In this lab we will create a CICD pipeline on Azure DevOps using AWS Tools for VSTS.
- An Amazon Web Services (AWS) account and an associated IAM User account.
- Validate access to the sample source code repository in Github by browsing to this url https://github.com/awsimaya/ECSFargate.git
- Azure DevOps aka Visual Studio Team Services (VSTS) account to set up Build and Release pipelines
This is a critical step. Ensure you follow the instruction accurately before you proceed. Here we will set the AWS region we are going to work on. It is necessary to follow the instructions carefully to ensure successful completion of the lab.
- Set your region to EU-WEST-1 (Ireland). See picture below and ensure your setup is set right.
[Optional] If you already have Secret Access Key ID and Secret Access Key of an IAM User account to be used with Azure DevOps then you can skip this section. In this section, we will create a new IAM user account that will be used by your Azure DevOps service to deploy resources in your AWS Account.
- Click on IAM Service
- In the navigation pane, choose Users and then choose Add user.
- Type the user name for the new user. This is the sign-in name for AWS.
- Select only programmatic access. This creates an access key for each new user. You can view or download the access keys when you get to the Final page.
- Click on Next: Permissions.
- Select Attach existing policies directly.
- Select Administrator Access. [Note: This is not a best practice to provide Administrator Access. Its recommended to follow least access privilege and limit permissions to the resources that would be required from AzureDevOps account. This could vary depending upon your use case and scenarios. Example you may chose to create different IAM User account for Non-Prod Vs Prod and appropriately provide the necessary permissions following least access privilege principle.]
- Click on Next: Review
- Review the settings and Click on Create User.
- Save the Secret Access Key and Access Key ID to be used later in this lab.
In this step, we will install AWS Tools for Azure DevOps on to your account. This will allow us to leverage the powerful features the add-on provides to created CICD tasks on AWS
- Navigate to Visual Studio Marketplace and click on Get it free button as shown in the image below

- If you're logged in to Azure DevOps already, you will be taken to your Azure DevOps account where you can select the Organization as shown below.

- Once you click, AWS Tools for VSTS will be installed on the organization successfully. You will screen like the below if the the process was successful. Click Proceed to organization

In this step, we will create a service connection to AWS on Azure DevOps. This will allow us to easily execute AWS specific tasks by simply selecting the service connection within the task itself. If you already have this configured in your Azure DevOps account then you can skip this step and go to next step.
- On your Azure DevOps home page, go ahead and create a project. Use default settings.
- Under Project Settings > Service connections, click on New Service connections and select AWS from that list
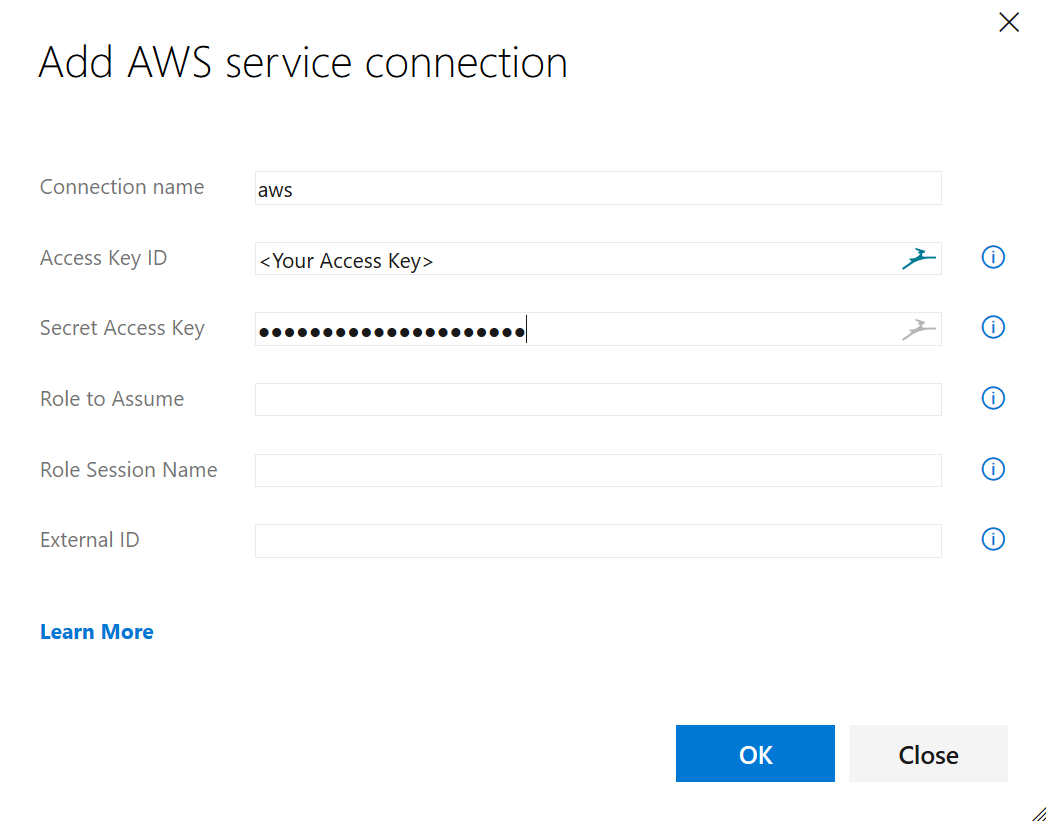
- You will see a window similar to the screenshot below. Give a connection name, enter the Access Key Id and Secret Access Key of the IAM User Account to be used by Azure DevOps. Click OK
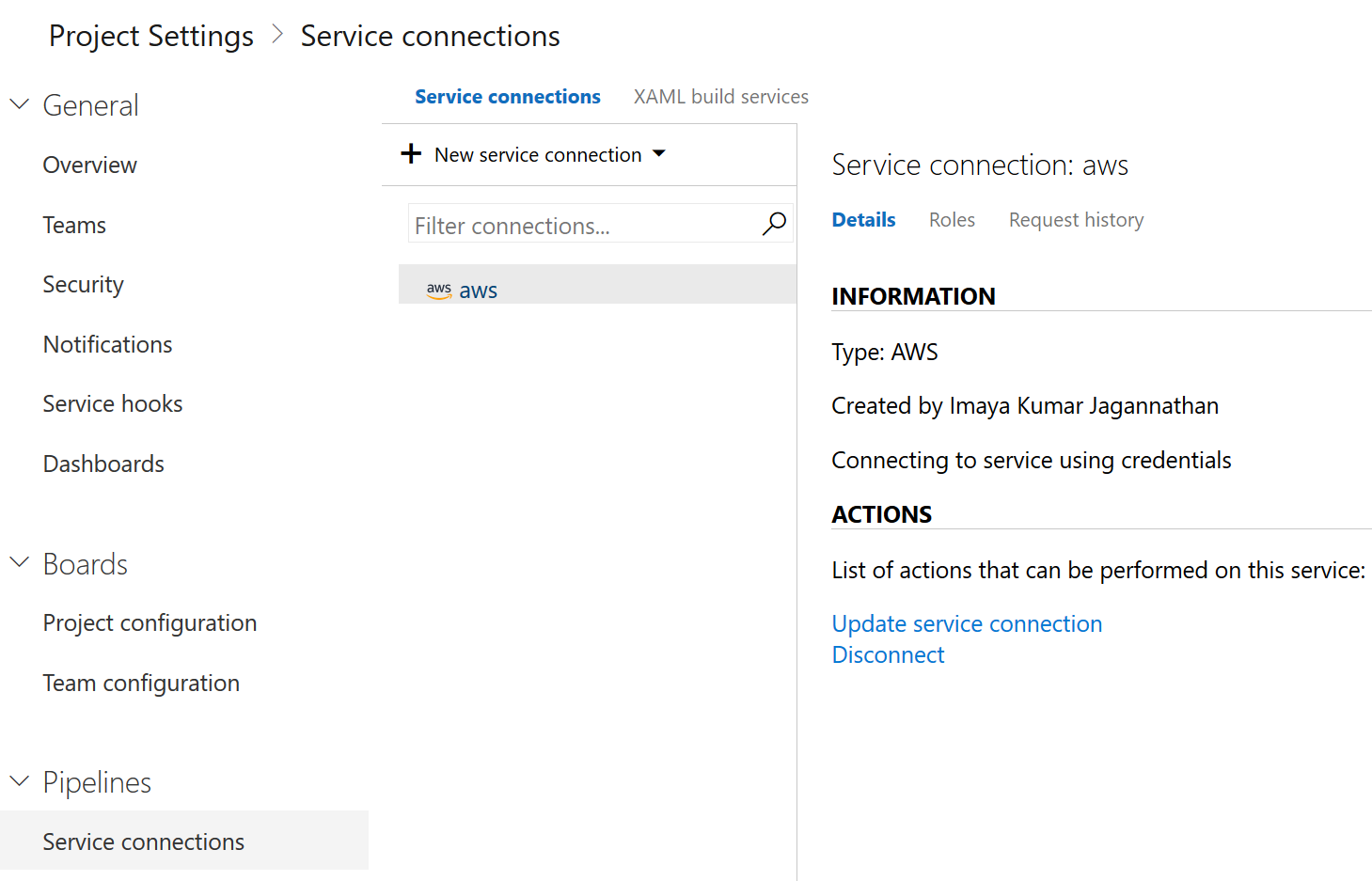
- You will see a screen like the one below once this process is complete
In this step, we will create a Build pipeline to build a docker container image that contains our application and also push it to AWS Elastic Container Repository. We will import an existing sample .Net Core Application code available in a public Github repository to clone it in Azure DevOps Git repository. Subsequently, we will create a new build pipeline for this application.
