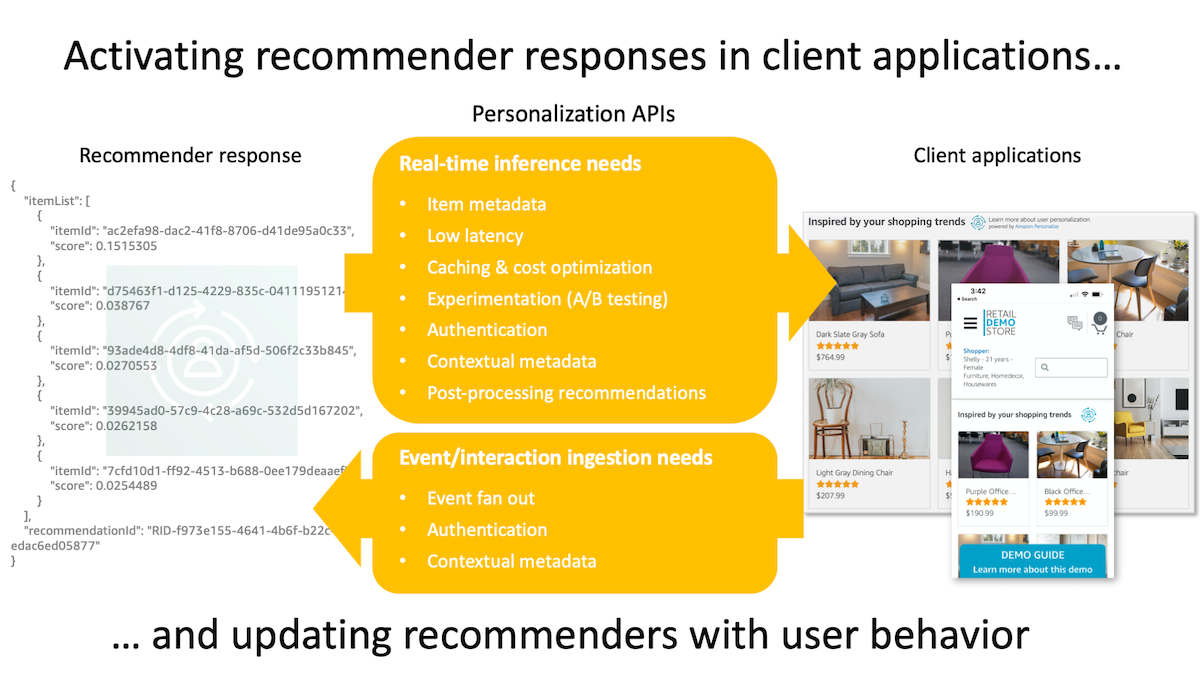
Machine learning recommenders are an effective tool to enhance the user experience in client applications through personalized product and content recommendations. However, putting recommendations to work in client applications and keeping these recommenders updated in real-time with in-app user behavior often requires building and maintaining complicated middleware components between your client applications and recommenders. This project provides the components necessary for deploying low-latency real-time APIs that sit between your client applications and recommenders. Key features include flexible/smart response caching, decorating recommender responses with the item metadata needed to render them in your applications, seamless A/B testing across your recommenders, API authentication, automatic user context, user event collection and fan out, and more.
