JP | EN
If you have deployed this project before, please check these upgrade procedures. Otherwise, you can ignore this.
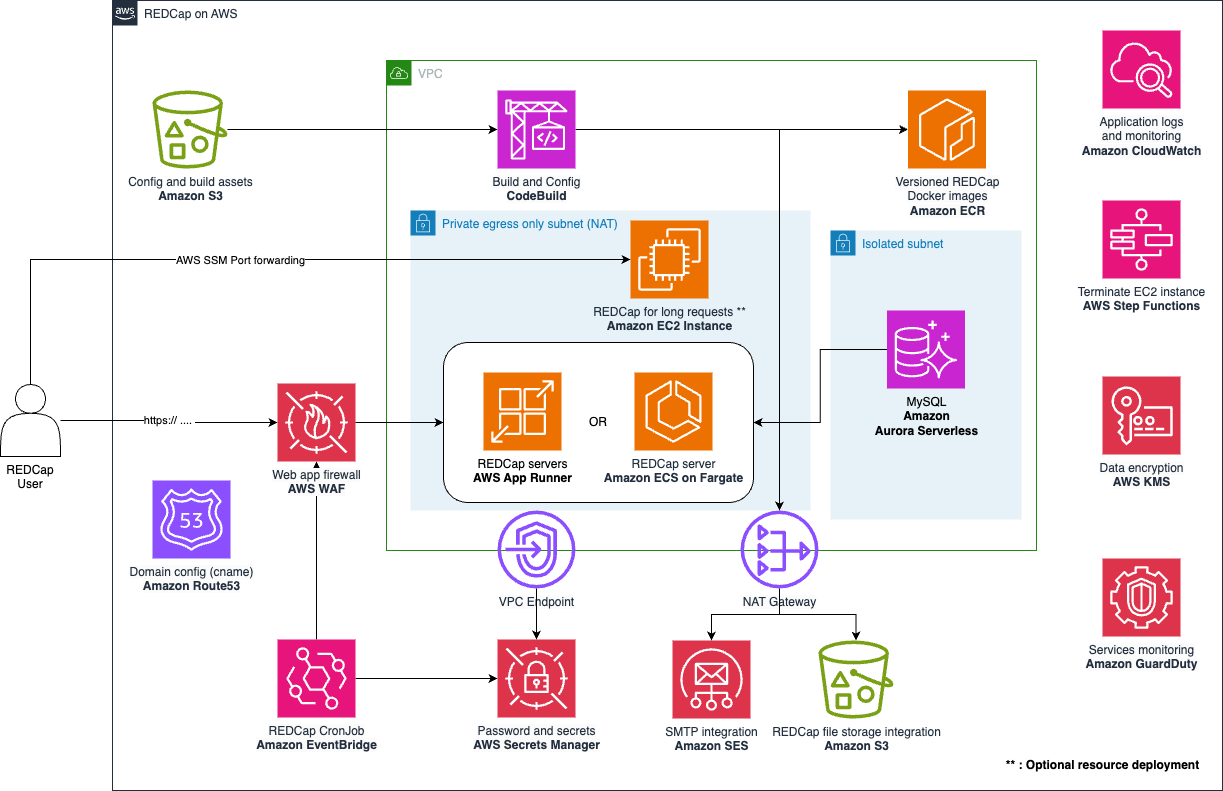
REDCap is a secure web application for building and managing online surveys and databases. It's specifically geared to support online and offline data capture for research studies and operations.
This project provides an automated way to deploy and manage a REDCap installation with autoscaling enabled services like AWS App Runner and Amazon Aurora Serverless. It's constructed using SST, an AWS CDK based framework with many out of the box constructors and many other features that can speed up the development of IaC.
The following guide is a quick startup, for more detailed documentation go to the general documentation.
