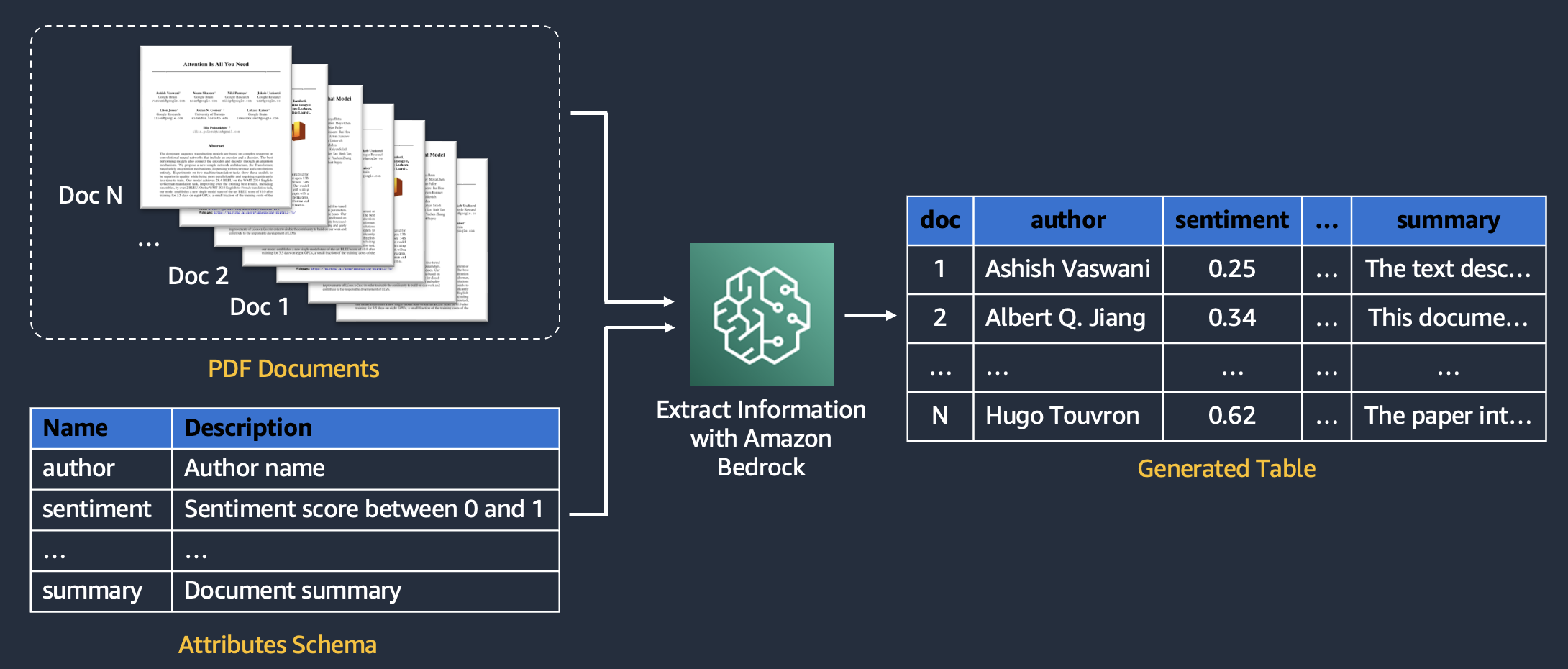
🚀 Extract information from unstructured documents at scale with Amazon Bedrock
Converting custom documents into a structured database is a recurring business task. Common use cases include creating a product feature table from article descriptions, extracting meta-data from internal documents, analyzing customer reviews, and more.
This repo provides an AWS CDK solution that extracts information from documents in minutes using generative AI.
The solution has the following key features:
- Extract different information types, including:
- Well-defined entities (e.g., name, title)
- Numeric scores (e.g., sentiment, urgency)
- Free-form content (e.g., summary, suggested response)
- Describe the attributes to be extracted from your docs without costly data annotation or model training
- Leverage multi-modal LLMs on Amazon Bedrock and/or Amazon Textract for information extraction and OCR
- Use Python API or demo UI to process PDFs, MS Office, images, and get JSON output
Example API call
Refer to the demo notebook for the API implementation and usage examples:
docs = ['doc1', 'doc2']
features = [
{"name": "delay", "description": "delay of the shipment in days"},
{"name": "shipment_id", "description": "unique shipment identifier"},
{"name": "summary", "description": "one-sentence summary of the doc"},
]
run_idp_bedrock_api(
documents=docs,
features=features,
)
# [{'delay': 2, 'shipment_id': '123890', 'summary': 'summary1'},
# {'delay': 3, 'shipment_id': '678623', 'summary': 'summary2'}]Example Web UI
To deploy the app to your AWS account, you can use a local IDE or create a SageMaker Notebook instance.
