This AWS Solution contains a demonstration of Generative AI, specifically, the use of Natural Language Query (NLQ) to ask questions of an Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL database. This solution offers three architectural options for Foundation Models: 1. Amazon SageMaker JumpStart, 2. Amazon Bedrock, and 3. OpenAI API. The demonstration's web-based application, running on Amazon ECS on AWS Fargate, uses a combination of LangChain, Streamlit, Chroma, and HuggingFace SentenceTransformers. The application accepts natural language questions from end-users and returns natural language answers, along with the associated SQL query and Pandas DataFrame-compatible result set.
The selection of the Foundation Model (FM) for Natural Language Query (NLQ) plays a crucial role in the application's ability to accurately translate natural language questions into natural language answers. Not all FMs are capable of performing NLQ. In addition to model choice, NLQ accuracy also relies heavily on factors such as the quality of the prompt, prompt template, labeled sample queries used for in-context learning (aka few-shot prompting), and the naming conventions used for the database schema, both tables and columns.
The NLQ Application was tested on a variety of open source and commercial FMs. As a baseline, OpenAI's Generative
Pre-trained Transformer GPT-3 and GPT-4 series models, including gpt-3.5-turbo, and
gpt-4, all provide accurate responses to a wide range of simple to complex natural language queries using an average
amount of in-context learning and minimal prompt engineering.
Amazon Titan Text G1 - Express, amazon.titan-text-express-v1, available through Amazon Bedrock, was also tested. This
model provided accurate responses to basic natural language queries using some model-specific prompt
optimization. However, this model was not able to respond to more complex queries. Further prompt
optimization could improve model accuracy.
Open source models, such as google/flan-t5-xxl and google/flan-t5-xxl-fp16 (half-precision
floating-point format (FP16) version of the full model), are available through Amazon SageMaker JumpStart. While
the google/flan-t5 series of models are a popular choice for building Generative AI applications, their
capabilities for NLQ are limited compared to newer open-source and commercial models. The
demonstration's google/flan-t5-xxl-fp16 is capable of answering basic natural language queries with sufficient
in-context learning. However, it often failed during testing to return an
answer or provide correct answers, and it frequently caused SageMaker model endpoint timeouts due to
resource exhaustion when faced with moderate to complex queries.
This solution uses an NLQ-optimized copy of the open-source database, The Museum of Modern Art (MoMA) Collection, available on GitHub. The MoMA database contains over 121,000 pieces of artwork and 15,000 artists. This project repository contains pipe-delimited text files that can be easily imported into the Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL database instance.
Using the MoMA dataset, we can ask natural language questions, with varying levels of complexity:
- Simple
- How many artists are there in the collection?
- How many pieces of artwork are there?
- How many artists are there whose nationality is Italian?
- How many artworks are by the artist Claude Monet?
- How many artworks are classified as paintings?
- How many artworks were created by Spanish artists?
- How many artist names start with the letter 'M'?
- Moderate
- How many artists are deceased as a percentage of all artists?
- Who is the most prolific artist? What is their nationality?
- What nationality of artists created the most artworks?
- What is the ratio of male to female artists? Return as a ratio.
- Complex
- How many artworks were produced during the First World War, which are classified as paintings?
- What are the five oldest pieces of artwork? Return the title and date for each.