Although this project is tightly integrated with Amazon Personalize, an AI service from AWS that allows you to easily create state-of-the-art ML recommenders based on your data, it also supports experimental backend integrations with personalization providers built with Amazon SageMaker, AWS Lambda, or HTTP endpoints. Key features include:
- Highly configurable multi-layer caching that reduces both end-to-end latency and the number of calls made to API endpoints and origin recommenders
- Multiple opinionted API deployment and authentication approaches including OAuth2, API keys, and no authentication
- Item metadata needed to render recommendations in client applications is automatically included in API responses (i.e., response decoration)
- Fan-out of incremental/streamed events to Amazon Personalize event trackers, Amazon Kinesis Data Streams, and Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose
- Automatically derive context from intrinsic data in each request to enhance the relevancy of recommendations, enrich incremental events, and resolve dynamic filter values
- Seamlessly perform A/B tests across different recommender implementations
- Dynamic and flexible configuration that makes it easy to safely deploy, monitor, and rollback configuration changes
- Automatic generation of application configuration given existing Amazon Personalize resources (optional)
- Automatic generation of OpenAPI/Swagger specification based on application configuration
- Deployment of Swagger web interface that allows for easy inspection and testing of API endpoints (optional)
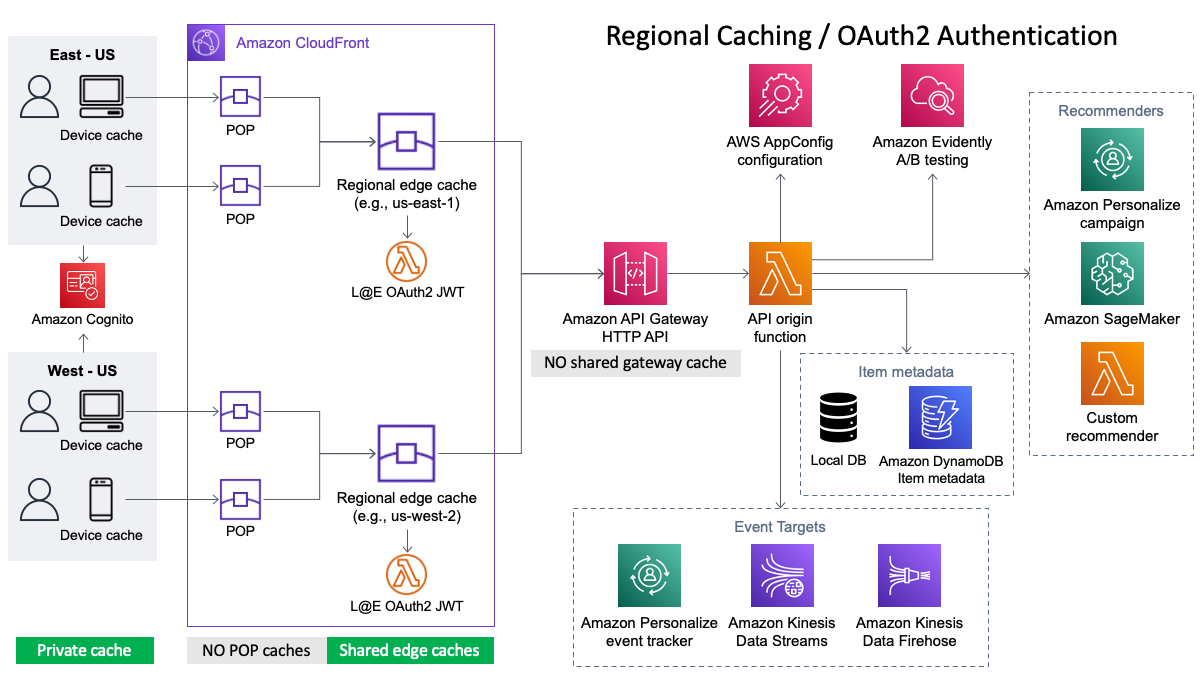
This solution provides opinionated architectures for several common deployment scenarios. The following diagram illustrates the components deployed for an API architecture that utilizes OAuth2 for authentication, CloudFront for regional shared caches, and Amazon API Gateway for API management. This is just one of the supported configurations. The API origin function is the heart of this solution.
See the installation instructions below for details on additional deployment scenarios with alternative authenication and caching approaches.
Depending on the deployment configuration selected, caching is automatically enabled at multiple points/layers in the request path.
- Amazon CloudFront is deployed as a CDN (content delivery network) in front of the APIs to provide a distributed shared cache and to reduce overall network latency.
- Control the maximum age that responses are cached at the individual recommender and request levels.
- Control whether responses can be cached in shared (CloudFront or API Gateway) and/or private (browser/device) caches.
- Configuration inheritance: set a single cache policy that applies to all recommenders with the option to override cache policies at the namespace and recommender levels.
- Automatic support for HTTP cache validation through
ETagresponse headers andIf-None-Matchrequest header inspection. - The result is reduced latency and fewer calls to your origin recommenders.
See the Caching documentation for details.