The following, is a serverless architecture designed for high availability with autoscaling. It allows a pay-as-you-go model, paying only for the AWS resources needed to run your application and it follows the AWS Well-Architected Framework
- AWS WAF: Firewall that controls the access to the application, you can configure what IP ranges are able to access REDCap and blocks un-authorized access to specific endpoints.
- AWS Secrets Manager: Automatically create and rotate secrets for services like the database and SES credentials for postfix.
- Amazon VPC: Application servers and database are deployed in private subnets.
- Amazon GuardDuty: (Optional) Monitoring and detection service for you AWS account.
- Amazon CloudWatch: Monitor your infrastructure and REDCap's Apache access logs.
- AWS KMS: Your data is always stored encrypted, including file storage, logs and database
- AWS App Runner: Provides load balancer, autoscaling and automatic container deployments to ensure your REDCap setup is always available.
- Amazon Aurora Serverless: With MySQL compatibility, Aurora serverless can auto scale your database as needed. MySQL Reader and writer configuration for REDCap is enabled by default.
- Amazon S3: For file storage, REDCap integration with Amazon S3 is the recommended setting and enabled by default.
- Amazon ECS on AWS Fargate: An alternative to AWS App Runner to run long user requests.
Deploy and update your architecture and REDCap's software updates from your local machine using AWS CDK.
- Backtrack your database by "rewinding" to a specific point-in-time. Default setting 24 hours.
- Daily Database snapshots (Backup).
- Automatic rollback of application servers in case of failure or misconfiguration (blue-green deployment)
- (Optional) Versioned file storage with Amazon S3
A registered domain name is highly recommended for this deployment. To see what alternatives you have please have a look at domain configuration section.
You need to install in your machine Node.js version >= v18.16.1. You can install it via package manager https://nodejs.org/en/download/package-manager.
It is recommended to use yarn >= 4.0.2, so after installing node, install it by
npm -g install yarnyarn installMake a copy of the provided sample and edit it to your needs:
cp stages.sample.ts stages.tsEach property described below allows you to configure your deployment.
| Property | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | Name given to each environment to be deployed. | String | * User defined |
| profile | AWS account profile. You need to specify what is set in ~/.aws/config |
String | * User defined |
| region | Specify the AWS region to be used when deploying the stack. | String | From AWS config |
| allowedIps | If you want to restrict the IPs from which you can access the REDCap application, set a list of allowed IP addresses. | Array | [''] |
| allowedCountries | If you want to restrict access to the application by a list of countries | Array | undefined or [] |
| redCapLocalVersion | Specify the version of REDCap you want to deploy. You need to place files named as redcap${redCapLocalVersion}.zip in packages/REDCap. If redCapS3Path below is set, it cannot be set. |
String | undefined, if redCapS3Path is set |
| redCapS3Path | Specify the version of REDCap you want to deploy. First, upload the REDCap application in zip format to S3 and specify the location of the file in the form ${s3BucketName}/${s3ObjectKey}. If redCapLocalVersion above is set, it cannot be set. |
String | undefined, if redCapLocalVersion is set |
| domain | Your DNS name to use in your REDCap installation. | String | undefined |
| subdomain | Subdomain where your REDCap service is, e.g. redcap.mydomain.com | String | undefined |
| hostInRoute53 [1] | Enables the provided domain/subdomain to be registered in Route53 to allow easy enablement of SES and App Runner domain validations | Boolean or String | true |