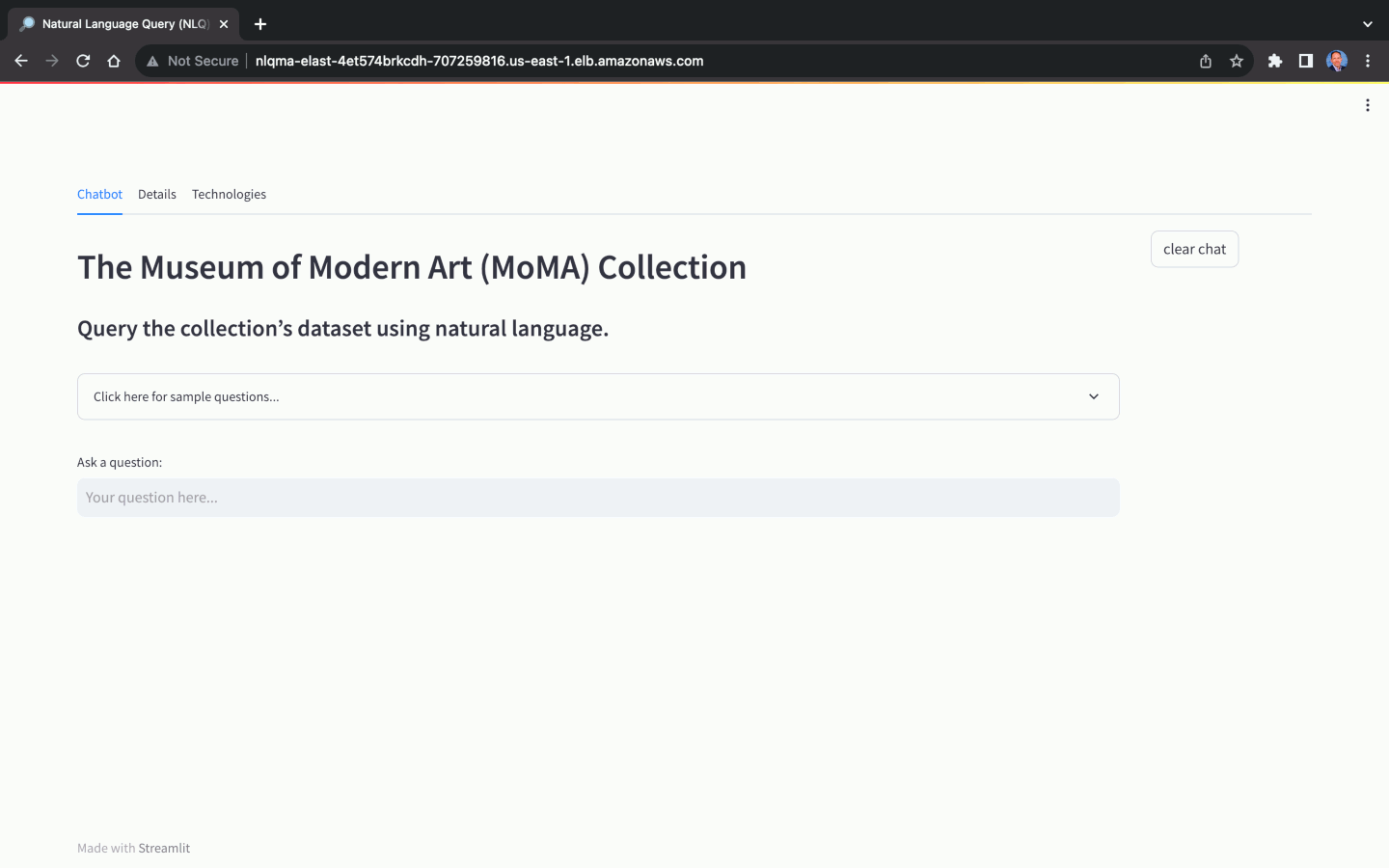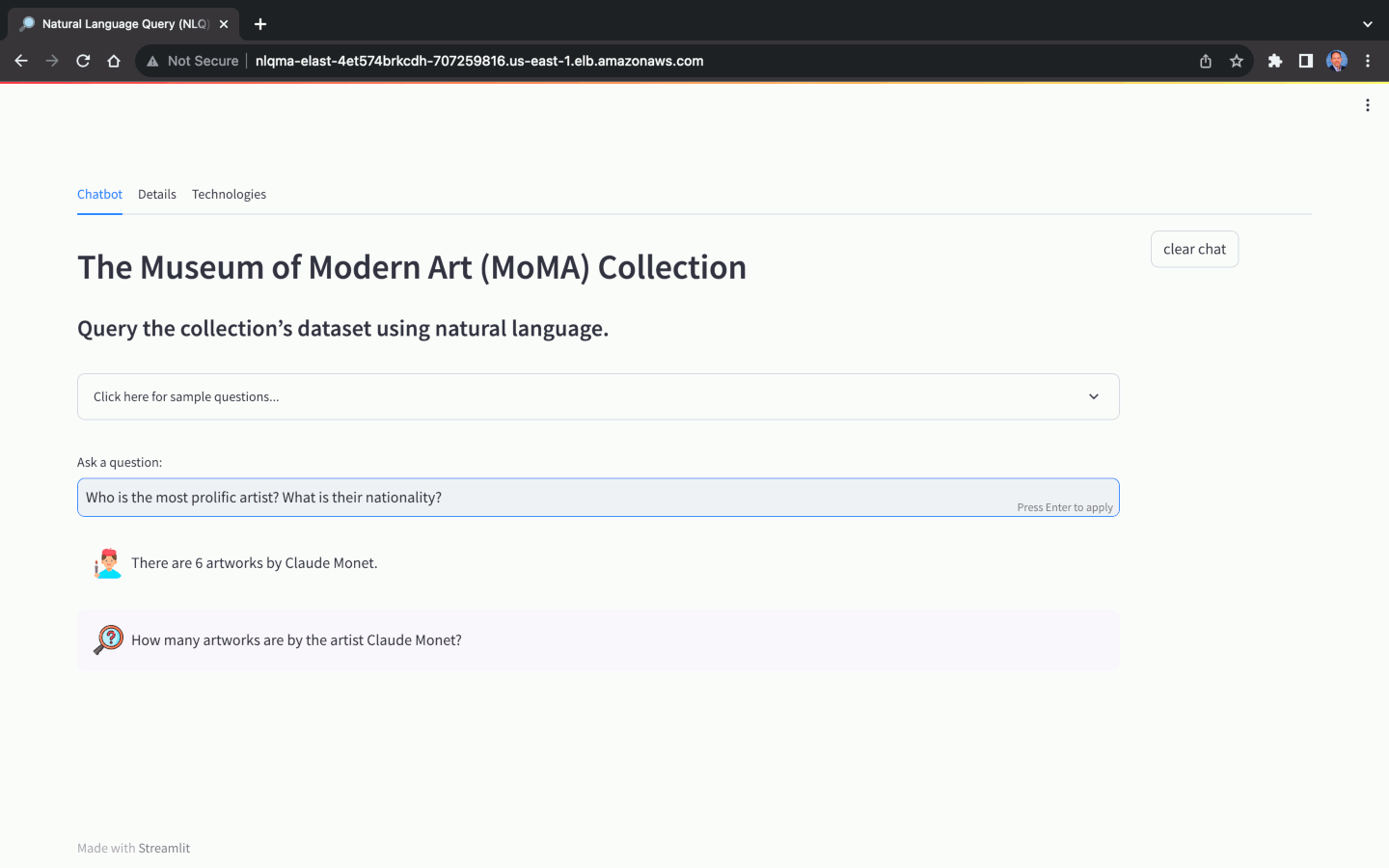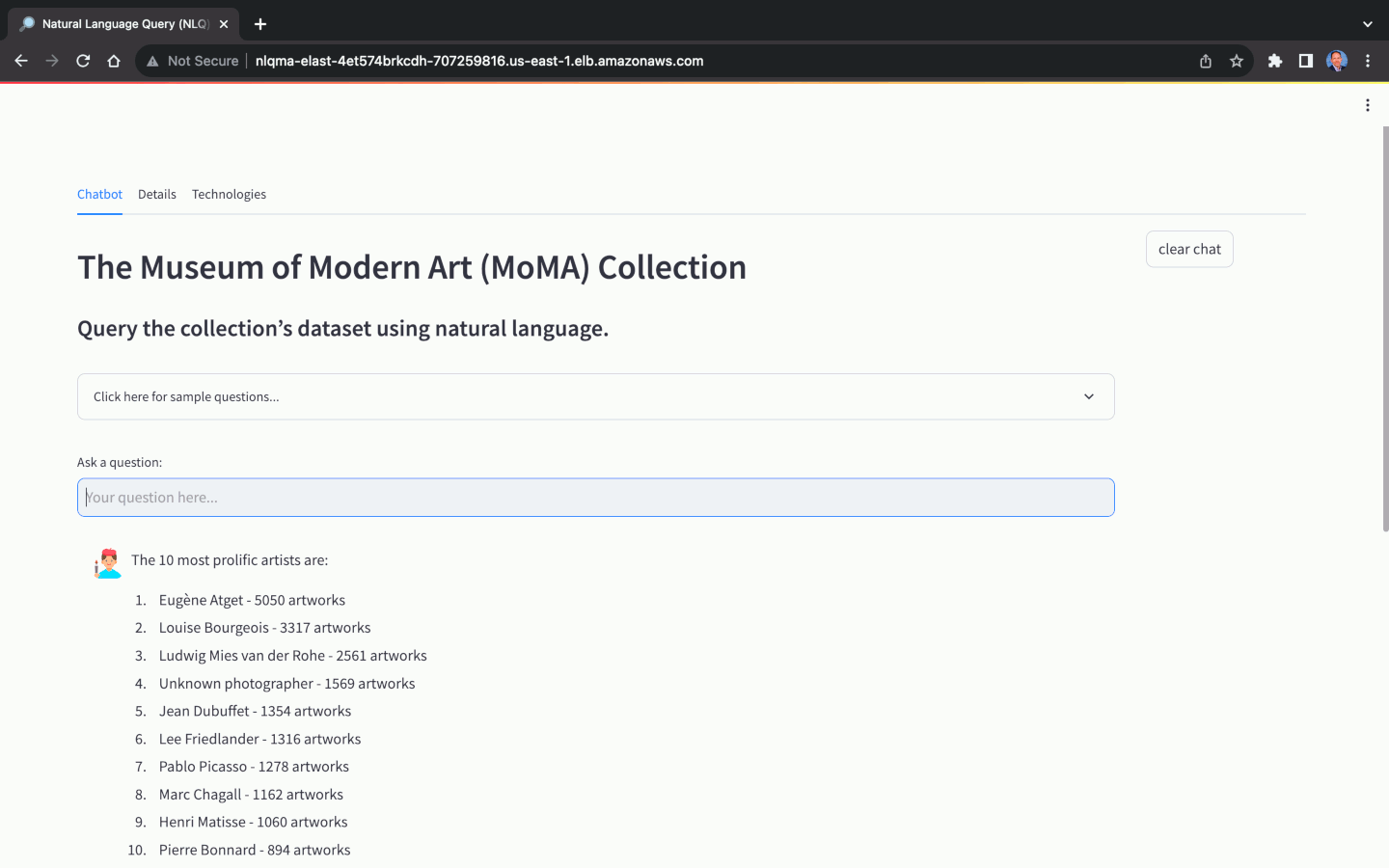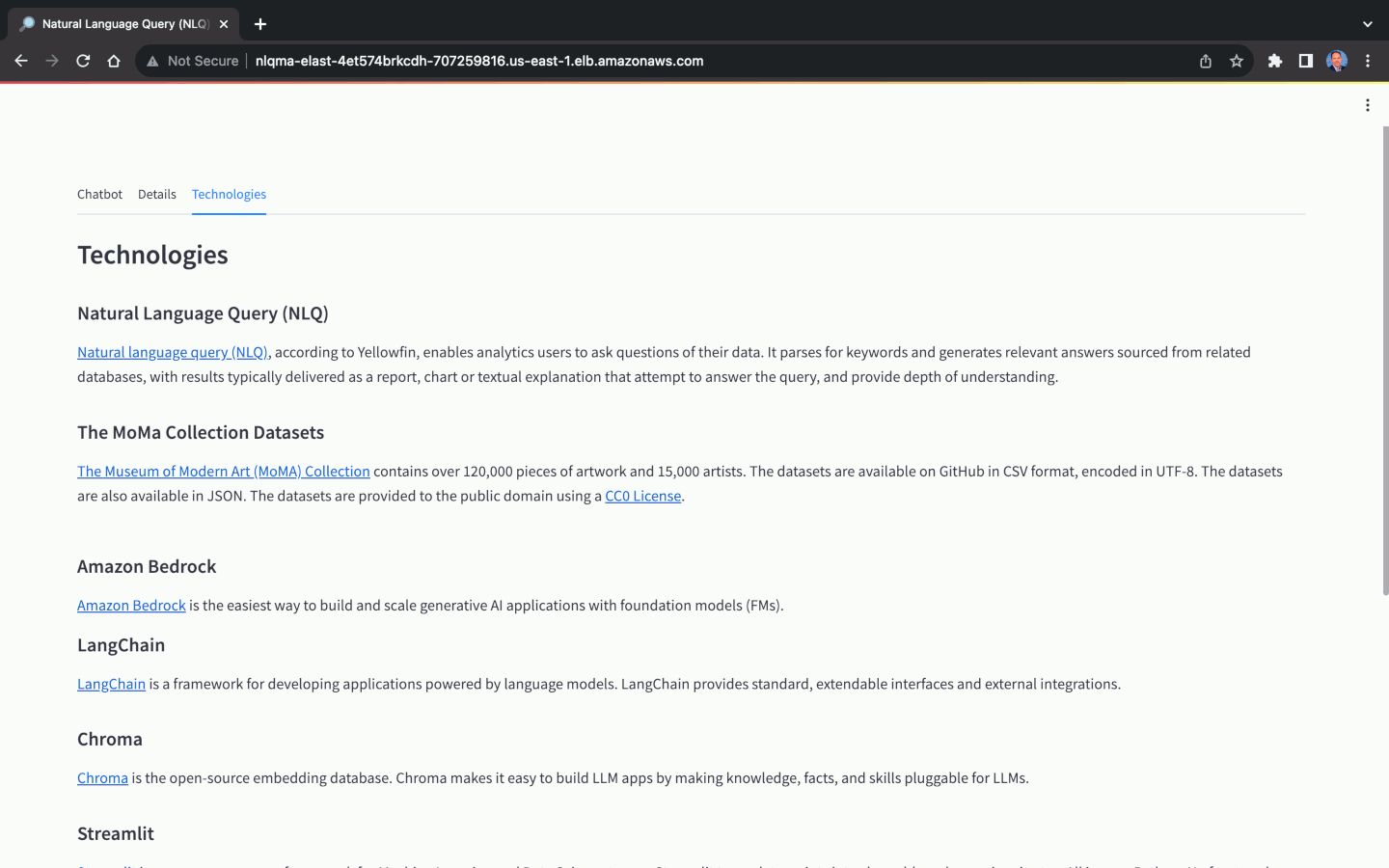
- What are the 10 most prolific artists? Return their name and count of artwork.
- Return the artwork for Frida Kahlo in a numbered list, including the title and date.
- What is the count of artworks by classification? Return the first ten in descending order. Don't include Not_Assigned.
- What are the 12 artworks by different Western European artists born before 1900? Write Python