A data structure is a specialized format for organizing, processing, retrieving and storing data. There are several basic and advanced types of data structures, all designed to arrange data to suit a specific purpose. Data structures make it easy for users to access and work with the data they need in appropriate ways. Most importantly, data structures frame the organization of information so that machines and humans can better understand it.
A linked list is a linear data structure that includes a series of connected nodes. Here, each node stores the data and the address of the next node. For example,
- Singly Linked List
- Doubly Linked List
- Circular Linked List
- Circular Doubly Linked List
- Dynamic memory allocation
- Implemented in stack and queue
- In undo functionality of softwares
- Hash tables, Graphs
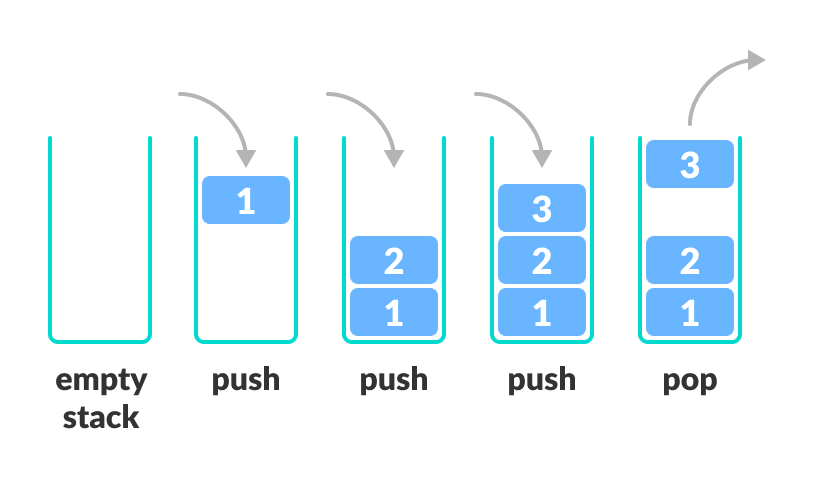
A stack is a linear data structure that follows the principle of Last In First Out (LIFO). This means the last element inserted inside the stack is removed first.
- To reverse a word
- In compilers
- In browsers
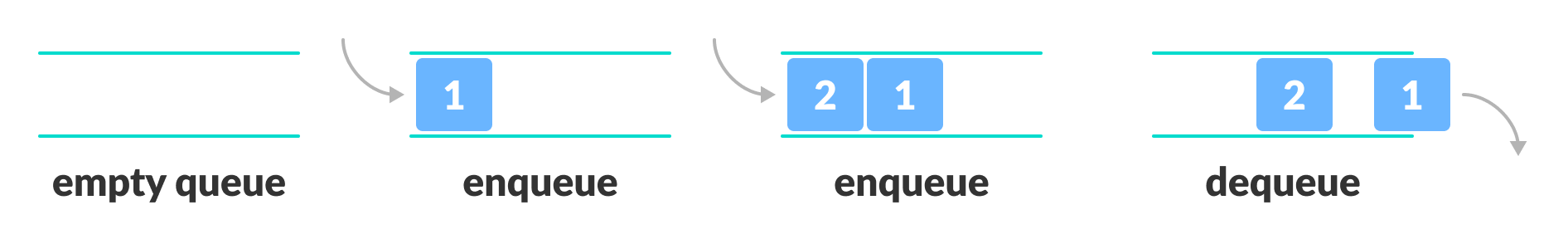
A queue is a useful data structure in programming. It is similar to the ticket queue outside a cinema hall, where the first person entering the queue is the first person who gets the ticket.
Queue follows the First In First Out (FIFO) rule - the item that goes in first is the item that comes out first.
- Simple Queue
- Circular Queue
- Priority Queue
-Double Ended Queue
- CPU scheduling, Disk Scheduling
- IO Buffers, pipes, file IO, etc
- Handling of interrupts in real-time systems.
- Call Center phone systems use Queues to hold people calling them in order.
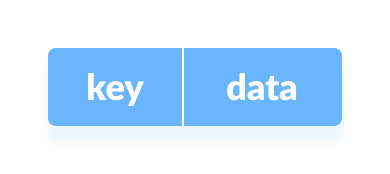
The Hash table data structure stores elements in key-value pairs where
Key: unique integer that is used for indexing the values.
Value- data that are associated with keys.
- Linear Probing
- Quadratic Probing
- Double Hashing
- Chaining Seperate
- Constant time lookup and insertion is required
- Cryptographic applications
- Indexing data is required
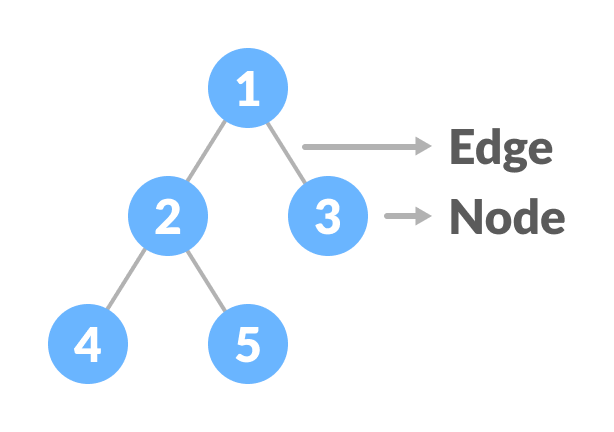
A tree is a nonlinear hierarchical data structure that consists of nodes connected by edges.
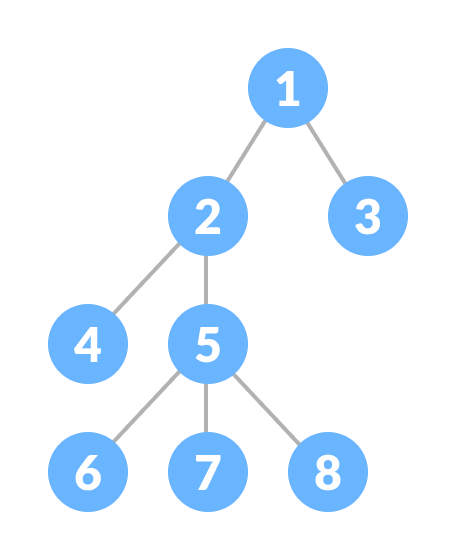
- Quickly check whether an element is present in a set or not.
- Most popular databases use B-Trees and T-Trees, which are variants of the tree structure to store their data
- Compilers use a syntax tree to validate the syntax of every program you write.
- Binary Tree
- Binary Search Tree (BST)
- AVL Tree
- B-Tree
A graph data structure is a collection of nodes that have data and are connected to other nodes.For Example, on facebook, everything is a node. That includes User, Photo, Album, Event, Group, Page, Comment, Story, Video, Link, Note...anything that has data is a node.