- Navigate to Repos page on the left navigation section. The screen should look similar to this below
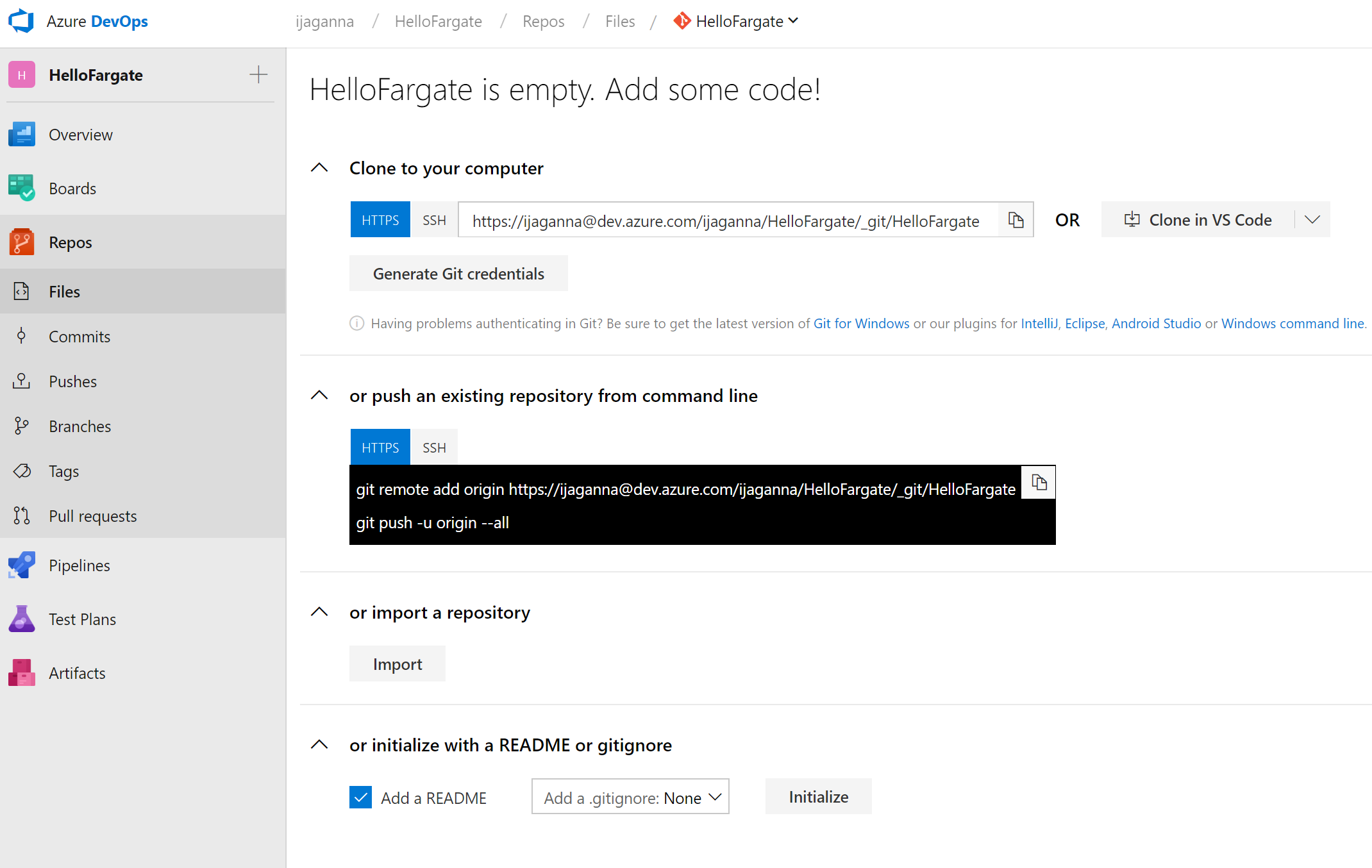
- Click on Import under or Import a repository
- Enter the GitHub URL (https://github.com/awsimaya/ECSFargate.git). Click Import.
- Now Azure DevOps will clone the project from GitHub into its own git repo.
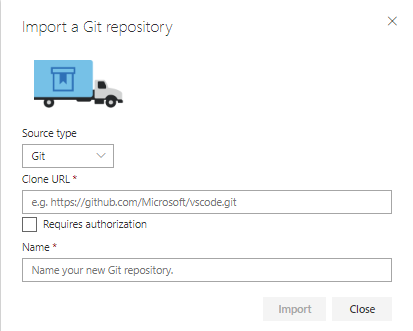
- You can also create a new project and/or repository to start from scratch. To create new project, go to home page in Azure DevOps and select + Create Project. To create new repository in existing project, you can select the Import repository from the Repos screen by providing the sample application code's Github repository link. Now Azure DevOps will clone the project from GitHub into its own git repo.
- Click Builds under Pipelines. On this page, click New Pipeline
- Your page should look like the one below. Click Use the visual designer link under Where is your code? section
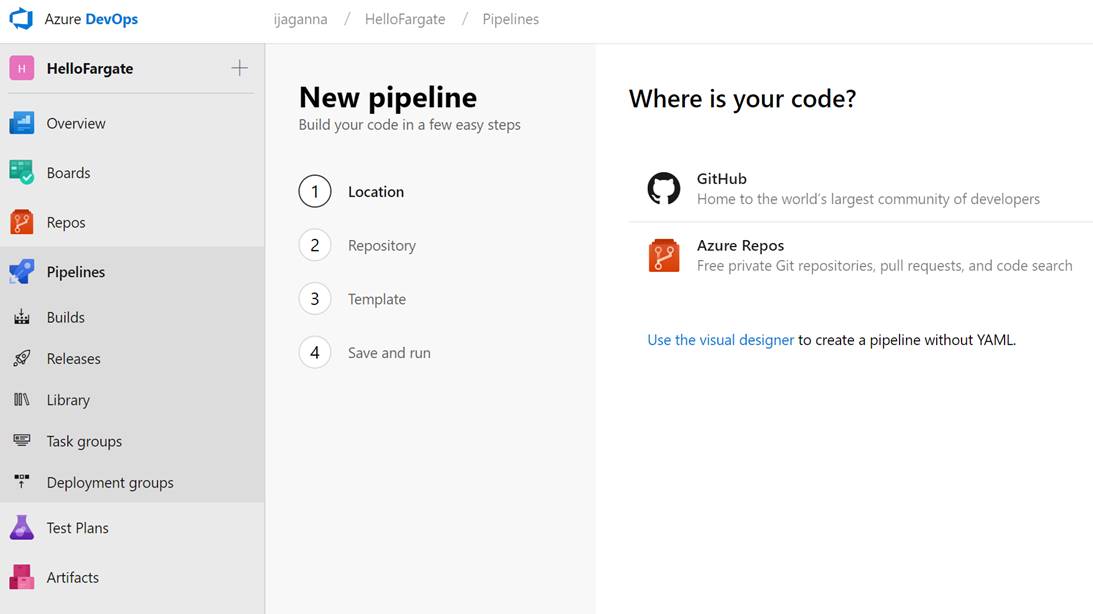
- In the next step, select the repo you want to connect to.