| email [2] | Sets and enable email notification from App Runner service status and used to validate this email identity if a domain is not provided in the stage | String | undefined |
| appRunnerConcurrency [3] | The number of requests that a single REDCap instance can process. When the value is exceeded, it will trigger the auto-scaling. | Number | 10 |
| appRunnerMaxSize | Sets the upper limit on the number of instance App Runner can scale. | Number | 2 |
| appRunnerMinSize | Sets the minimum number of warm instances. |
Number | 1 |
| cronSecret | Base string to create a hashed secret to allow access to https:<your_domain>/cron.php | String | 'mysecret' |
| cpu | The number of vCpu assigned to each instance | Cpu | Cpu.TWO_VCPU |
| memory | The amount of memory assigned to each instance | Memory | Memory.FOUR_GB |
| phpTimezone | Example: 'Asia/Tokyo', https://www.php.net/manual/en/timezones.php | String | UTC |
| port | Port number to be used in App Runner. | String | 8080 |
| rebuildImage [4] | Whether to rebuild the REDCap Docker Image each time it is deployed | Boolean | false |
| ec2ServerStack [5] | Configuration for a temporary EC2 instance for long running request | Object | undefined |
| ecs [6] | Configuration to use Amazon ECS on AWS Fargate instead of AWS App Runner | Object | undefined |
| dbReaders | Number of database read only instances | Number | undefined |
| dbSnapshotId | Database snapshot to create a new database cluster | String | undefined |
| generalLogRetention | Optional general log retention period for ECS Fargate, RDS and VPC logs | String | undefined |
| bounceNotificationEmail | The email address to receive notifications when an email sent from SES bounces logs | String | undefined |
-
[1]
hostInRoute53: is a required value. To use an existing Hosted Zone in Amazon Route 53, provide the domain name here. Usetrueto create a new Hosted Zone with the configureddomainvalue. Usefalseto not use Amazon Route 53 at all. UsinghostInRoute53allows this project to automatically configure Amazon SES with the domain and also create certificates for SSL connections. Otherwise, validate SES, App Runner, or any connection that requires a certificate manually with your own DNS provider. -
[2] If you specify an email, you will receive an email to subscribe to AWS App Runner service notifications, alerting you of services deployments and changes. This email will also be registered as an identity for AWS SES.
-
[3] Concurrency default value is 10. It is calculated after a minimum load testing over one instance with 2vCPU and 4GB. We recommended you perform some load monitoring for tunning this value according to your load usage.
-
[4] The first time the project is deployed, an automatic build is triggered. If no more changes are detected for the build, new images are not built for every deploy. Setting this to true will force a new image build for each deploy using a timestamp value. Reverting back to false, you'll need to deploy once to remove this timestamp.
-
[5] Ec2 server stack
-
[6] Use Amazon ECS on AWS Fargate instead of AWS App Runner for REDCap instances
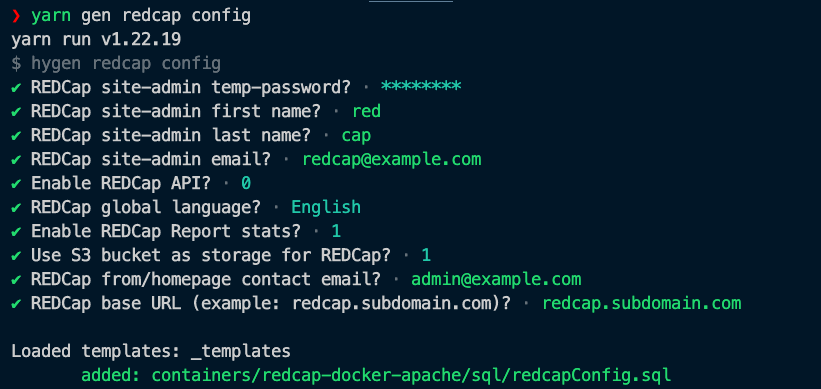
Before deploying, configure basic settings related to REDCap.
yarn gen redcap configYou can configure each setting interactively:
The configuration is stored in the database table redcap_config and can be updated each time you update your App Runner instances.
If you have enabled the options hostInRoute53 and/or domain in your stages.ts file, you can connect a domain name that you own to your REDCap deployment. This domain can be from:
- A domain registered in your account in Amazon Route 53
- A domain registered in an external AWS account in Amazon Route 53
- A domain registered in an external DNS provider.
For explanation purposes, we will assume we own the acme.com domain and our intention is to deploy REDCap at the redcap.acme.com.