Machine learning recommenders like Amazon Personalize often provide only a list of recommended item IDs in their inference responses. However, client applications typically need rich metadata for each item (e.g., name, description, price, category, genre, image URL, media URL, detail URL, etc) to be able to render recommended items in their UIs. Amazon Personalize does support returning item metadata with responses for campaigns and recommenders. However, this capability is limited to returning up to 10 columns per item and up to a maximum of 50 items per response (as opposed to 500 items without item metadata). There is also an additional cost for enabling item metadata in Amazon Personalize responses. If these limits are not enough to suppport your use case, the Personalization APIs project provides an item metadata sidecar implementation that stores item metadata either in a local database right where recommendations are retrieved in the API layer (for small and modest sized item catalogs) or in Amazon DynamoDB (for very large item catalogs). Both options provide very low-latency retrieval of item metadata that is automatically injected into recommender responses before returning them to your applications. This capability allows you to focus more on displaying recommendations in your client applications rather than building undifferentiating middleware to merge item catalog information into your recommendation responses.
See the Inference item Metadata documentation for details.
The Personalization API's /events endpoint provides a distribution point to send events to any combination of Amazon Personalize event trackers, Amazon Kinesis Data Streams streams, and Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose delivery streams. Or you can have the API send events just to a Kinesis data stream and then configure your own consumers downstream from Kinesis. This allows you to persist clickstream data in datastores such as S3 (data lake), OpenSearch, or Redshift and then build dashboards, perform deeper analysis, and more.
See the API entry points and Configuration documentation for details.
The current context of the end-user--their current device, current location, seasonality, and so on--can be extremely valuable signal to recommenders like Amazon Personalize. Contextual attributes allow recommendations to be personalized not only to the user's interest but also that are relevant to a moment in time. The Personalization APIs solution is able to derive user context based on intrinsic data available in the request and seamlessly pass that context to recommenders at inference and when new events are ingested. This relieves you from having to build logic into your client and server applications to derive and transmit contextual attributes.
See the Automatic context and Configuration documentation for details.
Deploying a recommender system is rarely a one-and-done effort. It's an iterative process. Comparing the effectiveness of one recommender against another and how they impact business objectives requires online testing. The most common online testing strategy is A/B testing where separate groups of end-users are presented different variations of recommendations and their behavior is measured to determine which variation produces the best results.
The Personalization APIs solution is integrated with Amazon CloudWatch Evidently, a new capability of CloudWatch that allows you to manage, deploy, and monitor A/B tests in your applications, which enables you to easily run your own A/B tests across different recommender implementations.
See the Experimentation documentation for details.
AWS AppConfig is used to manage the configuration for this solution. With AppConfig you can easily create, manage, and deploy API configuration changes as well as set deployment strategies to control roll out, bake time, and rollback changes.
At deployment time, you can have the project automatically generate a configuration based the recommenders, campaigns, and event trackers in one or more Amazon Personalize dataset groups in your AWS environment. This is a great way to save a lot of time setting up the foundation of your configuration. You can then take the generated base configuration and customize it further to suit your needs.
See the Configuration documentation for details.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Deploying this solution in your AWS account will create and consume AWS resources, which will cost money. Therefore, if after installing this solution you choose not to use it as part of your recommender API strategy, be sure to follow the Uninstall instructions below to avoid ongoing charges and to clean up all data.
There are two options for installing this solution. The easiest and most convenient installation option is using CloudFormation directly. If your application and recommenders are hosted in one of the AWS regions listed in Option 1 below, click the "Launch Stack" button for the appropriate region. Otherwise, to install the solution in another AWS region, use Option 2.
To support easy single-click deployments, this solution has been packaged and staged in the following regions. If your recommenders, such as Amazon Personalize resources, are hosted in one of these regions, it is recommended to use the appropriate "Launch Stack" button below. If your recommenders are in a different region, use Option 2.
| Region name | Region code | Launch |
|---|---|---|
| US East (N. Virginia) | us-east-1 |  |
| US East (Ohio) | us-east-2 |  |
| US West (Oregon) | us-west-2 |  |
| Europe (Ireland) | eu-west-1 |  |
| Asia Pacific (Sydney) | ap-southeast-2 |  |
To manually install this solution or to install this solution into a region not listed under Option 1 above, perform the following steps to install using the AWS Serverless Application Model (SAM) tool.
git clone git@github.com:aws-samples/personalization-apis.gitTo install using the SAM CLI, you first need the following tools locally installed.