- Click Continue.
- On the Select a template screen, select Empty Job as shown in the screenshot below and click Apply
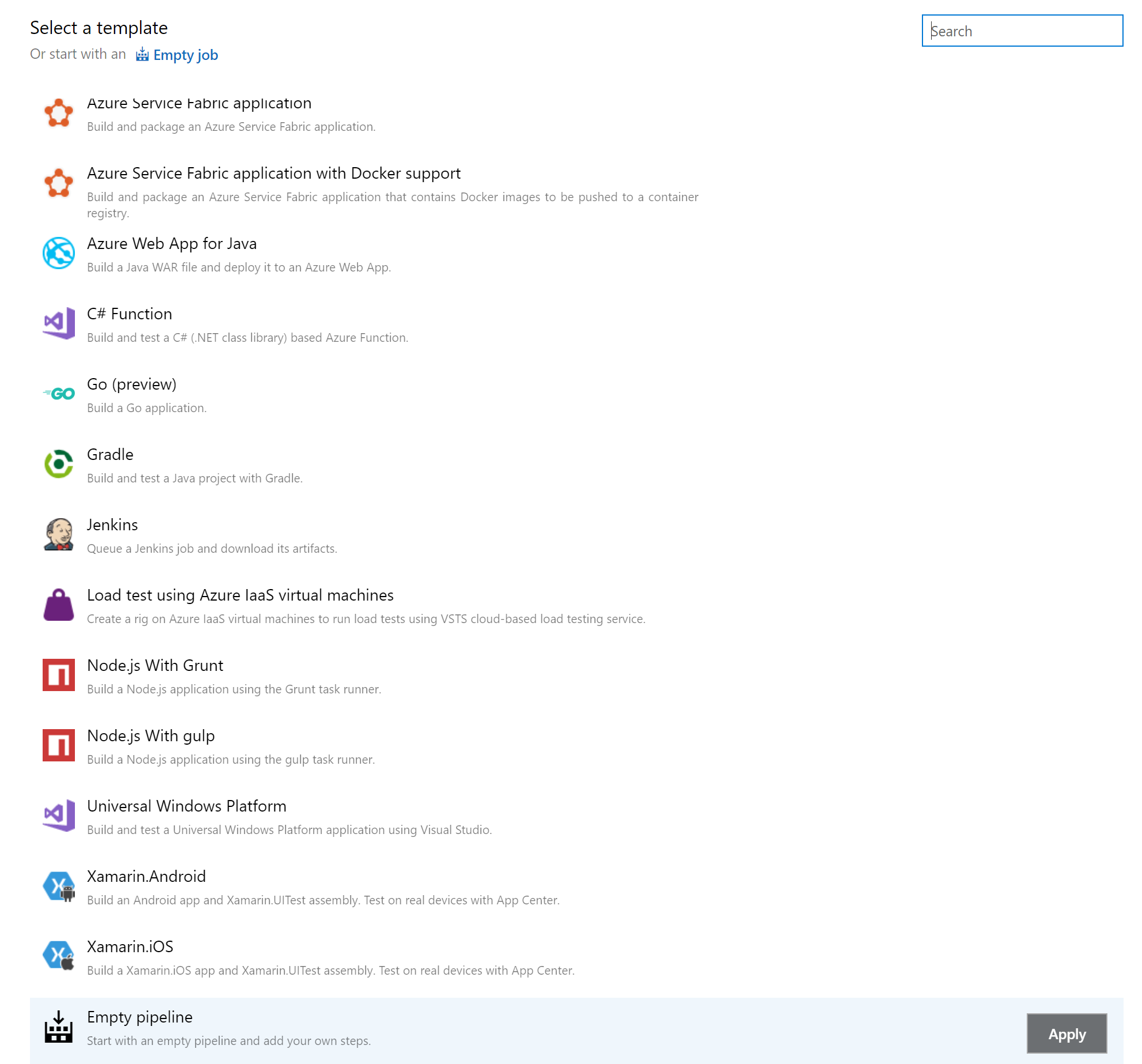
- Now you should be on the Tasks tab inside the Build pipeline. Here, to the right hand side for the drop down Agent Pool under Agent job, select Hosted Ubuntu 1604. More information on Microsoft-hosted agents in Azure DevOps can be found here (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/agents/hosted?view=vsts&tabs=yaml).
- Leave other fields to their default values.
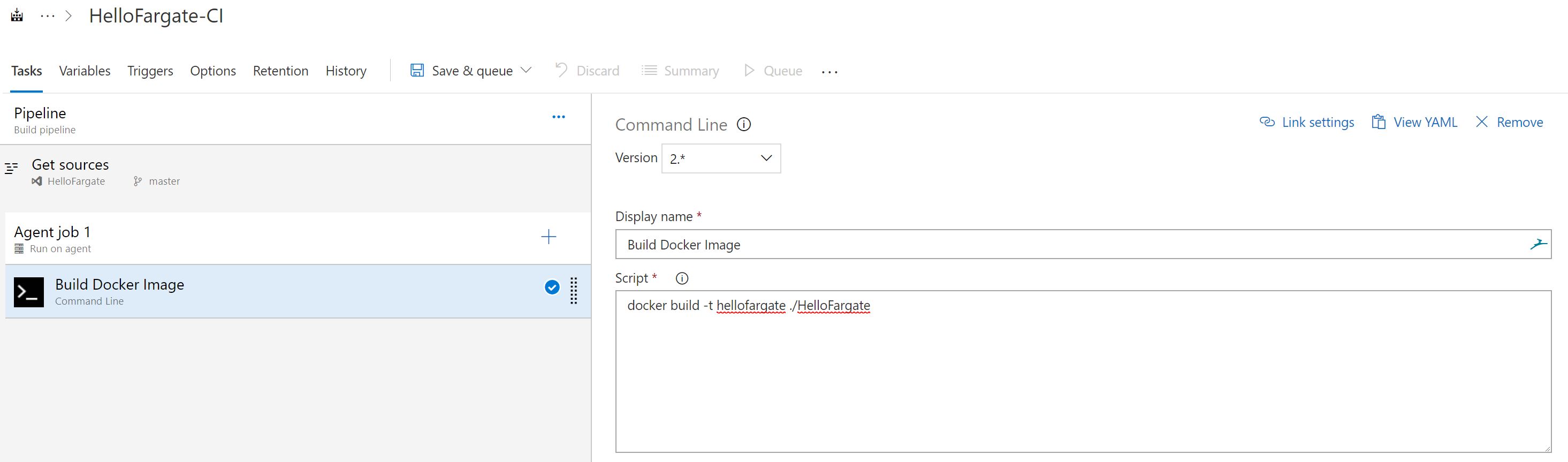
- Add a task by click on the + sign next to Agent job 1 on the left hand side. Type Command on the search bar on the right hand side. You should see the Command Line task as shown below and click Add.
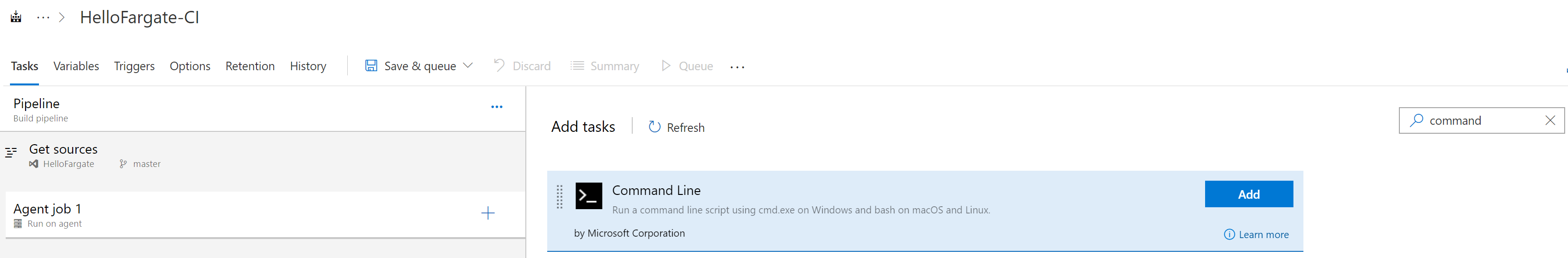
- Once added, name the task Build Docker Image and enter the command docker build -t hellofargate ./HelloFargate in the Script field as shown below. This command will tag the resulting docker image with 'hellofargate' (case sensitive) and provides HelloFargate folder in the repository as the build context (path to the Dockerfile). Syntax of the command is docker build [OPTIONS] PATH | URL | -. More details on docker build command can be found here (https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/build/).