For this case, our target is to deploy at redcap.acme.com. We assumed you have register a new domain, more info here and a Hosted zone already exists.
In this option, your stage config should look like this:
const prod: RedCapConfig = {
...baseOptions,
hostInRoute53: 'acme.com',
domain: 'acme.com',
subdomain: 'redcap', // <-- Create a new Hosted Zone named redcap.acme.com
...This will create a new Hosted Zone for redcap.acme.com and delegating to your exiting zone.
For this case, our target is to deploy at acme.com. We assumed you have register a new domain, more info here and a Hosted zone already exists.
In this option, your stage config should look like this:
const prod: RedCapConfig = {
...baseOptions,
hostInRoute53: 'acme.com', // <-- Use the existing zone
domain: 'acme.com',
subdomain: undefined, // or commented.
...This will use your exising zone to configure SES and create certificates. Be careful using this option. We also recommend to use this in a newly created zone without any apps or additional records in it.
If you own a domain name that is registered in a separated AWS account, you can easily add NS records with this project by deploying a special route53NS stage. This stage requires you to provide the AWS credentials profile of the external account.
We assume the external AWS account has a Hosted Zone with the DNS registered like acme.com.
-
Configure your
stage.ts, it should look like this:const prod: RedCapConfig = { ...baseOptions, hostInRoute53: true, domain: 'acme.com', subdomain: 'redcap', // <-- Create a new Hosted Zone named redcap.acme.com ...
-
Look at the console output after deploying for the output of
NameServers. This is a list of NS records we will be deploying for the external account. -
In the
stages.ts, find theroute53NSstage and configure as following:const route53NS: DomainAppsConfig = { ...baseOptions, profile: 'your_external_aws_profile', region: 'ap-northeast-1', // <-- update to your region apps: [ { name: 'redcap', // <-- Record name for the NS entry will be redcap.redemo.site. nsRecords: [ // <-- List of NS records from deployment output 'ns-11111.awsdns-11.org', 'ns-22.awsdns-22.com', 'ns-33.awsdns-33.net', 'ns-4444.awsdns-44.co.uk', ], }, ], domain: 'acme.com', // <-- Target external domain };
-
Deploy to the external account:
yarn deploy --stage route53NS
After a while, and if you are using AWS App Runner, the certificate validation will be complete for your domain. This can take 24-48 hours, but most of the time it can be much less.
This case is not yet fully supported. At the moment it can be achieved using manual intervention.
-
Configure your
stage.ts, it should look like this:const prod: RedCapConfig = { ...baseOptions, hostInRoute53: false, // <-- Do not create new Hosted Zone. domain: 'acme.com', subdomain: undefined, ...
-
Follow the steps to link a App Runner domain, configure SES domain identity and create an A record for your ECS ALB if required on your domain AWS account.
For this scenario, we will assume that we have registered our example DNS name acme.com in a external DNS provider.
-
Configure your
stage.ts, it should look like this (do not use theecsproperty):const prod: RedCapConfig = { ...baseOptions, hostInRoute53: true, // <-- Create a new Hosted Zone. domain: 'acme.site', subdomain: 'redcap', ...
-
From the terminal output, add the 4 Name Servers (NS) from your new Hosted Zone to your DNS provider with name
redcap.Type name NS TTL NS redcap ns-1267.awsdns-30.org. 1 Hour .... .... -
After a while, in the AWS Console / App Runner /
Custom domainsit should become greenActiveand you can access your domain with HTTPS. -
Also in the console, check the Amazon SES / Configuration / Identities, click your domain and check that the Identity status is
Verified
This case is not yet fully supported. At the moment it can be achieved using manual intervention.
-
Configure your
stage.ts, it should look like this:const prod: RedCapConfig = { ...baseOptions, hostInRoute53: false, // <-- Do not create new Hosted Zone. domain: 'acme.com', subdomain: undefined, ...
