GraphQL Java
GraphQL Best practices
GraphQL Java
GraphQLResolver vs GraphQLQueryResolver<DataClassName>
|
Warning
|
I still can’t grasp the difference and there is not official doc for these Classes! |
Exception Handling
Default GraphQL Exception Handler
DefaultGraphQLErrorHandler.processErrors is called for any Runtime.class or GraphQLException.class is called (thrown by ThrowableGraphQLError)
This project has common GraphQLExceptionHandler with 2 methods
-
ThrowableGraphQLError handle(GraphQLException graphQLException)-
For Client side errors (Giving MORE info about Client error)
-
-
ThrowableGraphQLError handle(RuntimeException graphQLException)-
For Server side errors (Giving NO info about Server error)
-
Custom GraphQL ErrorHandler
Can extend
GraphQLErrorHandlerfor custom exception handling.
-
Defined in
exception.CustomGraphQLErrorHandler -
CustomGraphQLErrorHandler.processErrorsis called instead ofDefaultGraphQLErrorHandler.processErrors
DataFetcherResult
Contains both data, errors and local context to be sent as final result to graphql server.
Mutation
Write operations
Upload file
Use DataFetchingEnvironment and DefaultGraphQLServletContext from the GraphQL Servers
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8080/graphql' \
--form 'operations="{\"query\":\"mutation {uploadFile}\" , \"variables\":{}}"' \
--form 'file=@"/D:/Coding/learngraphql-java/README.adoc"' // Remem ber this is of type File. CURL import on postman will fail this command
// "{"query":"mutation {uploadFile}" , "variables":{}}"DataFetchingEnviroment
Powerful object with useful methods for GraphQL interceptors
-
getSelectionSetUseful for DB layer -
getContext: Useful for Auth etc
Scalars
GraphQL spec includes default scalar types Int, Float, String, Boolean, and ID. Some applications need to support other atomic data types (such as Date) or add validation to an existing type(NonNegativeInteger)
To enable this
-
Define custom scalar types. Apollo Doc
-
Use library. Java GraphQL Scalar
Steps to use custom Scalar
-
Add
scalar <ScalarName>in.graphqlsor any GrpahQL file. -
For Java, create a Bean. Example
@Bean public GraphQLScalarType nonNegativeInt() { return ExtendedScalars.NonNegativeInt; }-
TODO: Typescript
-
3.
GraphQLServletListener
Interfaces for request states.
-
onRequest -
RequestCallback-
onRequest -
onSuccess -
onFinally
-
Pagination
// GET Bank Accounts Pagination
query GET_BANK_ACCOUNTS{
bankAccounts(first: 5, after: "<uuid>") {
edges {
cursor // uuid
node {
id
}
}
pageInfo {
hasPreviousPage
hasNextPage
startCursor
endCursor
}
}
}Response:
{
"data": {
"bankAccounts": {
"edges": [
{
"cursor": "NDEwZjU5MTktZTUwYi00NzkwLWFhZTMtNjVkMmQ0YjIxYzc3",
"node": {
"id": "410f5919-e50b-4790-aae3-65d2d4b21c77"
}
},
{
"cursor": "NDhlNGE0ODQtYWYyYy00MzY2LThjZDQtMjUzMzA1OTc0NzNm",
"node": {
"id": "48e4a484-af2c-4366-8cd4-25330597473f"
}
}
],
"pageInfo": {
"hasPreviousPage": true,
"hasNextPage": false,
"startCursor": "NDEwZjU5MTktZTUwYi00NzkwLWFhZTMtNjVkMmQ0YjIxYzc3",
"endCursor": "NDhlNGE0ODQtYWYyYy00MzY2LThjZDQtMjUzMzA1OTc0NzNm"
}
}
}
}Usually pagination is offset-based. ID-based based pagination uses unique identifier which is more reliable than offset-based.