code to output them with Matplotlib as a table. Include header row and font size of 12.
- Unrelated to the Dataset
- Give me a recipe for chocolate cake.
- Who won the 2022 FIFA World Cup final?
Again, the ability of the NLQ Application to return an answer and return an accurate answer, is primarily dependent on the choice of model. Not all models are capable of NLQ, while others will not return accurate answers. Optimizing the above prompts for specific models can help improve accuracy.
- For Option 1: Amazon SageMaker JumpStart, ensure that you have the required EC2 instance for the endpoint
inference, or request it
using Service Quotas
in the AWS Management Console (e.g.,
ml.g5.24xlargefor thegoogle/flan-t5-xxl-fp16model). Refer to the model's documentation for the choice of instance types. - Create the required secrets in AWS Secret Manager using the AWS CLI.
- Deploy the
NlqMainStackCloudFormation template. Please note, you will have needed to have used Amazon ECS at least one in your account, or theAWSServiceRoleForECSService-Linked Role will not yet exist and the stack will fail. Check theAWSServiceRoleForECSService-Linked Role before deploying theNlqMainStackstack. This role is auto-created the first time you create an ECS cluster in your account. - If you use Option 1: Amazon SageMaker JumpStart, build and push the
nlq-genai:2.0.0-smDocker image to the new Amazon ECR repository. Alternately, build and push thenlq-genai:2.0.0-bedrockornlq-genai:2.0.0-oaiDocker image for use with Option 2: Amazon Bedrock or Option 3: OpenAI API. - Create the Amazon RDS MoMA database tables and import the included sample data.