-
Once again click on the + symbol next to Agent job 1. Type aws on the search field which will list all AWS tasks.
-
Select AWS Elastic Container Registry Push task and click Add
-
Name the image Push Image to ECR. Select the name of the AWS Credentials you setup earlier under AWS Credentials drop down. Select EU (Ireland) [eu-west-1] as Region. Select Image name with optional tag for Image identity field. Enter hellofargate for the Source Image Name field. Enter latest for Source Image tag field. Enter hellofargaterepo for the Target Repository Name field (or if you named your ECR repo differently then use that name). Enter latest for the Target Repository Tag field. Now click on Save pipeline to save your changes. The screenshot below shows all the settings for easier understanding.
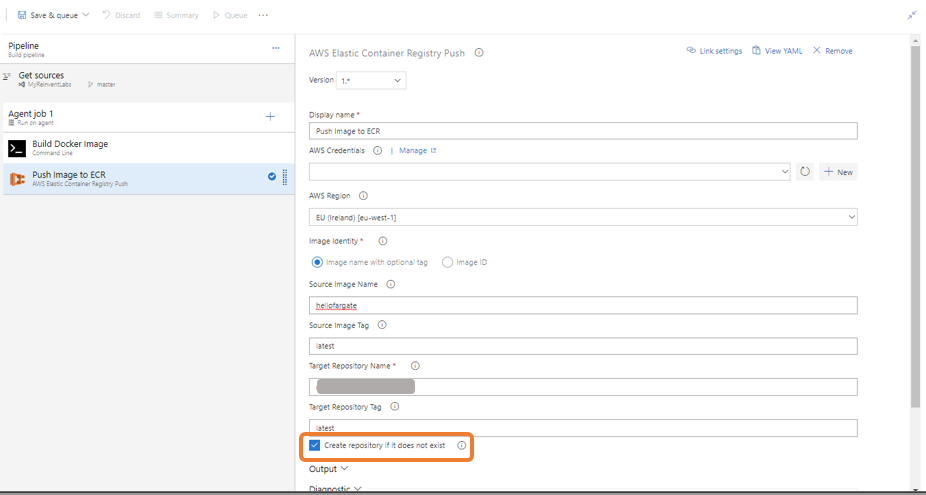
-
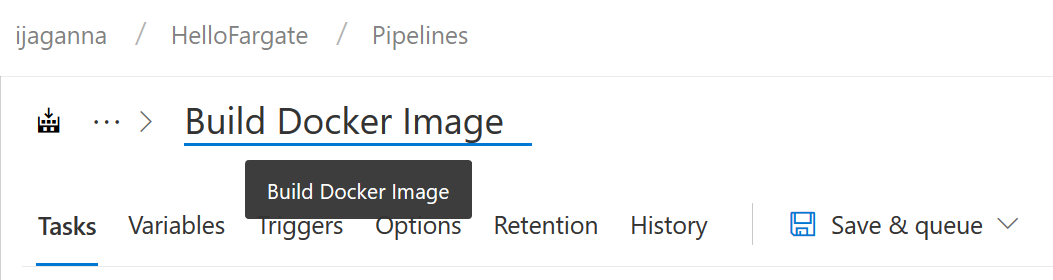
You can rename the build pipeline by just clicking on HelloFargate-CI at the top and typing a name as shown below
It might take around 2 minutes or so for the image to be published to the repository. Go ahead and start the next step (Create ECS Task Definition) till this gets completed.
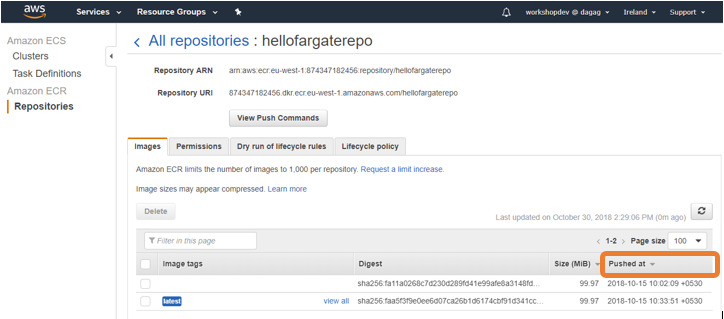
- Go to the AWS ECR console and click on hellofargaterepo repository and make sure there is a new entry and the Pushed at column reflects the latest timestamp
In this step, we are going to create a Task Definition that will be used to create the container instances in the cluster. A task definition is the core resource within ECS. This is where you define which container images to run, CPU/Memory, ports, commands etc.
- Login to AWS Console and navigate to Elastic Container Service home page
- Go to Repositories under Amazon ECR and click on the hellofargaterepo repository
- Select the value of Repository URI and press Ctrl+C or Cmd+C if you're using a Mac. You will need this in the next step
- Select Task Definitions and click on Create new Task Definition
- On the next screen, select FARGATE launch type and click Next
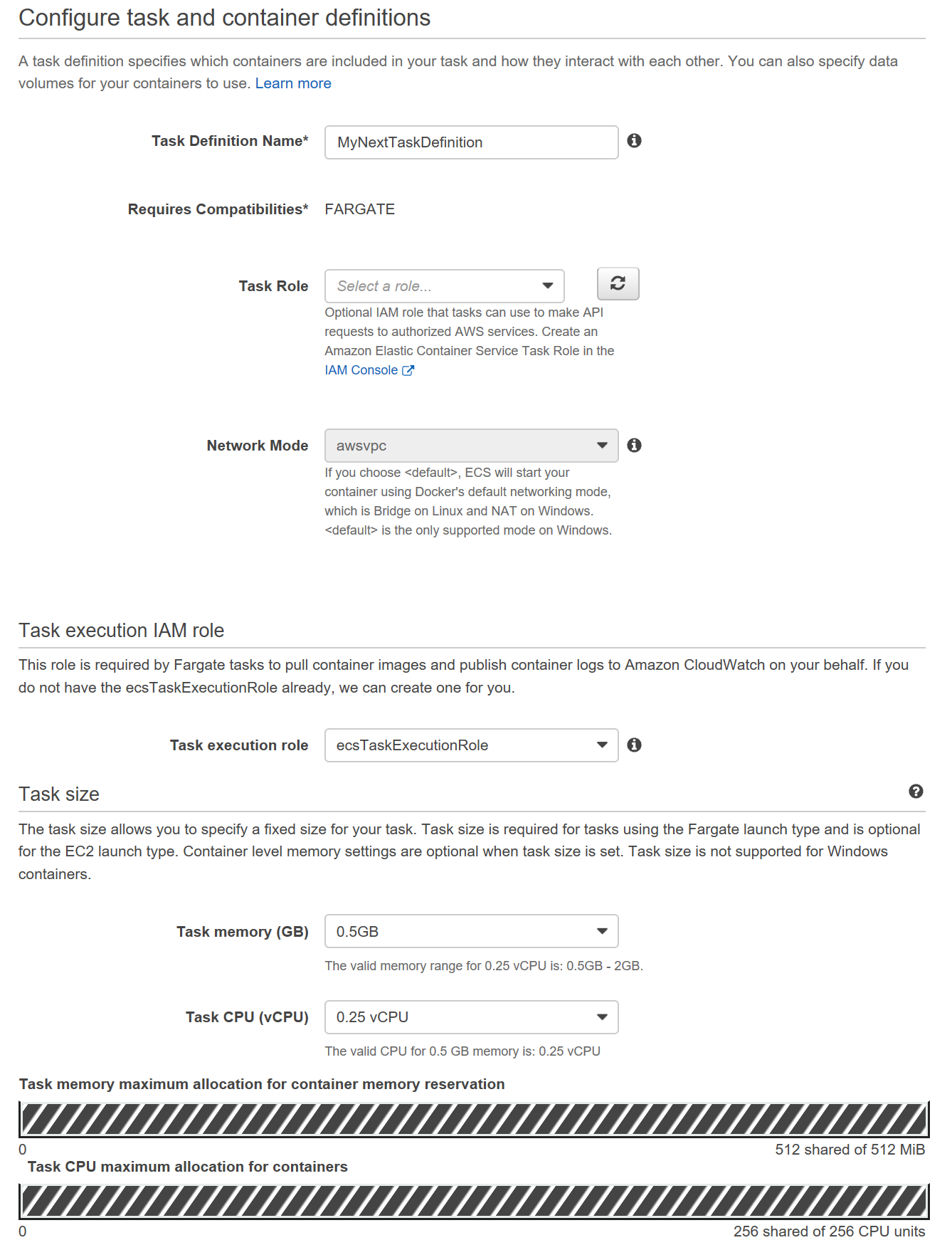
- On the next screen, give the Task Definition a name. In this exercise, I will call it MyNextTaskDefinition
- Leave Task Role and Network Mode fields to their default values.
