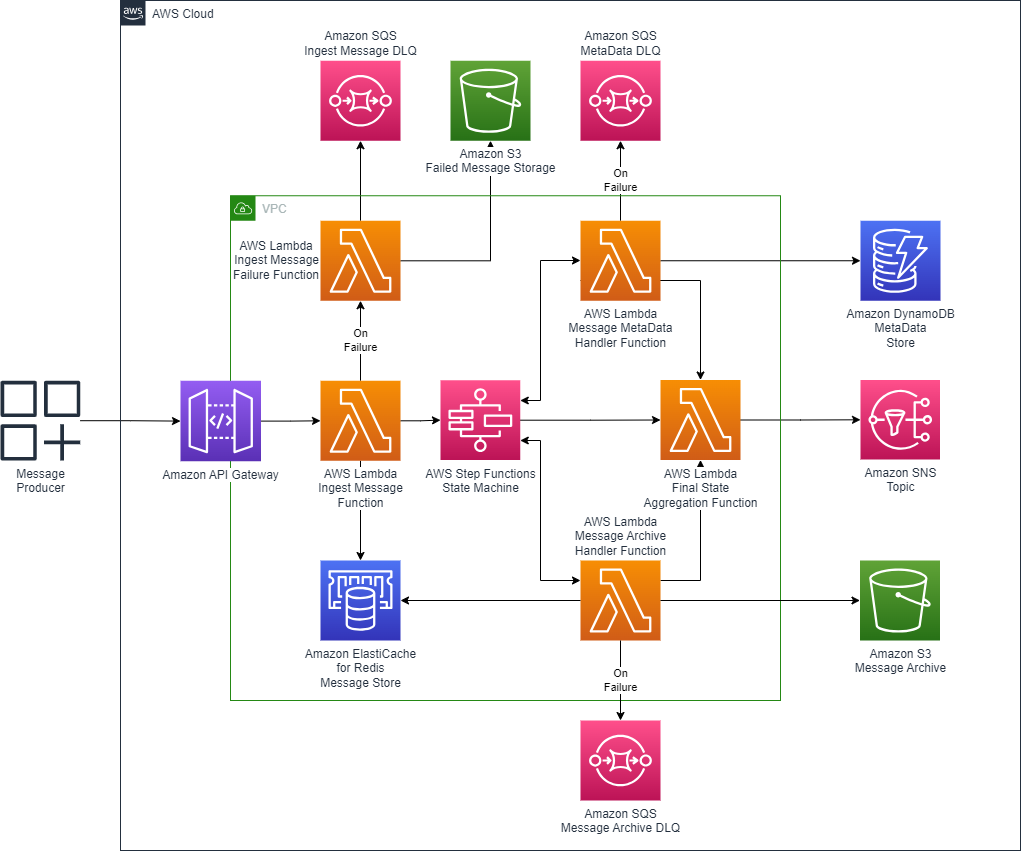
The architecture is designed for maximizing audit record ingestion performance. This system operates between the limit of most messaging systems (256Kb to 1Mb) and the limit for Lambda functions (6Mb). The primary source of latency is the time it takes for an audit record to be transmitted across the network. An AWS Lambda function to receive the message and an Amazon ElastiCache for Redis cluster provides initial blocking persistence layer write that provides better performance than S3. Once the data is persisted in ElastiCache, the AWS Step Functions workflow then manages the orchestration of the communication and persistence functions. The architecture diagram below models the flow of the audit record through the system.