- Add the
nlqappuser to the MoMA database. - Optionally, for Option 1: Amazon SageMaker JumpStart, deploy the
NlqSageMakerEndpointStackCloudFormation template. - For Option 1: Amazon SageMaker JumpStart, deploy the
NlqEcsSageMakerStackCloudFormation template. Alternately, deploy theNlqEcsBedrockStackCloudFormation template for use with Option 2: Amazon Bedrock or theNlqEcsOpenAIStacktemplate for use with Option 3: OpenAI API.
For Option 1: Amazon SageMaker JumpStart, ensure that you have the required EC2 instance for the Amazon
SageMaker JumpStart endpoint inference or request it
using Service Quotas
in the AWS Management Console (e.g., ml.g5.24xlarge for the google/flan-t5-xxl-fp16 model). Refer to the model's
documentation for the choice of instance types.
Make sure you update the secret values below before continuing. This step will create secrets for the credentials for
the NLQ application. NLQ application access to the database is limited to read-only. For Option 3: OpenAI API, this step
will create a secret to store your OpenAI API key. Master User credentials for the Amazon RDS instance are set
automatically and stored in AWS Secret Manager as part of the NlqMainStackCloudFormation template deployment. These
values can be found in AWS Secret Manager.
aws secretsmanager create-secret \
--name /nlq/NLQAppUsername \
--description "NLQ Application username for MoMA database." \
--secret-string "<your_nlqapp_username>"
aws secretsmanager create-secret \
--name /nlq/NLQAppUserPassword \
--description "NLQ Application password for MoMA database." \
--secret-string "<your_nlqapp_password>"
# Only for Option 2: OpenAI API/model
aws secretsmanager create-secret \
--name /nlq/OpenAIAPIKey \
--description "OpenAI API key." \
--secret-string "<your_openai_api_key"Access to the ALB and RDS will be limited externally to your current IP address. You will need to update if your IP address changes after deployment.
cd cloudformation/
aws cloudformation create-stack \
--stack-name NlqMainStack \
--template-body file://NlqMainStack.yaml \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--parameters ParameterKey="MyIpAddress",ParameterValue=$(curl -s http://checkip.amazonaws.com/)/32Build the Docker image(s) for the NLQ application, based on your choice of model options. You can build the Docker image(s) locally, in a CI/CD pipeline, using SageMaker Notebook environment, or AWS Cloud9. I prefer AWS Cloud9 for developing and testing the application and building the Docker images.
cd docker/
# Located in the output from the NlqMlStack CloudFormation template
# e.g. 111222333444.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/nlq-genai
ECS_REPOSITORY="<you_ecr_repository>"
aws ecr get-login-password --region us-east-1 | \
docker login --username AWS --password-stdin $ECS_REPOSITORYOption 1: Amazon SageMaker JumpStart
TAG="2.0.0-sm"
docker build -f Dockerfile_SageMaker -t $ECS_REPOSITORY:$TAG .
docker push $ECS_REPOSITORY:$TAGOption 2: Amazon Bedrock
TAG="2.0.0-bedrock"
docker build -f Dockerfile_Bedrock -t $ECS_REPOSITORY:$TAG .
docker push $ECS_REPOSITORY:$TAGOption 3: OpenAI API
TAG="2.0.0-oai"
docker build -f Dockerfile_OpenAI -t $ECS_REPOSITORY:$TAG .
docker push $ECS_REPOSITORY:$TAG5a. Connect to the moma database using your preferred PostgreSQL tool. You will need to enable Public access for the
RDS instance temporarily depending on how you connect to the database.
5b. Create the two MoMA collection tables into the moma database.
CREATE TABLE public.artists
(
artist_id integer NOT NULL,
full_name character varying(200),
nationality character varying(50),
gender character varying(25),
birth_year integer,
death_year integer,
CONSTRAINT artists_pk PRIMARY KEY (artist_id)
)
CREATE TABLE public.artworks
(
artwork_id integer NOT NULL,
title character varying(500),
artist_id integer NOT NULL,
date integer,
medium character varying(250),
dimensions text,
acquisition_date text,
credit text,
catalogue character varying(250),
department character varying(250),
classification character varying(250),
object_number text,
diameter_cm text,
circumference_cm text,
height_cm text,
length_cm text,
width_cm text,
depth_cm text,
weight_kg text,
durations integer,
CONSTRAINT artworks_pk PRIMARY KEY (artwork_id)
)5c. Unzip and import the two data files into the moma database using the text files in the /data subdirectory. The
both files contain a header row and pipe-delimited ('|').