- Select 0.5 GB for Task memory and 0.25 vCPU for Task CPU dropdowns respectively
- Your screen should look similar to the one below
- Click Add Container
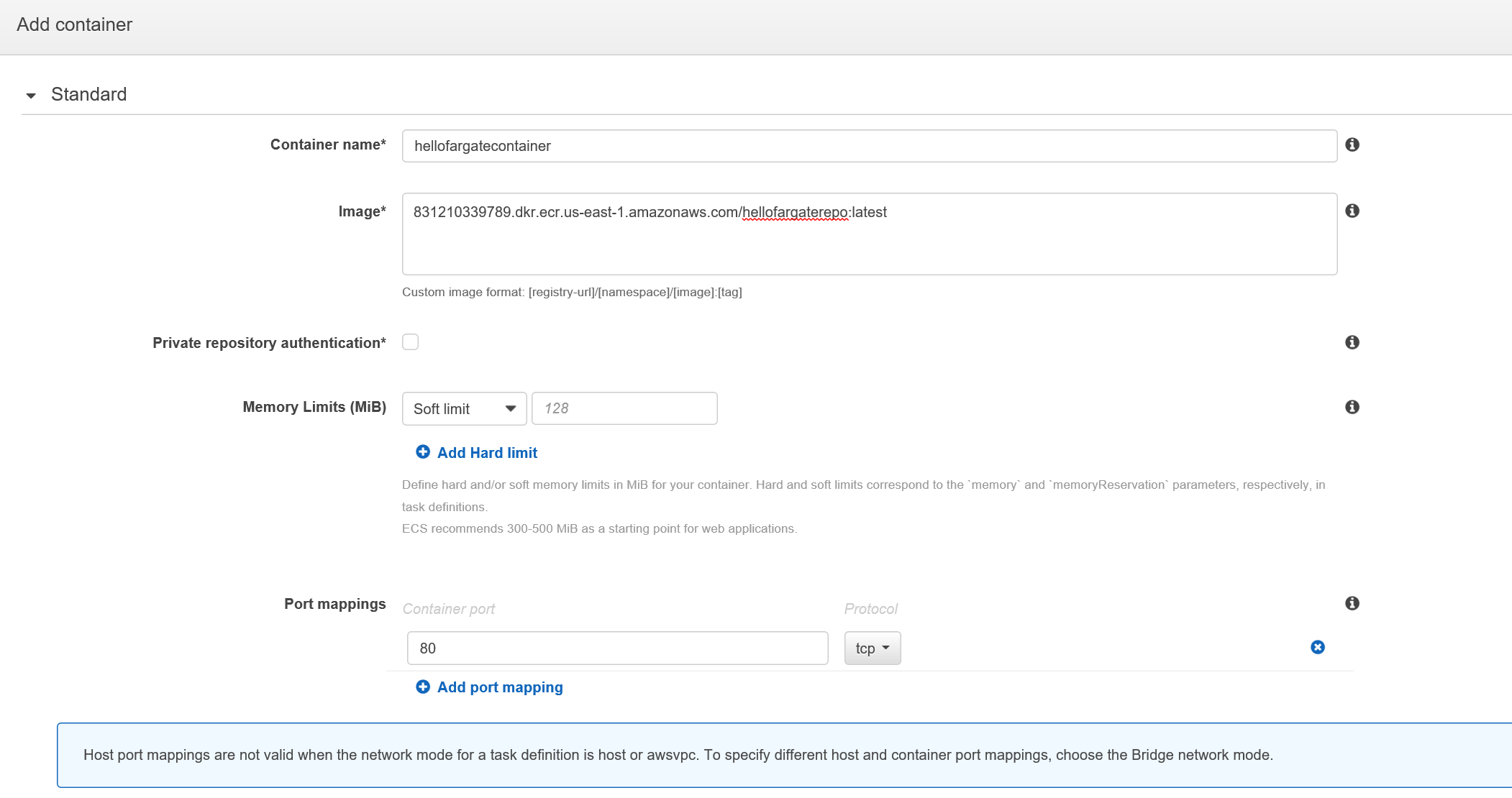
- Name the container as hellofargatecontainer
- Copy and paste the Repository URL from ECR and paste into Image textbox. Make sure you add the tag :latest to the end of the string. Ensure there are no white spaces at the end.
- Ignore the Private repository authentication and Memory Limits (MiB) fields
- Add 80 to Port mappings
- Ignore the Advanced container configuration section
- Click on Add button on bottom right corner
- Your screen should look similar to the one below
- Now click Create
- Your Task definition is created successfully
- Your screen should look similar to the one below

In this section we are going to create a Elastic Container Service cluster. A cluster typically has one or more nodes , which are the workermachines that run your containerized applications and other workloads.