We recommend using SageMaker to avoid installing extra requirements. Set up ml.m5.large instance and make sure the IAM role attached to the notebook has sufficient permissions for deploying CloudFormation stacks.
Clone the repo to a location of your choice:
git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/process-complex-documents-with-amazon-bedrock.gitWhen working from a SageMaker Notebook instance, run this script to install all missing requirements:
cd <folder with the downloaded asset>
sh install_deps.shWhen working locally, make sure you have installed the following tools, languages as well as access to the target AWS account:
- AWS CLI
- AWS Account: configure an AWS account with a profile
$ aws configure --profile [profile-name] - Node.js
- IDE for your programming language
- AWS CDK Toolkit
- Python 3.12
Navigate to the project folder and execute the following script to create a virtualenv on MacOS or Linux and install dependencies:
sh install_env.sh
source .venv/bin/activateOpen and modify the config.yml file to specify your project name and modules you would like to deploy (e.g., whether to deploy a UI).
stack_name: idp-bedrock-stack # Name of your demo, will be used as stack name and prefix for resources
...
streamlit:
deploy_streamlit: True- Open the target AWS account
- Open AWS Bedrock console and navigate to the region specified in
config.yml - Select "Model Access" in the left sidebar and browse through the list of available LLMs
- Make sure to request and enable access for the model IDs that are specified in
config.yml
Bootstrap CDK in your account. When working locally, use the profile name you have used in the aws configure step. When working from a SageMaker Notebook instance, profile specification is not required.
cdk bootstrap --profile [PROFILE_NAME]Note: you can easily configure multiple accounts and bootstrap and deploy the framework to different accounts.
Make sure the Docker daemon is running in case you deploy the Streamlit frontend. On Mac, you can just open Docker Desktop. On SageMaker, Docker daemon is already running.
cdk deploy --profile [PROFILE_NAME]You can delete the CDK stack from your AWS account by running:
cdk destroy --profile [AWS_PROFILE_NAME]or manually deleting the CloudFormation from the AWS console.
Deploying CDK / CloudFormation stacks requires near Admin Permissions. Make sure to have the necessary IAM account permissions before running CDK deploy. Here is a detailed list of minimal required permissions to deploy a stack.
When deleting the stack, it may delete everything except for the created S3 bucket, which will contain the uploaded documents by the user and their processed versions. In order to actually delete this s3 bucket, you may need to empty it first. This is an expected behavior as all s3 buckets may contain sensitive data to the users.
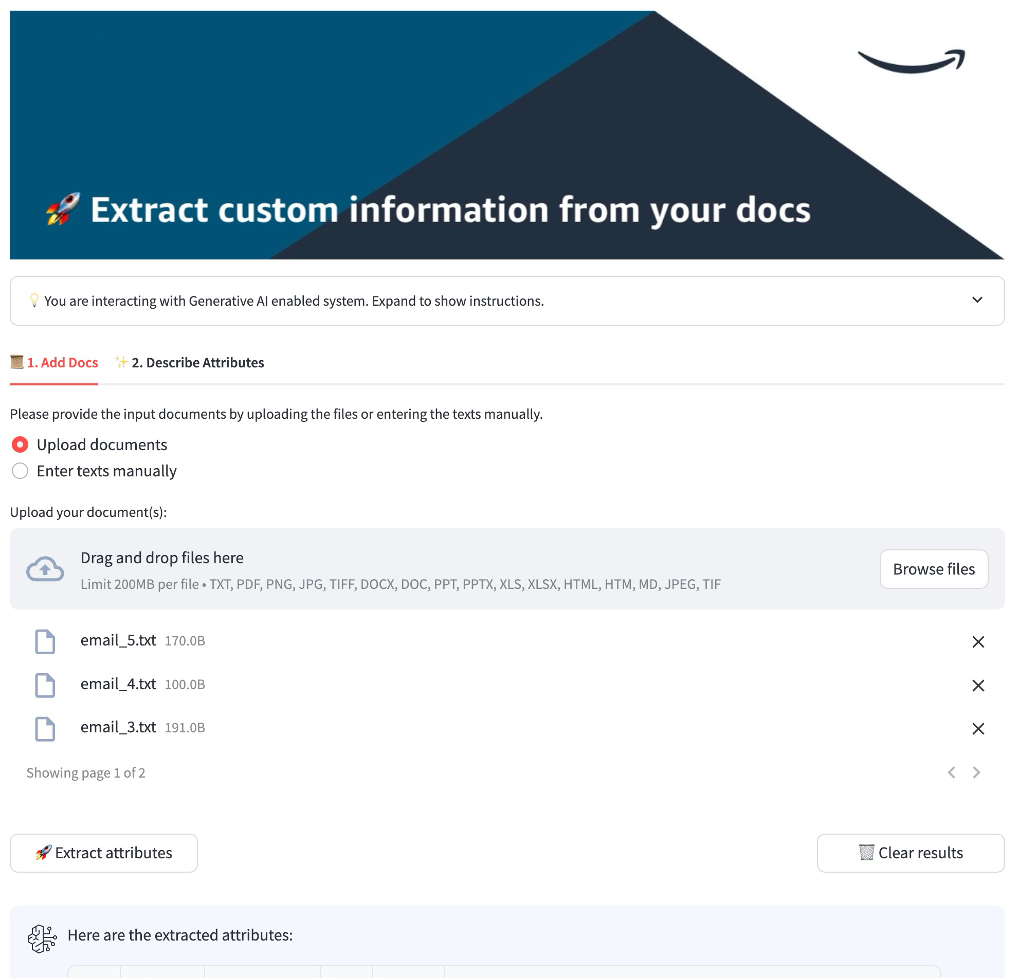
Follow steps in this notebook to run a job via an API call. You will need to:
- provide input document text(s)
- provide a list of features to be extracted
- Open the Cognito Console, choose the created user pool, and click create user
- Provide the user name and a temporary password or email address for auto-generated password
- Users will be able to log into the frontend using Cognito credentials
- The URL to access the frontend appears as output at the end of the CDK deployment under "CloudfrontDistributionName"
or
- Open the AWS console, and go to CloudFront
- Copy the Domain name of the created distribution
You can run the Streamlit frontend locally for testing and development by following these steps:
- Deploy the CDK stack once
- In