- AWS Command Line Interface: (link)
- AWS Serverless Application Model: (link)The deployment scripts have been created with AWS Cloud Development Kit (AWS CDK) v2 Link. The python version of the CDK has been used
- Python: Python 3.10 was used during the development and deployment of the solution
Note: This solution has been developed and tested on Windows and Amazon Linux 2
Folder structure:
├── infra
├── internal-json
├── media
├── src
| ├── commonLayer
| ├── finalStateAggregate
| ├── ingestFailure
| ├── ingestMessage
| ├── messageArchive
│ └── messageMetaData
├── statemachine
├── test_client
├── template.yaml
└── test_message.jsoninfraSAM templates for VPC and Redis stack creationinternal-jsonExamples of internal message payloadsmediaArchitecture diagramsrcCode to support Lambda functionscommonLayerUniversal constants, exception handler, and JSON template loader code with necessary universal Python librariesfinalStateAggregateBuilds final message to be sent to subscribersingestFailureIf the initial ingestion Lambda fails, this Lambda salvages the raw message and writes it to a S3 bucketingestMessageMain lambda process that receives the message from the client (via the API gateway), writes the payload to Redis, and initiates the Step FunctionmessageArchiveStores the message payload in S3 from RedismessageMetaDataStores the meta data about the message in DynamoDB
statemachineContains the JSON definition of the State Machinetest_clientCode and sample payload to exercise the API gateway and test the stacktemplate.yamlPrimary SAM definition that will create the stack
The incoming message requires three types of data:
- Message payload: treated as a block of data that does not require parsing, usually represented as Base64 data, but may be any JSON compatible format.
- Message metadata: Defined by the use case. A minimally suggested metadata contains source system identification, message type, and time/date stamps. In the walkthrough below, the original timestamp from the message producer is used as the timestamp for internal messages.
- Security Context: When the message producer authenticates and posts to the API Gateway endpoint, you can query the security context to get metadata about the source of the payload. This context includes security principles, receipt information, timestamp, environmental information (source IP and headers) and a message payload checksum. This context is stored in the DynamoDB metadata record and is queried from there by downstream systems.
The internal message contains data about the storage context and data for the Step Functions workflow to route the message.
- Message ID: generated by the ingest Lambda function.
- Message Metadata: contains system information plus metadata copied from the incoming message.
- Security Context: security context copied from the incoming message.
- Storage Context.
- ElastiCache for Redis reference information, e.g., cluster address and key.
- Amazon S3 reference information, e.g., bucket and key.
- Persistence flags, true or false that shows if the data has or has not been persisted.
- DynamoDB Metadata persistence reference information, e.g. table and key.
Information sent to downstream subscribers about messages received by the system.
- Message ID: generated by the ingest Lambda function.
- Message Metadata: repeated from incoming message.
- State information:
- Message Persisted in Amazon S3: True/False.
- Metadata Persisted in DynamoDB: True/False.
- Data storage information:
- ElastiCache for Redis reference, e.g., cluster address and key.
- Amazon S3 reference information, e.g., bucket and key.
- DynamoDB Metadata persistence reference information, e.g. table and key.
Prerequisites
- An Amazon account to deploy the stack into
- Credentials with AWS Region configured with permissions necessary to run SAM script (see AWS CLI documentation)
The following commands will build and deploy the stack
cd <project directory>
sam build
sam deploy --guidedThese are the parameters that are required:
- Stack Name: Name given to this deployment (example: serverless-messaging)
- AWS Region: Where to deploy (example: us-east-1)
- ElasticacheInstanceClass: EC2 cache instance type to use with (example: cache.t3.small)
- ElasticReplicaCount: How many replicas should be used with ElastiCache (recommended minimum: 2)
- ProjectName: Used for naming resources in account (example: serverless-messaging)
- MultiAZ: True/False if multiple Availability Zones will be used (recommend: True)
- The default parameters can be selected for the remainder of questions
The SAM script will ask for the following configuration items:
- ElasticacheInstanceClass What EC2 instance type to use with AWS ElastiCache Redis cluster. Recommend
cache.t3.smallfor low volume testing - ElasticReplicaCount How many instances/replicas of the ElastiCache to create. Recommend
2 - ProjectName Name to use with VPC naming. No recommendation
- MultiAZ Configure Redis to use MultiAZ deployment configuration. Recommend
true
MIT No Attribution
Copyright 2023 Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates.
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.