- Click on Clusters on the ECS home page
- Click on Create Cluster
- Select Networking Only option and click Next step
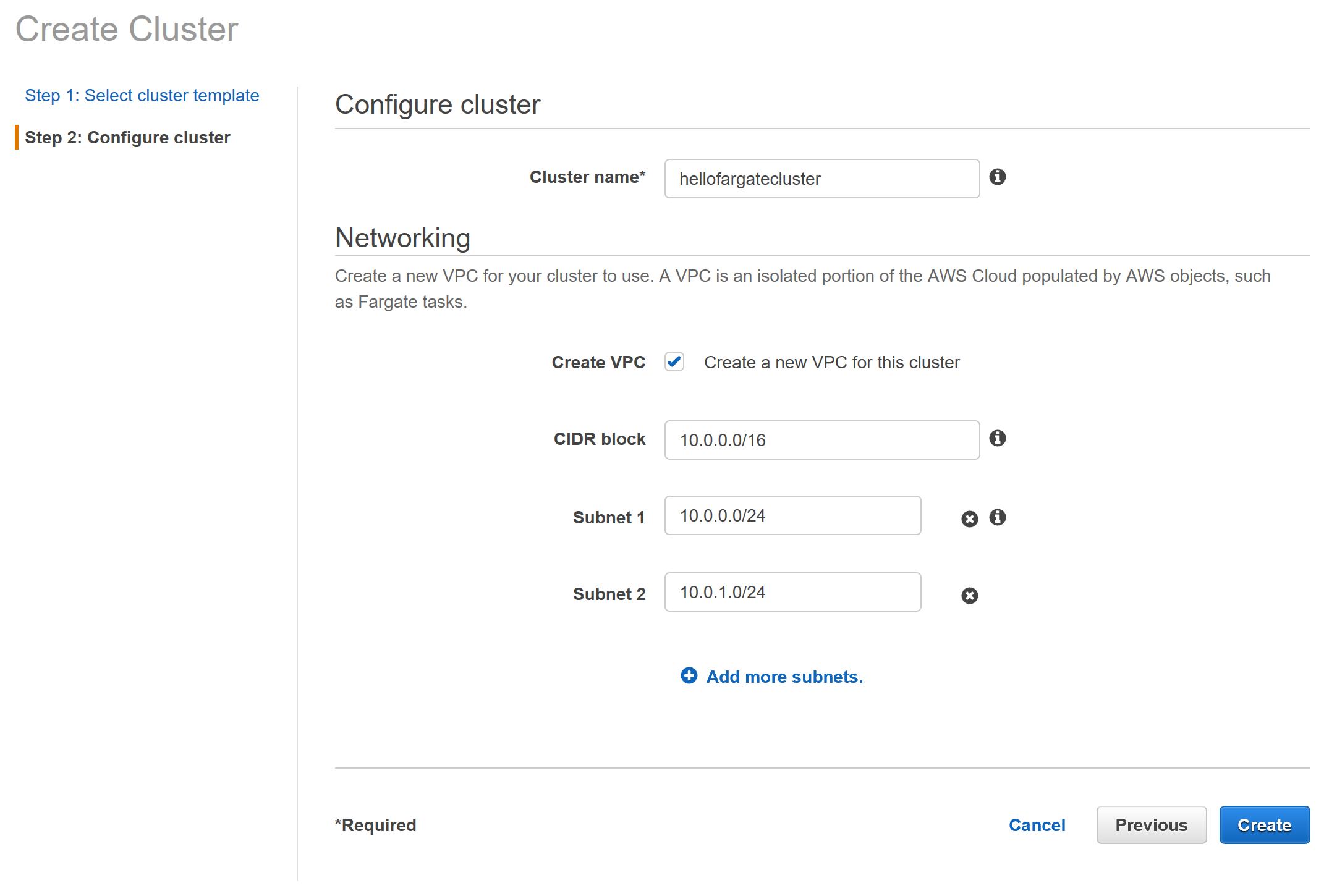
- Name the cluster as hellofargatecluster
- Check the Create VPC checkbox
- Type a CIDR range to allocate to your VPC and subnet. You may use online tools to validate subnet CIDR allocation (example https://cidr.xyz/ , https://www.site24x7.com/tools/ipv4-subnetcalculator.html)
- Delete Subnet 2 by clicking the x to the right and leave other values to default
- Click Create
This step will take about a minute to complete. In the background, AWS is creating a CloudFormation stack with all the input settings.
- ECS cluster is created sucessfully
Important: Once complete, make sure you take a note of the VPC name that we just created, since we will use it in the future steps
- Click on View Cluster to see the cluster
- On the newly created cluster page, click on Create under Services tab
- Select FARGATE for Launch type option
- Make sure the Task Definition and the Clusters are selected to the ones you just created
- Enter hellofargateservice for Service name field
- Enter 1 for Number of tasks field and leave everything else as is. Click Next step
- Make sure the VPC drop down has the name of the VPC you just created
- Click on the Subnects drop down and select the subnet that comes up
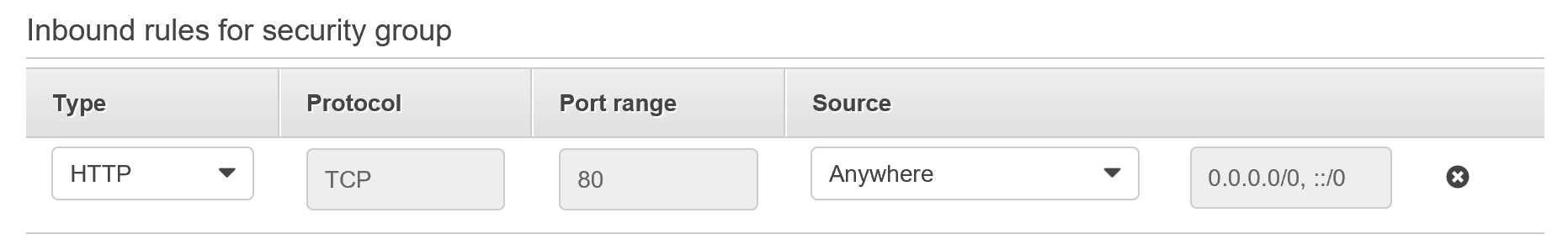
- Click on Edit for Security groups and ensure the Inboud rules for security group has Port 80 selected. Look at the image below for clarity. Click cancel to exit the Configure security groups page
- Select None for Load balancing
- Under Service Discovery (optional) section uncheck the Enable service discovery integration checkbox as this is not required for this lab and click Next Step
- Leave the Set Auto Scaling to Do not adjust the service's desired count as it is
- Do a quick review of the Review screen and click Create service
- The cluster service is now created successfully
- Click on View Service
- Go to the Tasks tab and check the Last status column. It will refresh its status to RUNNING and turn green once the provisioning is complete
- The current screen should look similar to the one below. Notice that the Last status column says PROVISIONING which means the taks is currently being executed
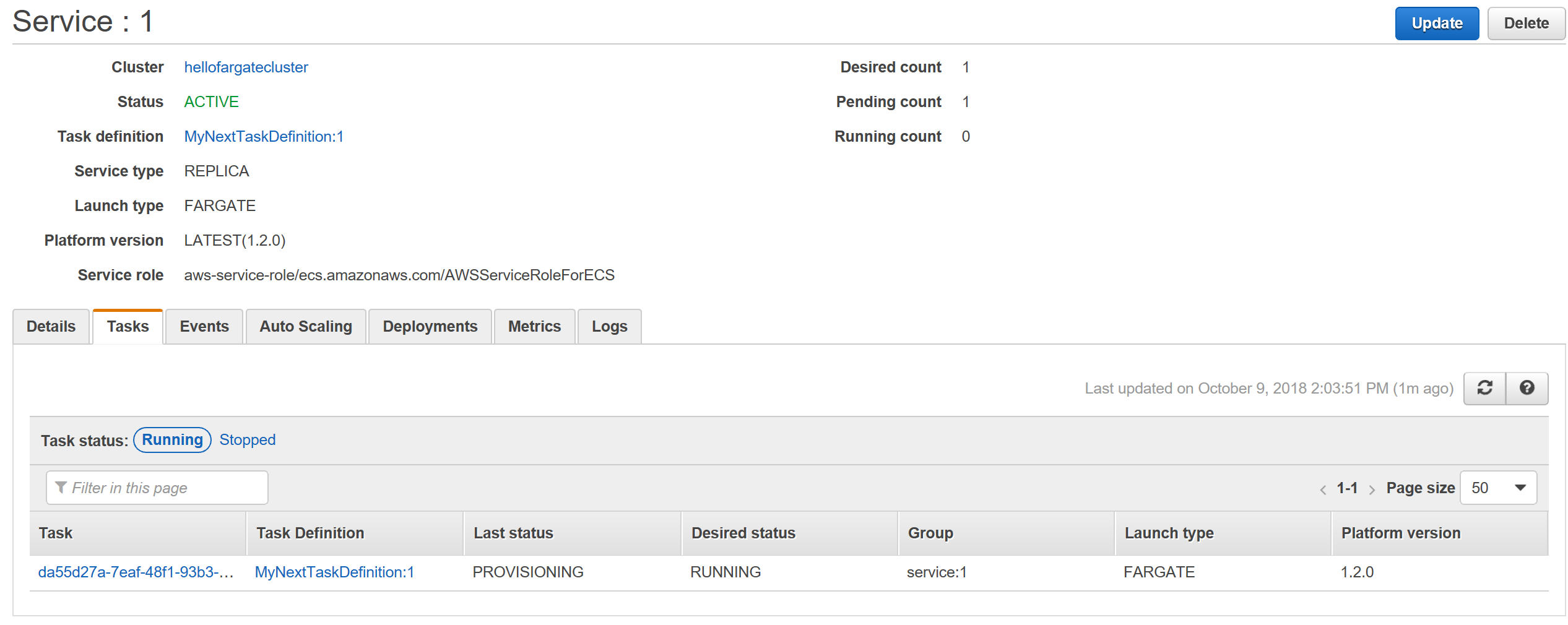
- Once the value on Last status column says RUNNING and is green, click on the task name under Task column
- Copy and paste the value of Public IP under Network on to a new browser tab and press Enter
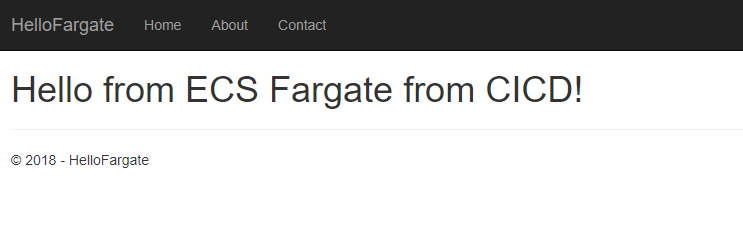
- You should see the home page of the your new application running on Amazon ECS Fargate
- Go to Releases page on your Azure DevOps project
- Click New pipeline
- Select Empty job under Select a template
- Enter Prod for Stage name field
- Change the name of the pipeline to Release to Prod.