# examples commands from pgAdmin4
--command " "\\copy public.artists (artist_id, full_name, nationality, gender, birth_year, death_year) FROM 'moma_public_artists.txt' DELIMITER '|' CSV HEADER QUOTE '\"' ESCAPE '''';""
--command " "\\copy public.artworks (artwork_id, title, artist_id, date, medium, dimensions, acquisition_date, credit, catalogue, department, classification, object_number, diameter_cm, circumference_cm, height_cm, length_cm, width_cm, depth_cm, weight_kg, durations) FROM 'moma_public_artworks.txt' DELIMITER '|' CSV HEADER QUOTE '\"' ESCAPE '''';""Create the read-only NLQ Application database user account. Update the username and password values in the SQL script, in three places, with the secrets you configured in Step 2 above.
CREATE ROLE <your_nlqapp_username> WITH
LOGIN
NOSUPERUSER
NOCREATEDB
NOCREATEROLE
INHERIT
NOREPLICATION
CONNECTION LIMIT -1
PASSWORD '<your_nlqapp_password>';
GRANT
pg_read_all_data
TO
<your_nlqapp_username>;Option 1: Amazon SageMaker JumpStart
cd cloudformation/
aws cloudformation create-stack \
--stack-name NlqSageMakerEndpointStack \
--template-body file://NlqSageMakerEndpointStack.yaml \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAMOption 1: Amazon SageMaker JumpStart
aws cloudformation create-stack \
--stack-name NlqEcsSageMakerStack \
--template-body file://NlqEcsSageMakerStack.yaml \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAMOption 2: Amazon Bedrock
aws cloudformation create-stack \
--stack-name NlqEcsBedrockStack \
--template-body file://NlqEcsBedrockStack.yaml \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAMOption 3: OpenAI API
aws cloudformation create-stack \
--stack-name NlqEcsOpenAIStack \
--template-body file://NlqEcsOpenAIStack.yaml \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAMYou can replace the default google/flan-t5-xxl-fp16 JumpStart Foundation Model, deployed using
the NlqSageMakerEndpointStack.yaml CloudFormation template file. You will first need to modify the model parameters in
the NlqSageMakerEndpointStack.yaml file and update the deployed CloudFormation stack, NlqSageMakerEndpointStack.
Additionally, you will need to make adjustments to the NLQ Application, app_sagemaker.py, modifying
the ContentHandler Class to match the response payload of the chosen model. Then, rebuild the Amazon ECR Docker Image,
incrementing the version, e.g., nlq-genai-2.0.1-sm, using the Dockerfile_SageMaker Dockerfile and push to the Amazon
ECR repository. Lastly, you will need to update the deployed ECS task and service, which are part of
the NlqEcsSageMakerStack CloudFormation stack.
To switch from the solution's default Amazon Titan Text G1 - Express (amazon.titan-text-express-v1) Foundation Model,
you need to modify and rdeploy the NlqEcsBedrockStack.yaml CloudFormation template file. Additionally, you will need
to modify to the NLQ Application, app_bedrock.py Then, rebuild the Amazon ECR Docker Image using
the Dockerfile_Bedrock
Dockerfile and push the resulting image, e.g., nlq-genai-2.0.1-bedrock, to the Amazon ECR repository. Lastly, you will
need to
update the deployed ECS task and service, which are part of the NlqEcsBedrockStack CloudFormation stack.
Switching from the solution's default OpenAI API to another third-party model provider's API,
such as Cohere or Anthropic, is similarly straightforward. To utilize OpenAI's models, you will first need to create an
OpenAI account and obtain your own personal API key. Next, modify and rebuild the Amazon ECR Docker Image using
the Dockerfile_OpenAI Dockerfile and push the resulting image,
e.g., nlq-genai-2.0.1-oai, to the Amazon ECR repository. Finally, modify and redeploy the NlqEcsOpenAIStack.yaml
CloudFormation
template file.
See CONTRIBUTING for more information.
This library is licensed under the MIT-0 License. See the LICENSE file.