assets/streamlit/.env, setSTACK_NAMEto the stack name you used. Setting the other environment variables is optional. By default those values will be read from AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store. If you wish to override those variables for local testing, you can set them in theassets/streamlit/.envfile.- Including Cognito client ID, API endpoint url, region, and S3 bucket name
- Provide AWS credentials
- You can add AWS credentials to the
assets/streamlit/.envfile - Or simply export credentials in your terminal, e.g.
export AWS_PROFILE=<profile>
- You can add AWS credentials to the
- Navigate to the frontend folder:
cd assets/streamlit - Create another environment with for the frontend
python3 -m venv .venv - Activate the environment
source .venv/bin/activate - Install frontend dependencies
poetry install - Start frontend on localhost
streamlit run src/Home.py - Copy the local URL from the terminal output and paste in the address bar of your browser
The following diagram illustrates the high-level architecture of this solution:
Core team:
 |
 |
|---|---|
| Nikita Kozodoi | Nuno Castro |
Contributors:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Romain Besombes | Zainab Afolabi | Egor Krasheninnikov | Huong Vu | Aiham Taleb | Elizaveta Zinovyeva |
Acknowledgements:
See CONTRIBUTING for more information.
Note: this asset represents a proof-of-value for the services included and is not intended as a production-ready solution. You must determine how the AWS Shared Responsibility applies to their specific use case and implement the needed controls to achieve their desired security outcomes. AWS offers a broad set of security tools and configurations to enable out customers.
- Input data:
- Note that the solution is not scoped for processing regulated data.
- Network & Delivery:
- CloudFront:
- Use geography-aware rules to block or allow access to CloudFront distributions where required.
- Use AWS WAF on public CloudFront distributions.
- Ensure that solution CloudFront distributions use a security policy with minimum TLSv1.1 or TLSv1.2 and appropriate security ciphers for HTTPS viewer connections. Currently, the CloudFront distribution allows for SSLv3 or TLSv1 for HTTPS viewer connections and uses SSLv3 or TLSv1 for communication to the origin.
- API Gateway:
- Activate request validation on API Gateway endpoints to do first-pass input validation.
- Use AWS WAF on public-facing API Gateway Endpoints.
- CloudFront:
- Machine Learning and AI:
- Bedrock
- Enable model invocation logging and set alerts to ensure adherence to any responsible AI policies. Model invocation logging is disabled by default. See https://docs.aws.amazon.com/bedrock/latest/userguide/model-invocation-logging.html
- Consider enabling Bedrock Guardrails to add baseline protections against analyzing documents or extracting attributes covering certain protected topics.
- Comprehend
- Consider using Amazon COmprehend for detecting and masking PII data in the user-uploaded inputs.
- Bedrock
- Security & Compliance:
- Cognito
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) in each Cognito User Pool.
- Consider implementing AdvanceSecurityMode to ENFORCE in Cognito User Pools.
- KMS
- Implement KMS key rotation for regulatory compliance or other specific cases.
- Configure, monitor, and alert on KMS events according to lifecycle policies.
- Cognito
- Serverless:
- Lambda
- Periodically scan all AWS Lambda container images for vulnerabilities according to lifecycle policies. AWS Inspector can be used for that.
- Lambda
This library is licensed under the MIT-0 License. See the LICENSE file.