- Now your screen should look similar to the below screenshot
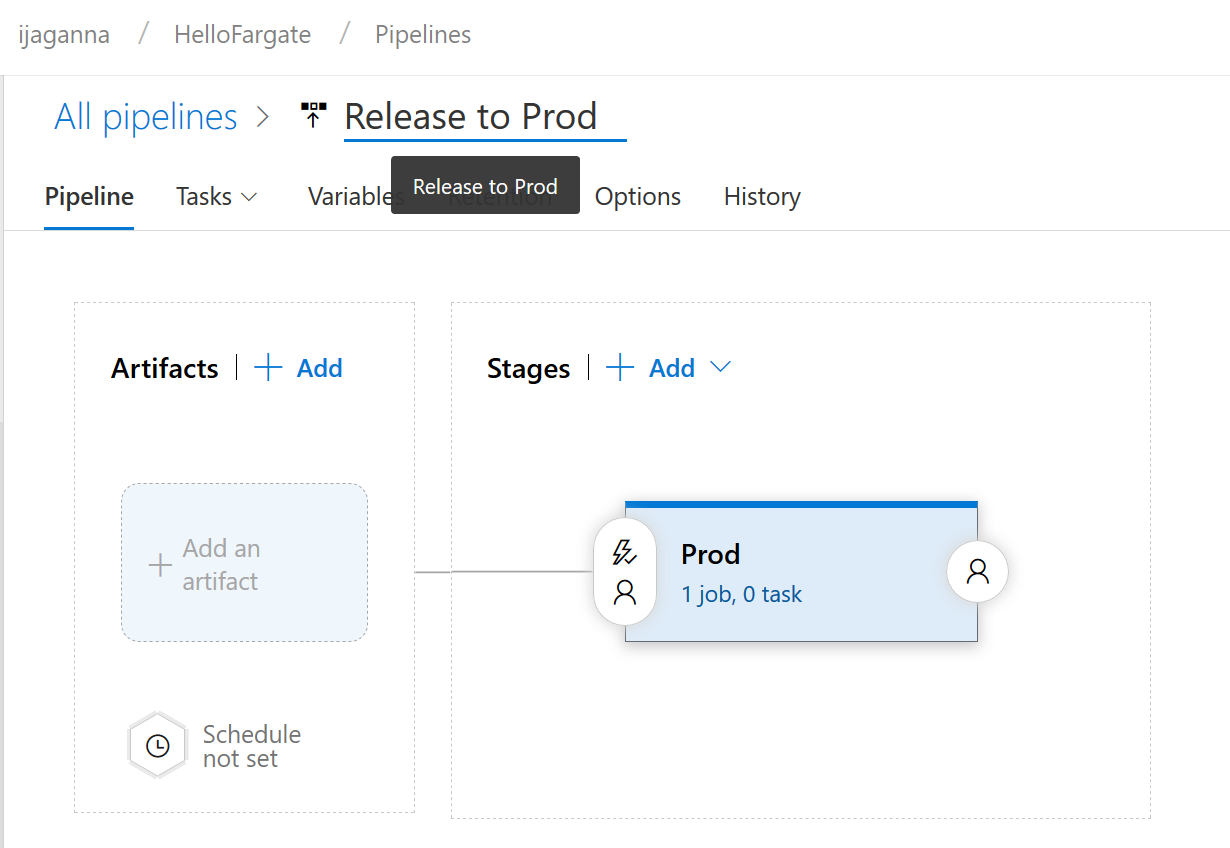
- Hover your mouse over 1 job, 0 task link and click on the + sign that becomes visible. This will allow you to add new tasks to the pipeline.
- In the next screen, under Agent job, select Hosted 2017 for Agent pool drop down
- Now click on the + sign next to Agent job and type Command in the search field. Select the Command Line task and click Add
- Name the task Install AWS CLI and enter pip install awscli in the Script field
- Click on the + sign next to Agent job. Type aws in the search field. Select AWS CLI task and click Add
- Name the new task Update ECS Service. Select the name of the AWS credential you configured earlier.
- Select EU (Ireland) [eu-west-1] as region
- Enter ecs in the Command field.
- Enter update-service in the Subcommand field.
- Enter --cluster hellofargatecluster --service hellofargatecontainer-service --force-new-deployment in the Options and parameters field
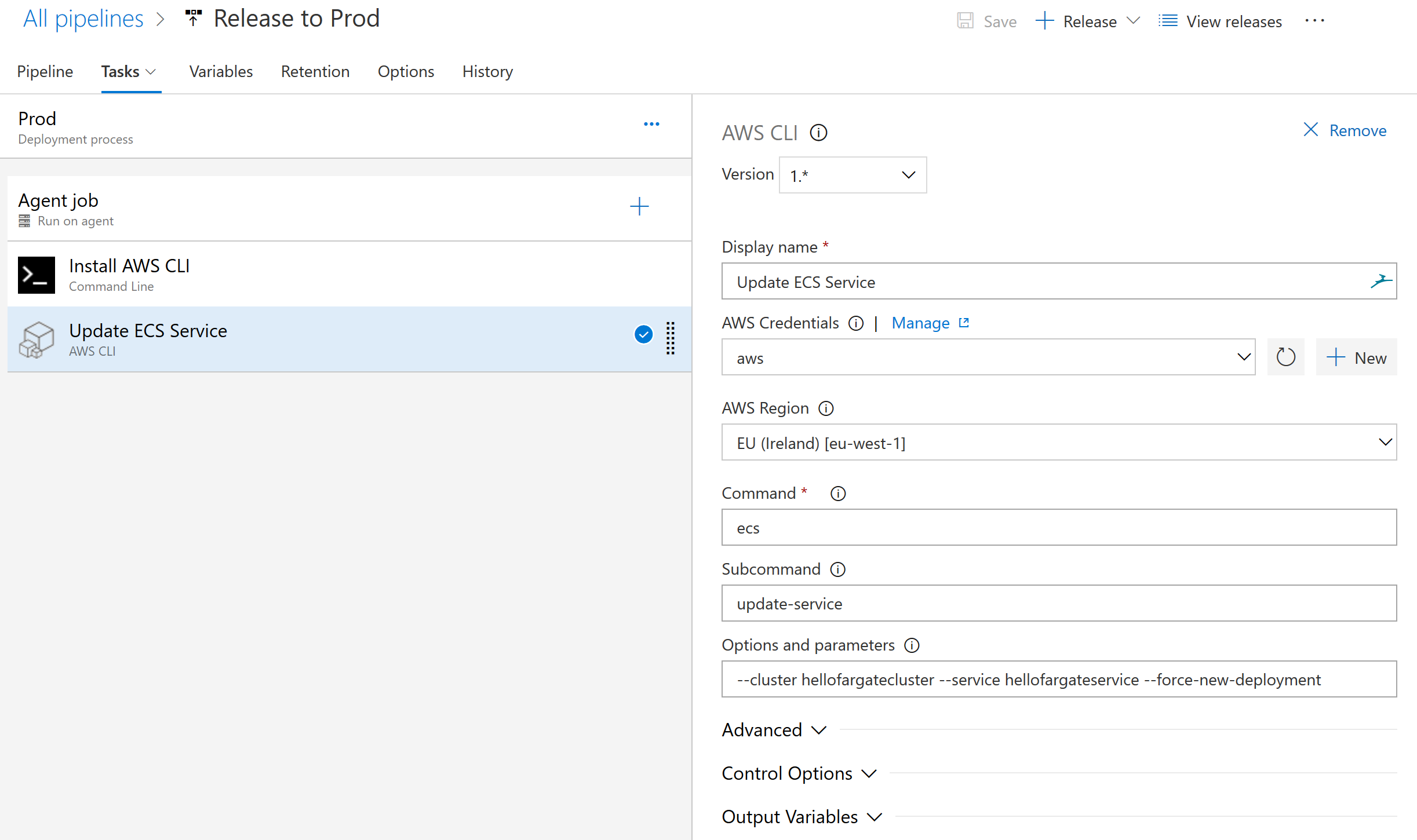
- Save the changes.