- SAM CLI - Install the SAM CLI
- Python 3 installed
- Docker - Install Docker community edition
Then ensure you are logged in to public.ecr.aws in Docker so SAM can download the Docker build images by running the following command in your shell.
aws ecr-public get-login-password --region us-east-1 | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin public.ecr.awsTo build and deploy the application for the first time, run the following command in your shell:
cd personalization-apis
sam build --use-container --cached
sam deploy --guidedThe sam build --use-container --cached command will build and package the source of the solution. The sam deploy --guided command will prompt you for deployment configuration information and ultimately deploy the solution in your AWS account. Be sure to deploy the solution in the same AWS region where your recommenders reside.
If you are asked multiple times to confirm
PersonalizationHttpApiFunction may not have authorization defined, Is this okay? [y/N], be sure to answeryto each one.
When installing using either option above, you are presented with several deployment parameters. These parameters control how the solution is configured to match your desired environment configuration.
| Parameter name | Type | Valid values | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ApplicationName | String | Alphanumeric | Application name used to name AppConfig application. Enter a name that represents your application. | |
| EnvironmentName | String | Alphanumeric | 'prod' | Application environment name (such as "dev", "staging", "prod", etc). Used as the stage name in API Gateway and to organize application configuration resources in AppConfig. |
| TimeZone | String | Time zone name | 'UTC' | Initialize the solution's time zone to match your default local time zone. This is used as the default time zone if the user's time zone is not available when determining time-based automatic context. |
| AuthenticationScheme | String | 'OAuth2-Cognito', 'ApiKey', or 'None' | 'OAuth2-Cognito' | Desired authentication scheme to protect API access. Note that "ApiKey" requires "API-Gateway-REST" for the API entry point type. If you select "OAuth2-Cognito", be sure to deploy the edge authentication solution as well (must be done separately in us-east-1 only). |
| CreateCognitoResources | String | 'Yes' or 'No' | 'Yes' | Create Amazon Cognito user pool and client that can be used to create OAuth2 tokens for API authentication. Only applicable when the authentication scheme is "OAuth2-Cognito". If you have an existing Cognito user pool, select "No". |
| ApiEntryPointType | String | 'API-Gateway-HTTP' or 'API-Gateway-REST' | 'API-Gateway-HTTP' | API entry point type for requests that access the personalization APIs. "API-Gateway-REST" is recommended when the authentication scheme is "None" or "OAuth2-Cognito" for the best performance and lowest cost. |
| CacheScheme | String | 'CloudFront', 'API-Gateway-Cache', 'Both', 'None' | 'CloudFront' | Caching scheme to deploy with the API entry point type. Note that using "API-Gateway-REST" for the API entry point type includes a CloudFront distribution that is transparently managed by API Gateway. However, this distribution does not include caching so you should select "API-Gateway-Cache" with "API-Gateway-REST". |
| GenerateConfigDatasetGroupNames | String | Dataset group names or 'all' | Specify one or more Amazon Personalize dataset group names (separated by a comma) or 'all' and a personalization APIs configuration will be automatically generated during deployment by checking the dataset groups for recommenders, campaigns, and event trackers. | |
| CreateSwaggerUI | String | 'Yes' or 'No' | 'Yes' | Create public Swagger web UI that can be used to inspect and test APIs. |
The following table lays out the different deployment combinations in more detail with the recommended combination for each authentication type in bold.
| Auth scheme | Entry point type | Cache scheme | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| None | API-Gateway-HTTP | CloudFront | Lower latency, lower cost, best for distributed user base. |
| None | API-Gateway-REST | API-Gateway-Cache | Slightly higher latency and higher cost. |
| ApiKey | API-Gateway-REST | API-Gateway-Cache | Only valid combination option for ApiKey auth scheme. |
| N/A | Not viable - APIGW HTTP does not support API Keys | ||
| OAuth2-Cognito | API-Gateway-HTTP | CloudFront | JWT validation using L@E function. Preferred due to more distributed caches, lower latency, and lower cost. |
| OAuth2-Cognito | API-Gateway-REST | API-Gateway-Cache | JWT validation must be done in API Gateway with API-Gateway-REST (edge optimized) |
Note: the following steps assume you already have one or more recommenders created and deployed in the same AWS account and region where this solution was deployed.