-
Follow the steps to link a App Runner domain, configure SES domain identity and create an A record for your ECS ALB if required on your DNS provider.
The default deployment with AWS App Runner will provide you a HTTPS domain that you can use for testing your deployment. However, we do recommend you to manually register a new domain name in Amazon Route 53 and follow the instructions here to complete your installation.
More info:
Run deployment by entering the following command.
yarn deploy --stage <your_stage_name>Warning: Do not deploy more than one stage/environment at a time.
Once the deployment is complete, you'll see output like this:
By default, SES is deployed in sandbox mode, meaning that any email you send that is not a valid identity will fail. REDCap's configuration check, that sends an email to <redcapemailtest@gmail.com>, will fail due this. You can request production access from the AWS console. More info here
The installation by default assumes your MAIL FROM domain to be in the form of mail.<your_domain.com>. If this is not the case, you can modify the Backend.ts file and the property mailFromDomain to the SimpleEmailService constructor to specify one.
Before performing a version upgrade in a production environment, be sure to test your changes in another environment for testing. Setup development environment
Change the redcapLocalVersion or the redCapS3Path of the environment you want to update with the file location pointing to the new version. If you have a local copy of redcap, place it as redcap<version>.zip in the packages/REDCap/releases directory. Example: packages/REDCap/releases/redcap13.7.2.zip
Same as the initial deployment, run the deployment with the command below.
Warning: Do not use REDCap's internal upgrade mechanism. This only updates a single container and not your entire fleet on AWS App Runner.
yarn deploy --stage <your_stage_name>This is an AWS Codebuild process that will build the new docker image and trigger a new App Runner deployment. To do this, you have two options:
- Go to your AWS Management Console.
- Codebuild and Build Projects.
- Click on the selected environment and press
Start Build.
- Check for the terminal output
UpdateDeploymentCommandand copy the command - Paste and execute to call the AWS cli and start the update and deployment process.
To monitor the status, you can use the AWS CLI or access the AWS Console to check AWS CodeBuild and later the Blue-Green deployment of AWS App Runner.
It's important to mention that this lambda execution is automatically called only for the first time you deploy your architecture. Future executions are considered
updatesto the service and are designed to be in a step-by-step manner.
Before executing this command, it is recommended to do a database snapshot or get familiar with Aurora backtrack window feature in case of failure.
Once deployment is complete, REDCap's database is updated/migrated by accessing https://<your_domain>/upgrade.php?auto=1.
Alternatively, you can access in your browser to https://<your_domain>/upgrade.php and click on Option A --> Upgrade to upgrade the database tables.
There are few warnings that you might see after deployment. The expected ones are:
Some non-versioned files are outdated -, if you are not deploying the latest REDCap versionMYSQL DATABASE CONFIGURATION -, some of the recommended settings by REDCap should be executed with care, as they can lead to out of memory errors. Please check you use case, and if you need to change parameters, you can do it in the database stackInternal Service Check: Checking communication with the REDCap survey end-point -, this test is executed in a way that AWS WAF is blocking it, but the endpoint https://your_domain/surveys/ should be accessible from a normal browser. You can check this blocked byAWS#AWSManagedRulesCommonRuleSet#NoUserAgent_HEADERin the AWS WAF console.- MyCap
NOT making API Call - CRITICAL -, this test is also blocked by AWS WAF as previous number (3).
For more detail, please refer Path to production.
AWS App Runner has a request timeout of 120 seconds. This might not enough for all REDCap's operations like importing/exporting project data. To overcome this limitation, we offer two additional deploying alternatives with Amazon EC2 Server and Amazon ECS on Fargate.