In this step, we will create a release using the release pipeline we created in the previous step. Doing this will deploy the container into the cluster using the task definition it is configured to.
- Go to Releases and select the release pipeline you created earlier.
- You should see a screen similar to the one below. Click Create a release
- Select Prod in the drop down for Stages for a trigger change from automated to manual and click Create
- In the next screen, click on Release-1 that appears on the green bar

- Your next screen will look similar to the one below. Hover the mouse arrow on Prod stage rectangle. Click on Deploy button.
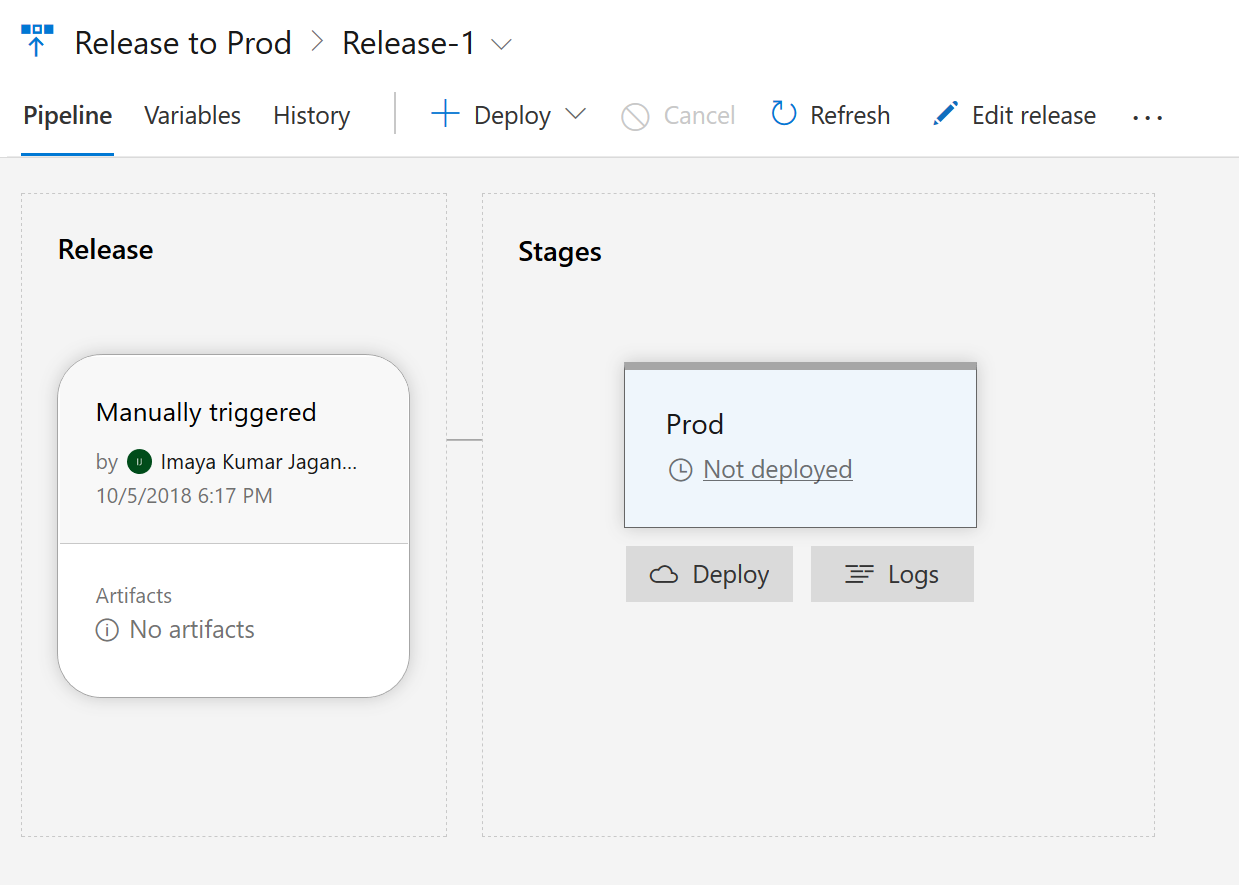
- Simply click Deploy in the pop-up screen
- The job will be queued and will be picked up once an agent gets free. After its complete, your screen should look like the one below
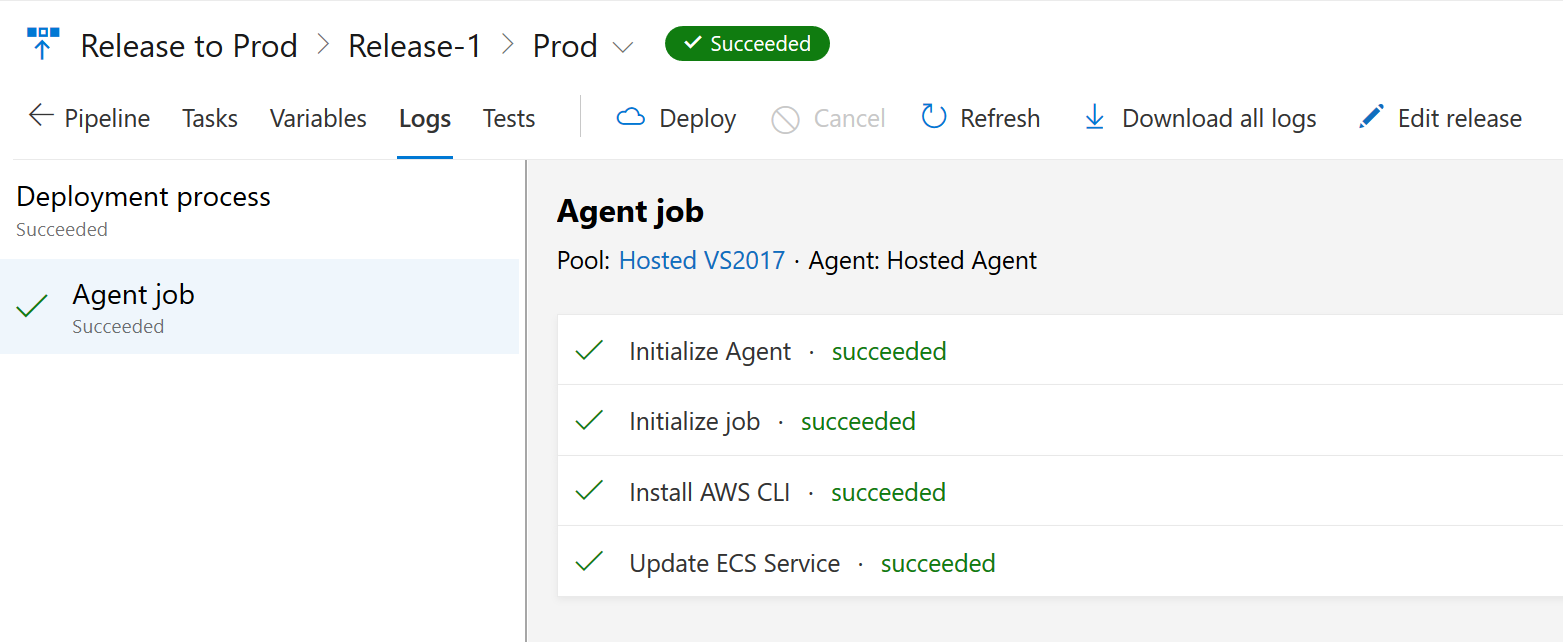
- Now you have a fully functional Build and Deploy pipeline setup for your application running on Amazon Elastic Cluster Service
- Go ahead and make some simple change to the project and do a git push to the repo.
- Queue a Build and a Release to see your changes reflecting successfully on your target environment