The solution retrieves its configuration details from AWS AppConfig. When the solution is initally deployed, you can have it automatically generate a base configuration based on the current Amazon Personalize resources in your account (see the GenerateConfigDatasetGroupNames template parameter above). Otherwise, a skeleton/empty configuration is created in AppConfig. Before the solution can serve responses from your recommenders, you must first update the skeleton configuration to match your recommender deployments. See the configuration documentation for details. The samples folder provides some minimal configurations that can help get you started.
If you choose to use one of the item metadata sidecar implementations, you will need to prepare and upload your item metadata to an S3 bucket. This step is not required if you're using item metadata returned by Amazon Personalize.
Once your recommenders are configured in AppConfig, it's time to upload your item metadata to the S3 bucket created by the solution. The uploaded item metadata file contains the attributes of each item that are needed to render them in your client applications (e.g., item name, description, category, genre, image URL, price, media URL, etc). Your item metadata file needs to be contained in a single JSON file in the JSON Lines format. The solution will automatically detect when you upload your metadata file to the proper folder in the S3 bucket and load your metadata into the datastore setup in your configuration. Be sure to update and deploy your configuration with the appropriate item metadata configuration before uploading your item metadata. See the item metadata documentation for details.
If you deployed the Personalization APIs solution with the ApiKey or None authentication scheme, you can skip this step.
In order to authenticate OAuth2 JWT tokens from Amazon Cognito within CloudFront, you must deploy the OAuth2 edge authentication resources. These resources must be deployed into the us-east-1 AWS region since they include a Lambda@Edge function that must be deployed to CloudFront (which can only be done from the us-east-1 region).
You can install the OAuth2 edge resources into the us-east-1 region using the "Launch Stack" button below.
If you'd rather install the OAuth2 edge resources manually using AWS SAM, execute the following commands at the command line (the deploy_edge_auth.sh shell script can also be used as a shortcut).
sam build --use-container --cached --template-file template-edge.yaml && sam deploy --region us-east-1 --config-file samconfig-edge.toml --guidedOnce deployment finishes successfully, sign in to the AWS console, switch to the N. Virginia - us-east-1 region, browse to the Lambda service page, find the EdgeAuthFunction, and deploy it to the CloudFront distribution created when you installed the solution as a Viewer Request. See the API authentication documentation for details.
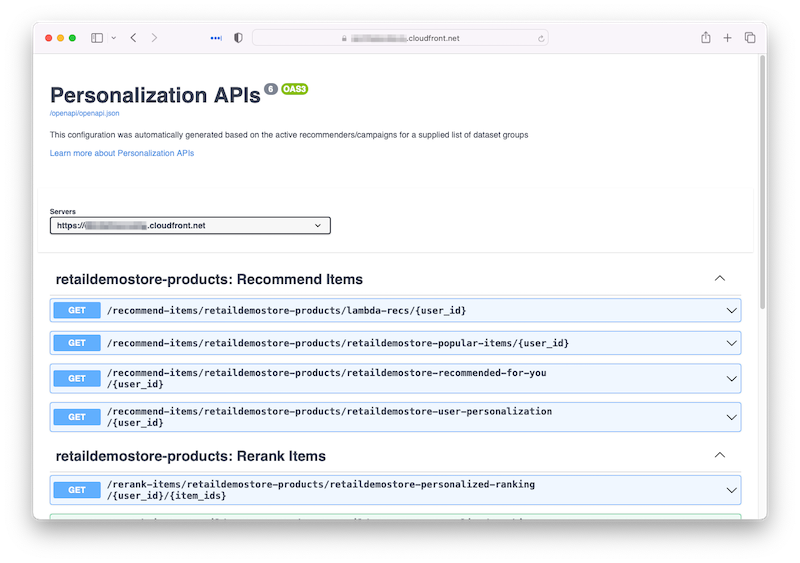
At this point you should be able to test the Personalization API endpoints. You can do this with a utility like Swagger UI, Postman, or the cURL command. This solution automatically generates an OpenAPI/Swagger specification file each time the application configuration is updated. You can find the generated OpenAPI spec file in the staging bucket under /openapi/openapi.json (you can find the staging bucket name in the CloudFormation output parameters). If you deployed the solution with the CreateSwaggerUI parameter set to Yes, a public web UI endpoint was created that hosts the generated OpenAPI/Swagger specification. See the SwaggerUI CloudFormation output parameter for the URL to this endpoint. Otherwise, the generated OpenAPI/Swagger spec file can be downloaded from the staging bucket and imported into a tool such as Postman.