This table can help you decide when to use the options:
| Use case / Deployment | EC2 Server | App Runner | ECS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Import big REDCap projects | OK (Requires AWS credentials) | X | OK (max 4000 sec) |
| Regular use | X | OK | OK |
| Regular use with request over 120 seconds | X | X | OK (max 4000 sec) |
It is a temporary stack that deploys an Amazon EC2 instance running the same REDCap docker image build for AWS App Runner. AWS users can then tunnel to this EC2 REDCap server from a local computer. This way, your request are limited only by your PHP, Apache configurations and Internet connectivity.
You will require AWS credentials to login.
-
Make sure you have installed in your computer the Session Manager plugin https://docs.aws.amazon.com/systems-manager/latest/userguide/session-manager-working-with-install-plugin.html.
-
To deploy this new stack with the EC2 instance, you have to configure your stage file with the
ec2ServerStackproperty:const dev: RedCapConfig = { ... ec2ServerStack: { ec2StackDuration: Duration.hours(3), }, };
The
ec2StackDurationparameter defines how long this instance should run, after this time it will be destroyed. -
Deploy your stage and wait for the output. It will show the command to start the tunnel
ssmPortForward. It looks similar to this:ssmPortForward: aws ssm start-session --target i-00000000000 --document-name AWS-StartPortForwardingSession --parameters '{"portNumber":["8081"],"localPortNumber":["8081"]}' --region ap-northeast-1 --profile redcapIn your computer, open a terminal run this command. Open a browser and visit https://localhost:8081. You will need to accept the warning about the self-signed certificate to access REDCap. This key and certificate can be updated to provide your own if you wish, the files are in the certificates folder.
-
CORS: Depending on what REDCap feature you will use; you might encounter CORS issues for some modules. If this happens, you will need to configure the
REDCap base URLin the Control Center to point your proxy e.g.https://localhost:8081, this will cause issues for your current users that are running under the configured domain, so please use it with caution and do not forget to revert the changes after you have finished your workload. -
StateMachine: If you wish to delete the
ec2ServerStackthat is still inside the time duration, you will need to stop the state machine first so CloudFormation can delete the resources.
To use REDCap with Amazon ECS, you will need a domain name to create a certificate for the ECS ALB more info. REDCap will not operate correctly without this certificate.
After following the steps in 5. Domain configuration or having a domain activate in Amazon Route 53, the deployer will attempt to create the certificate. If you want to provide your own certificate, you can modify the RedcapService.ts to provide a certificate ARN.
this.ecsService = new EcsFargate(this.stack, `${this.app.stage}-${this.app.name}-ecs-service`, {
app: this.app,
...
certificate: {
fromArn: 'your_certificate_arn' // <-- update
},
});You must also make sure you configure the state.ts variables for hostInRoute53: true, and domain: '<you_redcap_domain>'.
As an example, the ECS deployment is activate by this stage:
const stag: RedCapConfig = {
...baseOptions,
hostInRoute53: true,
phpTimezone: 'Asia/Tokyo',
domain: 'redcap.mydomain.dev',
redCapS3Path: 'redcap-bucket/redcap13.7.21.zip',
cronSecret: 'asecret',
email: 'myemail@mydomain.dev',
ecs: { // <-- ecs config.
memory: '4 GB',
cpu: '2 vCPU',
scaling: {
maxContainers: 3,
minContainers: 1,
requestsPerContainer: 100,
cpuUtilization: 90,
},
},Important: Test you change in a development environment first. If you have previously deployed this project using AWS App Runner and choose to use Amazon ECS, only the AWS App Runner resources will be destroyed, this does not include Amazon S3 buckets for data storage or database. This only change can take up to 20 minutes to complete.
In your stages.ts add the parameter dbSnapshotId with the snapshot name as value and deploy.
const test: RedCapConfig = {
...baseOptions,
// ...more options
dbSnapshotId: 'redcap-dev', // Snapshot name.
};This will create a new database cluster and delete the existing one.
To delete an environment and all its resources, run the following command:
yarn destroy --stage <your_stage_name>By default, a database SNAPSHOT will be created while executing this command.
This software is licensed under the MIT-0 license