Custom Context
We have custom context so that we can intercept network request and get info such as header from HttpServletRequest from GraphQLServletContext
We used GraphQLServletContext in junction with GraphQLServletContextBuilder to get Context info.
|
Note
|
user_id is the header name given in HTTP Headers in GraphQL playground.
|
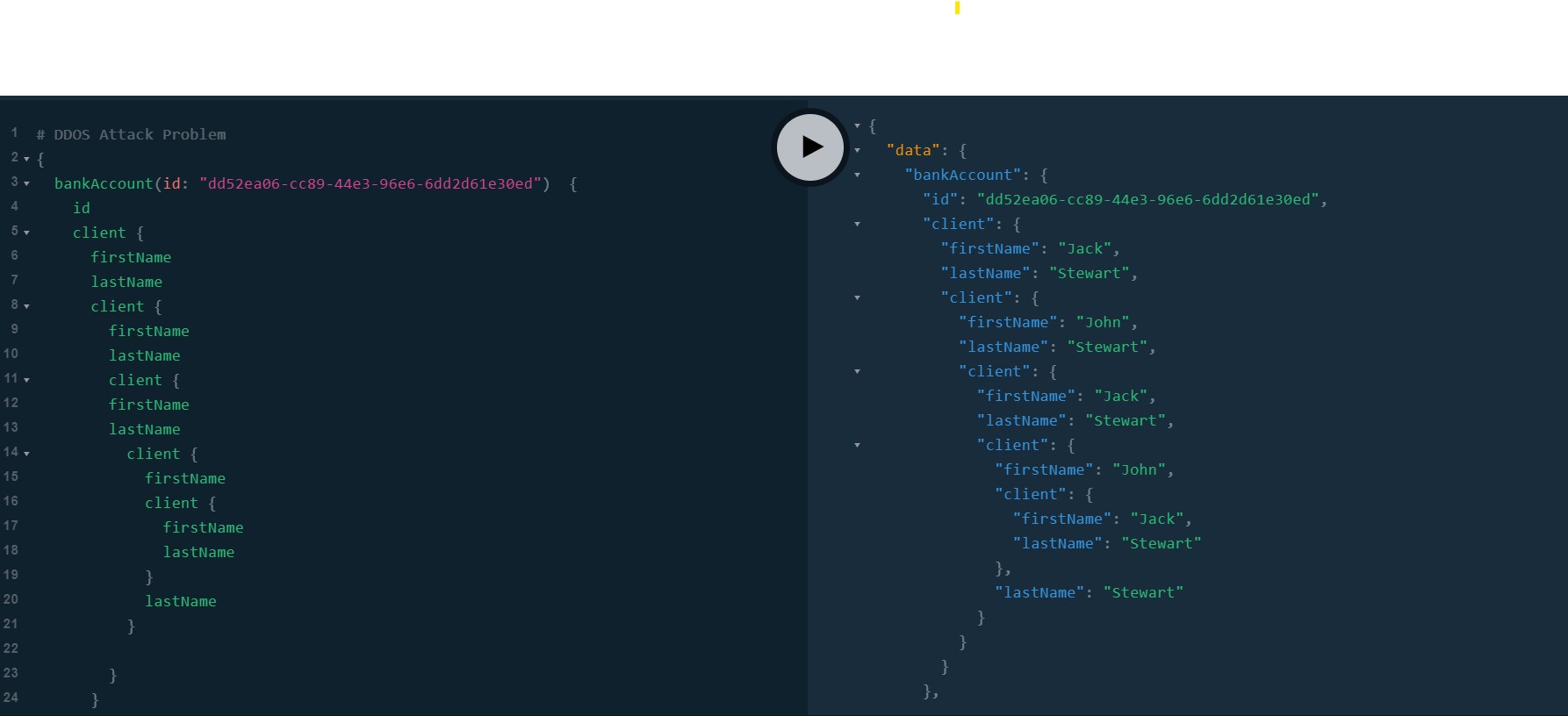
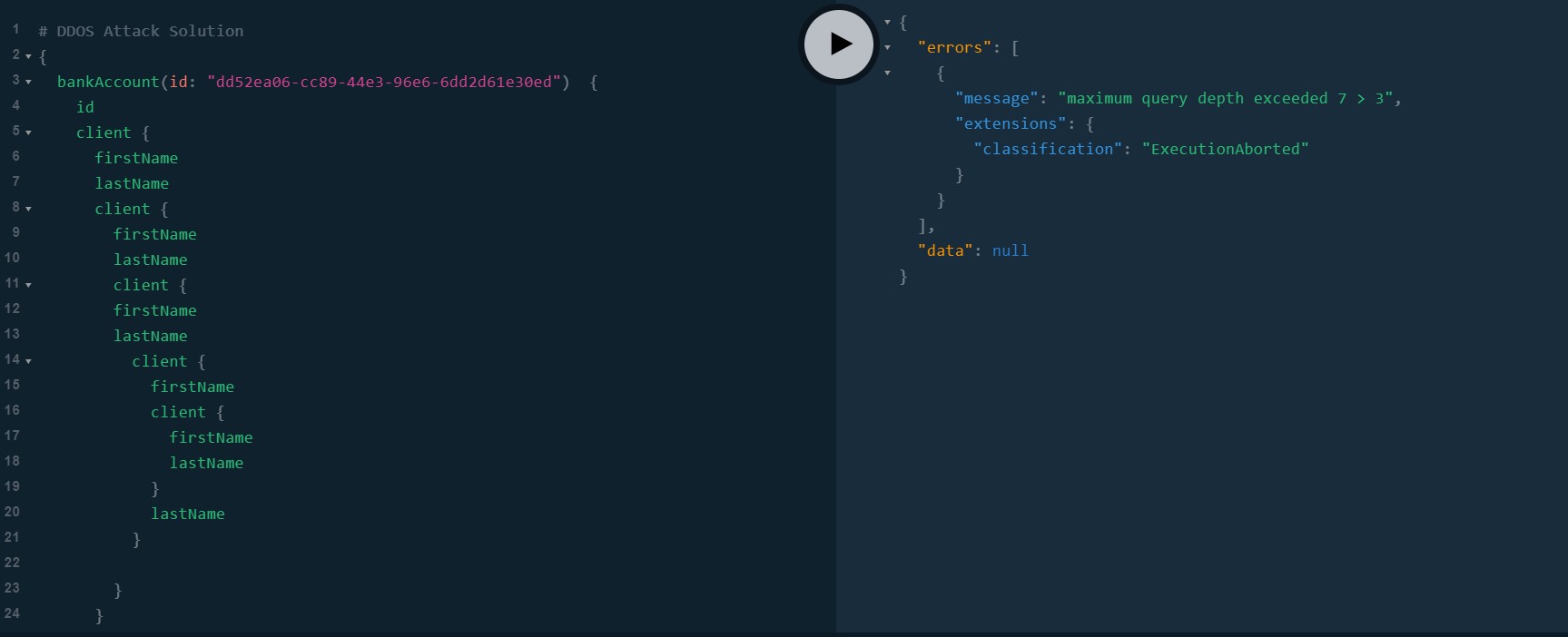
N+1 Problem
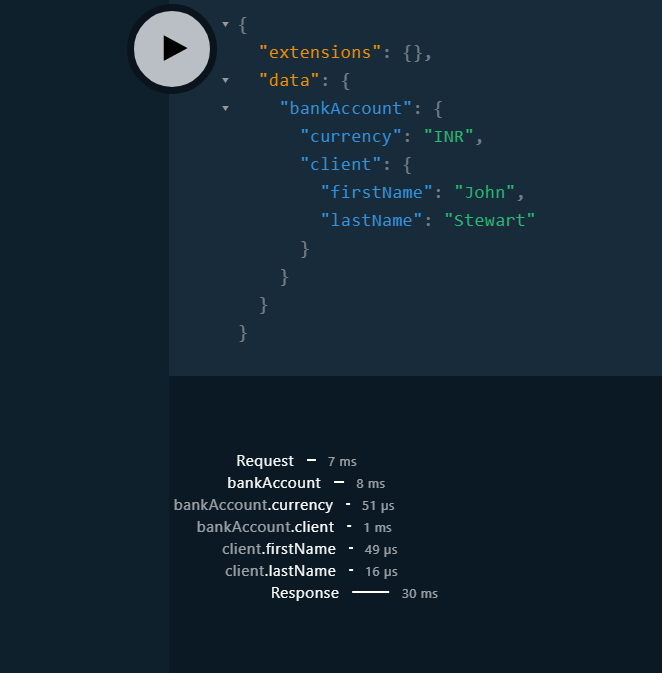
Instrumentation and Tracing
Data Loader
Very important.
|
Warning
|
Please read this Github Java Dataloader doc |