The root URL to use for testing your APIs depends on the deployment configuration you selected when installing the solution:
- If you deployed with the
API-Gateway-RESTAPI entry point type:- Use the value of the
RestApiEndpointUrlCloudFormation output parameter as your API root URL (you can also find this URL in the AWS console for API Gateway)
- Use the value of the
- If you deployed with
CloudFrontorBothcache scheme:- Use the value of the
ApiCdnUrlCloudFormation output parameter as your API root URL (you can also find this URL in the AWS console for CloudFront)
- Use the value of the
- If you deployed with
Nonecache scheme:- Use the value of the
HttpApiEndpointUrlCloudFormation output parameter as your API root URL (you can also find this URL in the AWS console for CloudFront)
- Use the value of the
The remainder of the API URL path depends on the configuration you created in Step 3. See the API entry points documentation for details.
Note that the OpenAPI spec file and the Swagger UI already have the CloudFront and API Gateway base endpoint URLs configured.
You can further customize the base API configuration as follows:
- Add your own domain name and SSL certificate to the CloudFront distribution or API Gateway endpoint (only if you deployed with the
API-Gateway-RESTAPI entry point type). - Update the base CORS configuration to only allow requests from the origins of your client applications.
- If you deployed with a configuration that includes CloudFront, you can further protect the origin API endpoint (API Gateway) using AWS WAF that will prevent clients from calling API Gateway directly. Details here.
- Setup Provisioned Concurrency for the personalization_api_function. The ARN for this function can be found in the CloudFormation output parameters (either
PersonalizationHttpApiFunctionorPersonalizationRestApiFunctiondepending on your deployment options) or in the AWS Lambda console.
The easiest way to uninstall/delete this solution is using the CloudFormation page in the AWS console. Just find and select the CloudFormation stack name you used to install the solution and click "Delete". Alternatively, you can use AWS CLI to delete the CloudFormation stack. Assuming you used the default application name for the stack name (personalization-apis), you can run the following command:
aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name personalization-apisIf you used a stack name other than personalization-apis, substitute your stack name in the command above.
Q: I'm using one of the item metadata sidecar implementations and I uploaded item metadata to the staging bucket but I do not see the item metadata in my API responses. What's wrong?
A: Some things to check:
- Make sure that you added
inferenceItemMetadataconfiguration(s) to the namespaces in the solution's configuration in AppConfig and that you deployed these changes. This must be done before you upload your item metadata file to the staging bucket. Deploying a configuration change in AppConfig requires creating a new hosted configuration version, starting a deployment of that version, and waiting for it to be deployed to the solution. You can verify that the updated configuration is active by inspecting theX-Personalization-Config-Versionresponse header from the API. This header's value is the value of theversionfield in your configuration. - Make sure you uploaded your inference item metadata file into the correct folder in the staging bucket. See the inference item metadata documentation for details.
- It can take some time for configuration changes to be fully deployed to the origin function (< 1 minute), item metadata datastores to be populated (depends on size of uploaded metadata file), and for any prior cached responses without metadata to be refreshed. Give it a few minutes or try API requests for different user IDs or item IDs to bypass cached responses. Note that the
localdbapproach has a defaultsyncIntervalof 300 seconds. This means it can take up to 5 minutes for the API origin functions to synchronize DBM files from the staging bucket. - Inspect the CloudWatch logs for the
LoadItemMetadataFunctionfor errors that can help troubleshoot underlying issues.
If you encounter a bug, please create a new issue with as much detail as possible and steps for reproducing the bug. Similarly, if you have an idea for an improvement, please add an issue as well. Pull requests are also welcome! See the Contributing Guidelines for more details.
This sample code is made available under a MIT-0 license. See the LICENSE file.